Method of reducing neuronal cell damage
A neuron cell, monoamine neurotransmitter technology, applied in the direction of extracellular fluid diseases, nervous system diseases, botany equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problem that amphetamine will not improve recovery and other problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
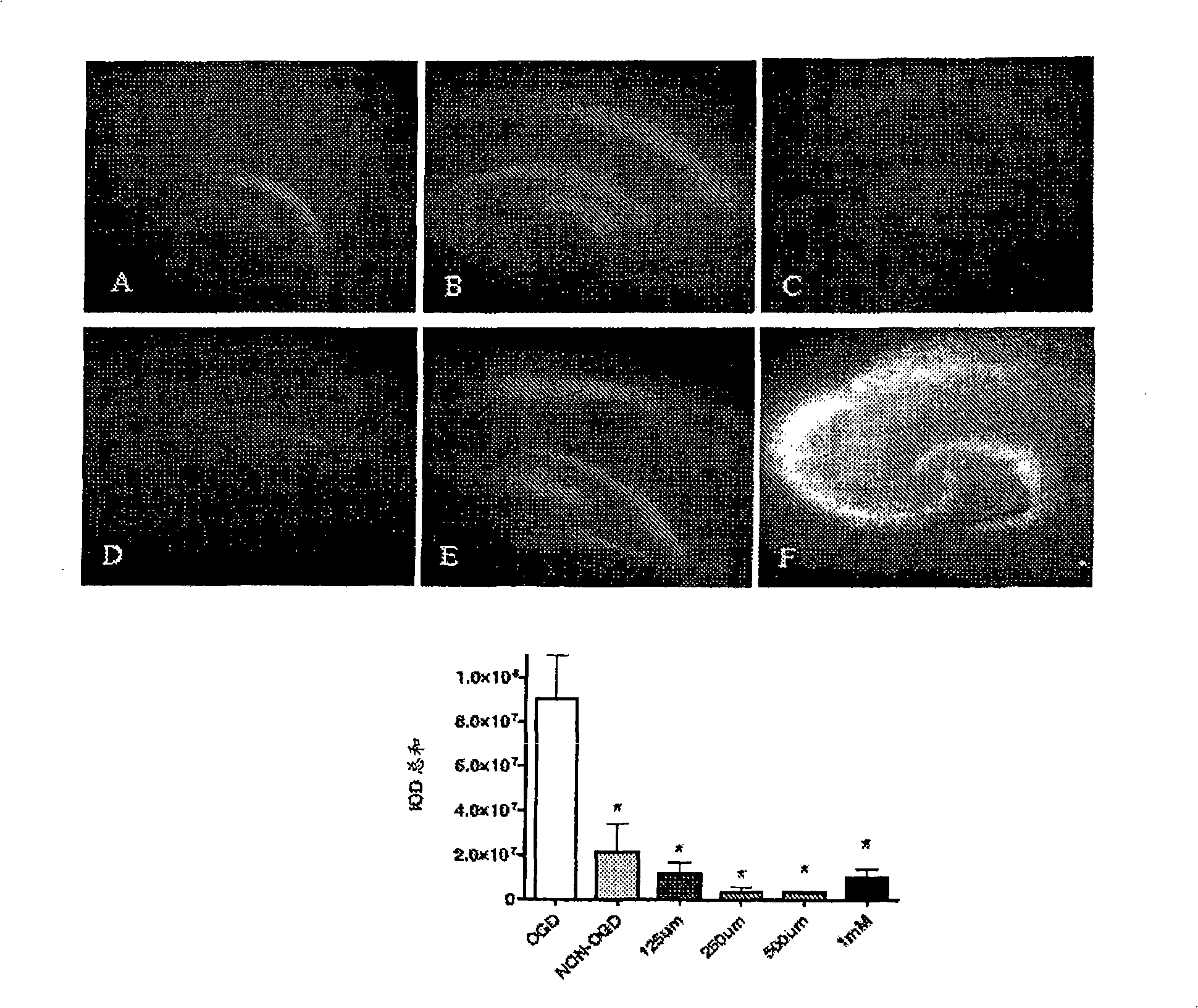
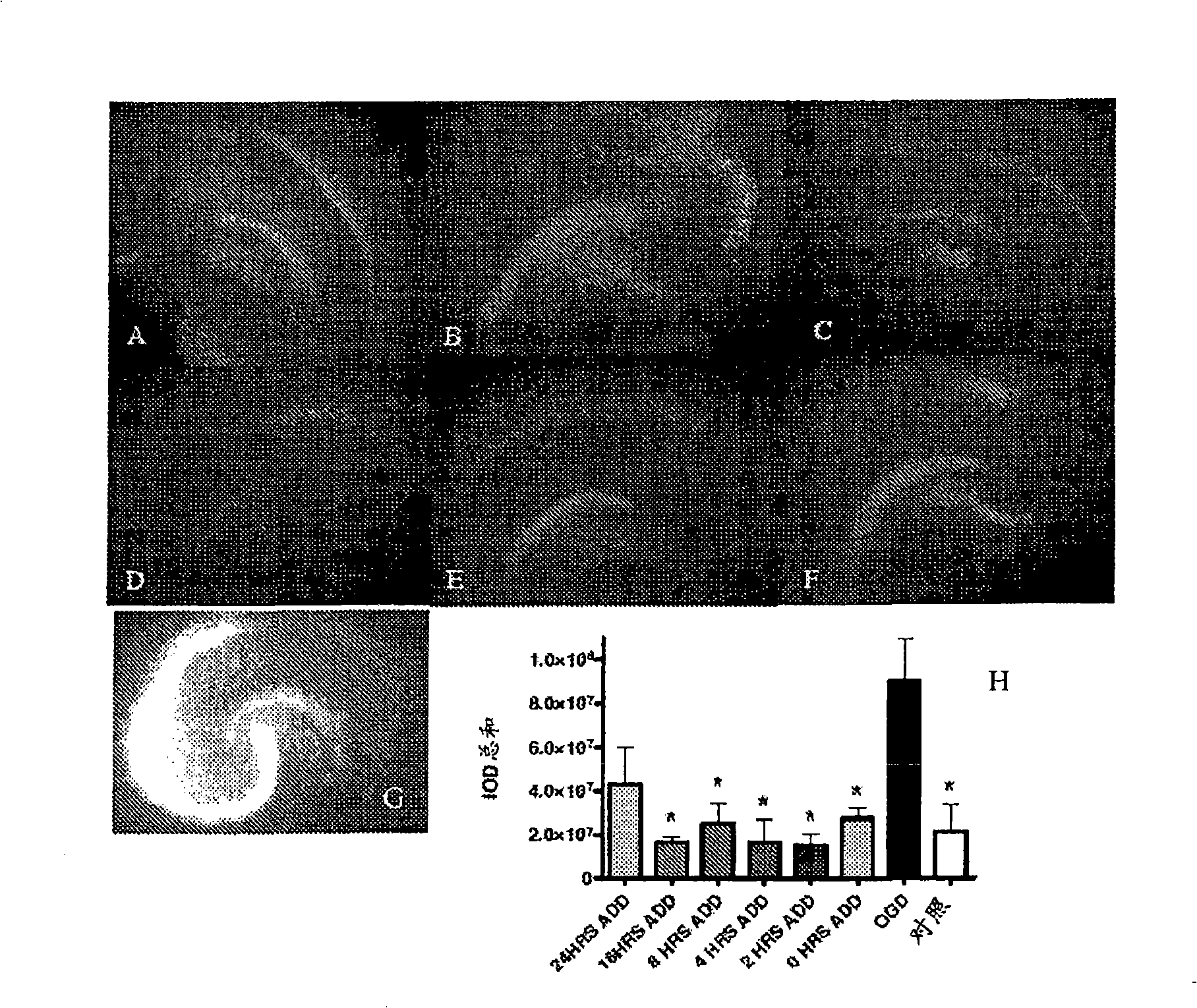
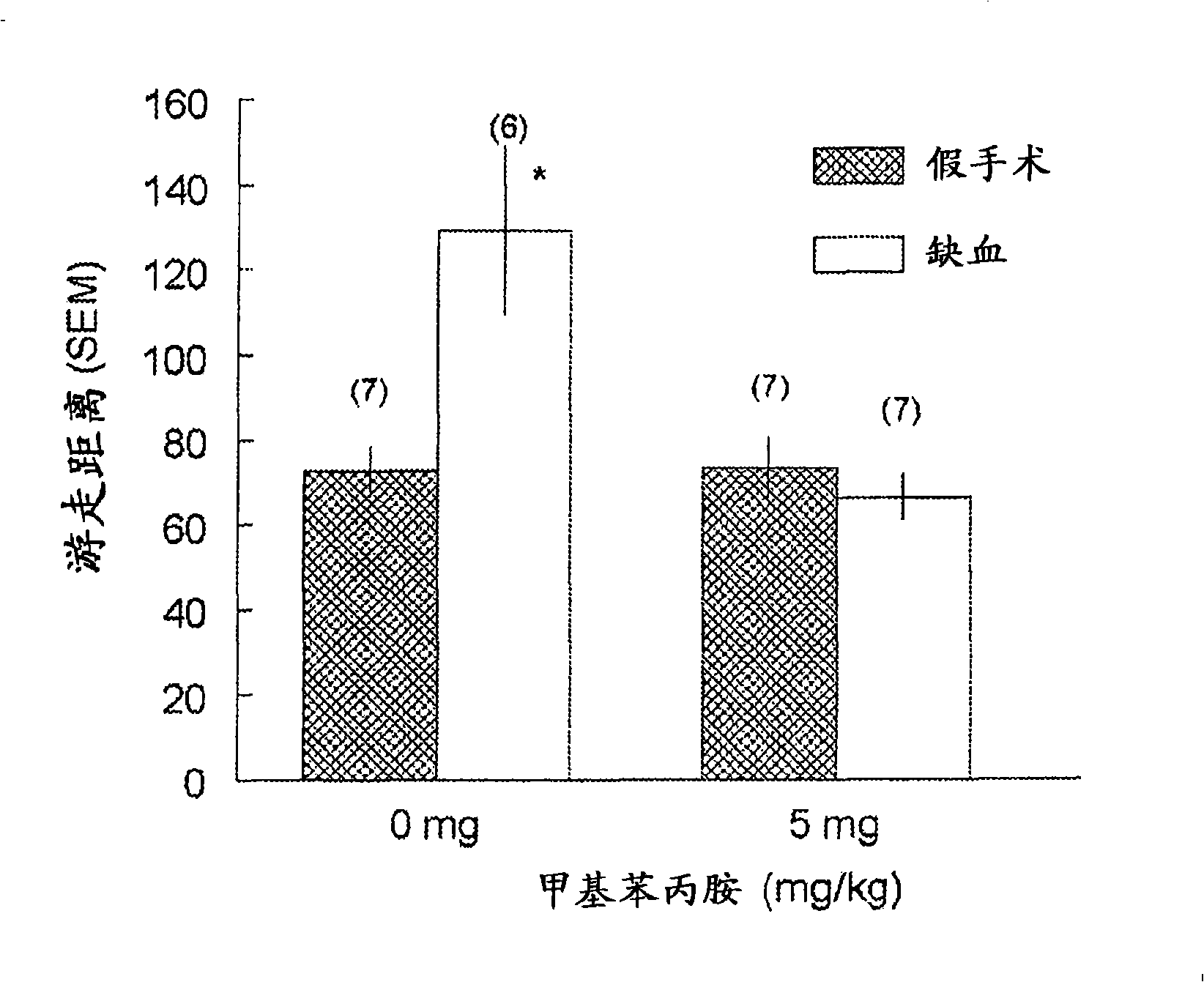
[0051] The neuroprotective efficacy of amphetamines after transient ischemic injury has not been previously investigated. In this study, methamphetamine (MA) was evaluated using in vitro and in vivo models of transient cerebral ischemia. For the in vitro model, rat hippocampal slice cultures were challenged under hypoxia and glucose deficiency. In a second series of experiments, the in vivo neuroprotective efficacy of MA was investigated using a combination of a 5-minute 2-VO occlusion gerbil model and behavioral testing. During this study it was surprisingly found and demonstrated that administration of MA within 16 hours after transient cerebral ischemia is indeed neuroprotective, reducing neuronal cell damage, including death.
[0052] Materials and methods
[0053] 1.1 Animals
[0054] All experimental animal manipulations were approved by the University Institutional AnimalCare and Use Committee. Twenty-eight adult male Mongolian gerbils (gerbils) weighing 60-80 gm we...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com