Strategy for retroviral immunotherapy
A technology of retroviruses and subjects, applied in the direction of retroRNA viruses, viruses, antiviral agents, etc., can solve problems such as the lack of an effective vaccine strategy for HIV infection, and achieve a complete therapeutic effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0130] To demonstrate the present invention, a murine AIDS model was used.
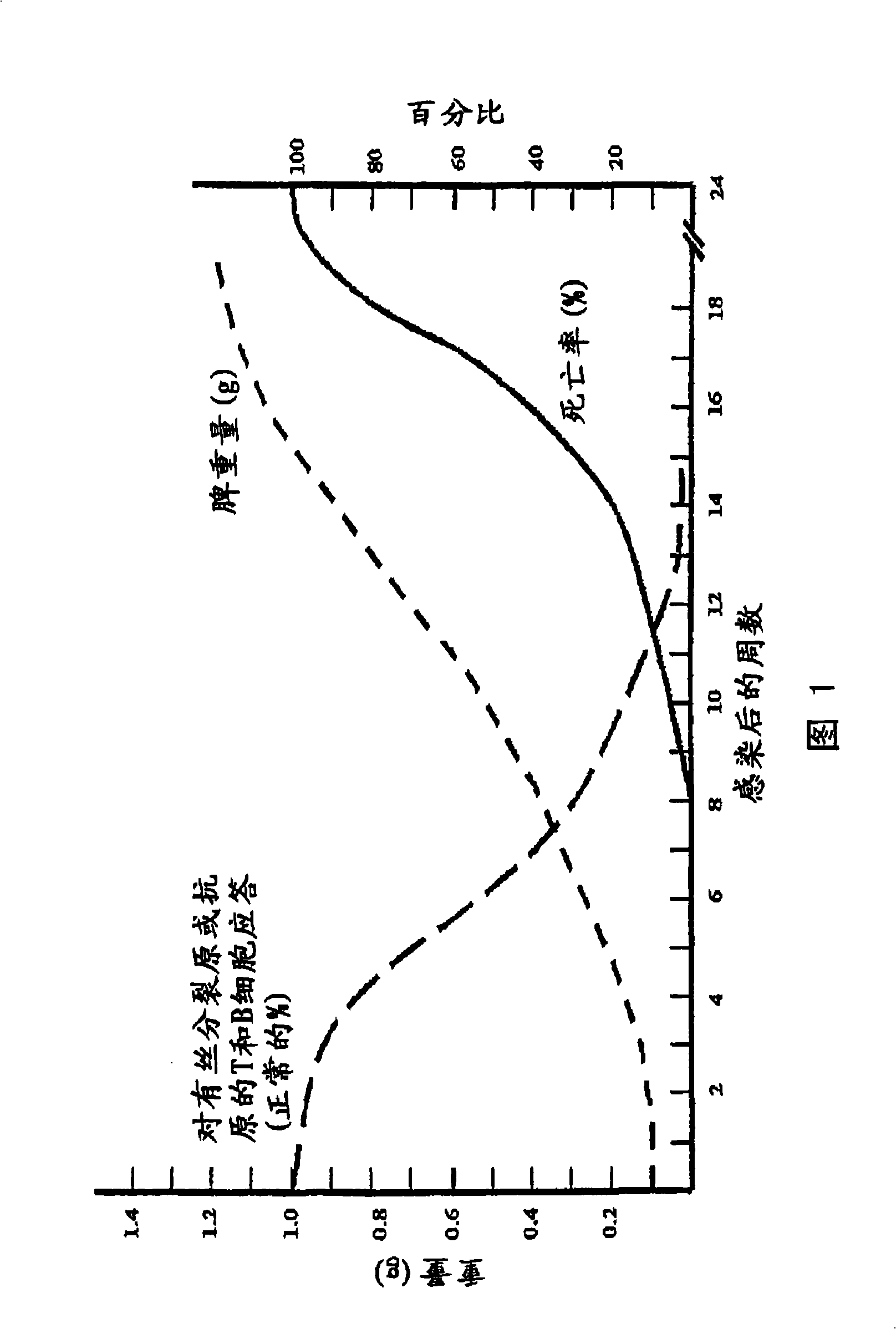
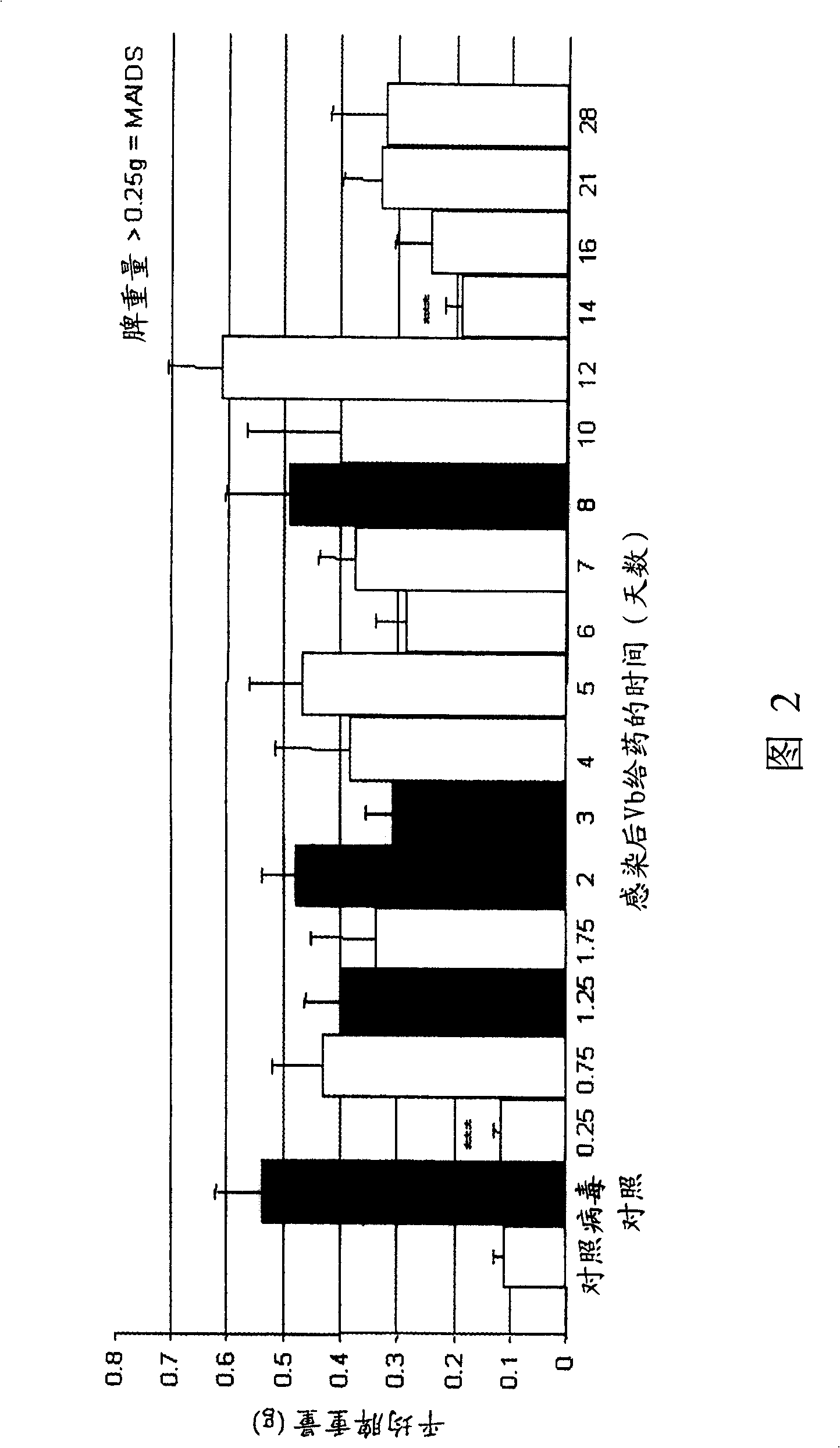
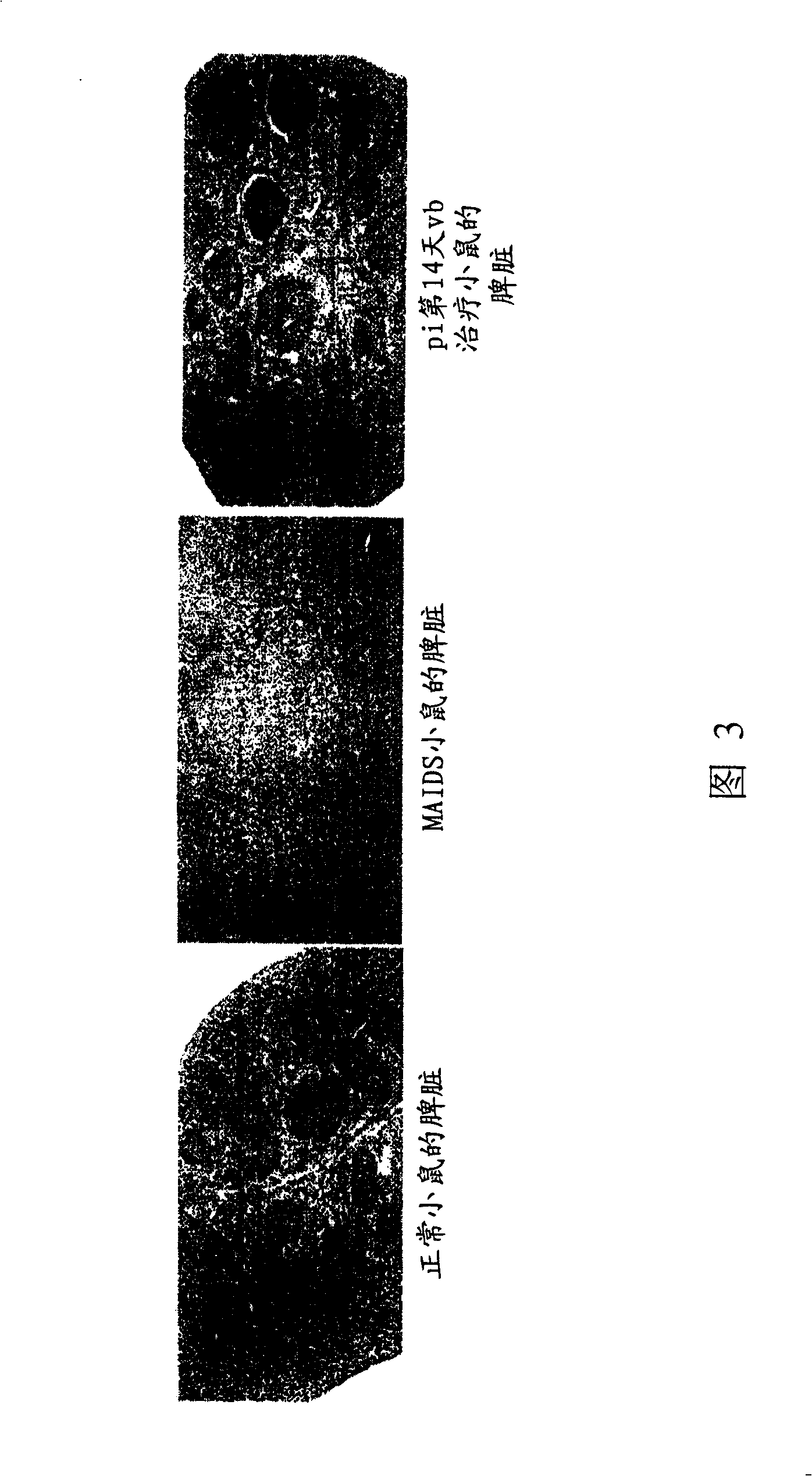
[0131] Murine AIDS (MAIDS) pathology induced by LP-BM5 murine leukemia virus (MuLV) in susceptible mice is a useful tool for studying the mechanisms of retrovirus-induced immunodeficiency. This MAIDS animal model exhibits many of the features of human AIDS. Infection of susceptible strains, such as C57BL / 6 mice with LP-BM5, leads to the development of chronic splenomegaly, hypergammaglobulinemia, and T- and B-cell immunodeficiency. In vitro, there is progressive impairment of the ability of T and B cells to respond to mitogenic or specific antigenic stimulation. In vivo, infected mice became increasingly susceptible to invasion with various opportunistic organisms and developed B-cell lymphomas. Mortality was first observed at 8-10 weeks post-infection (pi), and all mice died within 24 weeks (Figure 1). These changes in immune function reflect complex changes in the phenotype and function of all co...
Embodiment 2
[0172] Human patients with HIV infection were placed on HAART for at least 6 months before withdrawal of treatment. Viral load and c-reactive protein levels in samples obtained during and after HAART were determined using standard techniques.
[0173] as in Figure 18 As seen in , the results showed an increase in viral load after HAART ended. Then the viral load decreases due to the activity of effector cells, and then increases again due to the regulation of effector cells. c-reactive protein levels approximately reflect viral load, suggesting that measurement of this protein can be used as a marker of effector cell viability as well as viral load.
Embodiment 3
[0175] Vaccines containing retroviral antigenic polypeptides are administered to human patients with HIV infection. Examples of such vaccines are discussed in Dennehy (2001) and Moore et al. (2001).
[0176]Following vaccine administration, c-reactive protein levels were analyzed as generally described in Example 2. Preferably, the level of c-reactive protein is determined at least every 24 hours. Naturally, the patient should be checked for any signs, eg, other viral or bacterial infections that could lead to elevated c-reactive protein levels. In the absence of such signs, continue to monitor C-reactive protein levels until they peak and begin to decrease. As an indication of effector cell modulation, anti-CD4+ antibodies are administered to the subject at a standard dose, eg, 300 mg, approximately when c-reactive protein levels begin to decrease.
[0177] The patient is then continued to be monitored for HIV markers, such as determination of viral load. Treatment may be...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com