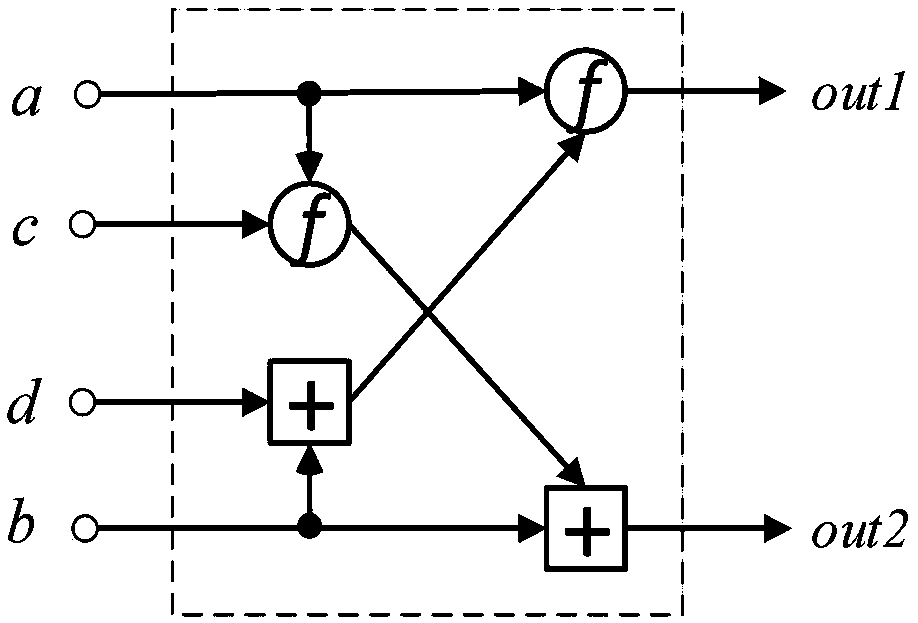
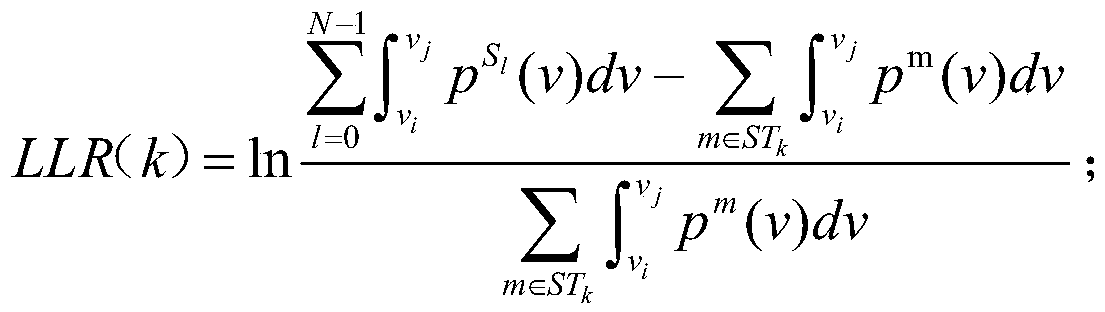Patents
Literature
75results about How to "Reduce Decoding Latency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
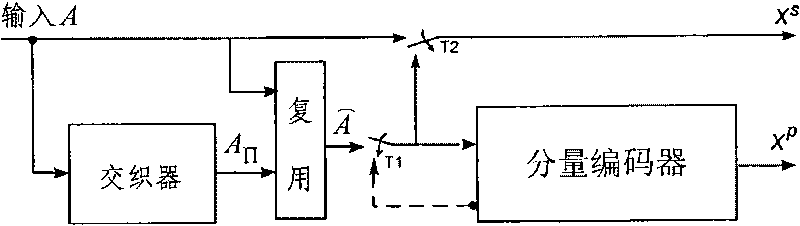
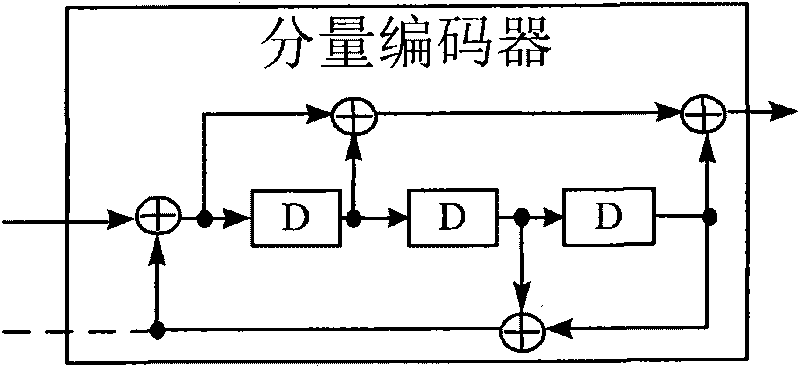
Polar code encoding modulation method applicable to any high-order modulation
ActiveCN106230489AImprove performanceOvercoming the lack of high complexitySpatial transmit diversityError correction/detection using block single space codingChannel capacityComputer science
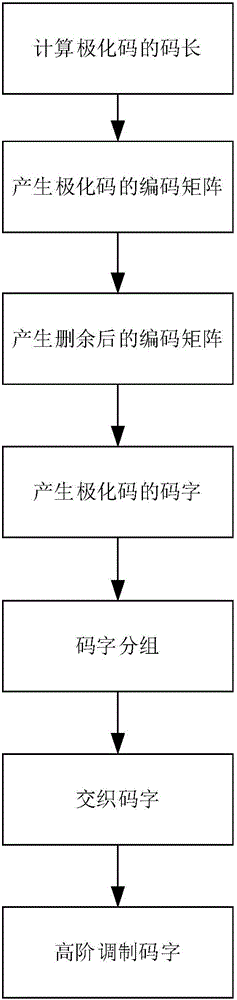
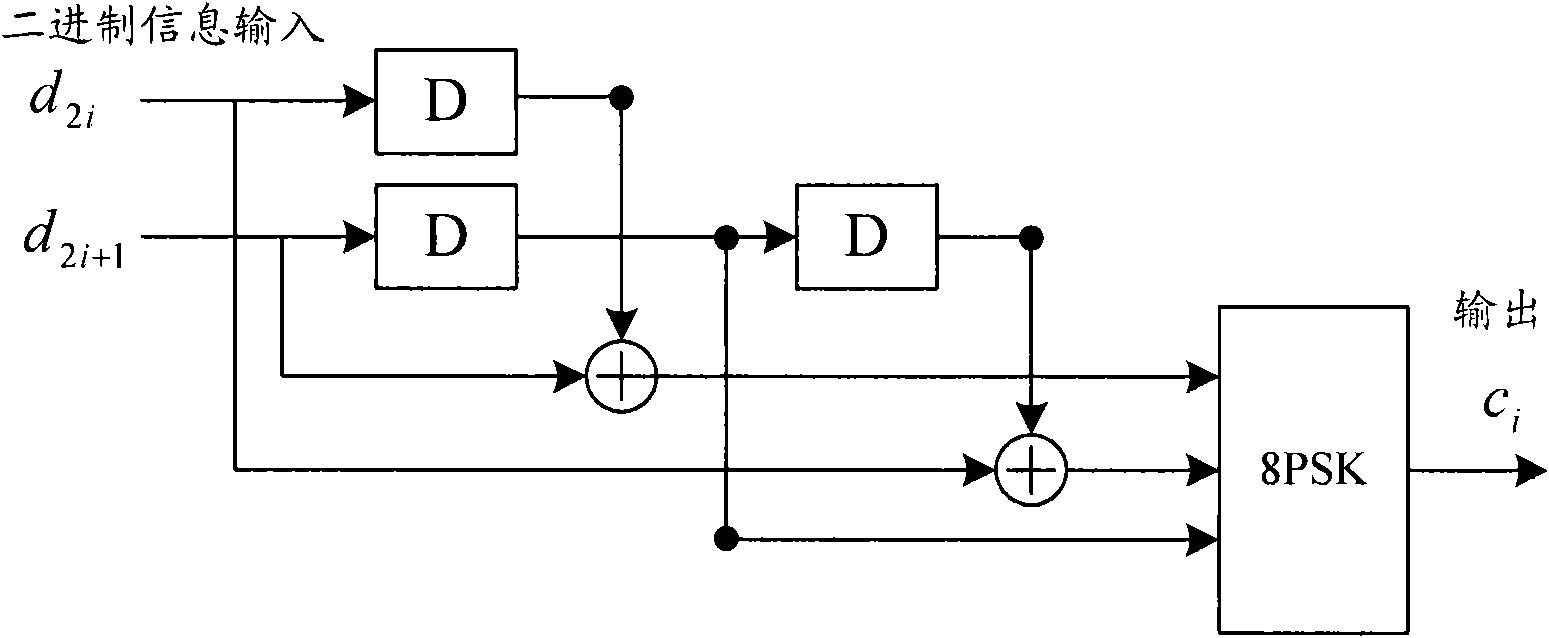
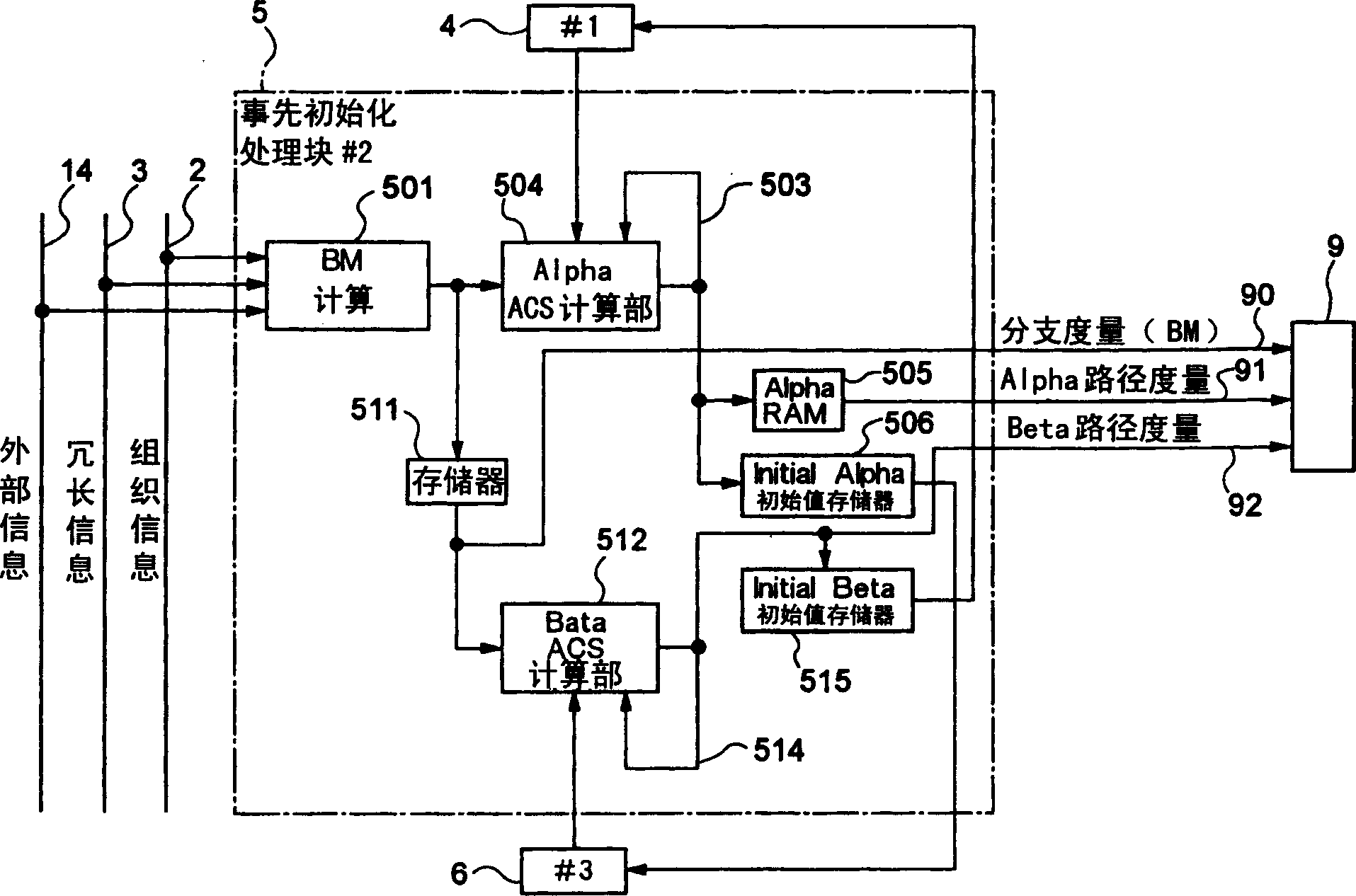
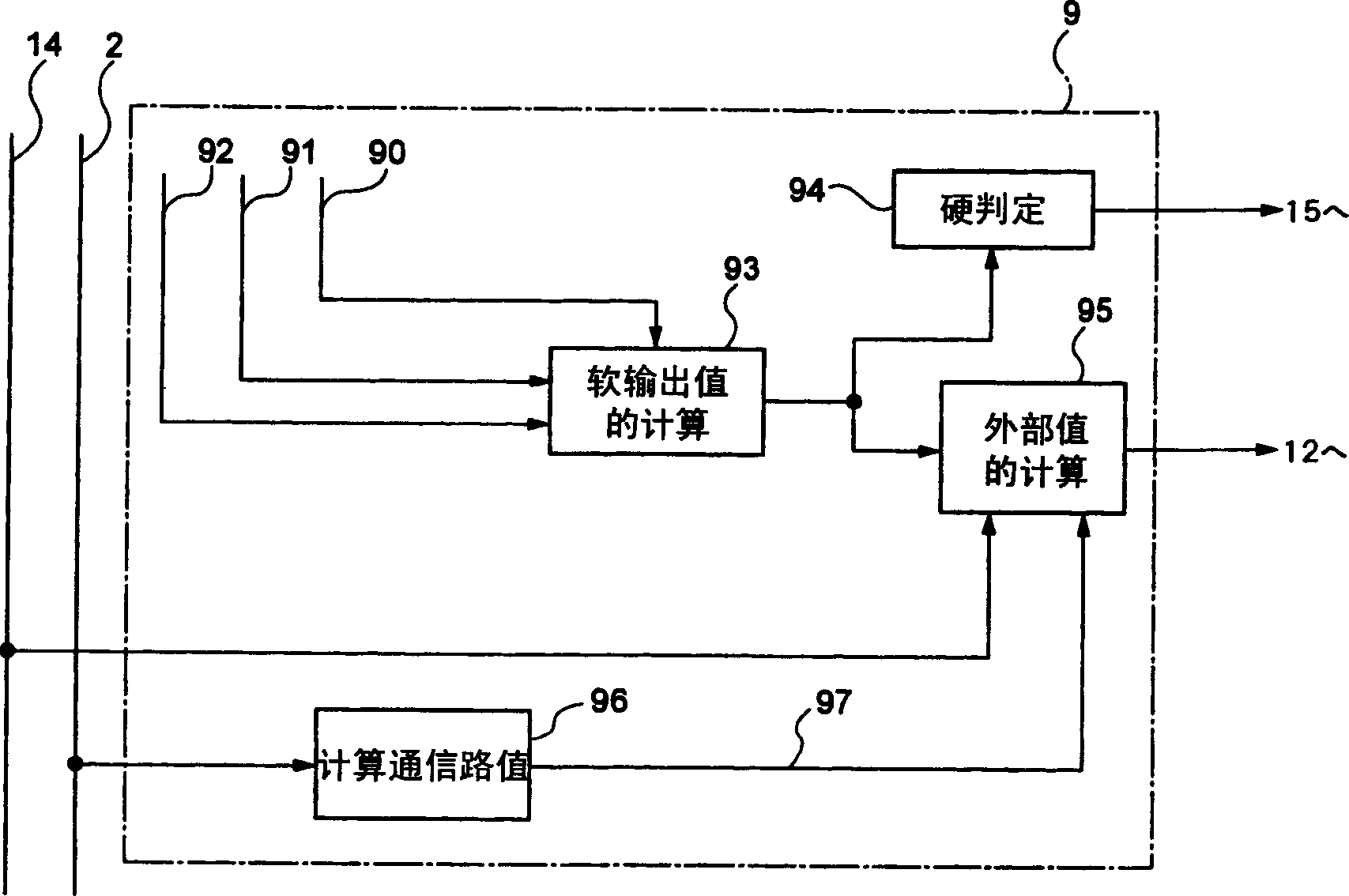
The invention discloses a polar code encoding modulation method applicable to any high-order modulation. The method comprises the concrete steps of (1), calculating the code length of a polar code; (2), generating an encoding matrix of the polar code; (3), generating the encoding matrix after puncturing; (4), generating code words of the polar code; (6) interleaving the code words; and (7), carrying out high-order modulation. According to the method, the code words are interleaved by employing a grouping interleaving technology, the polar effect of a channel is intensified with the combination of the polar characteristic of the polar code itself and the capacity differences of high-order modulation sub-channels, and the performance of the polar code is improved. According to the method, the encoding matrix is punctured according to a column weight, the decoding delay is reduced, and the programming realization complexity of a decoding algorithm in a programmable device is reduced. The flexibility of the polar code in the high-order modulation is improved, and the polar code has good performance.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Dual-binary system tailbaiting Turbo code coding method and apparatus
InactiveCN101083512AImprove throughputEliminate the phenomenon of "error flat bottom"Error preventionError correction/detection by combining multiple code structuresTurbo codedCode rate
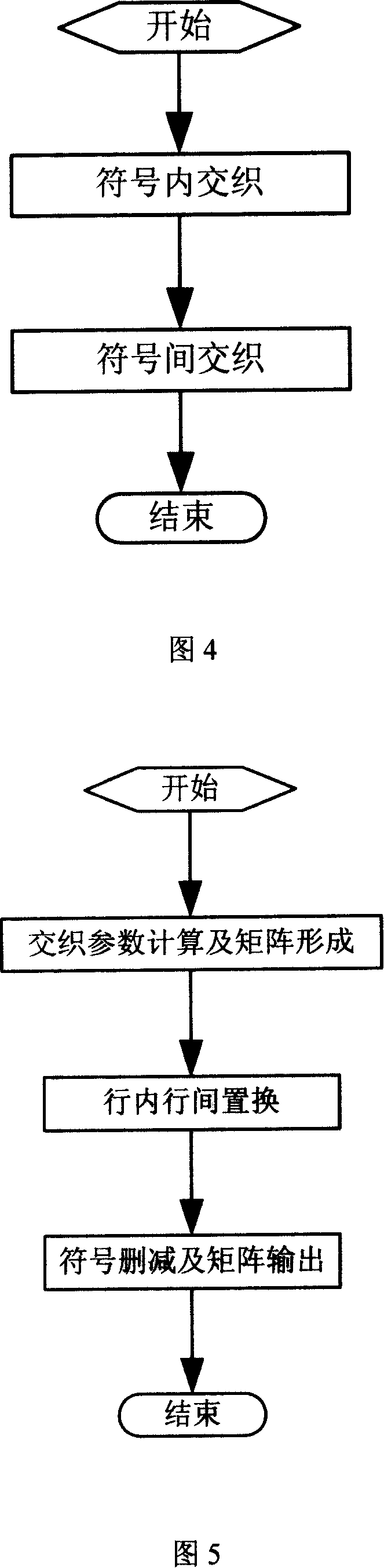
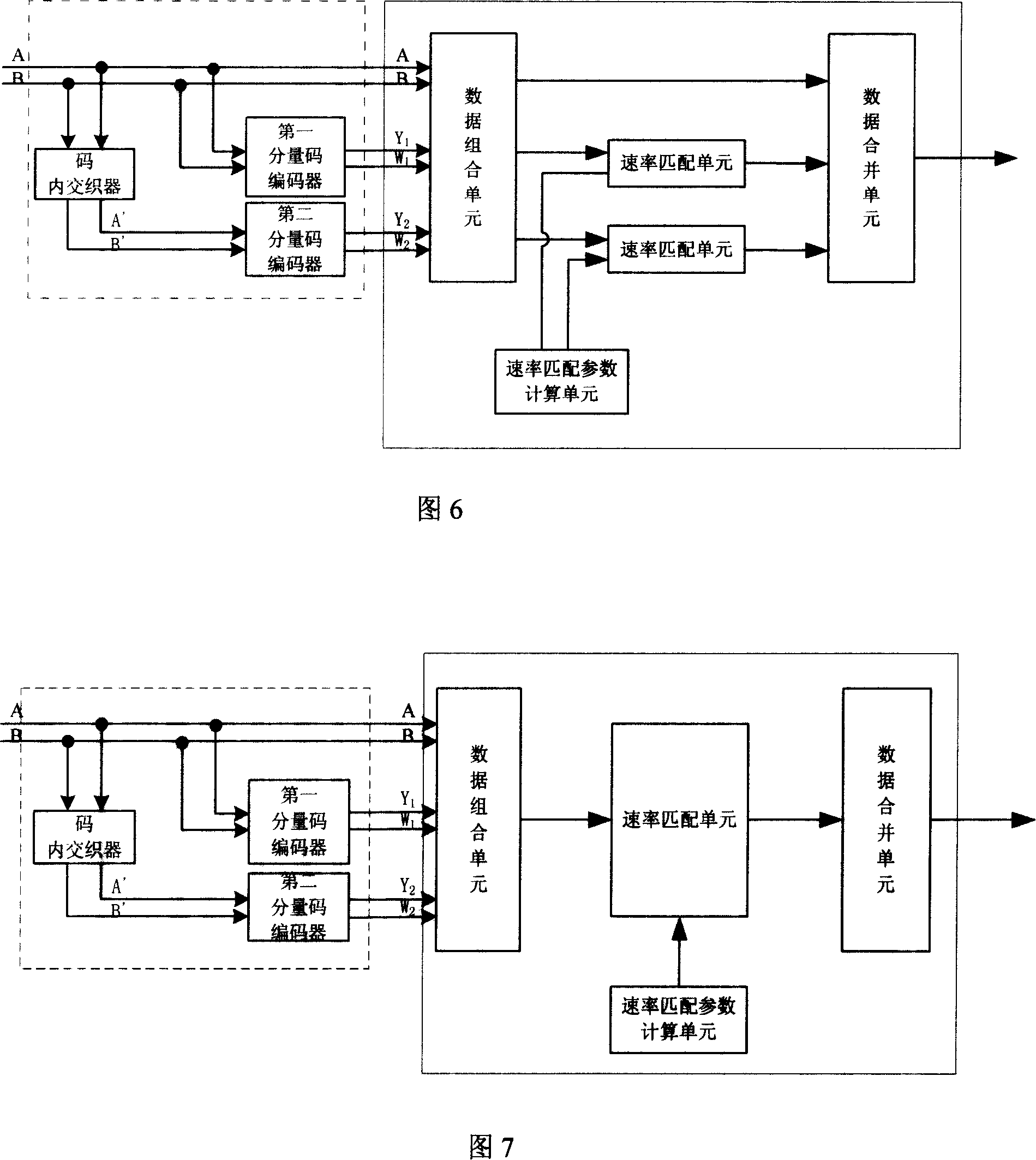
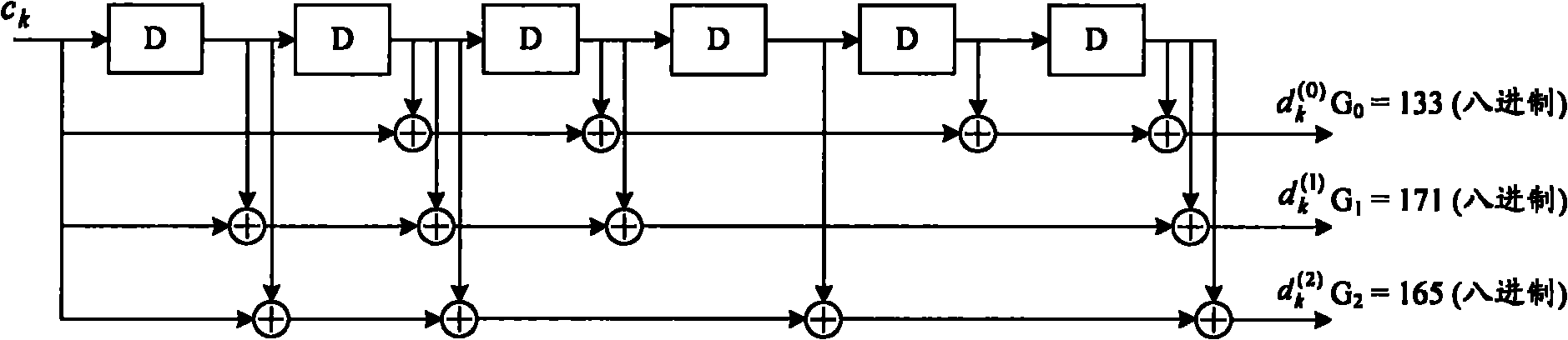
The invention publishes the equipment and a method of double binary system for Turbo code encoding, which solve the problem that could not support any even number information block length and the random code rate in existing technology. The invention includes: The first component code encoder, the second component code encoder, the mark interweave and the speed matching device. The invention method includes the following step: the system sent the bit sequence to the first component code encoder, the mark interweave and the speed matching device; create check bit in the first component code encoder; carry on data interior exchange in the code interweaves for every other a pair of data; structure the matrix, carry on replace between each line; create two check bit in the second component code encoder; output bit sequence by the speed matching device to the system, the first component encoder and a second component encoder carries on the number rate match, so can obtain the code rate needed. Thus, it can support any even number information block length and the random code rate.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Encoder, decoder and encoding and decoding methods
ActiveCN101841339AProcessing speedReduce complexityError correction/detection using single space codingDecoding methodsDifferential modulation
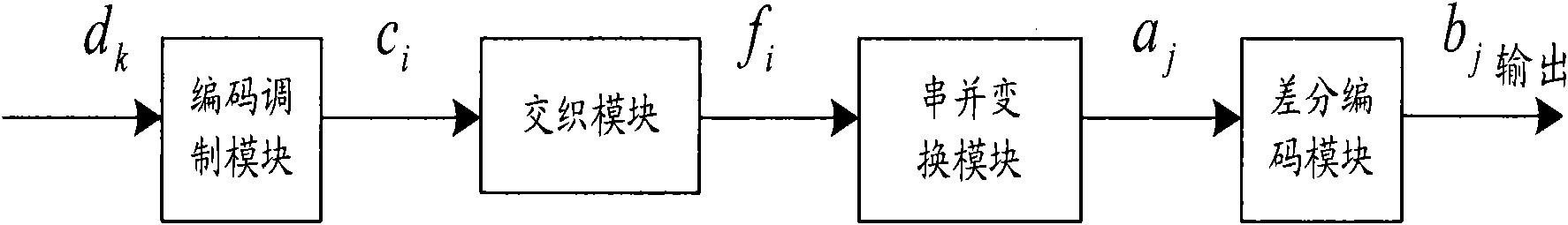
The invention discloses an encoder which comprises an encoding and modulating module, an interweaving module, a serial-parallel transformation module and a differential encoding module. After an input information sequence line is modulated and encoded by the encoding and modulating module, weighting and differential encoding processing is respectively carried out for multipath parallel signals through the differential encoding module, and an encoding signal is obtained and output. The invention also discloses a decoder and a decoding method. In the technical scheme disclosed by the invention, through adopting a simpler and highly efficient data processing method, the complexity of decoding and demodulation algorithms of a differential encoding technology and a differential modulation technology is reduced, the processing delay is reduced, and the speed of data processing is improved.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
Recursive block Markov superimposed encoding method
ActiveCN106972865ASimple codingFlexible structureError correction/detection using convolutional codesBit-lengthChannel capacity
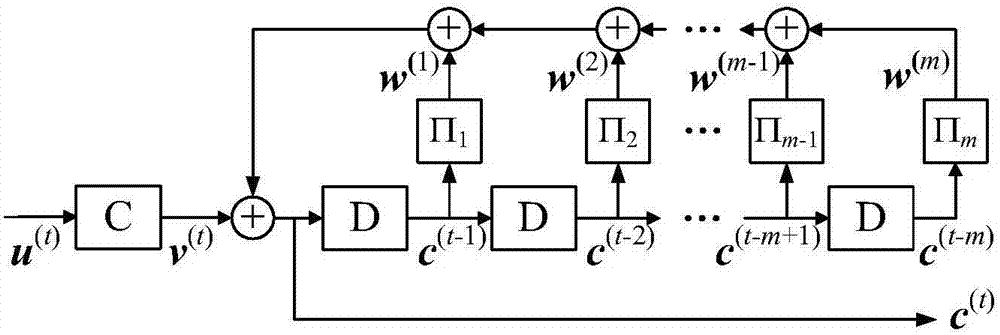
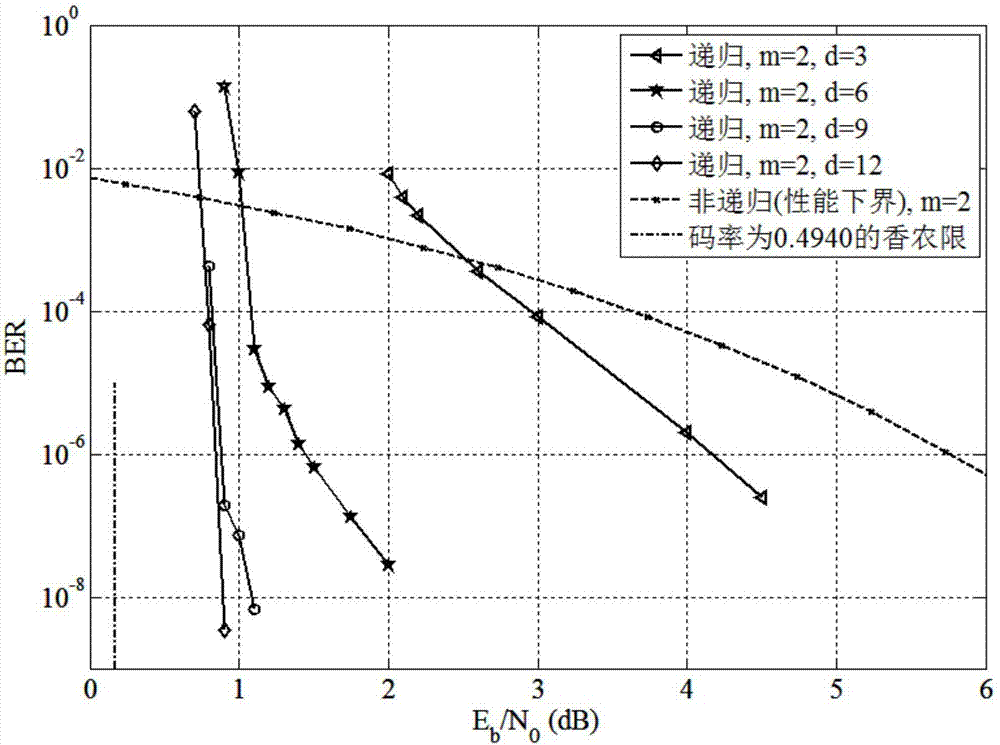
The invention belongs to the field of digital communication and digital storage, and especially relates to a recursive block Markov superimposed encoding method. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: taking a short code of which the code length is n and the information bit length is k as a basic code, and encoding an information sequence FORMULA of which the length K is equal to kBL to a code word FORMULA of which the length N is equal to nB(L+T), wherein the encoding method includes the following steps: firstly, dividing the information sequence FORMULA of which the length K is equal to kBL into L equal-length blocks FORMULA, ensuring that the length of each block is kB, and aiming at t that is equal to -1, -2, ..., -(m-1), -m, initializing a sequence FORMULA of which the length is nB to an all-zero sequence; and then, at the time of t that is equal to 0, 1, ..., L-1, sending a sequence FORMULA of which the length is kB to a basic code encoder C for encoding to obtain an encoded sequence FORMULA of which the length is nB, and combining the fed-back FORMULA to calculate the t(th) sub-sequence FORMULA of the code word FORMULA. The recursive block Markov superimposed encoding method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of approaching the channel capacity, achieving simple encoding and flexible structure, and the like. Compared with a non-recursive block Markov superimposed encoding method, the method disclosed by the invention has lower decoding delay and decoding complexity, and has a very low error floor in decoding performance.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Quasi-cyclic low density parity-check code (QC-LDPC) decoder and decoding method
ActiveCN101976584AShorten the overall cycleReduce Decoding LatencyStatic storageDecoding methodsCheck digit
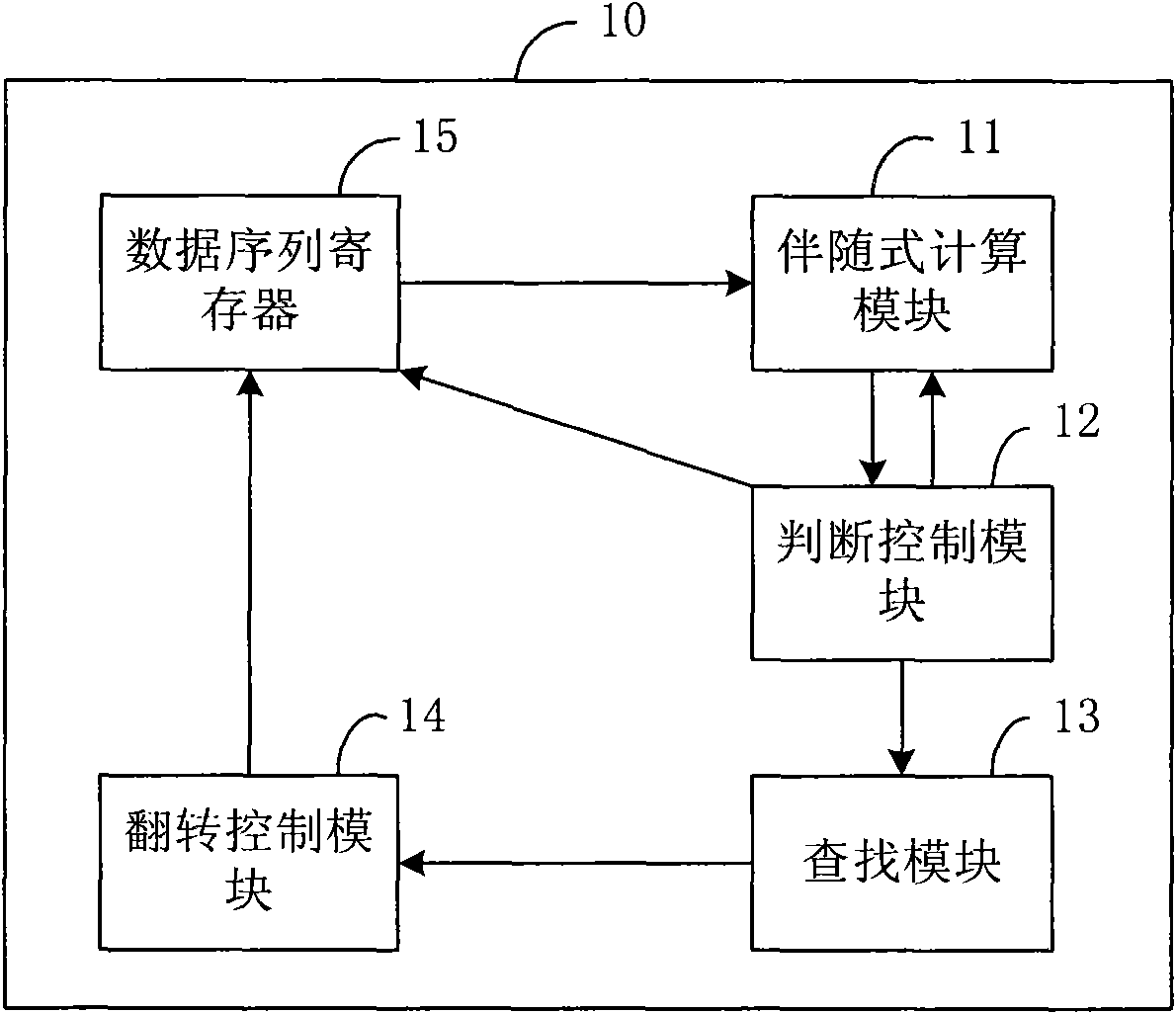
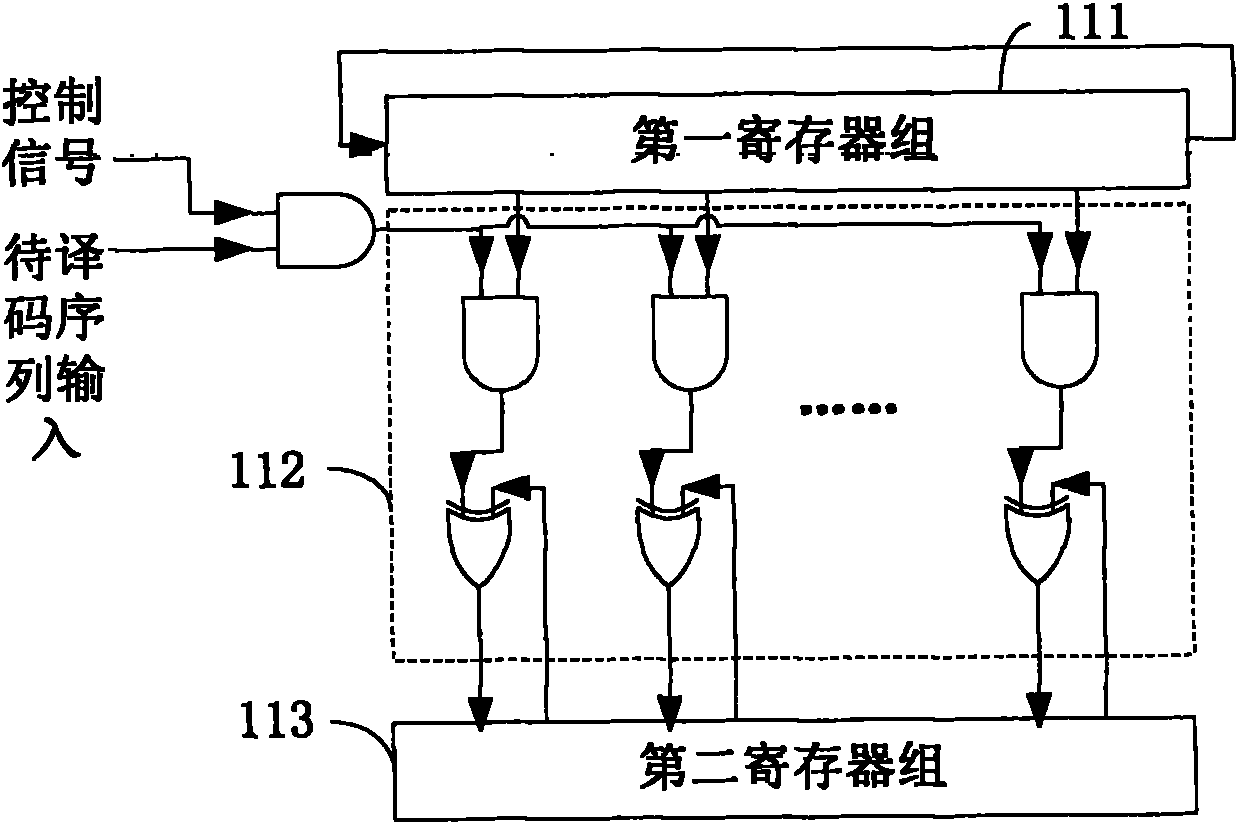
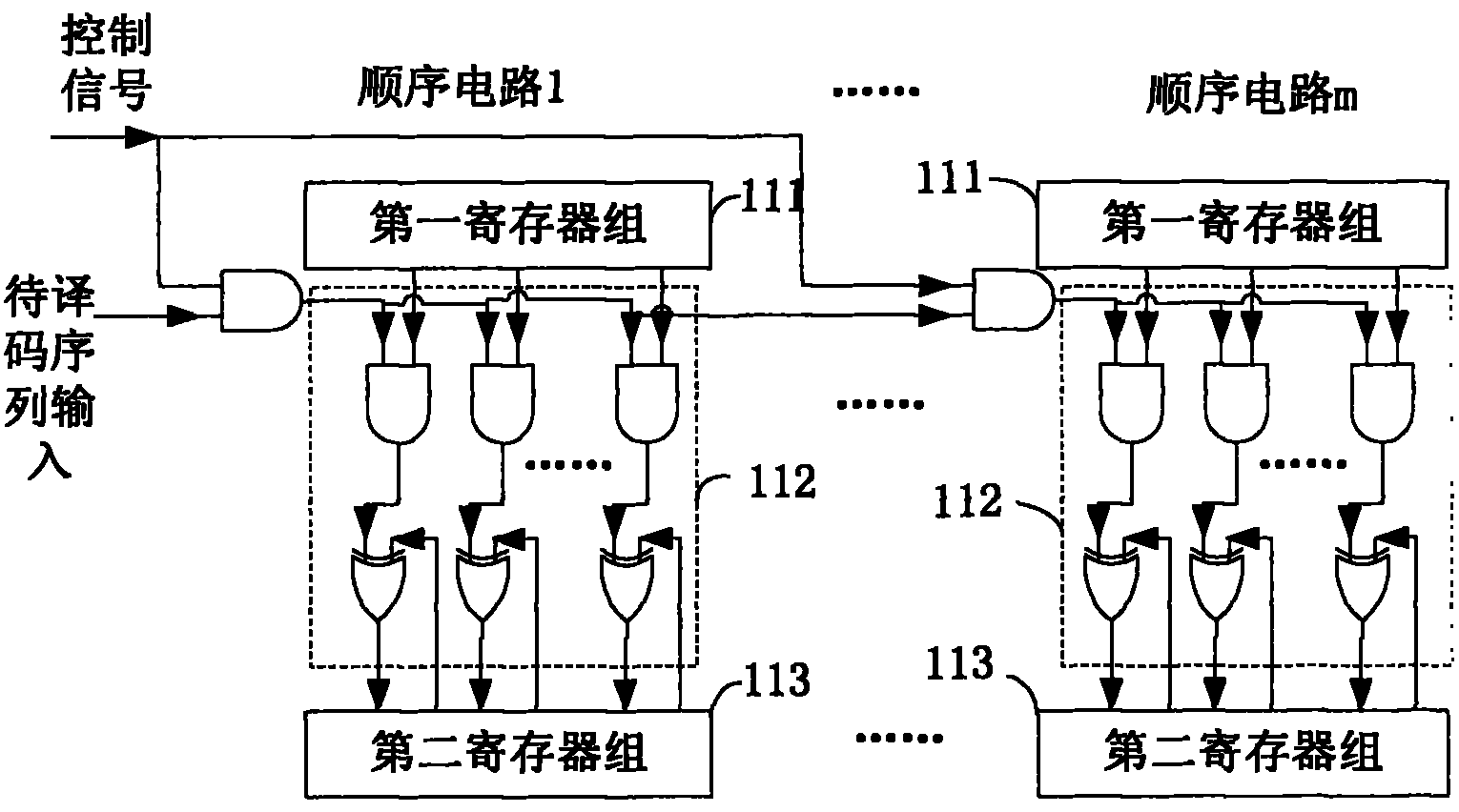
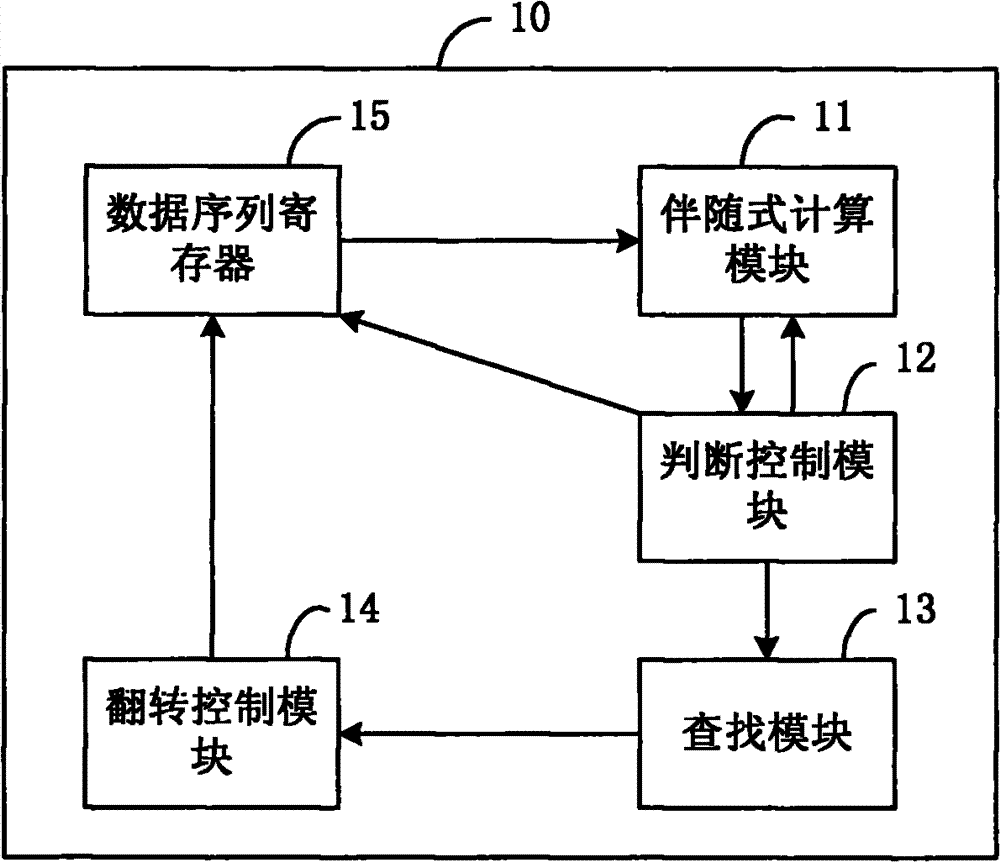
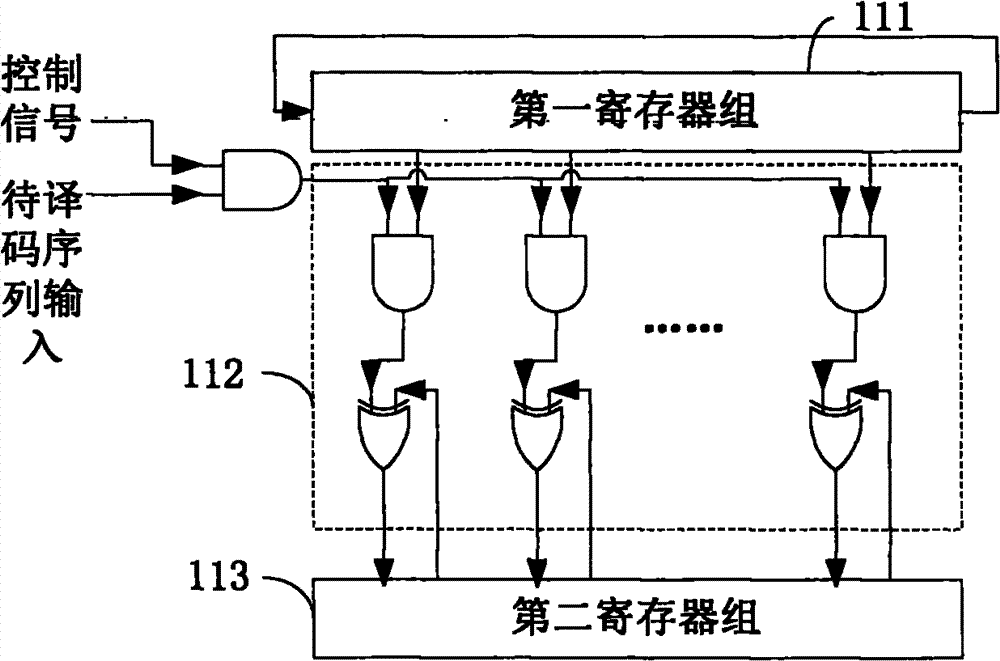
The invention discloses a quasi-cyclic low density parity-check code (QC-LDPC) decoder. The QC-LDPC decoder is applied to solid state disk error correction systems, and comprises a syndrome calculation module, a judgment control module, a searching module and an overturn control module, wherein the syndrome calculation module is used for calculating the syndrome of a code sequence to be decoded; the judgment control module is used for judging whether the syndrome is an all-zero vector or not, and controlling to finish the syndrome calculation and outputting the current code sequence as a decoding result if the syndrome is the all-zero vector; the searching module is used for calculating the set of the number of code elements which do not meet a check equation in the code sequence to be decoded and searches the position of a maximal value in the set when the syndrome is not the all-zero vector; and the overturn control module is used for overturning the code element which corresponds to the position of the maximal value in the set in the code sequence to be decoded, and inputting an updated code sequence to be decoded into the syndrome calculation module. The invention correspondingly provides a QC-LDPC decoding method. Thus, by using the decoder and the decoding method, the syndrome calculation can be controlled to be finished when error correction is finished, and the decoding period and decoding delay are lowered.
Owner:RAMAXEL TECH SHENZHEN
Parallel decoding method and device for polarization codes
ActiveCN106788453AReduce Decoding LatencyDecoding speed is fastCode conversionError detection onlyDecoding methodsDegree of parallelism
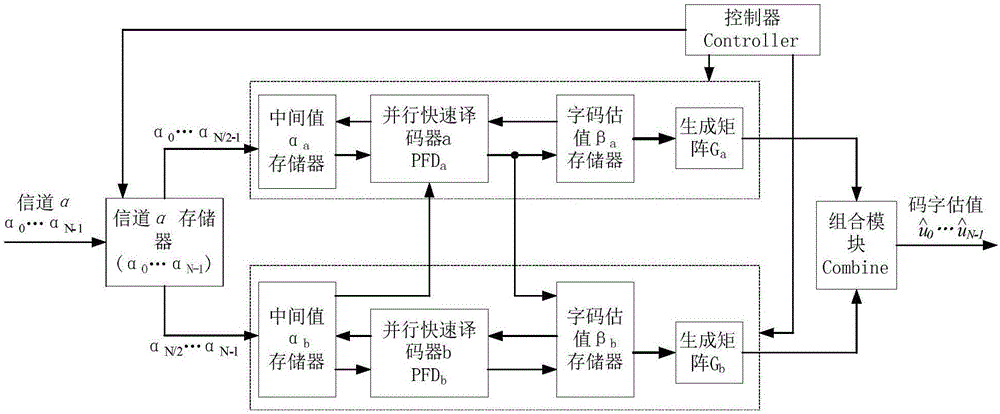
The invention discloses a parallel decoding method and device for polarization codes, belongs to the field of wireless communication, and particularly relates to a parallel decoding method for polarization codes. Based on the defect of high decoding delay of a Fast-SSC algorithm, the invention provides a parallel quick method, two parallel Fast-SSC decoders are adopted, channel information is divided into two parts during decoding, and decoding is performed by the two parallel decoders, so that the decoding delay of the Fast-SSC algorithm is effectively reduced. The method has the same bit error rate as the Fast-SSC algorithm, but is faster in decoding speed than the Fast-SSC algorithm; and when the two Fast-SSC decoders are parallel, the parallelism is improved by about 40% over the Fast-SSC algorithm.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
An LDPC code decoding method based on threshold voltage drift perception
ActiveCN109887537AImprove decoding performanceReduce Decoding LatencyError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsRead-only memoriesCoding decodingVoltage reference
The invention discloses an LDPC code decoding method based on threshold voltage drift perception, and the method comprises the steps of obtaining a current drift parameter of a flash memory page P towhich to-be-decoded data belongs, and obtaining the threshold voltage distribution D of a storage unit in the current flash memory page P according to the corresponding relation between the thresholdvoltage distribution of the storage unit and the drift parameter; taking the voltage at each tail end point of the standard read reference voltage and the threshold voltage distribution D as a sampling voltage, and determining the voltage range [vi, vj] where the threshold voltage of each storage unit is located by applying different sampling voltages; calculating soft decision information according to the voltage range [vi, vj], and performing LDPC code decoding on the to-be-decoded data according to the soft decision information, wherein the drift parameter comprises the erasing frequency and the data storage time, and v is smaller than vj. According to the invention, the soft decision information can be accurately acquired by utilizing the drift characteristic of the threshold voltage of the storage unit, so that the decoding performance of the LDPC code can be improved, and the decoding delay is reduced.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
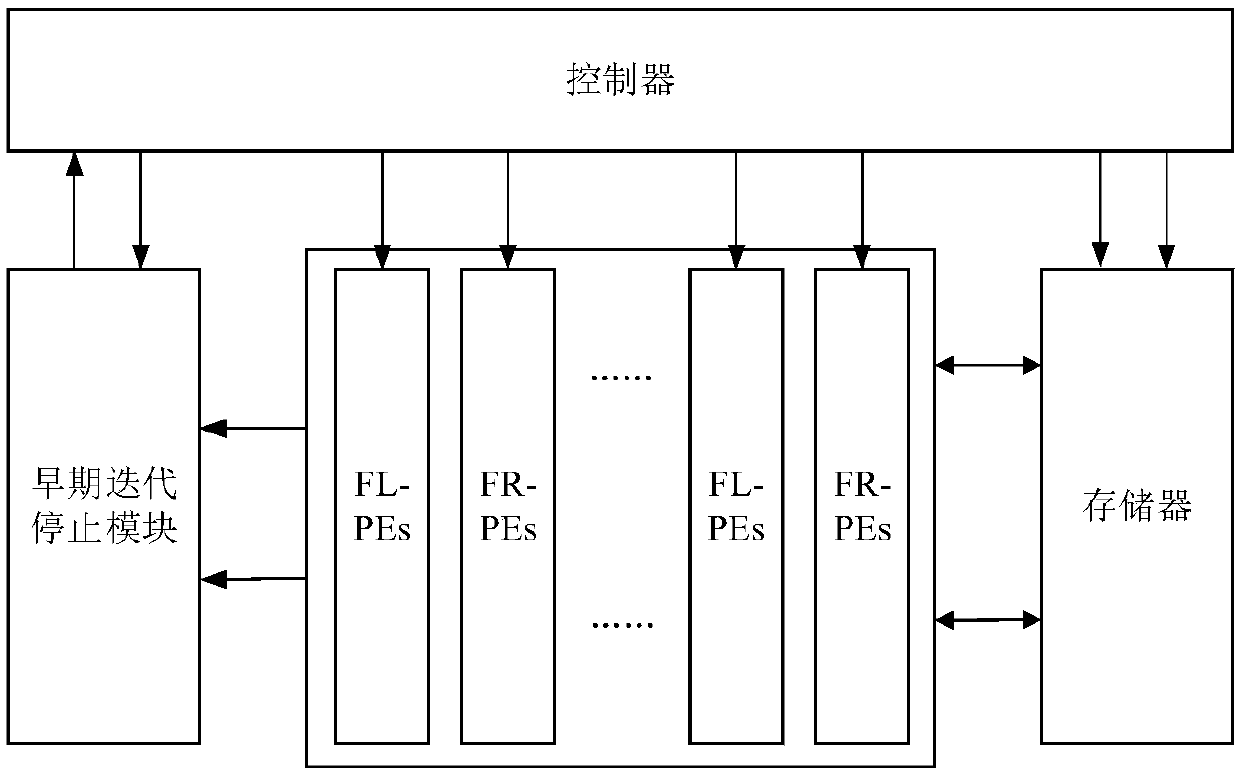
Polar code BP decoding method and device based on multi-stage updating processes
ActiveCN108039891AReduce the number of iterationsReduce Decoding LatencyCode conversionError correction/detection using linear codesIteration processComputer engineering
The invention discloses a polar code BP decoding method and device based on multi-stage updating processes. A hardware device is mainly composed of a BP decoder, a controller, a processing element module, an early iteration stopping module and a storage. The decoding method comprises the steps of: (S1), pre-setting the maximum iteration time of the BP decoder; (S2), decoding polarization by usinga multi-stage flooding BP decoding algorithm; and (S3), performing CRC check on a decoding result in an iteration process, wherein if the CRC check is passed, the decoder stops iteration and outputs the decoding result; and otherwise, iteration is continuously carried out till the time is up to the maximum iteration time. According to the polar code BP decoding method and device based on the multi-stage updating processes provided in the invention, parallel decoding through multiple sets of PEs having opposite initial iteration directions is used; therefore, the iteration time is further reduced under the early iteration stopping standard; a test result is displayed in a range of 2-3.5 dB; therefore, the average iteration time is reduced by 31.7-36.5%; and the decoding delay is effectivelyreduced.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
High-speed Turbo decoding method and device
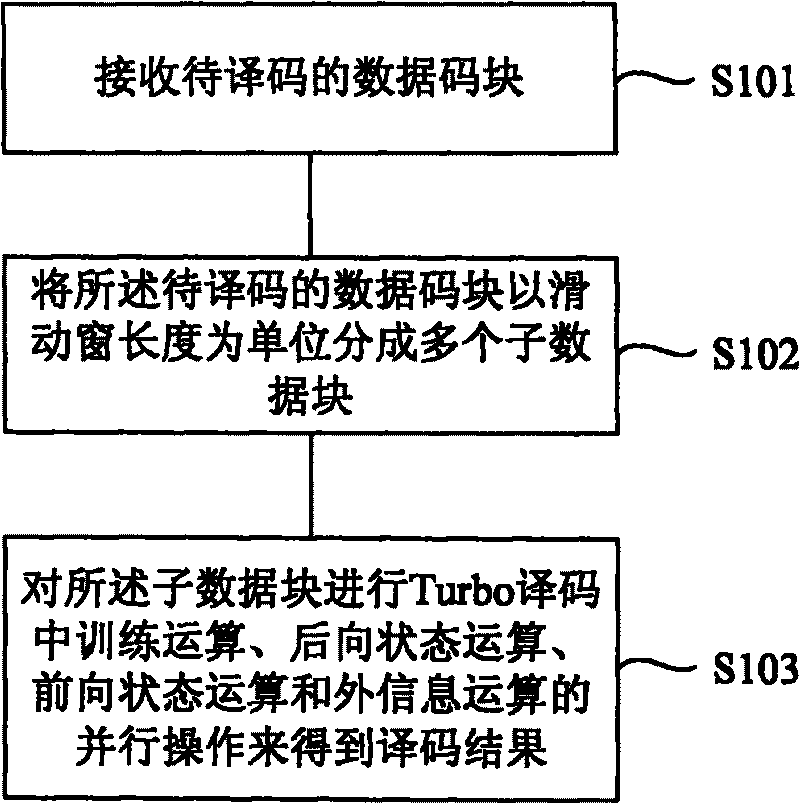
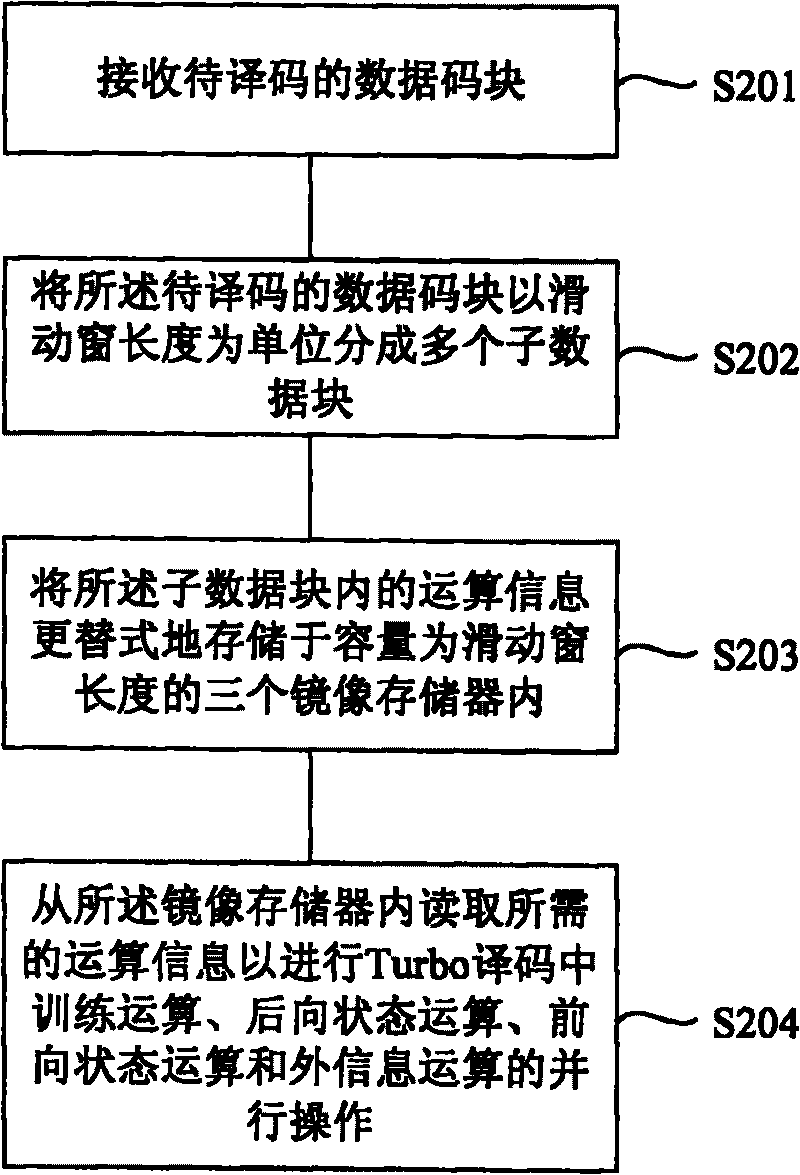
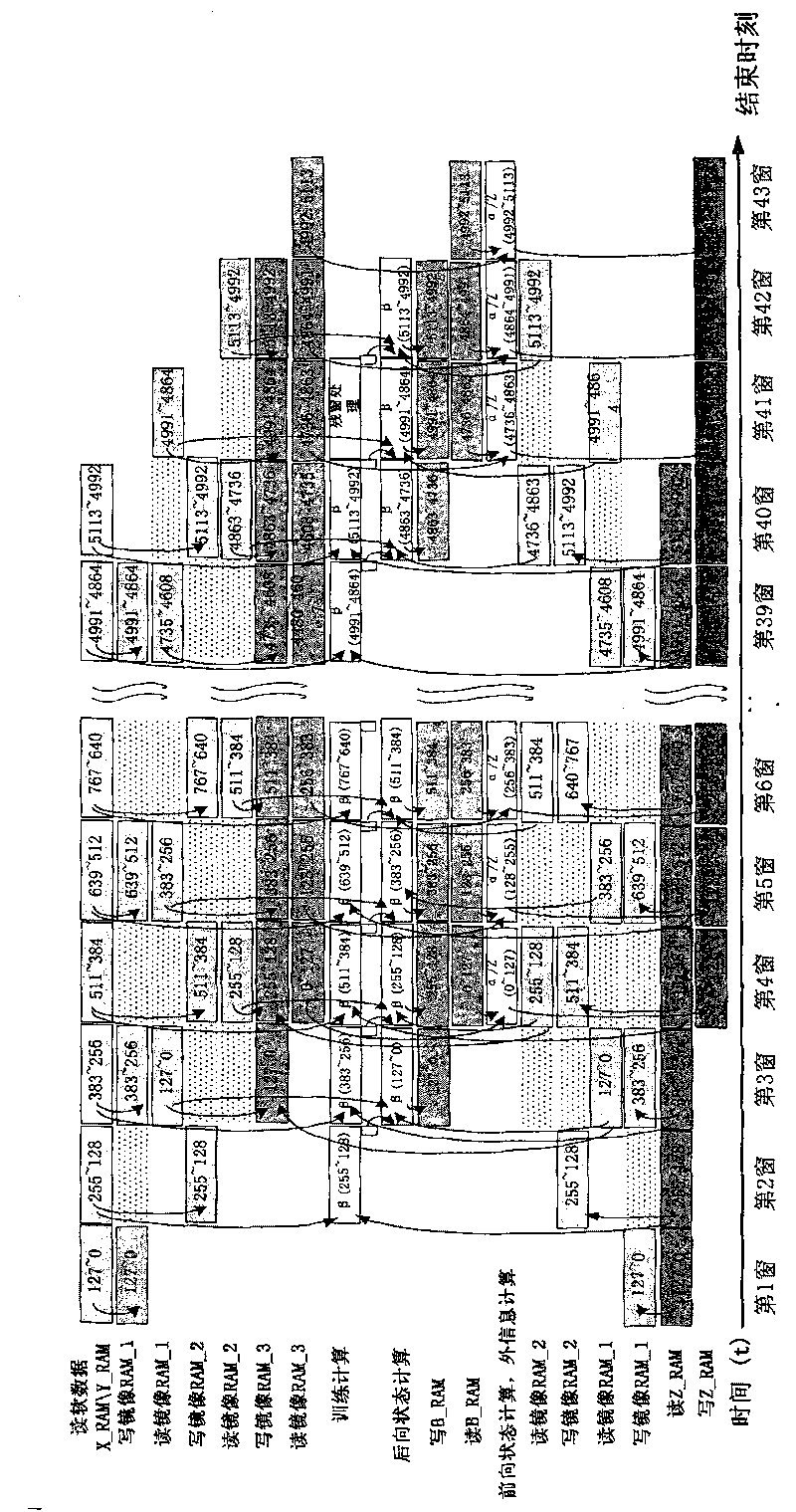
ActiveCN101707510AImprove decoding performanceReduce Decoding LatencyError preventionCoding blockTurbo decoding
The embodiment of the invention provides a high-speed Turbo decoding method and a device thereof, wherein the method comprises the following steps: receiving a data code block to be decoded; dividing the data code block to be decoded into a plurality of sub-data blocks by taking length of a sliding window as a unit; and conducting parallel operations including training operation, backward state operation, forward state operation and external information operation during Turbo decoding on the sub-data blocks to obtain the decoding result. The embodiment of the invention has the following beneficial effect: by conducting the parallel operations including the training operation, the backward state operation, the forward state operation and the external information operation to the sub-data blocks, decoding delay is shortened while keeping high decoding performance.
Owner:HONOR DEVICE CO LTD
LDPC decoder and method for decoding implementation
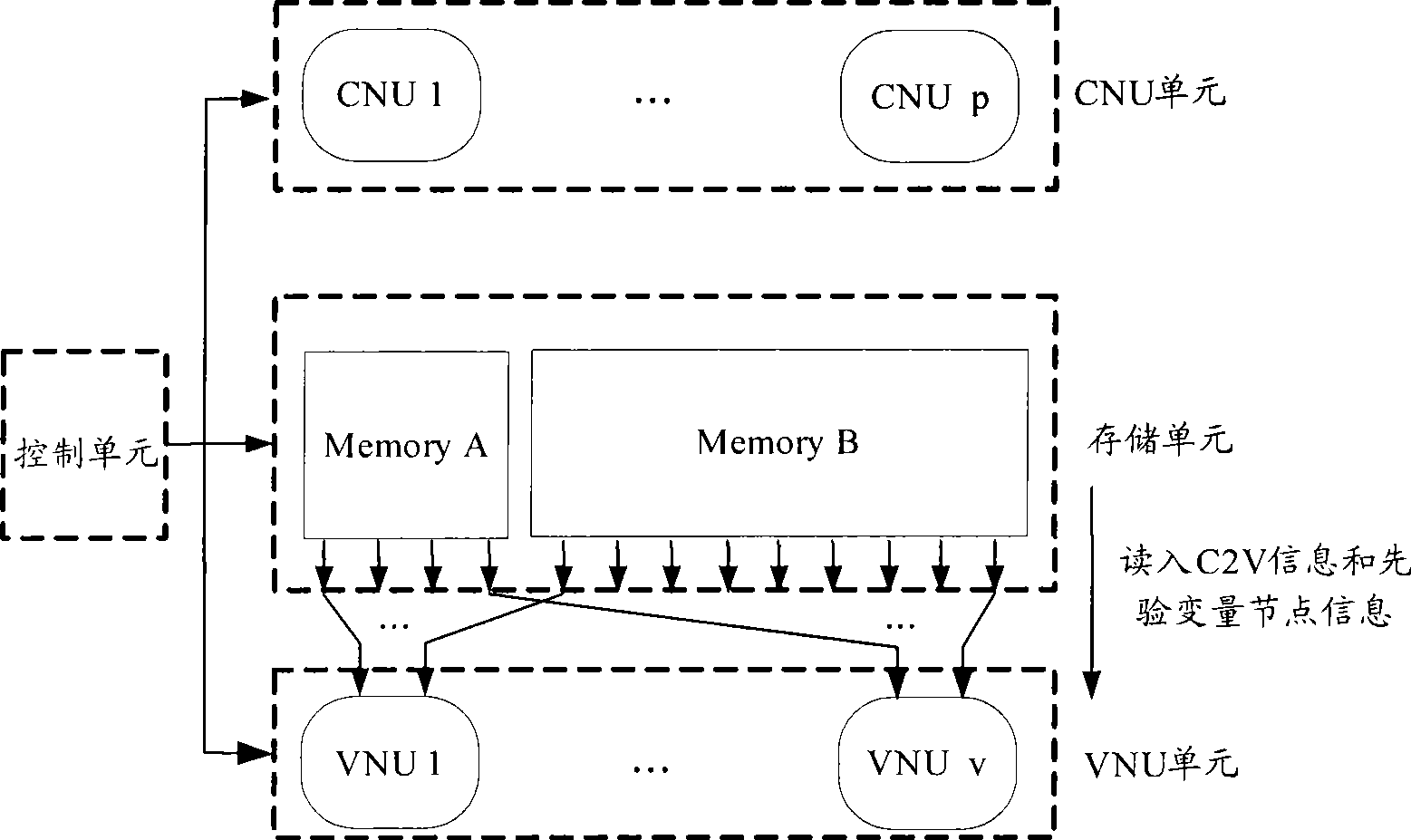
InactiveCN101478312ATake advantage ofFast convergenceError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsLow densityRate of convergence
The invention discloses a low-density parity check (LDPC) encoder and a method thereof for realizing coding. In the LDPC encoder, information of a variable node is refreshed by a currently participant check node after processing of each level is completed during the information transfer process; and the variable node also participates in other check nodes, so that a VCVNU unit uses the refreshed variable node information when processing the level including the other check nodes. Therefore, the variable node information is refreshed continuously between the levels, and the information transfer mechanism is different from the existing mechanism completely; the information transfer mechanism of the LDPC encoder utilizes the known information more fully, so the convergence speed is increased, less iteration times are used to complete the coding, decoding delay is reduced, and the decoding performance is enhanced at the same time. At the same time, a memory cell is saved to a great extent because C2V information is simplified greatly, thereby effectively saving the memory space.
Owner:INNOFIDEI TECHNOLOGIES INC
Coding method and coding device for polar codes
ActiveCN107204779AReduce decoding complexityReduce Decoding LatencyError preventionCode conversionComputer hardwareCommunications system
The invention provides a coding method for Polar codes in a communication system. The coding method is characterized by comprising constructing an input bit sequence with length of N according to an information bit index set or frozen bit index set, wherein the input bit comprises an information bit and a frozen bit; wherein the construction process comprises an information bit index set or a frozen bit index set which corresponds with other partial bits according to the information bit index set or the frozen bit index set that corresponds with partial bits in a to-be-constructed input bit sequence, thereby obtaining the information bit index set or the front bit index set of the input bit sequence with the length of N; wherein the partial bits are 1 / m of the input bit sequence, N and m are integral power of 2, and furthermore N>m; and performing coding on the Polar codes according to the constructed input bit sequence.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
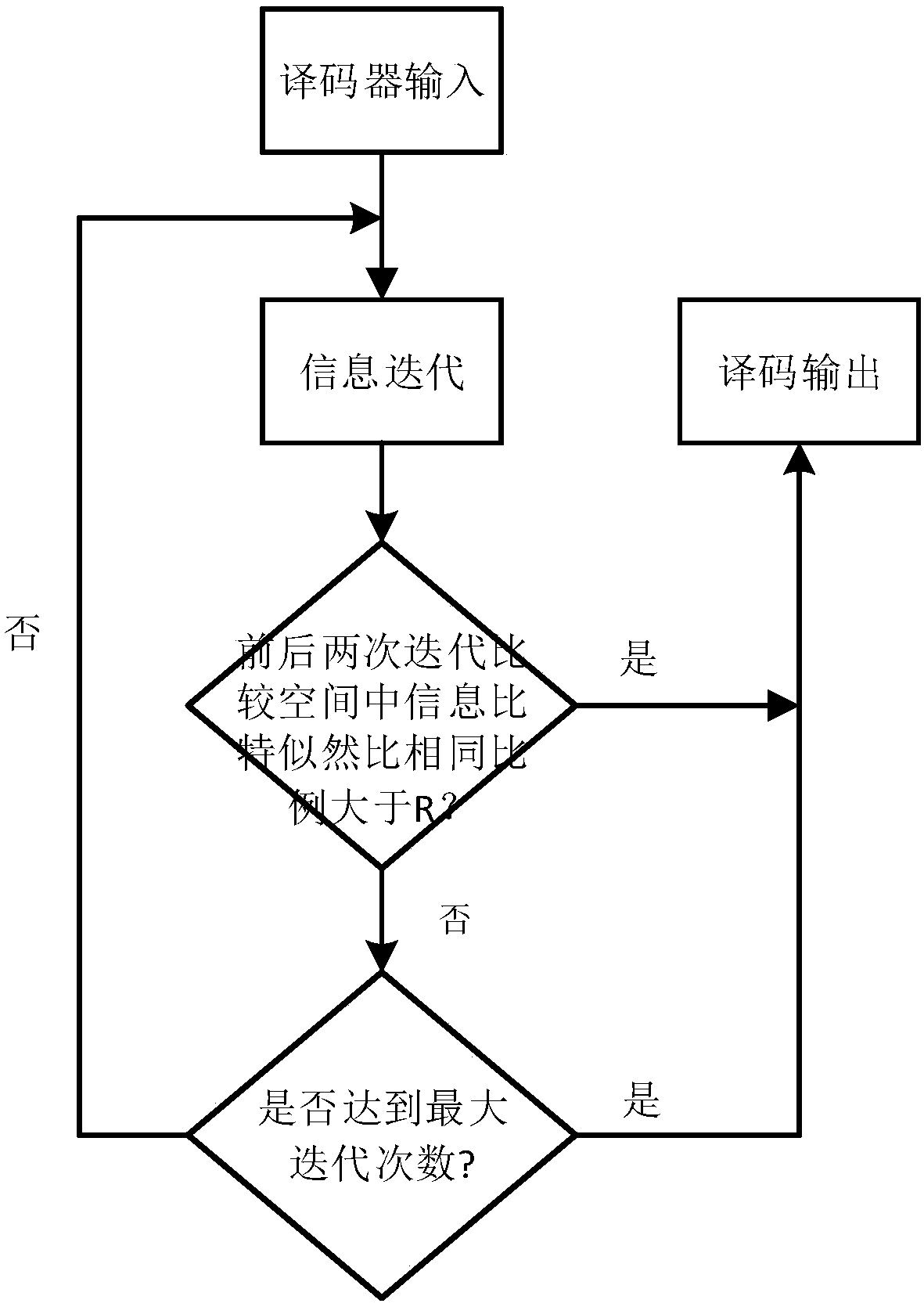
Polarization code early iteration stopping method based on partial information bit likelihood ratio
ActiveCN107612560AReduce the number of iterationsReduce computational complexityError preventionError correction/detection using linear codesComputation complexityRound complexity
The invention discloses a polarization code early iteration stopping method based on partial information bit likelihood ratio. The polarization code early iteration stopping method comprises the following steps: S1) presetting maximum iteration times of BP (Belief-Propagation) decoding; S2) decoding polarized decoding information by using a BP decoding algorithm; and S3) comparing partial information bit likelihood ratios output by adjacent two iterative decoding after primary iteration is finished; if the proportion of the same information bit likelihood ratio in a preset comparison space reaches a preset threshold, stopping iteration and outputting a decoding result obtained by current iteration, otherwise, continuing iteration till a preset maximum iteration time is reached. In each iteration process, previous and next partial information bit likelihood ratios output by an iterative decoder are judged. If the proportion of the same information bit likelihood ratio in the comparisonspace reaches the preset threshold, iteration is stopped, so that the computation complexity of decoding is lowered greatly; decoding time delay is reduced; and hardware resource consumption is lowered effectively.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Realization method of low complexity performance limit approximate Turbo decoder
ActiveCN105634508AImprove error correction performanceReduce complexityCode conversionError correction/detection by combining multiple code structuresRound complexityLinear approximation
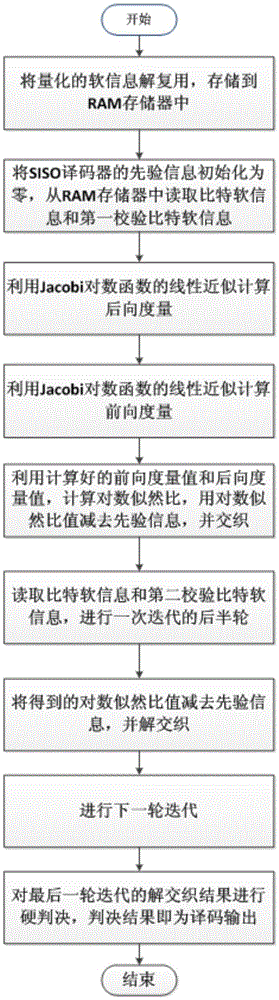
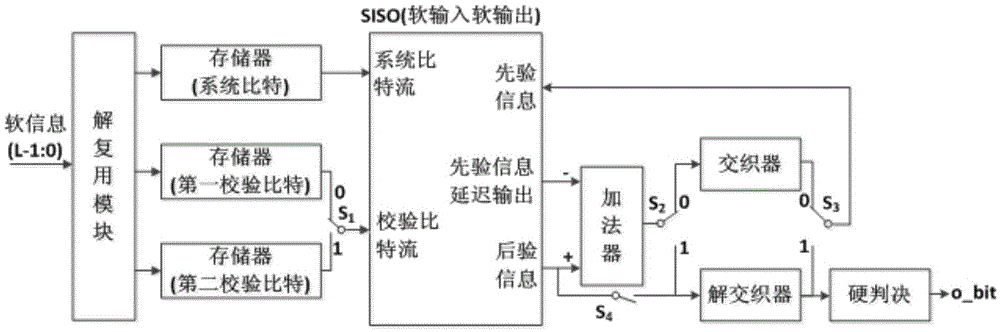
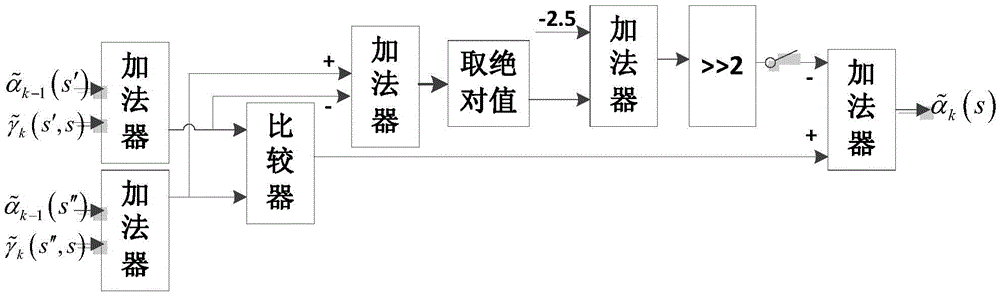
The invention discloses a realization method of a low complexity performance limit approximate Turbo decoder, mainly solves the problems that a traditional Turbo decoder based on a searching table is high in complexity and a decoder based on a Max-Log-MAP algorithm is poor in performance. The method comprises following steps: demultiplexing input soft information streams; storing in an RAM; selecting data from the RAM by an SISO (soft input soft output) decoder according to decoder station indication signals; iteratively calculating backward measurement, forward measurement and a log-likelihood ratio, wherein a Log-MAP algorithm based on linear approximation is adopted, the same SISO decoder is iteratively multiplexed in front and back stages; reversely accessing an interleaving address unit; and interleaving and de-interleaving external information. According to the method of the invention, through carrying out linear approximation to the Log-MAP algorithm, compared with a traditional approximate scheme, a better error correction performance is obtained; compared with a scheme based on the searching table, the complexity is greatly reduced; and the method is applicable to an LTE system.
Owner:XIAN INSTITUE OF SPACE RADIO TECH
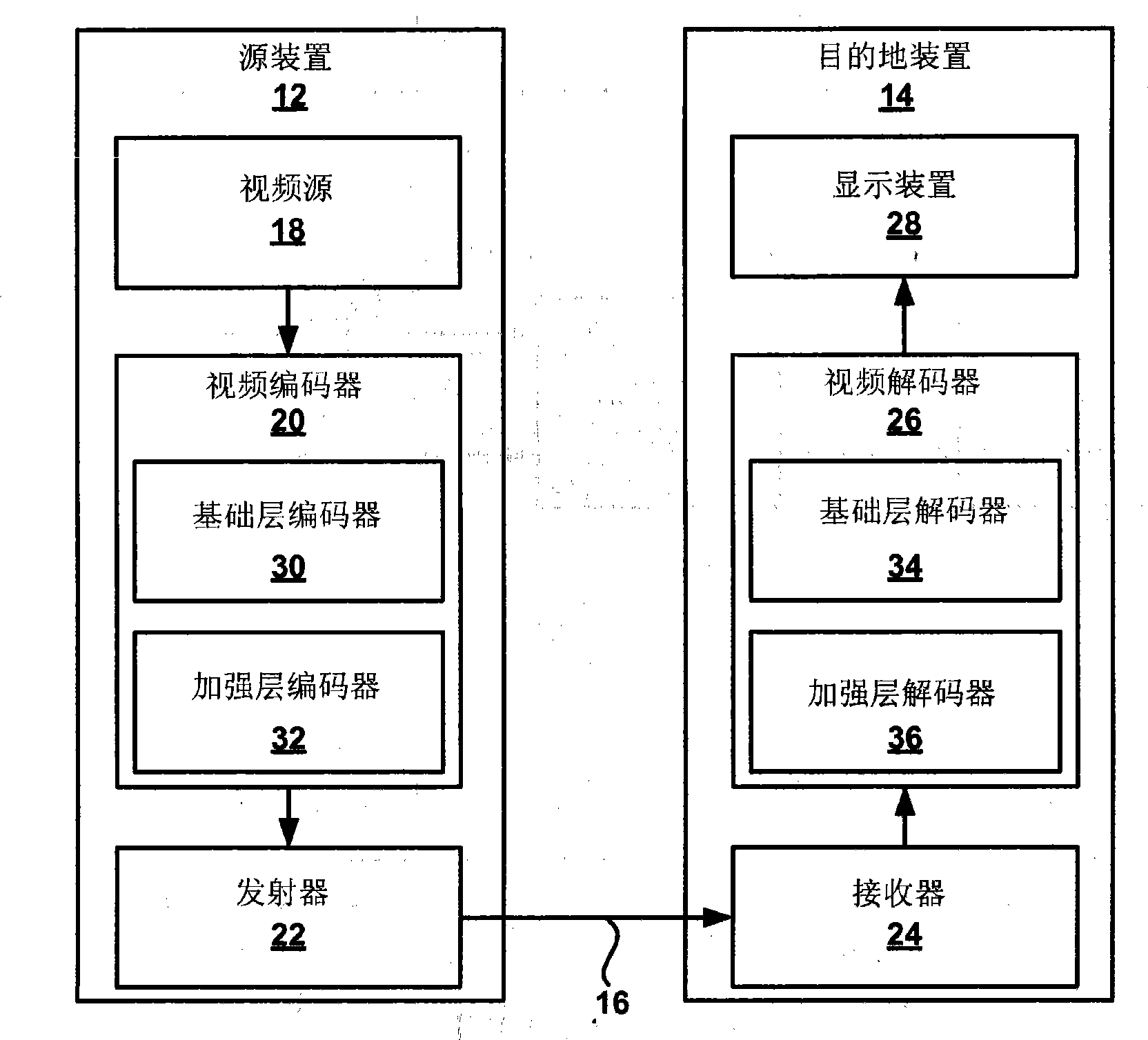
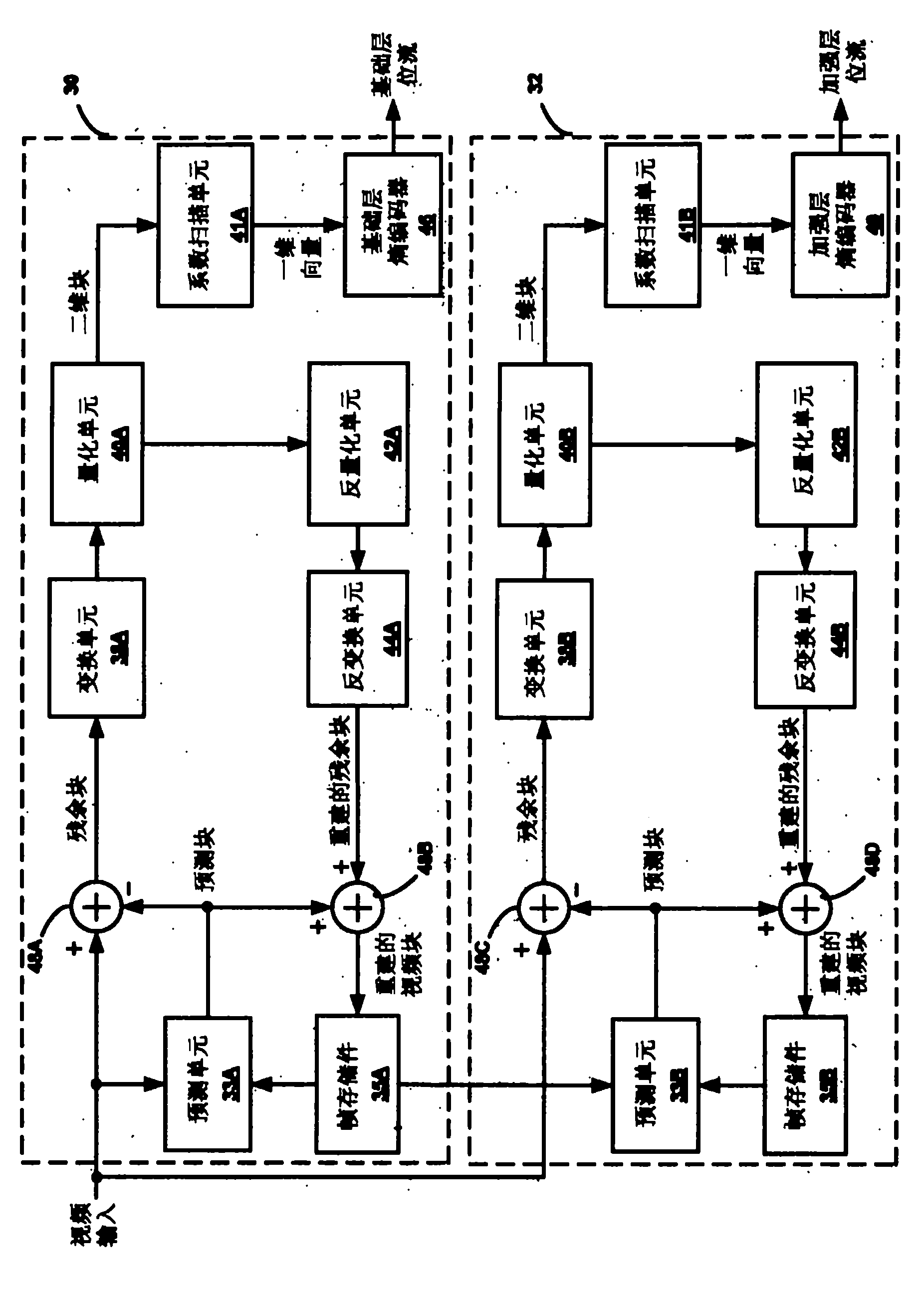
Improved enhancement layer coding for scalable video coding
InactiveCN101855908AReduce the numberReduce decoding complexityTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationNonzero coefficientsComputer architecture
This disclosure describes scalable video coding techniques. In particular, the techniques may be used to encode refinements of a video block for enhancement layer bit streams in a single coding pass, thereby reducing coding complexity, coding delay and memory requirements. In some instances, the techniques encode each nonzero coefficient of a coefficient vector of the enhancement layer without knowledge of any subsequent coefficients. Coding the enhancement layer in a single pass may eliminate the need to perform a first pass to analyze the coefficient vector and a second pass for coding the coefficient vector based on the analysis.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
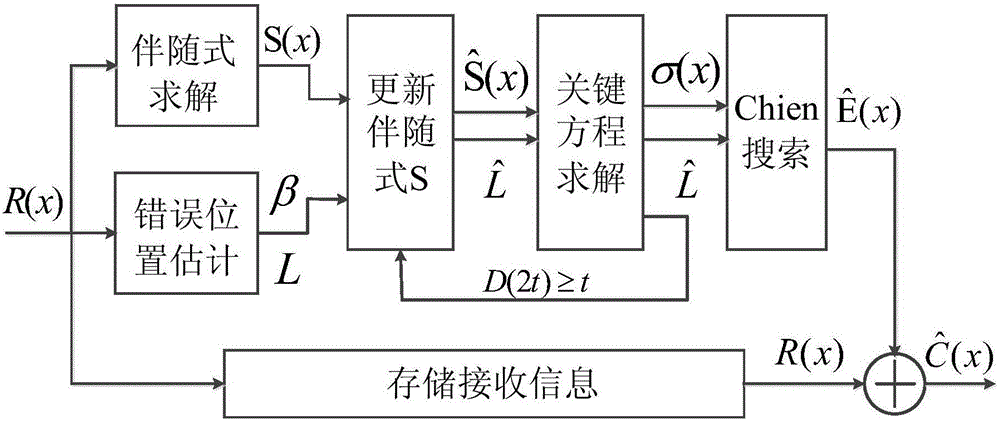
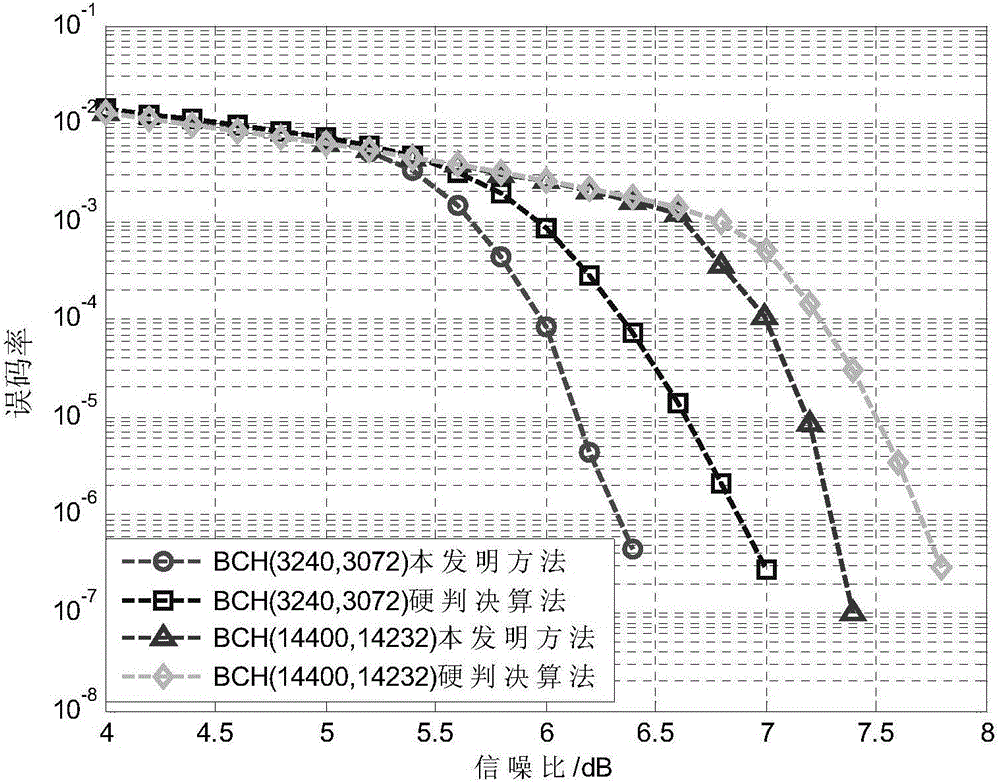
Improved BCH soft-decision decoding algorithm
ActiveCN105812000AReduce Decoding LatencyImprove error correction performanceCode conversionCyclic codesRound complexityImproved algorithm
The invention discloses an improved BCH soft-decision decoding algorithm with the object of resolving the problem in the prior art that a current BCH soft-decision decoding algorithm is complex to perform and decoders are often too much delayed. The improved algorithm is performed through the following steps: firstly, choosing t positions of code symbols with least credibility, according to inputted soft information, as estimated error positions and seeking the numbers of error positions in their corresponding finite fields; conducting hard decision to the inputted soft information for binary BCH codes and seeking an initial adjoint polynomial; fourthly, seeking a polynomial for error positions based on the updated adjoint polynomial; if the supreme power from the polynomial for error positions is less than the maximally correctable number t of a BCH decoder, then seek the error image patterns; otherwise, go back to the third step; and completing decoding by correcting the codes obtained by hard decision to the error image patterns. According to the invention, the soft decision decoding algorithm is made less complex and delay of decoders is shortened, and the algorithm can be applied in error control coding.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Code modulation method based on complete response CPM (continuous phase modulation) and Turbo product code
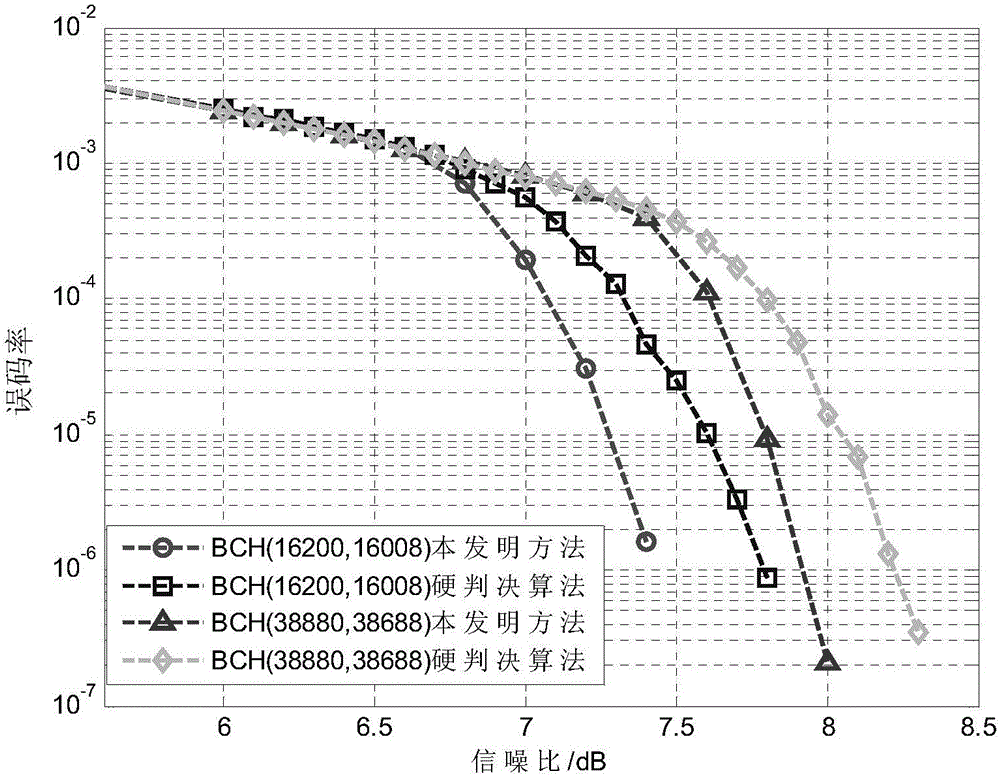
InactiveCN102223204AGood bit error performanceReduce Decoding LatencyError preventionComplete responseSymbol mapping
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
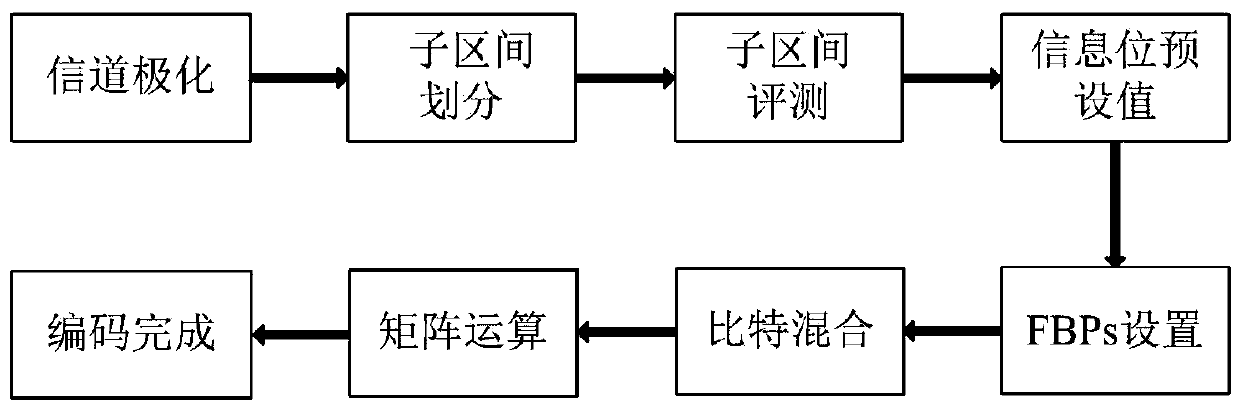
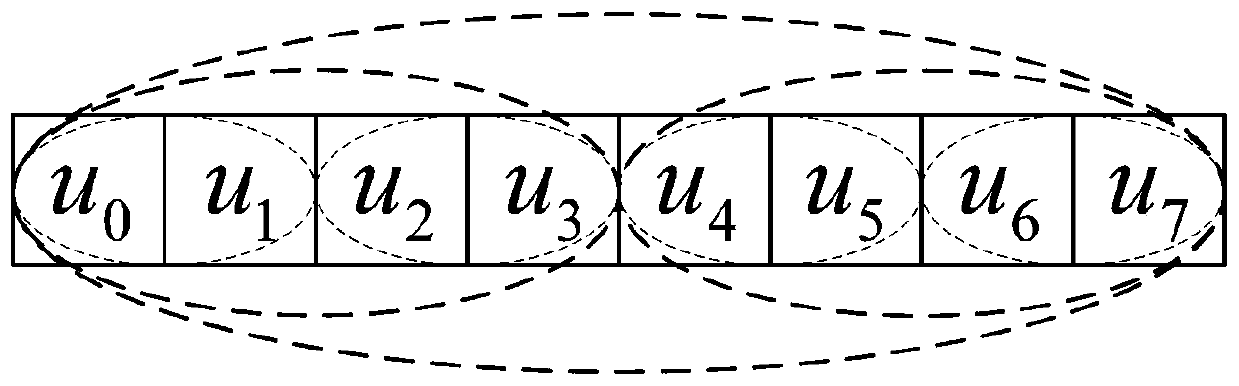
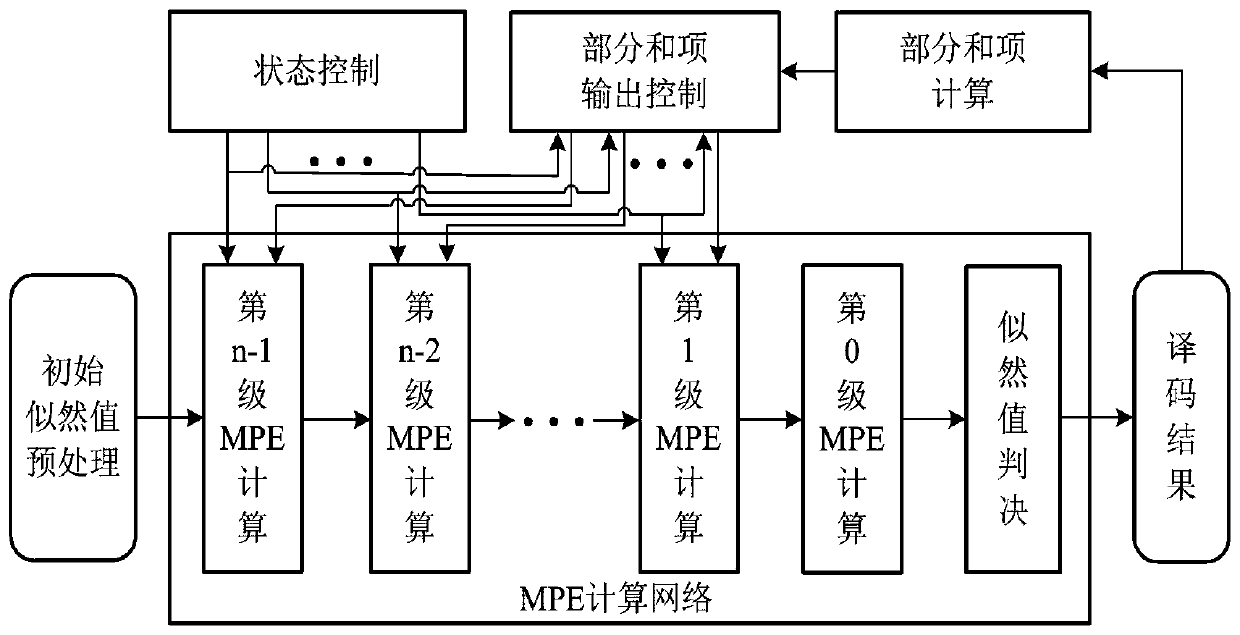
Polar code encoding method and polar code serial offset decoding method and circuit based on frozen bit pairs
ActiveCN110022188AImprove decoding speedStrong and flexible configuration capabilityError preventionError correction/detection using linear codesDecoding methodsBit pairing
The invention discloses a polar code encoding method based on frozen bit pairs and a polar code serial offset decoding method and circuit. The whole encoding process can be mainly divided into channelpolarization, sub-interval division, sub-interval evaluation, information bit preset values, frozen bit pair setting, bit mixing and matrix operation. The decoding circuit comprises an initial likelihood value preprocessing module, a control state module, a partial sum item calculation module and an MPE calculation network module. The decoder further reduces the decoding delay, improves the datathroughput rate, reduces the consumption of hardware resources, and improves the overall performance of the decoder.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
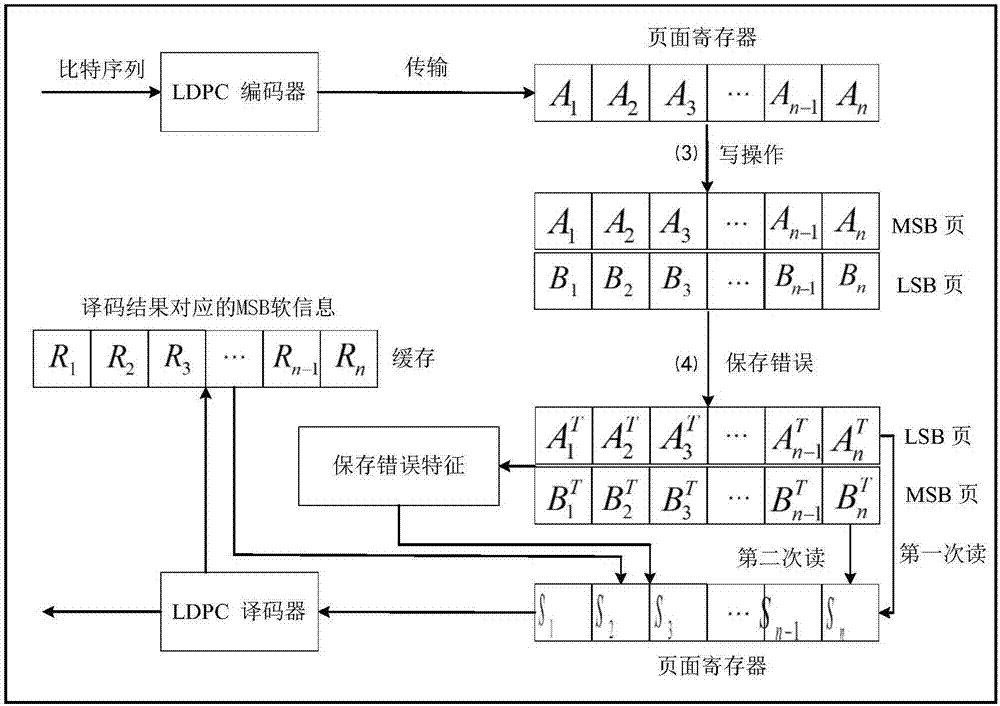
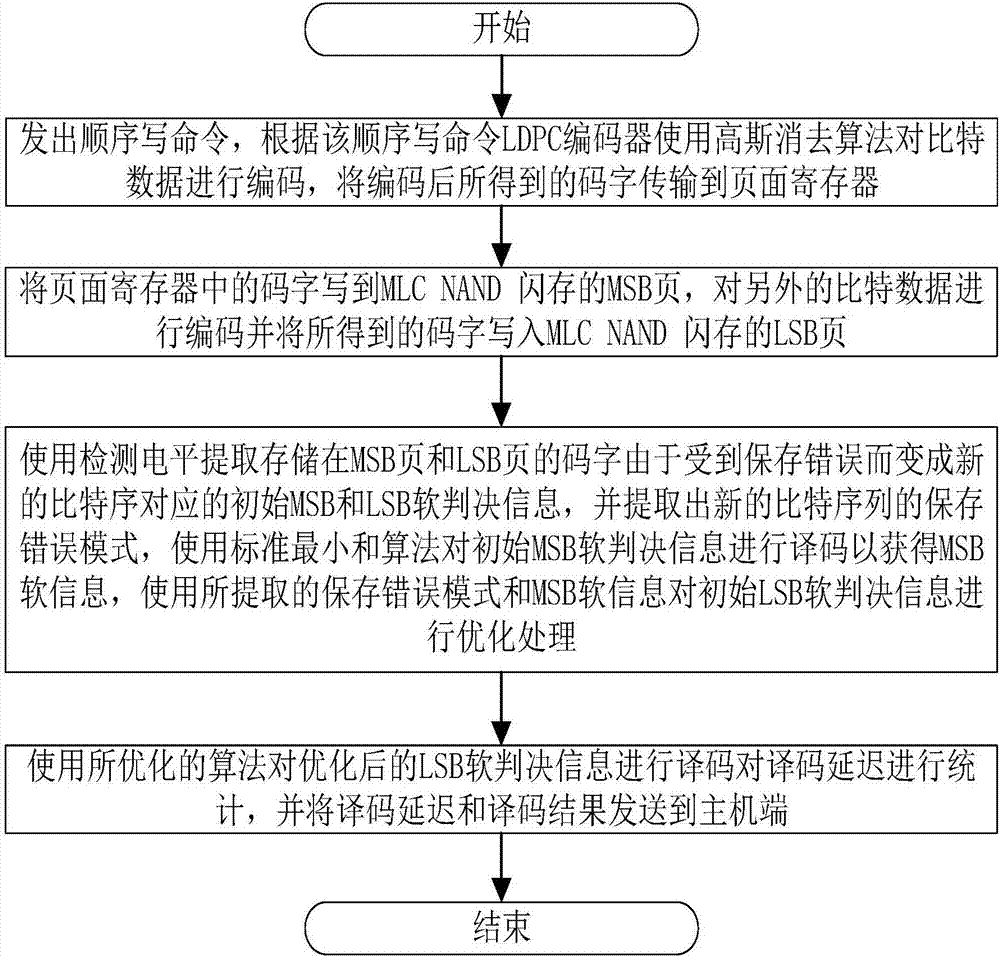
Method for reducing LDPC decoding delay based on error characteristics of flash memory pages
ActiveCN107395214ASolve the problem of unbalanced decoding delayImprove decision accuracyError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionDependabilityData reliability
The invention discloses a method for reducing an LDPC decoding delay based on error characteristics of flash memory pages. As the manufacturing process of an MLC NAND flash memory is improved, the size of memory cells becomes smaller and coupling interference between the cells becomes stronger, as a result, a high bit error rate is caused, and the high bit error rate seriously affects the reliability of data. LDPC codes with a high error correction capability are widely used to ensure the data reliability. However, when the LDPC codes are used, an MSB page and an LSB page of the MLC NAND flash memory have unbalanced decoding delays, the decoding delay of the LSB page is higher than the decoding delay of the MSB page, and since the LSB page has a quite high bit error rate, the reading performance of an MLC flash memory is poor. According to the invention, favorable information is provided for LSB page decoding according to a decoding result of the MSB page and a save error mode so that the decoding delay of the LSB page is reduced, the decoding delay gap between the two pages is narrowed, and the reading performance of the MLC flash memory is improved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Low-complexity serial offset list bit flipping decoding method
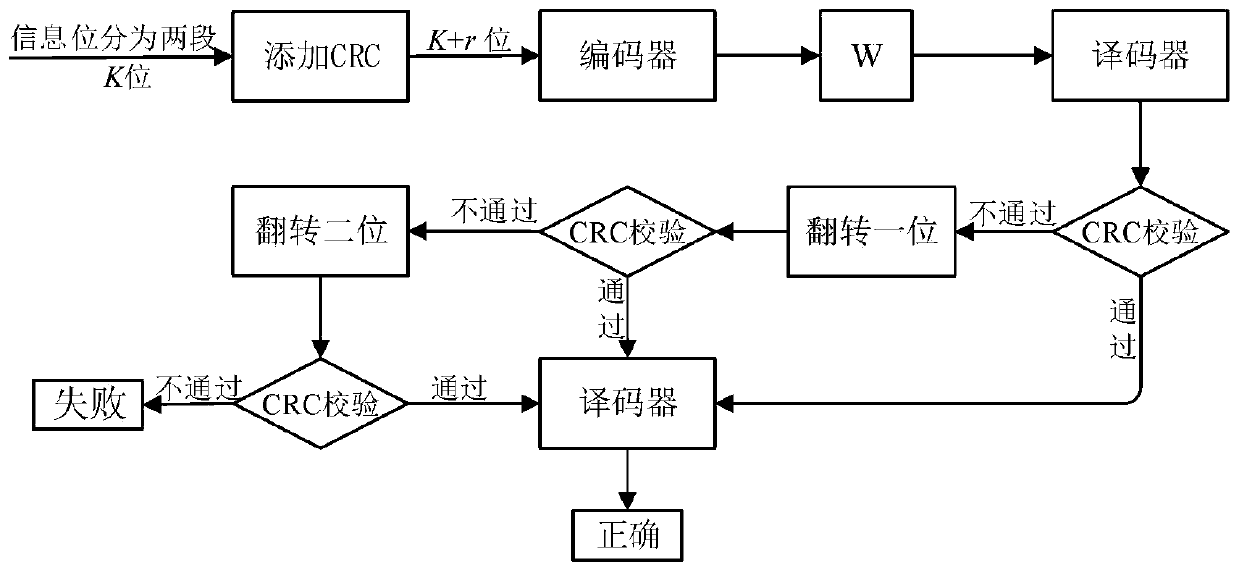
InactiveCN110474648AImprove decoding and error correction capabilitiesReduce decoding complexityError correction/detection using linear codesError detection onlyDecoding methodsLow complexity
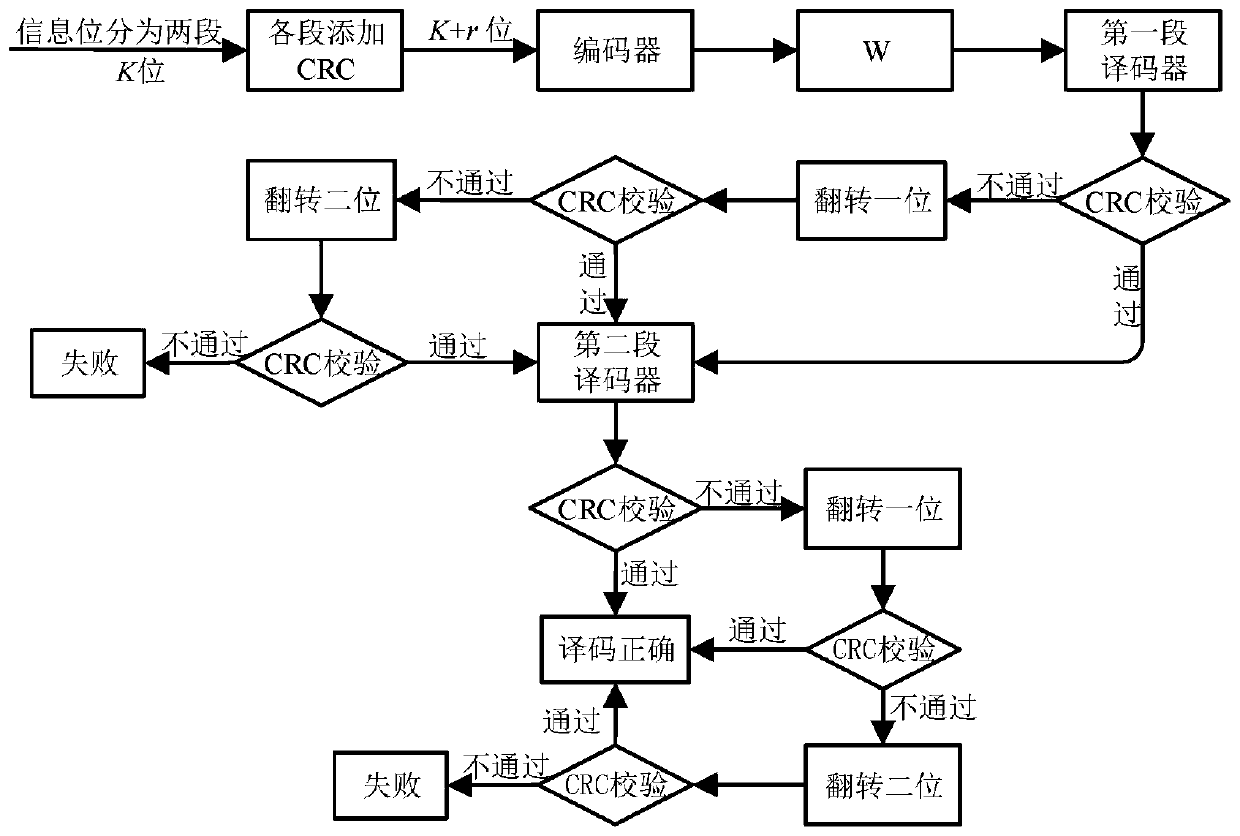
The invention discloses a low-complexity serial offset list bit flipping decoding method, which comprises the following steps of: firstly, segmenting according to position information, respectively adding cyclic redundancy check (CRC) bits to each segment, and determining a key set of each segment offline; in the decoding part, performing decoding in sequence according to the front-back sequence of all the segments, under the condition that serial offset list 1-bit flipping decoding fails, trying a 2-bit flipping decoding process, and the probability of error correction is increased. By adopting the segmented CRC assisted SCL bit flipping decoding method, the decoding complexity can be significantly reduced, and better performance gain can be obtained.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Real-time decoding method and device in coding time-slot ALOHA system
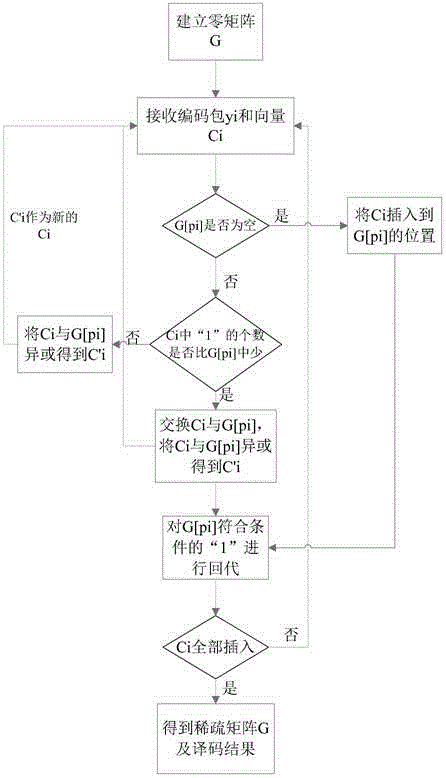
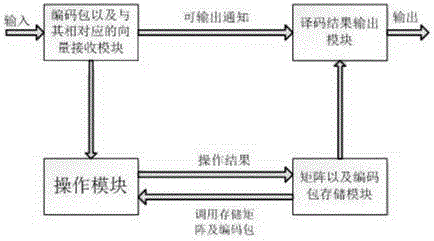
The invention relates to a real-time decoding method and device in a coding time-slot ALOHA system and belongs to the technical field of multiple access. The device comprises a storage module, a code packet yi and vector ci receiving module, a ci operation module and a decoding result output module; the storage module and the code packet yi and vector ci receiving module both are connected with the ci operation module and the decoding result output module, respectively; the storage module is used for storing a matrix and code packets corresponding to vectors of various rows of the matrix; the code packet yi and vector ci receiving module, is used for receiving the code packets and the vectors thereof arriving sequentially, and outputs each received packet to the ci operation module every time the packet is received, and after the feedback of the ci operation module to the last packet is obtained, the decoding result output module is notified of outputting; the ci operation module is used for performing operations on input ci and yi, the matrix and the code packets corresponding to the vectors of various rows of the matrix according to a preset rule; the decoding result output module is used for outputting the matrix and the code packets corresponding to the vectors of various rows of the matrix. Compared with the prior art, the real-time decoding device has the advantages of real-time decoding, high throughput and low complexity.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Encoding and decoding methods for shortening Turbo product code
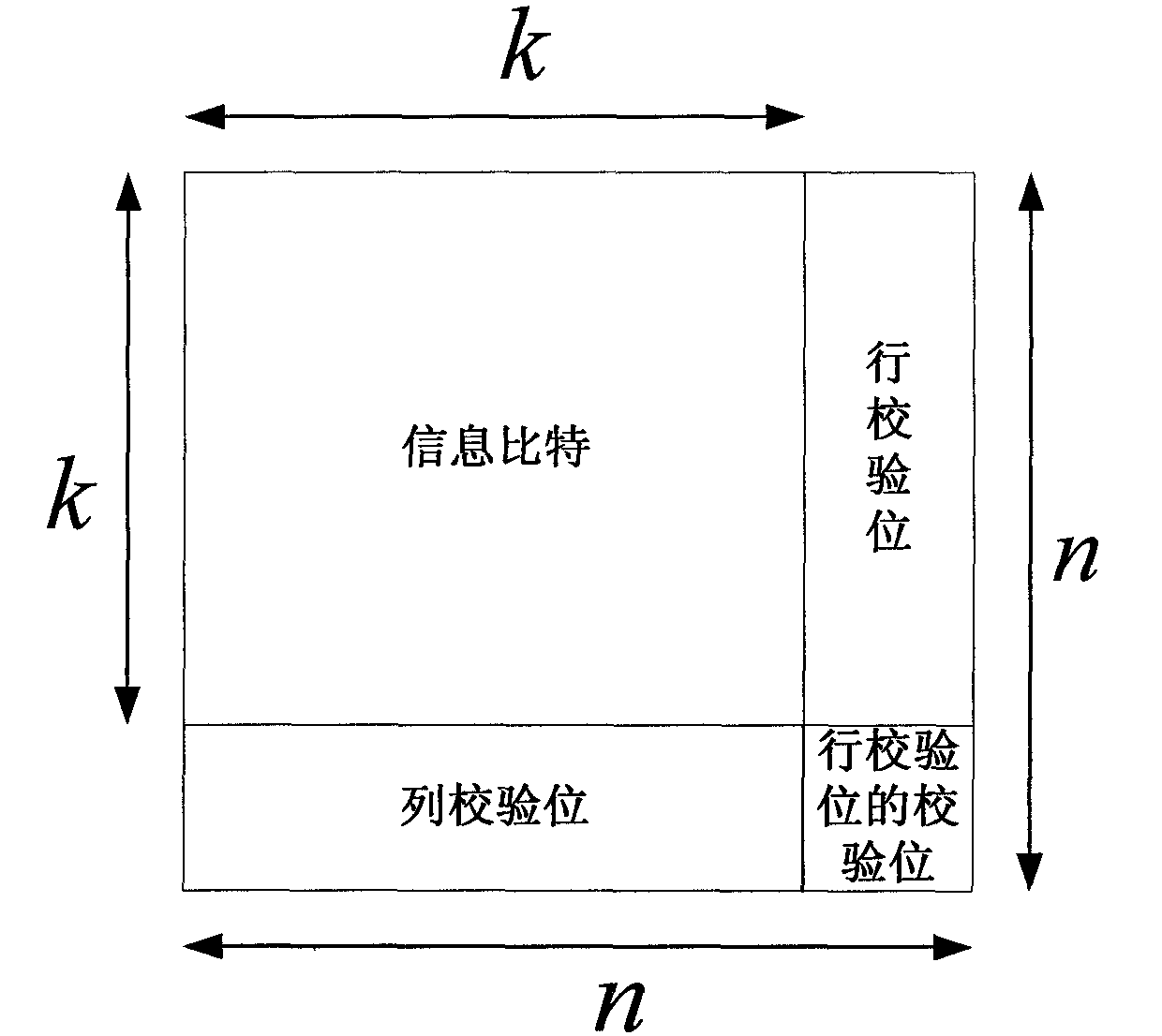
InactiveCN101958720BIncrease storage resourcesImprove data throughputError correction/detection by combining multiple code structuresParallel encodingTheoretical computer science
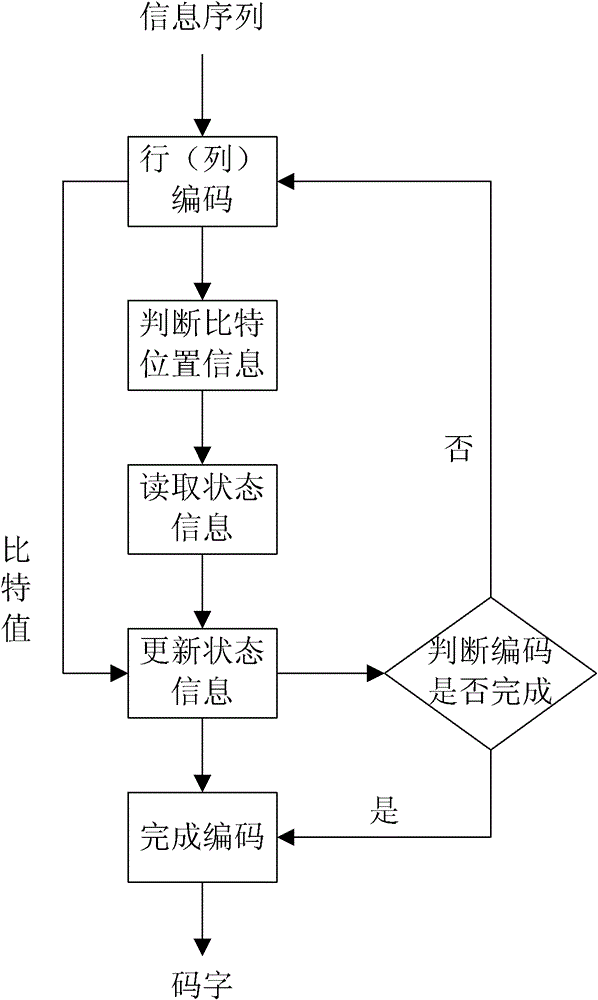
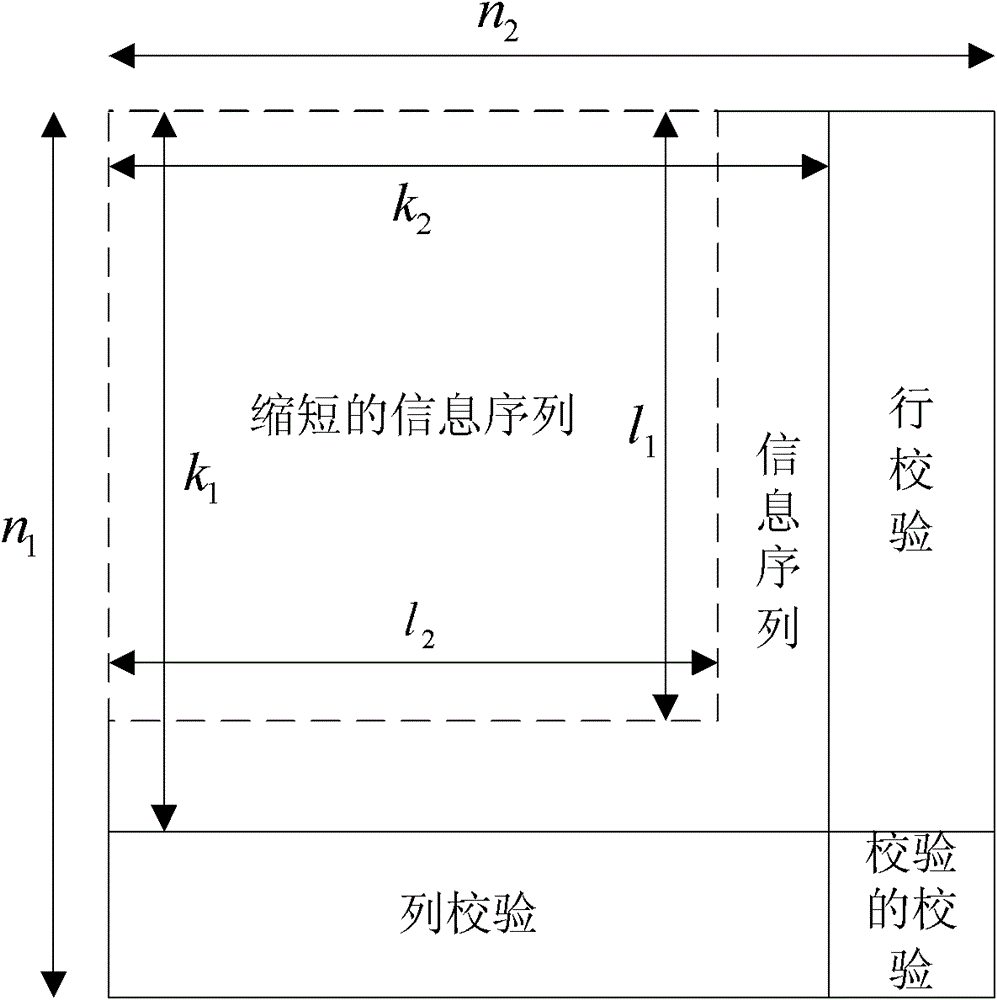
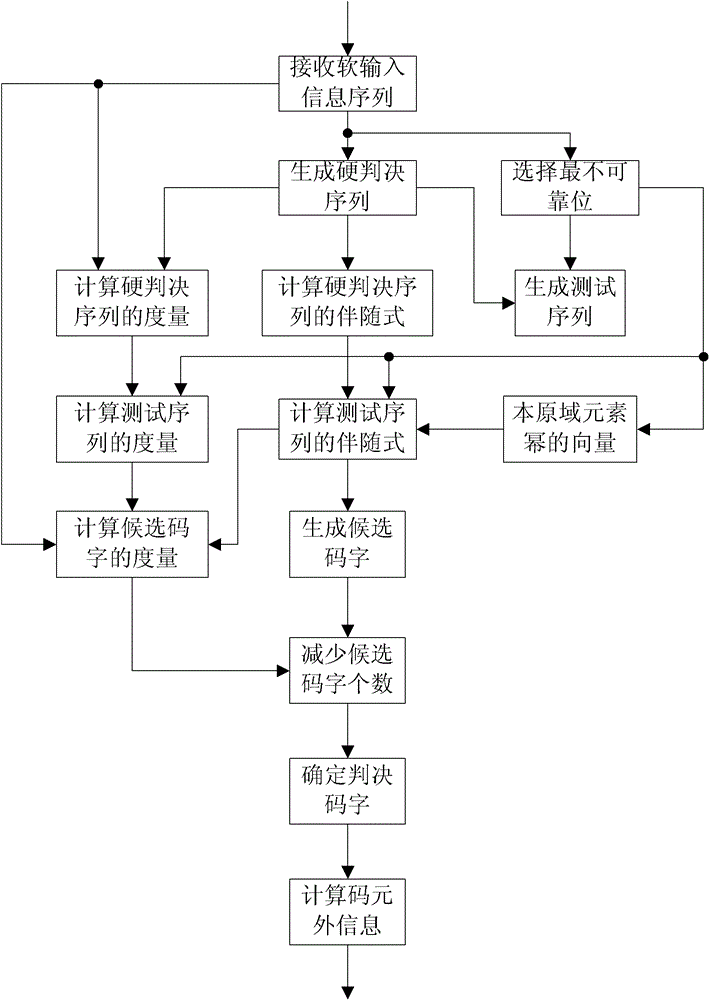
The invention relates to encoding and decoding methods for shortening a Turbo product code. The encoding method comprises the following steps of: performing row or column encoding on an information sequence to be encoded; performing parallel encoding on code words of row or column component codes generated by the row or column encoding; and judging whether the encoding is finished. The decoding method comprises the following steps of: generating a hard decision sequence of a soft-input information sequence; selecting the least reliable bits in the soft-input information sequence; generating a test sequence according to the hard decision sequence and the least reliable bits; decoding the test sequence to generate candidate code words; calculating the measurement of the candidate code words and the soft-input information sequence; reducing the number of the candidate code words; determining decision code words according to the measurement of the candidate code words; and calculating external information of each code element in the decision code words. The encoding method has the advantages of improving data throughput and reducing encoding delay; and the decoding method has the advantages of saving a mass of logical resources and storage resources, particularly well balancing decoding complexity and data throughput under the condition of longer code length of component codes.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
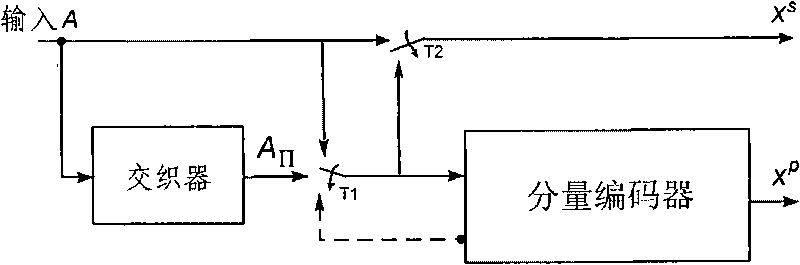
Turbo code encoder, decoder, encoding method and decoding method
ActiveCN101753153AReduce complexityReduce processing latencyError correction/detection by combining multiple code structuresTurbo codedComputer engineering
The invention discloses a Turbo code encoder and an encoding method. The Turbo code encoder comprises an interleaver and a component encoder. After the component encoder encodes the input information sequences, bits fed back by the component encoder are encoded and are distributed to the last place of information bit and the last place of check bit and the bits are output. Since the encoder adopts only one component encoder and the number of tail bits is reduced, the encoding processing delay is effectively reduced, the encoding complexity is simplified and the encoding speed and the rate matching speed are improved. The invention additionally discloses a decoder and a decoding method. By adopting the technical scheme, the invention has the advantages that the encoding and decoding complexity and the processing delay are reduced, and encoding speed and decoding speed are improved.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
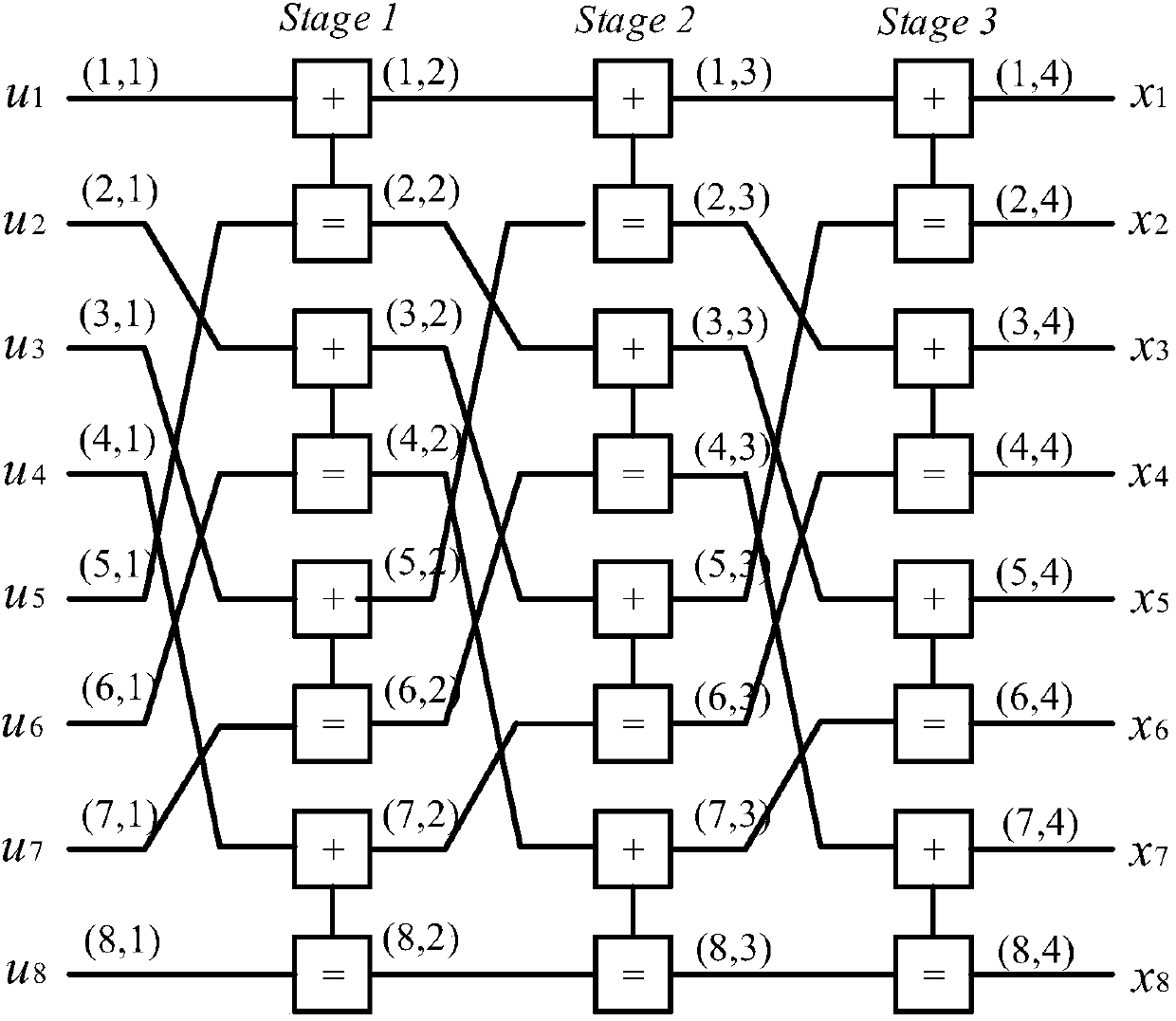
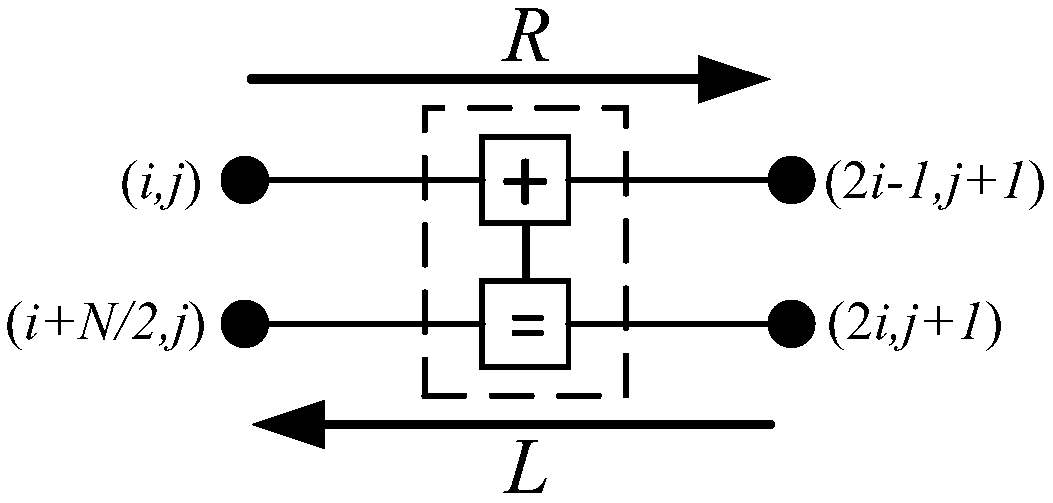
Method for establishing pipelined belief propagation (BP) polar decoder hardware architecture and decoder hardware architecture
ActiveCN109547035AReduce consumptionIncrease profitCode conversionError correction/detection using linear codesHardware architectureResource consumption
The invention provides a method for establishing a pipelined belief propagation (BP) polar decoder. The method comprises the following steps: step 1, setting the maximum number of iterations of BP decoding; step 2, decoding polar encoding information by using a BP decoding algorithm; step 3, updating a node information value in each iteration process; and step 4, establishing hardware architectureof the pipelined BP polar decoder. According to the method in the invention, each iterative process is carried out according to the information updating mode. Compared with the existing pipelined BPpolar decoder, under different code lengths, when iteration is carried out once, the decoding delay can be reduced by 33.45% to 34.52%, the utilization rate of the BCB is increased by 50.13% to 51.32%; and when the code length N is equal to 1024 bits, and the maximum number of iterations is 40 times, the resource consumption of a memory can be reduced by 25.6% to 38.76%, and the frequency is improved by 19.4% to 31.45%, thereby effectively reducing the decoding delay and hardware resource consumption, and improving the hardware utilization rate.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Decoding method and decoder
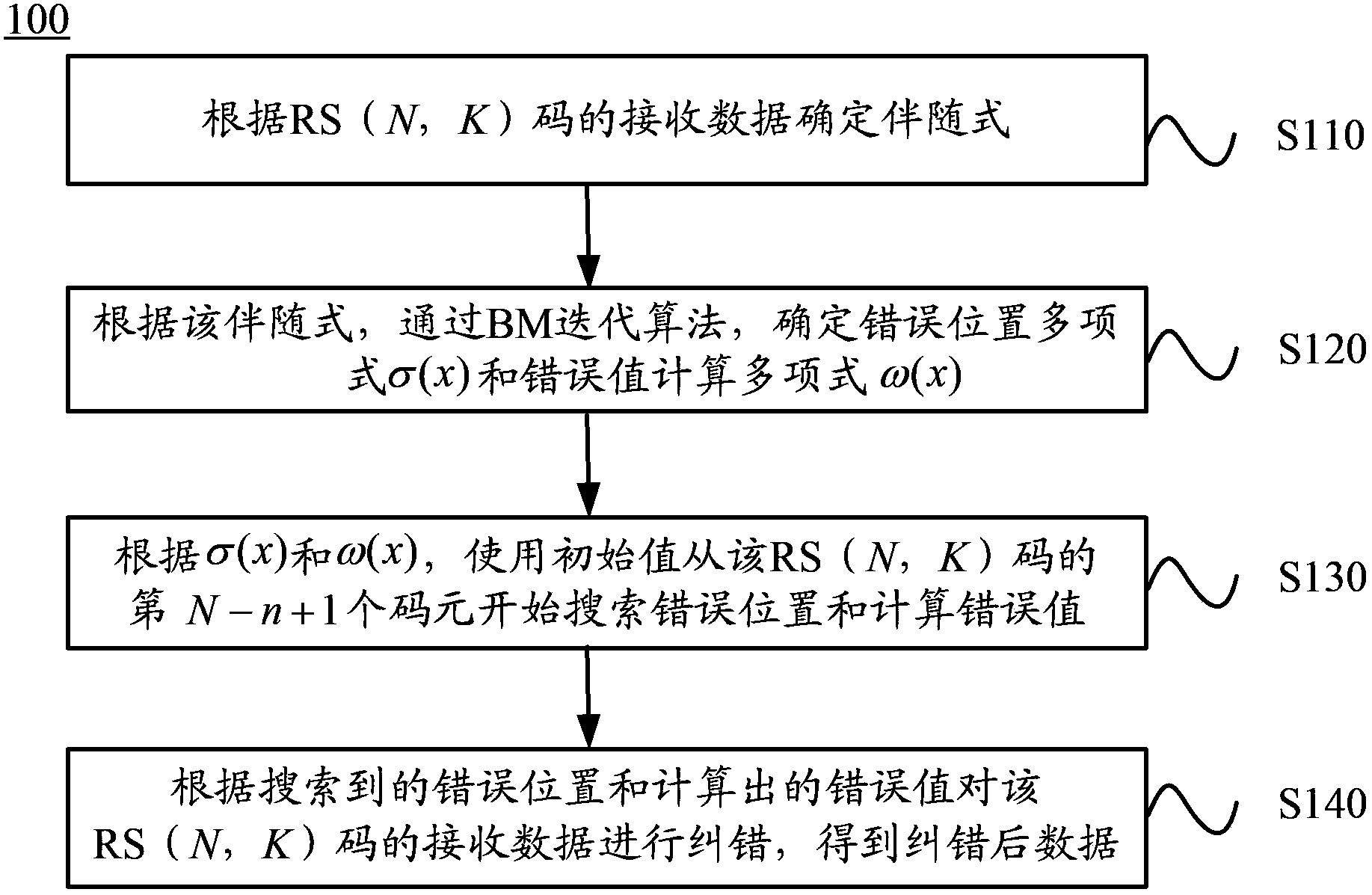
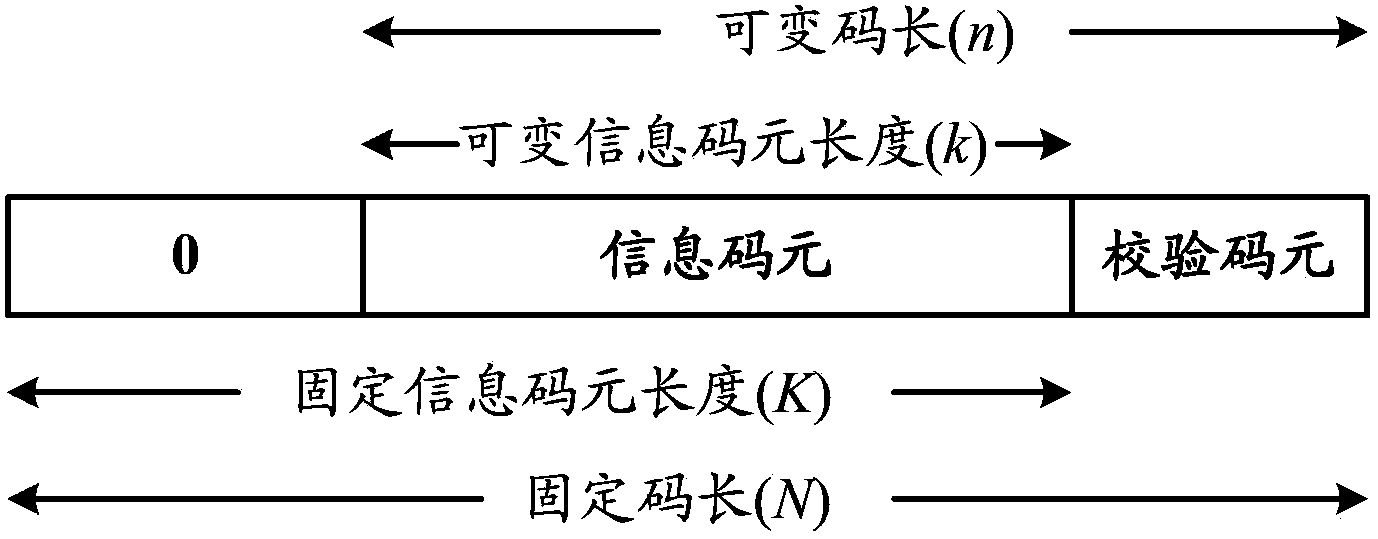
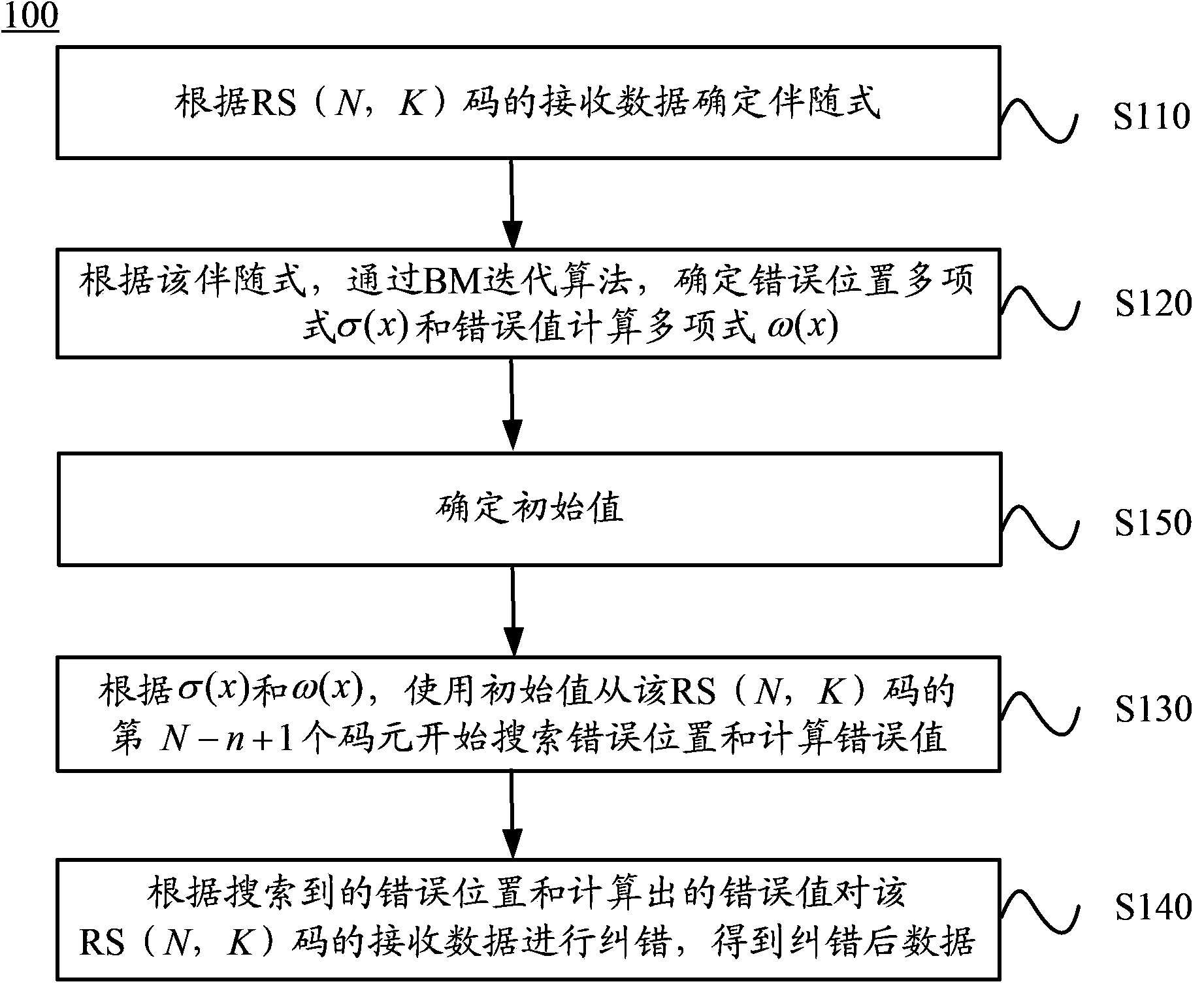
ActiveCN104052502ACode length reductionReduce Decoding LatencyCyclic codesDecoding methodsCalculation error
The invention discloses a decoding method and a decoder. The method comprises: according to receiving data of a reed-solomon (RS) (N,K) code, a syndrome is determined, wherein the actual length of the shortened code of the RS (N,K) code is n; on the basis of the syndrome, an error locator polynomial sigma (x) and an error value calculation polynomial omega (x) are determined by using a BM iterative algorithm; according to the sigma (x) and the omega (x), an error position and a calculation error value are searched by starting with the (N-n+1)th code element in the RS (N,K) code by using an initial value, wherein the initial value includes an alpha <j (N-n+1)> and an alpha <-(N-n+1)> and j is equal to 1, 2, ... or t; the receiving data of the RS (N,K) code are corrected based on the searched error position and the calculated error value so as to obtain corrected data. According to the decoding method and decoder provided by the embodiment of the invention, an iteration for searching calculation and error value calculation can be reduced from prefect code length times to actually effective code length times, thereby improving the decoding efficiency.
Owner:南通云尚找家纺电子商务有限公司
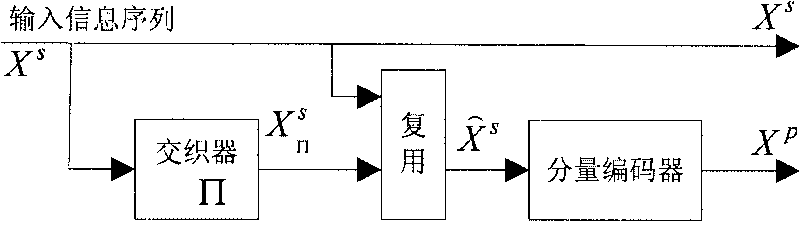
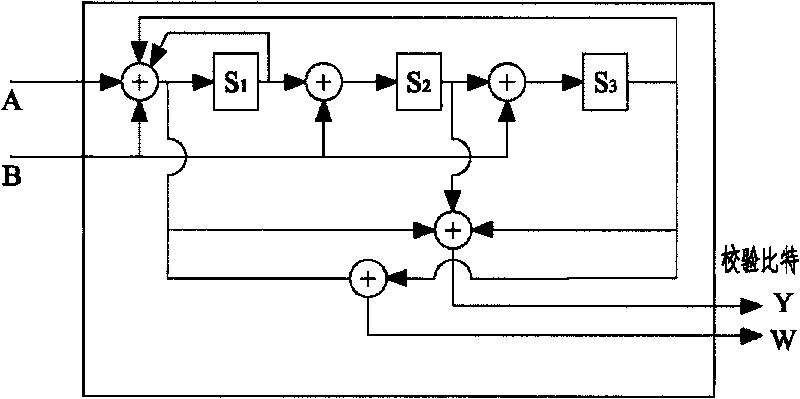
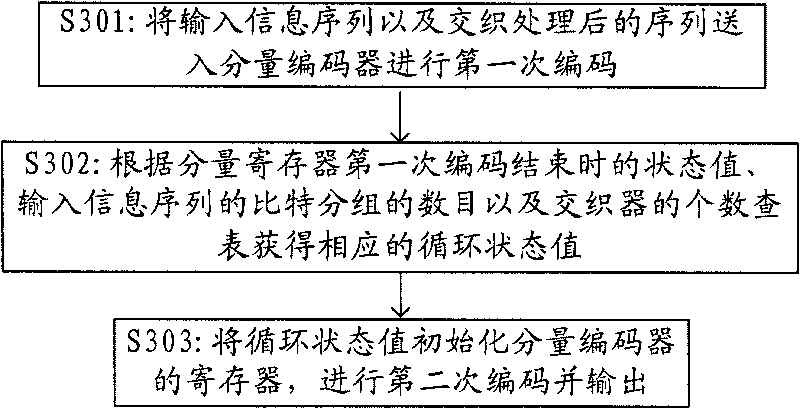
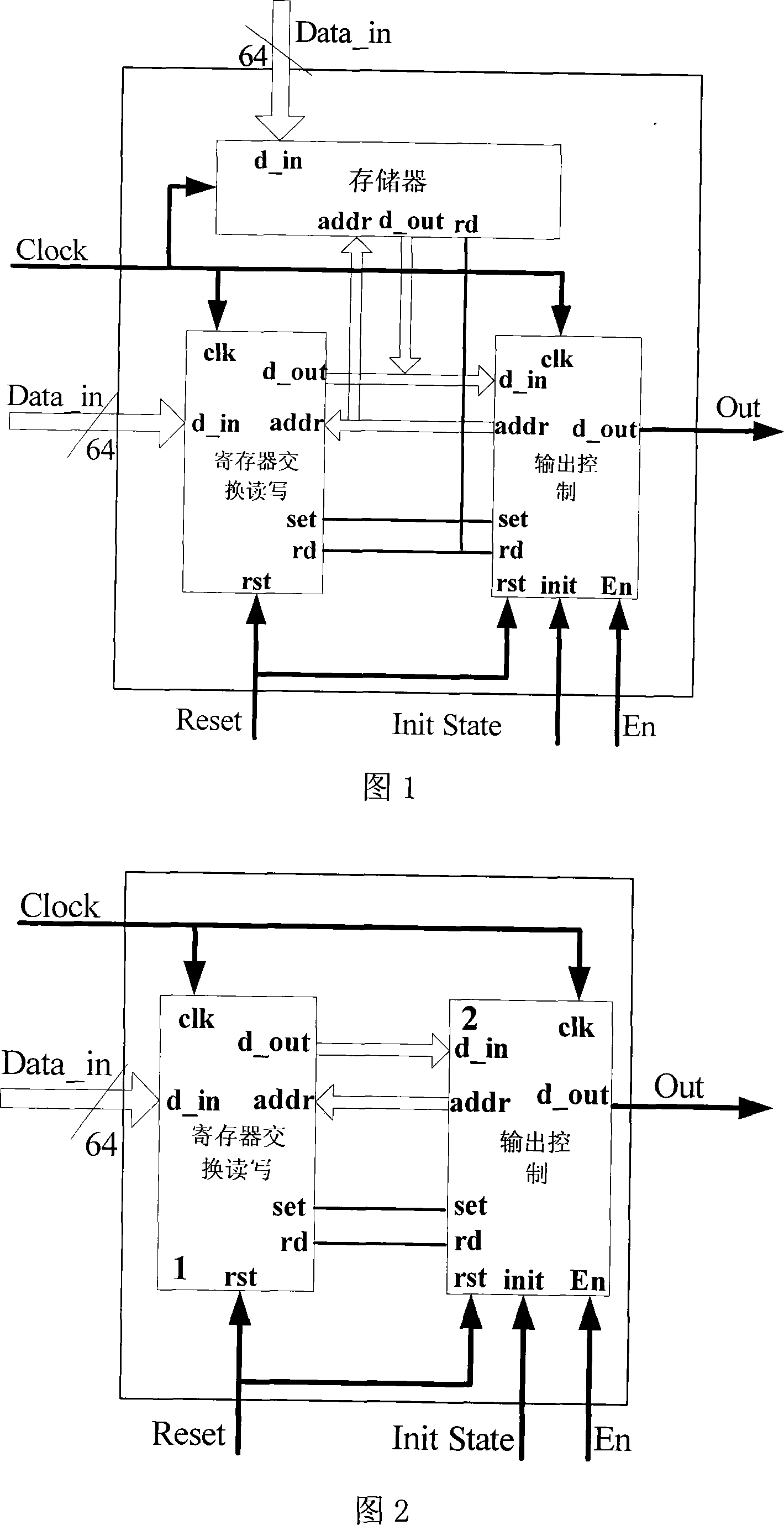
Turbo code encoder, decoder, encoding method and decoding method
ActiveCN101753154AReduce complexityReduce processing latencyError correction/detection by combining multiple code structuresProcessor registerTurbo coded
The invention discloses an encoder and an encoding method. The encoder conducts a first time continuous encoding to the input information sequences and the interleaved input information sequences through a component encoder. Based on the result of the continuous encoding, a cyclic state value is calculated and is used to initialize the register of the component encoder to set the state value of the register of the component encoder to the cyclic state value. Then, the component encoder conducts a second time continuous encoding to the input information sequences and the interleaved input information sequences and outputs a second time continuous encoding result used as a final encoding result. The invention additionally discloses a decoder and a decoding method. By adopting the technical scheme, the invention has the advantages that the encoding and decoding complexity and the processing delay are reduced, and encoding speed and decoding speed are improved.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
High-speed residual path management module of Viterbi decoder
InactiveCN101145789AImprove decoding speedReduce Decoding LatencyError correction/detection using convolutional codesOther decoding techniquesViterbi decoderDigital signal processing
The invention relates to a survivor path management module in a high speed Viterbi decoder, belonging to the field of integrated circuit design and the digital signal processing technology. The invention comprises two modules: a register exchange reader module and an output control module. Based on HTF architecture with the length of each block fixed, the decoding depth X is divided into a plurality of blocks and each is of 6-bit in length. After the each operation of HTF, the data existing in the register is of the state point of the first 6 time of the survivor path passing through the present state. When being output, the correct initial register is traced and output. The process saves the back-track process of each block, and the judging process of the access and the memory module of the bit. The invention has the advantages of enhancing the decoding speed, reducing the decoding delay and output interval and increasing the data-processing capacity of the system.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Encoding method and encoding apparatus based on mixed automatic retransmission communication
ActiveCN101321044BFlexible structureLow costError prevention/detection by using return channelCode conversionData operationsStructural unit
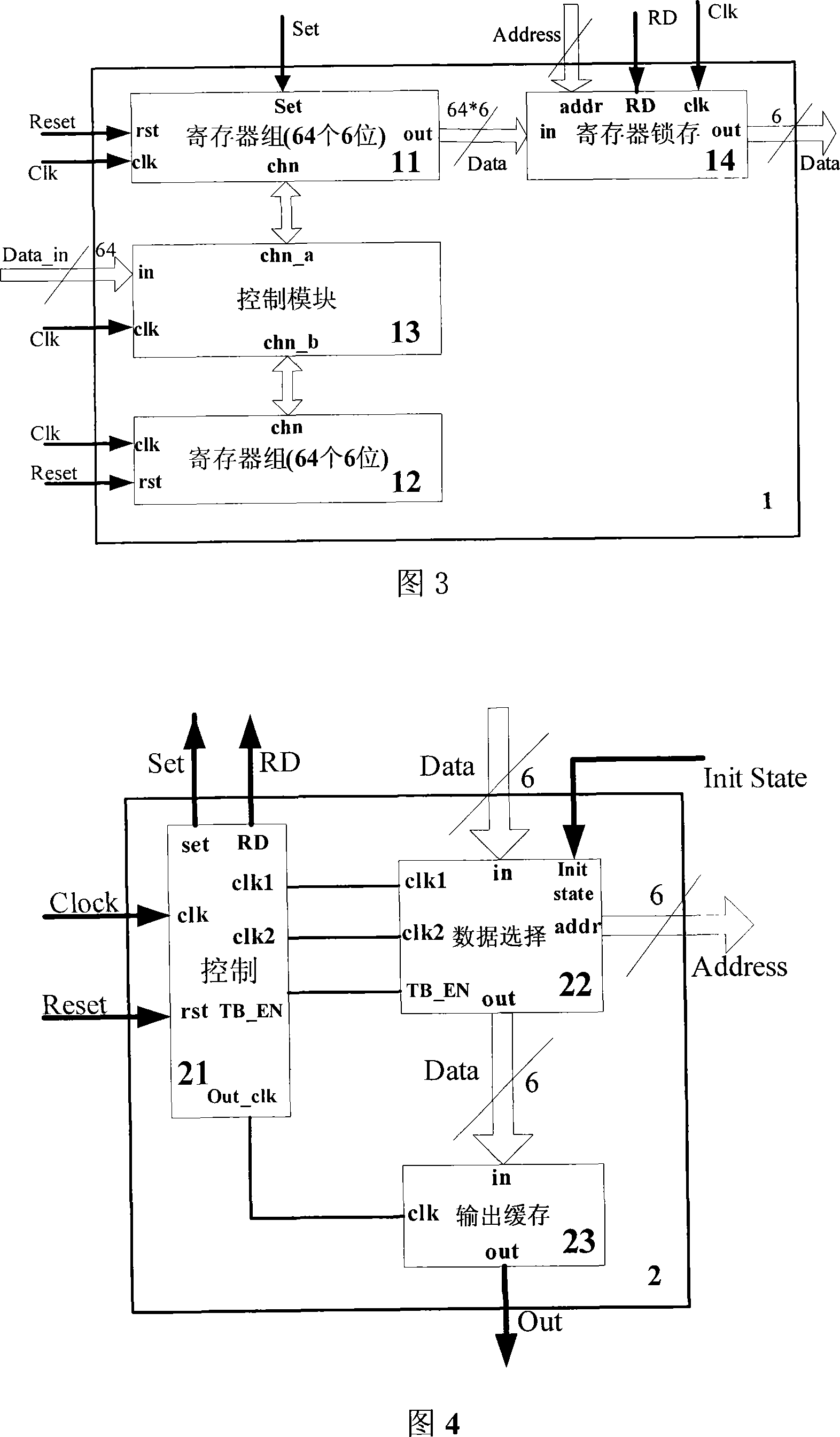
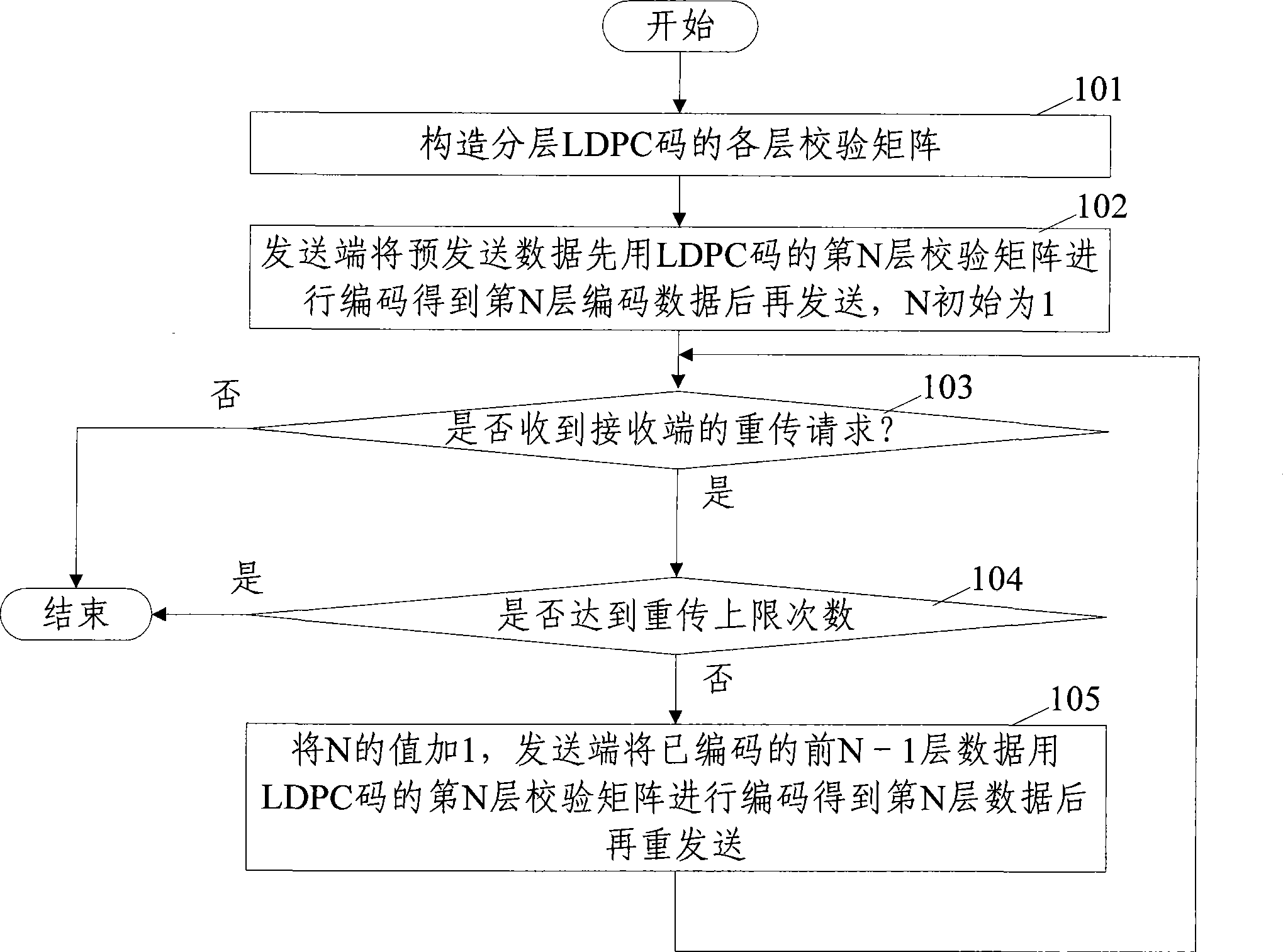
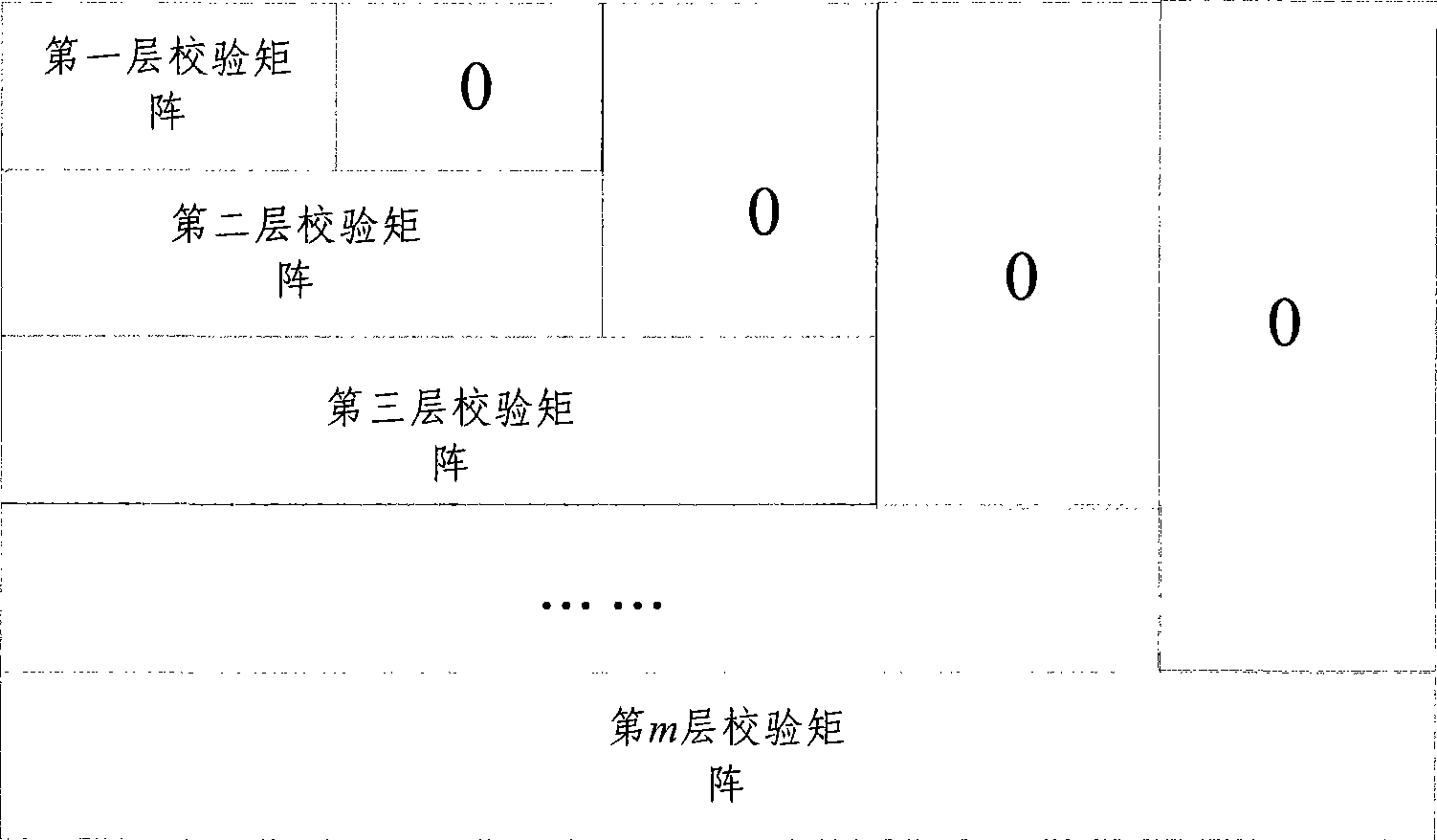
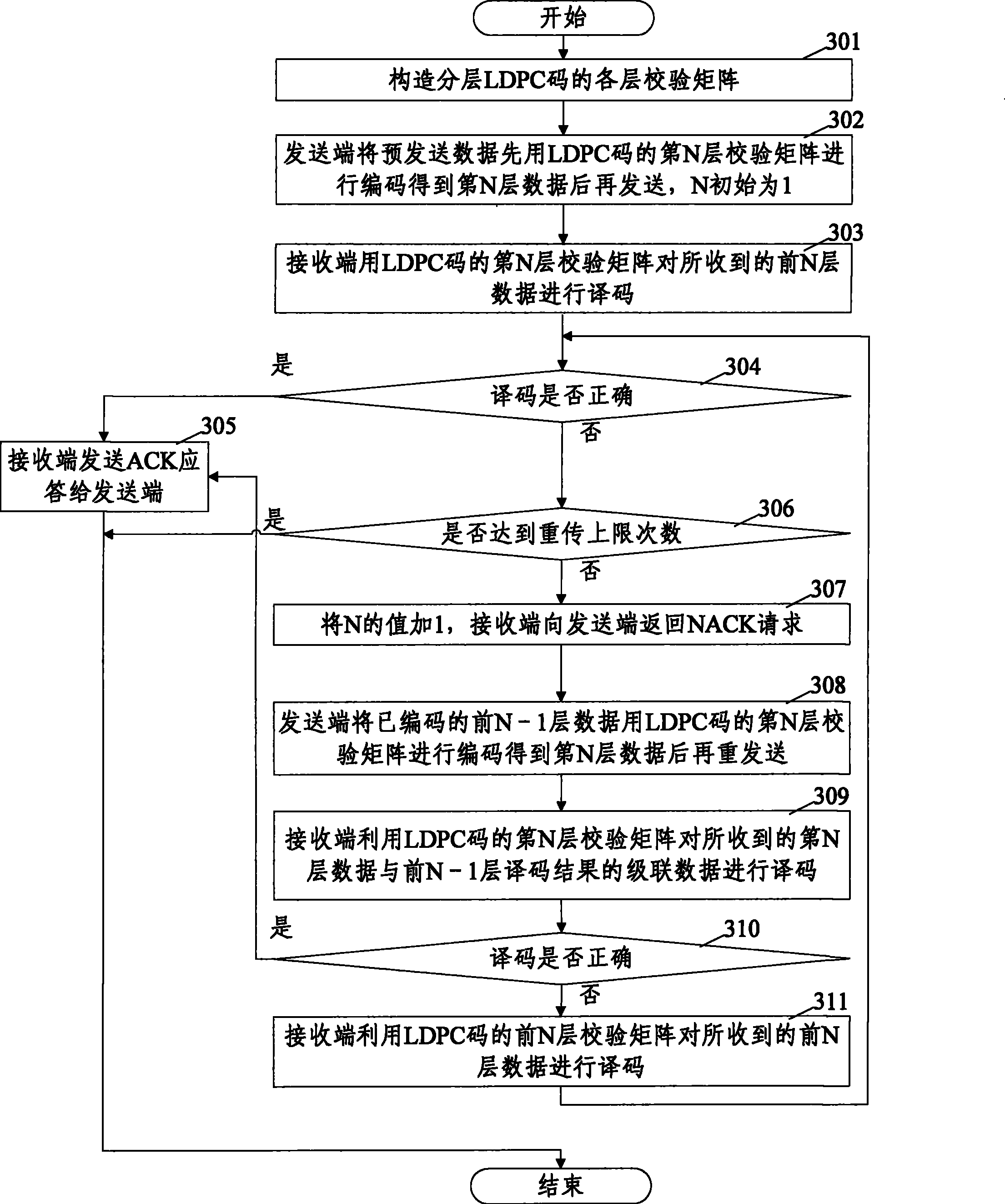
The invention discloses a coding method based on the hybrid automatic retransmission (HARQ) communication, according to the method, the layering LDPC code is used as the error correcting code, and the layering LDPC code is used to perform the layering coding on the received data at the data transmitting end. The invention also discloses a coding device based on the hybrid automatic retransmission communication, comprising an error correcting code structural unit, for structuring each layer of check matrix of the layering LDPC code, and using the layering LDPC code as the error correcting code. The device also includes a code unit arranged at the data transmitting end, for performing the layering code on the received data through the layering LDPC code structured by the error correcting code structural unit. According to the method and the device, the cost of the system is reduced, the coding delay is shortened, the coding performance is advanced, which is applicable for the high speed data operation.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
Polar code path merging method and device and decoding device
ActiveCN111162798AReduce the number of searchesReduce Decoding LatencyCode conversionError correction/detection using linear codesAlgorithmEngineering
The embodiment of the invention discloses a path merging method for Polar code decoding, and the code length of the Polar code is N. The method comprises the steps: obtaining L survival paths, beforedecoding, determined by the decoding of the first M bits of the Polar code; decoding the (M + 1) th bit to the (M + k) th bit of the Polar code to obtain 2k * L extended paths; determining L survivalpaths after decoding from the 2k * L extension paths according to the reliability of the (M + 1) th bit to the (M + k) th bit of the Polar code; wherein N is a positive integer power of 2, k is a positive integer greater than or equal to 2, M is a positive integer multiple of k, and L is a positive integer.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Turbo decoder and turbo decoding method
InactiveCN1645751AReduce Decoding LatencyIndeterminate eliminationOther decoding techniquesCode conversionComputer architectureStaging operation
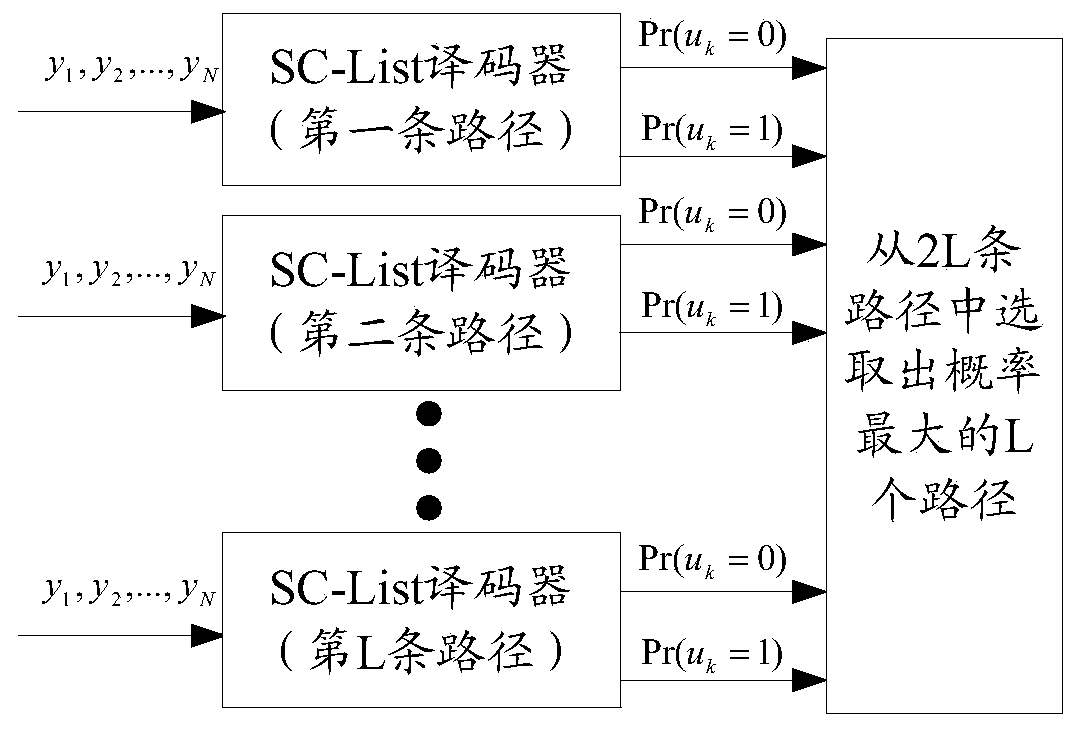
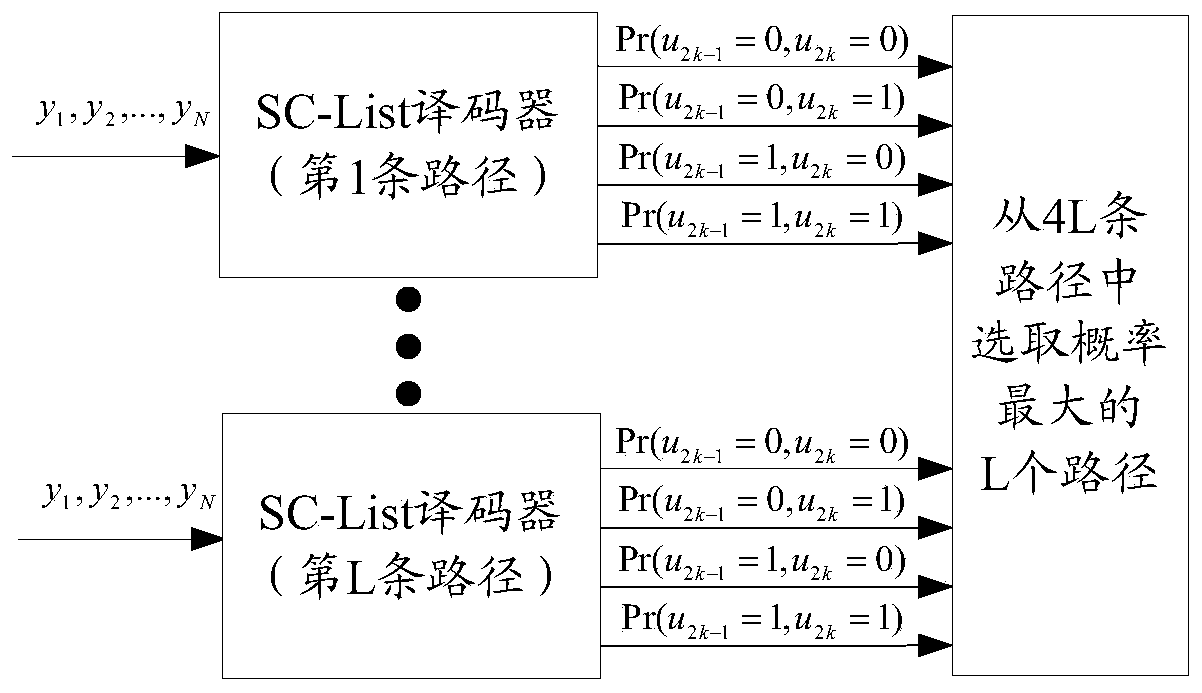
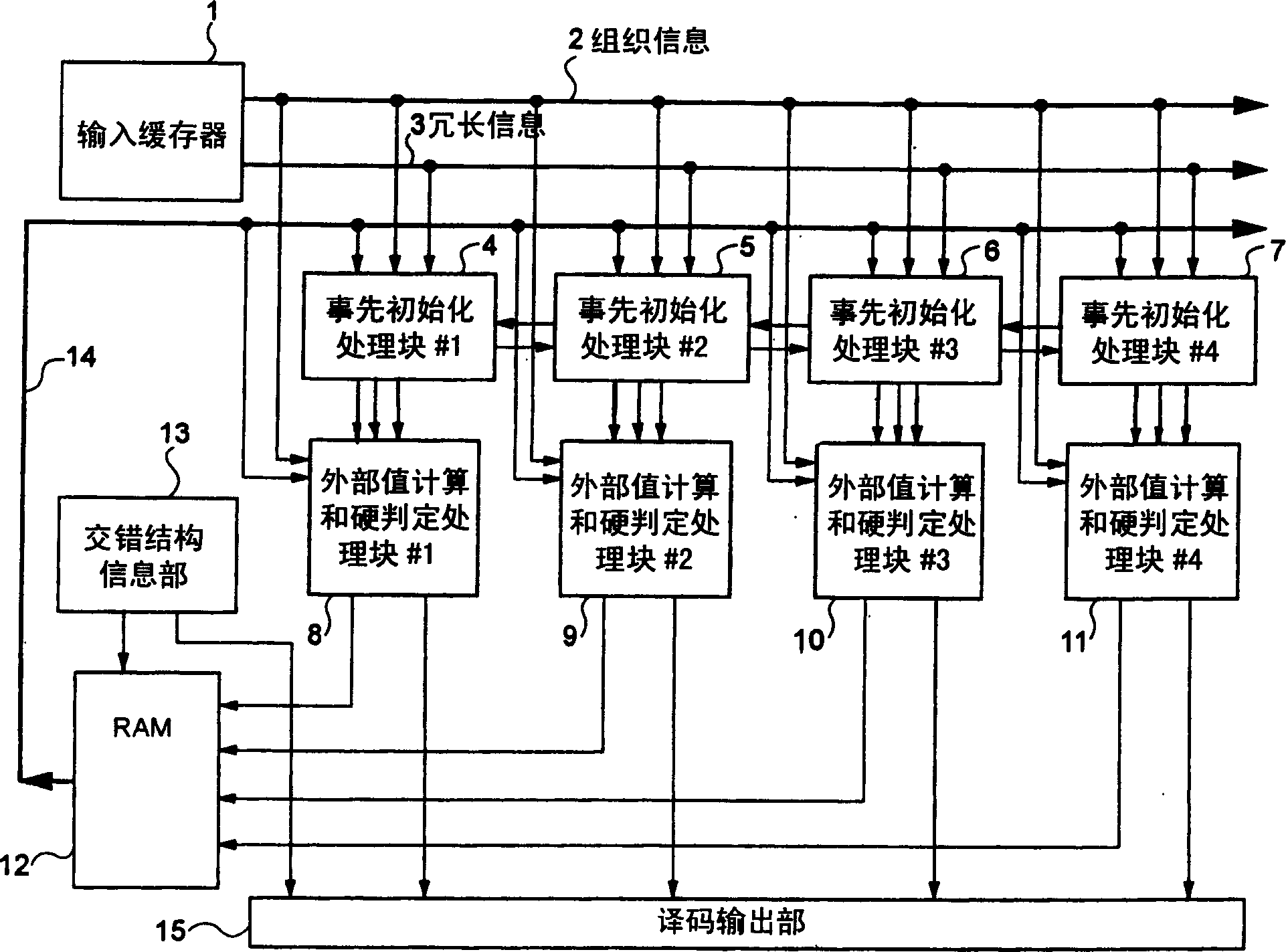
The invention provides a turbo decoding method.The turbo encoded data is divided into first to N-th (N is an integer of >=2) subcode data which are in turn decoded in parallel, pre-initialization means 4-7 (when N=4) where an initial value for calculating the forward path metric of second and subsequent subcode blocks is set as the final stage operation value in the prestage subcode block, and an initial value for calculating the backward path metric of (N-1)th and preceding subcode blocks is set as the final stage operation value in the poststage subcode block are provided. After the pre-initialization of path metric values, external value calculating / hard judging blocks 8-11 decode respective subcode blocks in parallel.
Owner:NEC CORP
Quasi-cyclic low density parity-check code (QC-LDPC) decoder and decoding method
ActiveCN101976584BShorten the overall cycleReduce Decoding LatencyStatic storageSolid-state driveCoded element
The invention discloses a quasi-cyclic low density parity-check code (QC-LDPC) decoder. The QC-LDPC decoder is applied to solid state disk error correction systems, and comprises a syndrome calculation module, a judgment control module, a searching module and an overturn control module, wherein the syndrome calculation module is used for calculating the syndrome of a code sequence to be decoded; the judgment control module is used for judging whether the syndrome is an all-zero vector or not, and controlling to finish the syndrome calculation and outputting the current code sequence as a decoding result if the syndrome is the all-zero vector; the searching module is used for calculating the set of the number of code elements which do not meet a check equation in the code sequence to be decoded and searches the position of a maximal value in the set when the syndrome is not the all-zero vector; and the overturn control module is used for overturning the code element which corresponds to the position of the maximal value in the set in the code sequence to be decoded, and inputting an updated code sequence to be decoded into the syndrome calculation module. The invention correspondingly provides a QC-LDPC decoding method. Thus, by using the decoder and the decoding method, the syndrome calculation can be controlled to be finished when error correction is finished, and the decoding period and decoding delay are lowered.
Owner:RAMAXEL TECH SHENZHEN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com