Potent combinations of zidovudine and drugs that select for the K65R mutation in the HIV polymerase
A medicament and dosage technology, applied in the direction of pharmaceutical formulations, antiviral agents, carbohydrate active ingredients, etc., can solve the problems of high toxicity compliance, non-elimination of HIV-1, decline, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
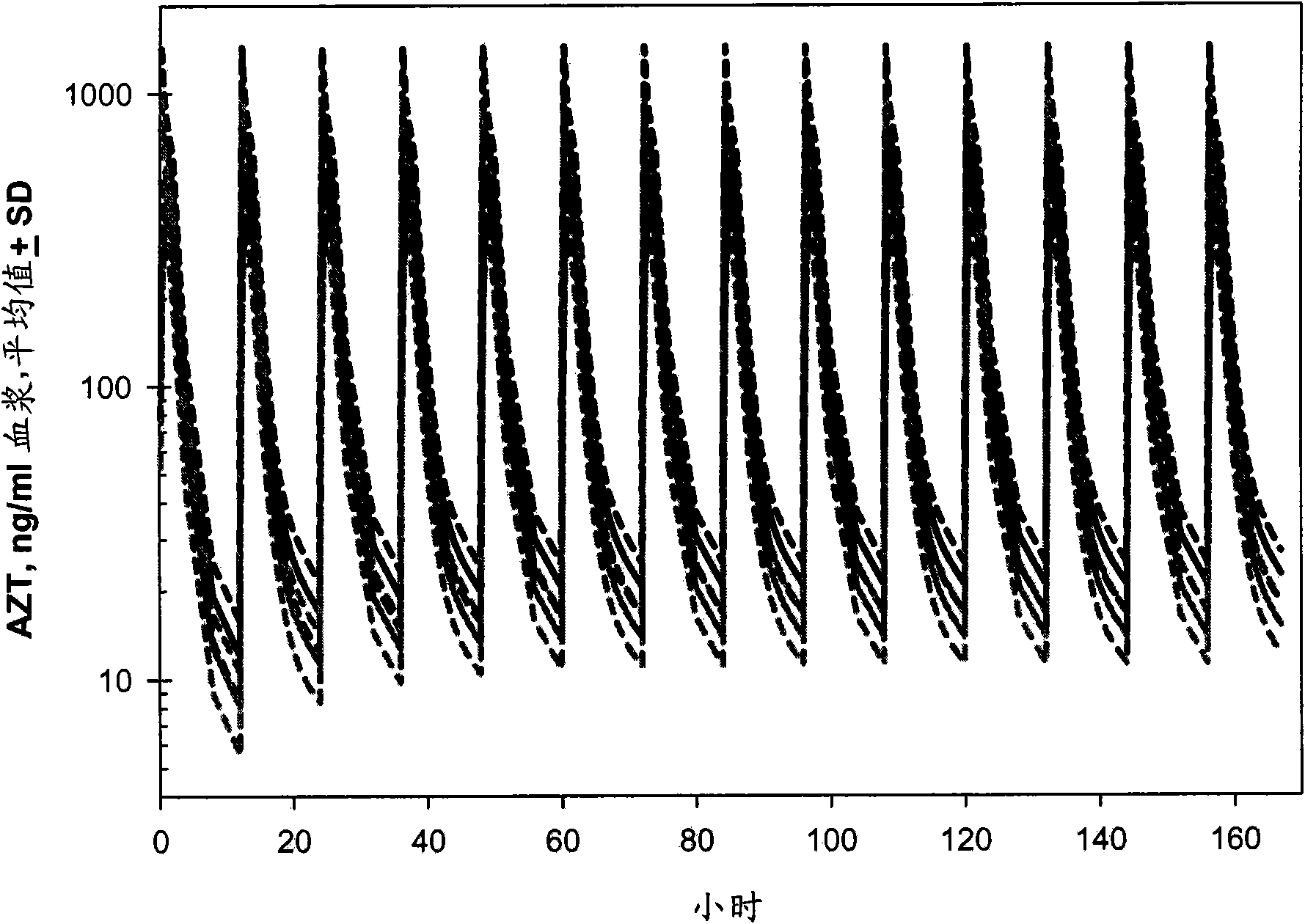
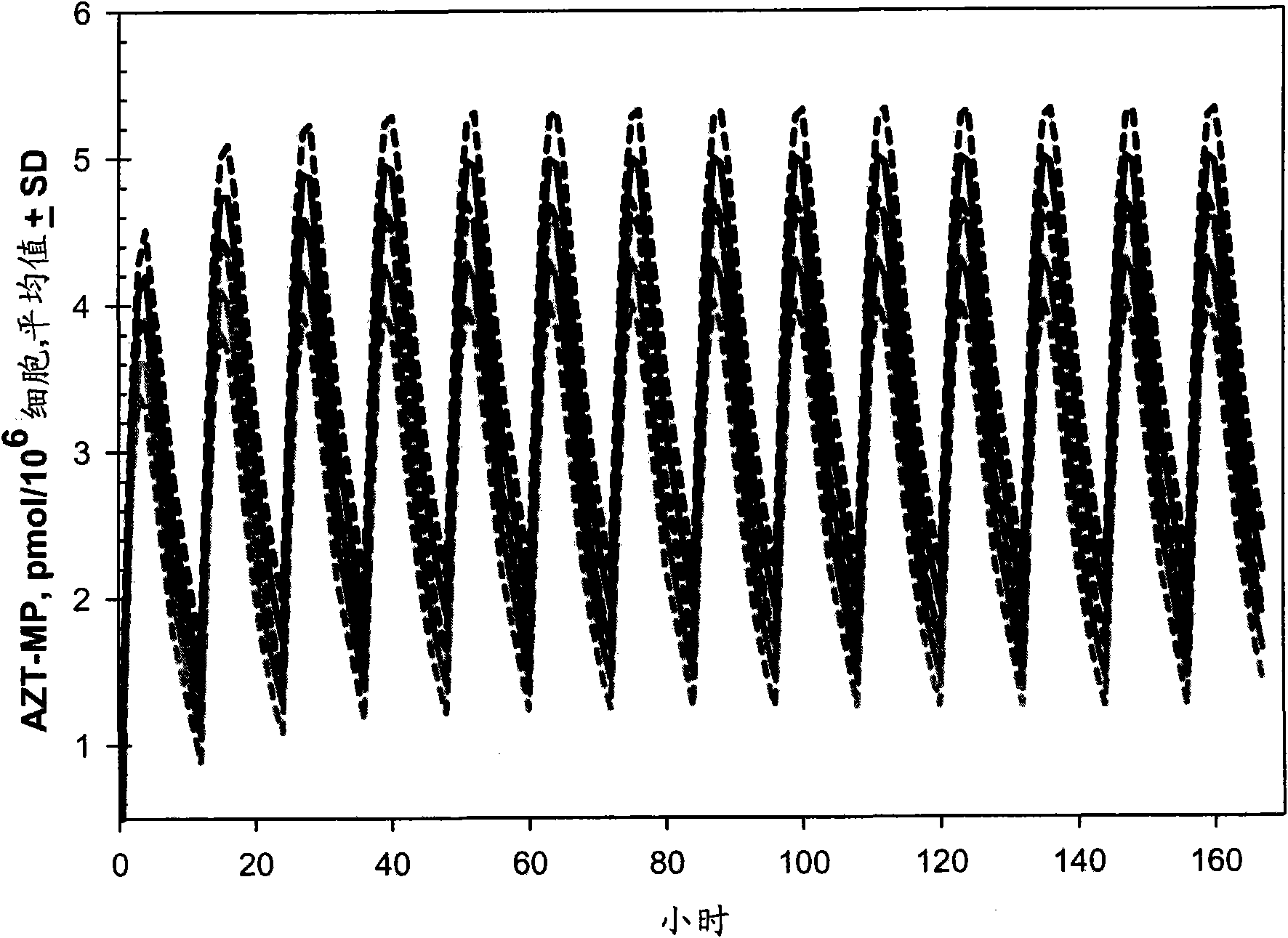
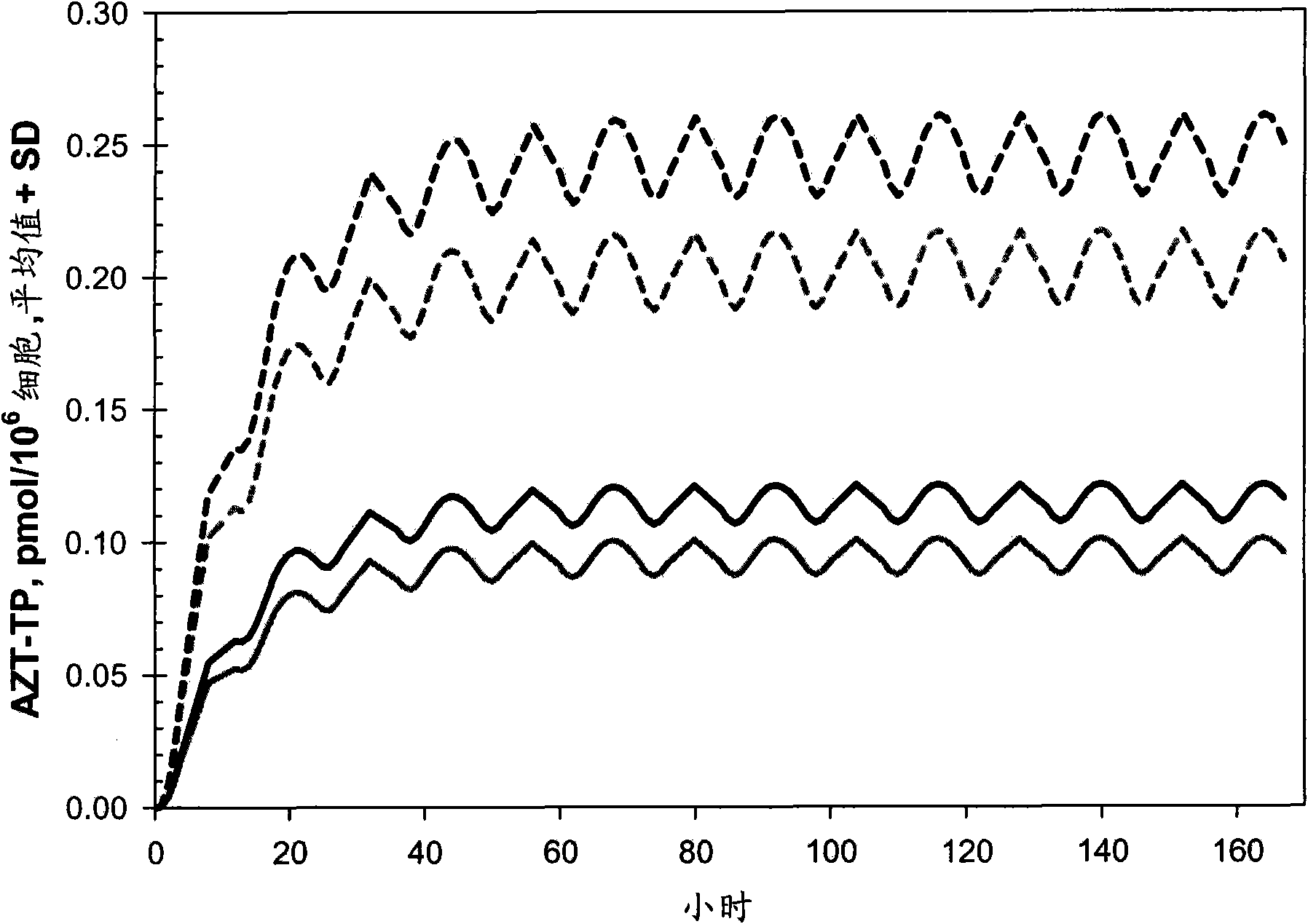
[0134] Example 1: Computer Simulation Study to Determine Optimal AZT Dose Range
[0135] The current first-line highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) for the treatment of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1) infection combines two nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs) together with protease inhibitors (PIs) or non- - Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTI) (12, 13, 40) in combination. These drug combinations significantly reduced mortality and morbidity due to HIV-1 infection in developed countries (7). The failure of existing therapies to eradicate HIV-1 infection is due to compartmentalization of the virus and its underlying properties (58, 59). Thus, chronic therapy maintains the standard of care for the foreseeable future. Although the choice of HAART regimen was able to partially minimize cross-resistance and thereby delay the emergence of resistant virus, all regimens ultimately failed, mainly due to lack of adherence to rigorous regime...
Embodiment 2
[0172] Example 2: Synergy between amdosovir and zidovudine in a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled study in HIV-infected subjects
[0173] background
[0174] Amdosovir (AMDX; DAPD) has been well studied in 6 trials in nearly 200 subjects. In human lymphocytes, zidovudine (AZT) synergizes with DAPD and prevents selection for K65R mutations and thymidine analog mutations (TAMs). In computer simulations, the toxicity of lower doses of AZT could be reduced by reducing AZT monophosphate (AZT-MP) accumulation while maintaining the antiviral effect. The objective of the study was to examine the virological response to DAPD in HIV-infected subjects with and without reduced doses of AZT (ie, 200 mg twice daily, and the approved dose, 300 mg twice daily).
[0175] method
[0176] Subjects with HIV RNA viral load (VL) ≥ 5,000 copies / mL participated in the experiment and were randomly given 1:1:1 DAPD 500mg twice a day: DAPD 500mg+AZT 300mg twice a day: DAPD 500mg within 10 da...
Embodiment 3
[0183] Example 3: Dose Study on Effect of DAPD / AZT Combination Therapy and Mean Viable Cell Volume (MCV)
[0184] 24 subjects participated in the experiment [placebo (n=2), AZT 200mg (n=2), AZT 300mg (n=2), DAPD 500mg (n=6), DAPD / AZT 200mg (n=6), and DAPD / AZT 300mg (n=6)] and treated for 10 days. Blood indices including hemoglobin (g / dl) and mean corpuscular volume (MCV, femtoliter (fL)) were measured at screening 1 day before treatment and on days 5, 10, and 20 of treatment . One subject receiving DAPD / AZT 200 had a Grade 1 decrease in hemoglobin observed on Days 10 and 20, and microcytosis was observed at baseline and at all other sampling points. An increase in MCV (97 femtoliters (fL), normal 86±6) was observed at Day 20 in one subject receiving DAPD / AZT 300. At day 20, the trend in hemoglobin reduction from baseline was DAPD / AZT 300 ≥ AZT 300 ≥ DAPD / AZT 200 > AZT 200 > DAPD > placebo (results as Image 6 shown), while the rising trend of MCV from baseline was DAPD / AZT...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com