Serial interpretation method for low density parity check code
A low-density parity and check code technology, which is applied to the application of error detection coding of multiple parity bits, error correction/detection using block codes, transmission systems, etc., can solve the problem of variable node message cycle oscillation in the ring, Decoding performance is reduced to different degrees, BP decoding performance is reduced, etc., to achieve the effect of improving decoding performance, reducing impact, and reducing decoding complexity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
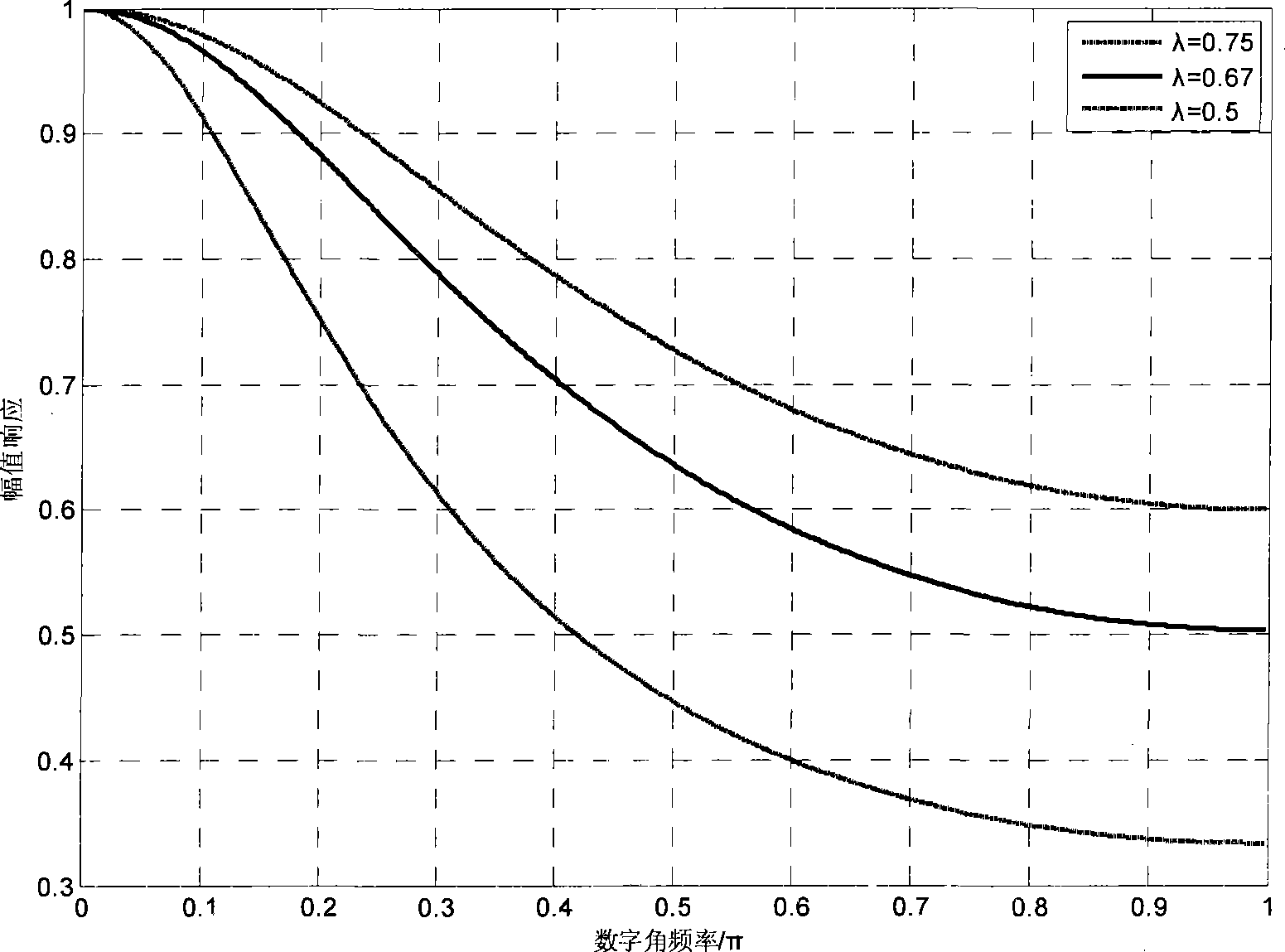
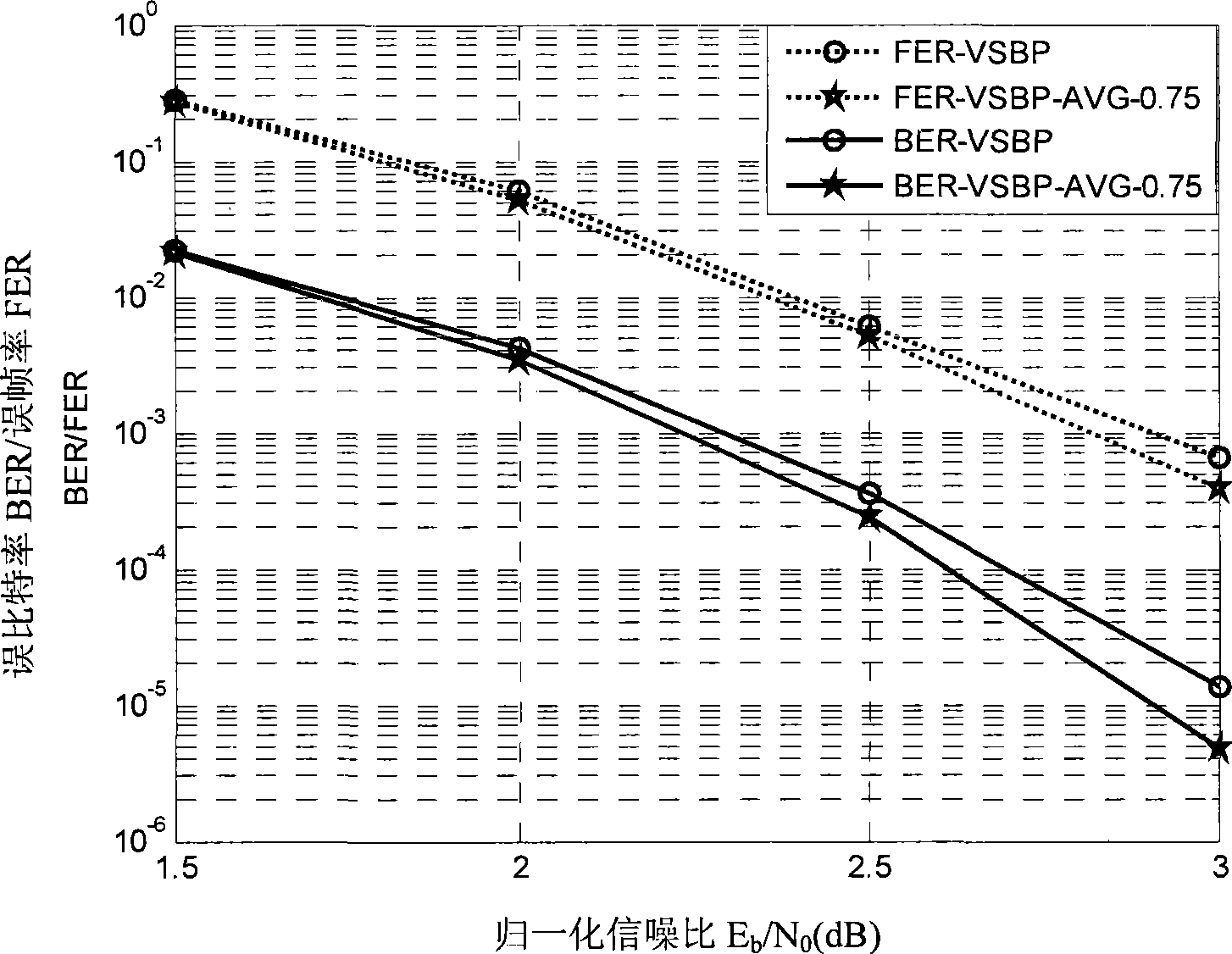
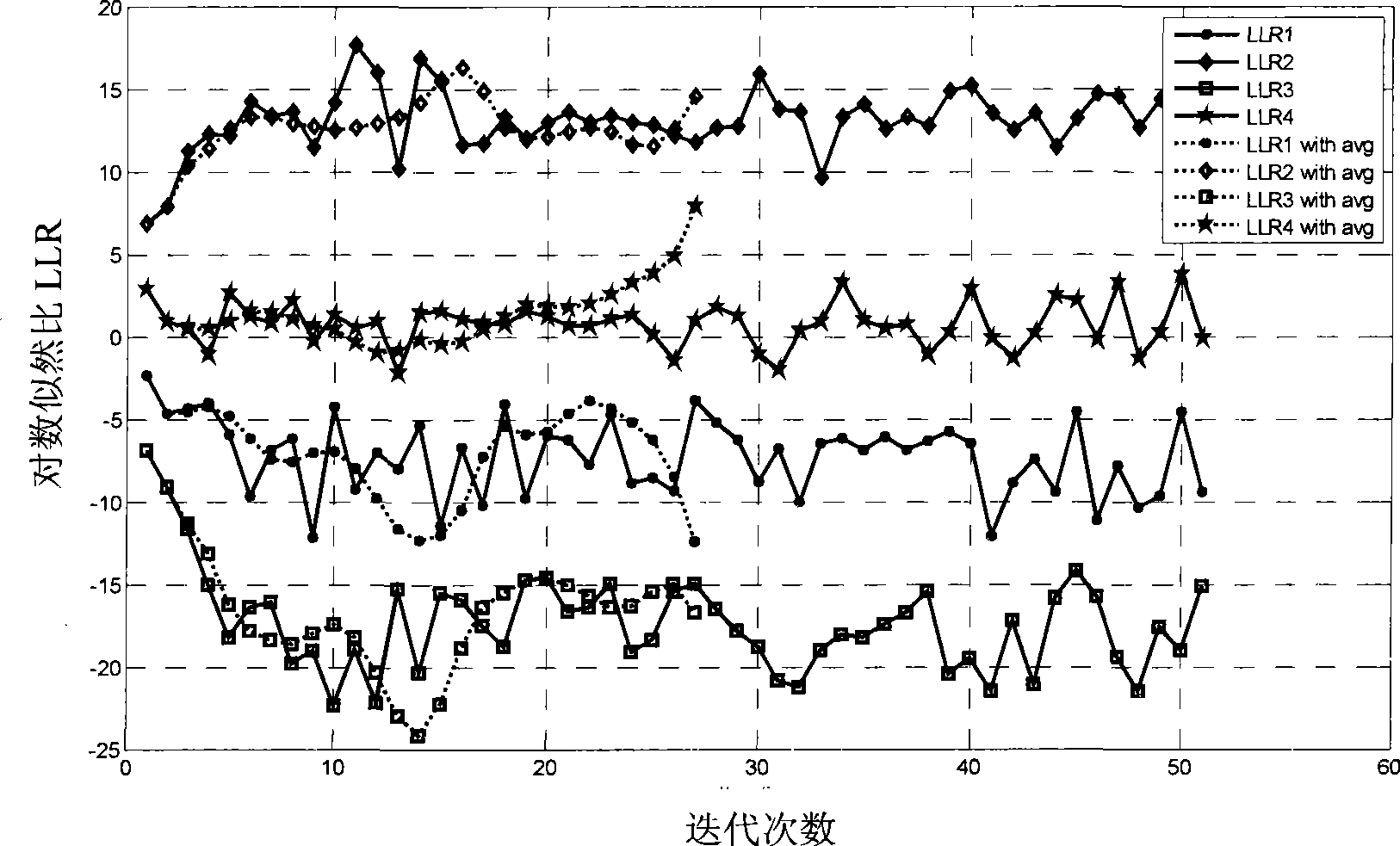
[0039] Below in conjunction with the contrast of accompanying drawing, the present invention is described further, and the magnitude response when wood invention adopts λ=0.75, λ=0.67, λ=0.5 is as attached figure 1 As shown, it can be seen that when 0<λ<1, it is a low-pass filter. With the increase of λ, the passband continues to widen. When λ=1, it is equivalent to no filtering function. By adjusting the value of λ, the oscillation of the variable node to the check node message in the BP decoding process can be effectively controlled. When λ changes from large to small, the impact of oscillation on decoding performance can be further weakened, but at the same time it will affect the normal BP Iteratively decodes the delivery of messages. When uncorrectable errors caused by message oscillation are dominant, λ can be appropriately increased to improve decoding performance.
[0040] The improved decoding algorithm steps of the present invention are as follows:
[0041] Initializ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com