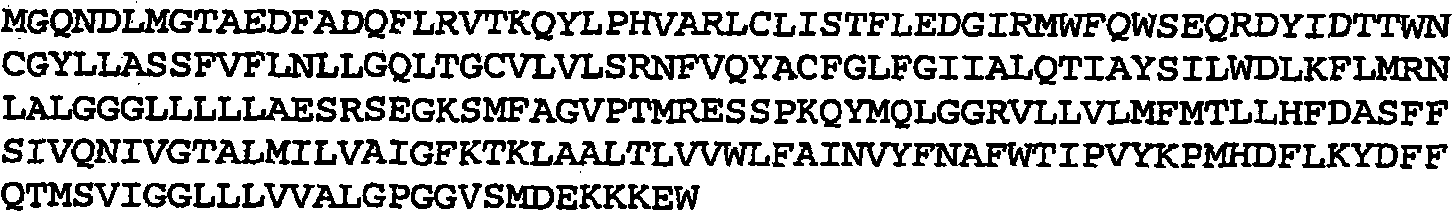Regulators of protein misfolding and neuroprotection and methods of use
A misfolding, protein technology, applied in the field of protein misfolding and neuroprotective regulators and applications, can solve the problem of ineffective or redundant treatment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0153] Example 1: Screening for genes that regulate protein aggregation in Parkinson's disease using RNAi
[0154] A transgenic C. elegans line overexpressing α-synuclein::GFP has been developed, which results in the formation of visible α-synuclein aggregates that can be visualized by fluorescence microscopy. Gene expression is under the control of the unc-54 promoter to direct expression in the body wall. Another transgenic nematode line containing α-synuclein::GFP+TOR-2 was used for RNAi screening of candidate genes related to protein aggregation. The presence of TOR-2 in α-synuclein::GFP+TOR-2 nematodes prevents aggregation of α-synuclein::GFP fusion proteins in body wall muscle cells, resulting in diffuse fluorescence. For protein aggregation of polyglutamine, it has been reported that TOR-2 has similar inhibition on protein aggregation (Caldwell et al. Hum MoI Genet. 2003 Feb 1; 12(3): 307-19). This transgenic organism allows a rapid screening method by feeding RNAi to...
Embodiment 2
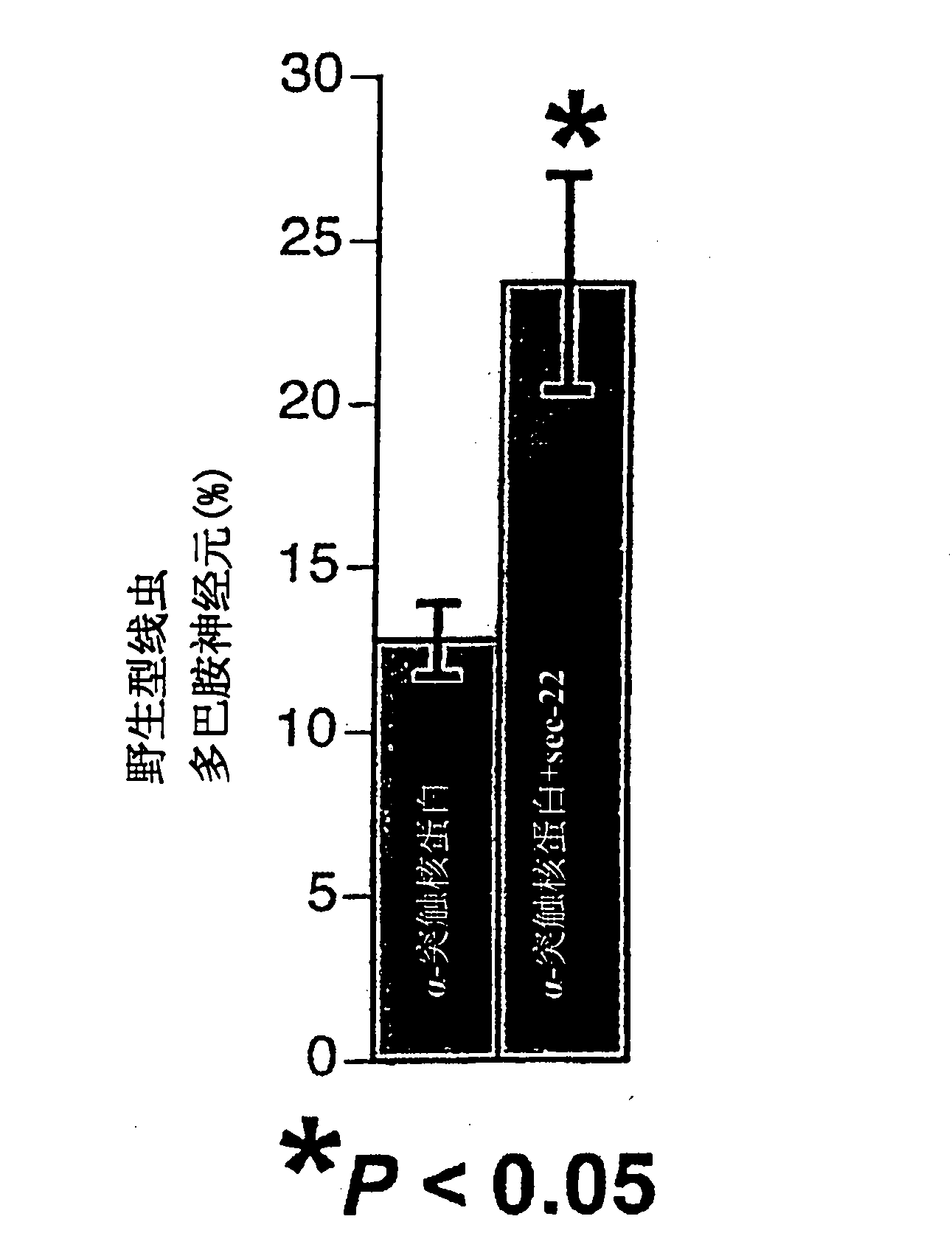
[0160] Example 2: Neuroprotection of dopamine neurons by expression of candidate genes after overexpression of α-synuclein
[0161] Novel C. elegans isogenic lines specifically designed for screening candidate Parkinson's disease genes were used to demonstrate neuroprotection. This novel isogenic line contains chromosomally integrated transgenes overexpressing human α-synuclein and GFP within dopamine neurons to assess neurodegeneration in vivo during development and aging. This line exhibits approximately 30-40% degeneration at day 4 of adulthood in C. elegans development and provides an ideal tool for studying environmental / genetic factors in which α-synuclein susceptibility may affect dopaminergic neurodegeneration. Positive RNAi screen candidate genes were systematically evaluated by crossing animals overexpressing the corresponding cDNA in dopamine neurons of the alpha-synuclein strain, followed by a search for evidence of neuroprotection. This strain is also used for me...
Embodiment 3
[0174] Example 3: Method for Detecting Protein Changes Using Microarrays and Diagnosing Human Susceptibility to Parkinson's Disease or Suffering from Parkinson's Disease
[0175] Preparation of Parkinson's disease microarray
[0176] Parkinson's disease microarrays can be fabricated using standard commercial microarray technologies, such as spotting microarrays or high-density oligonucleotide-based platforms used by Affymetrix. A moderate to large number of genes and / or transcripts are selected for analysis, ie expression (or response) profiling. Nucleic acid sequences that can be monitored using the method of the present invention include, but are not limited to, the genes listed in the GenBank.RTM database of the National Center for Biotechnology Information (website ncbi.nlm.nih.gov), and the sequences provided by other public or commercial databases (eg, NCBI EST sequence database, EMBL nucleotide sequence database; Incyte's (Palo Alto, Calif.) LifeSeq.TM. database and Ce...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap