Adaptive group of pictures (AGOP) structure determination
A picture, picture type technology, applied in the direction of image communication, TV, electrical components, etc., can solve the problem of inaccurate effective compression and so on
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
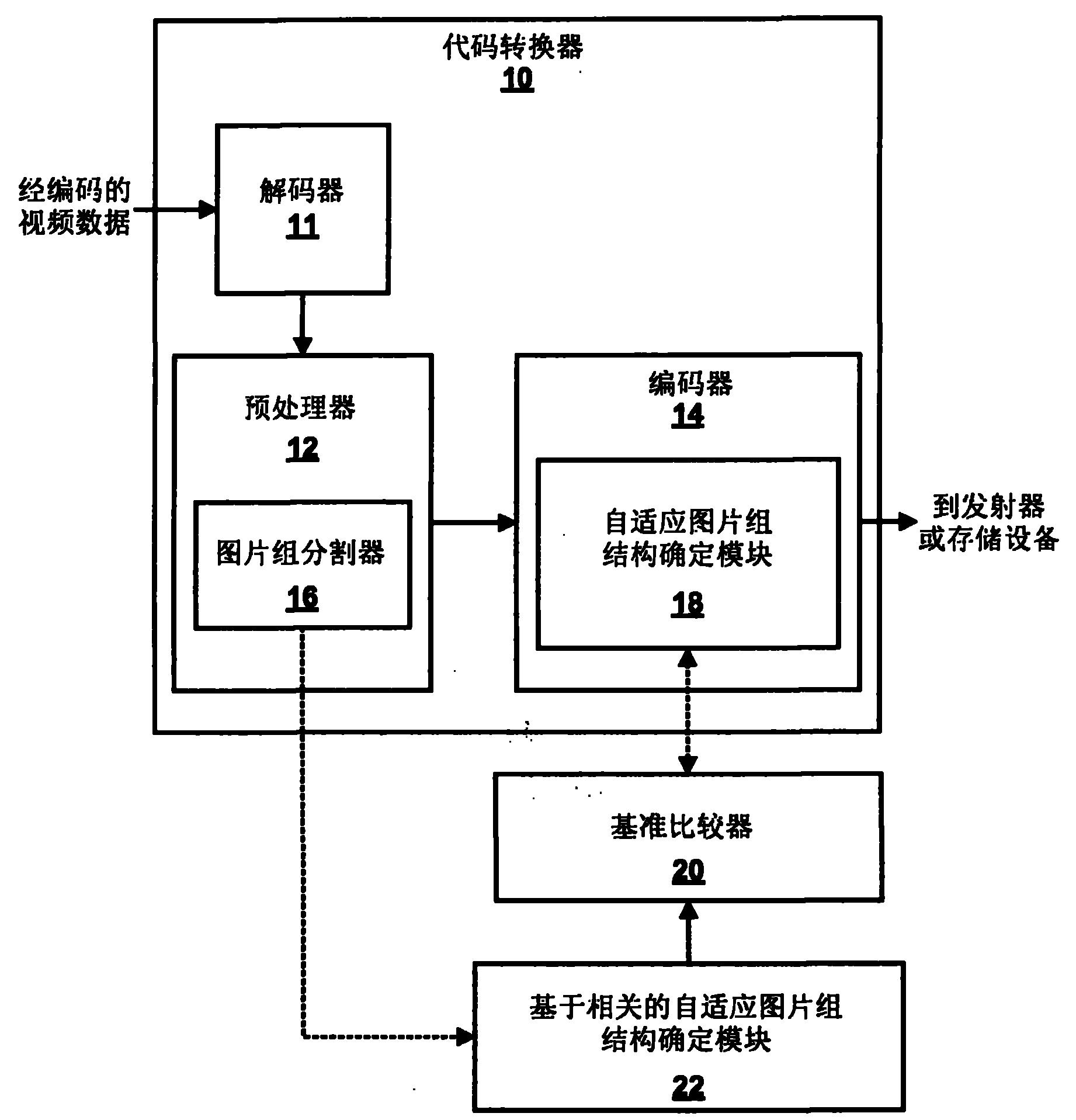
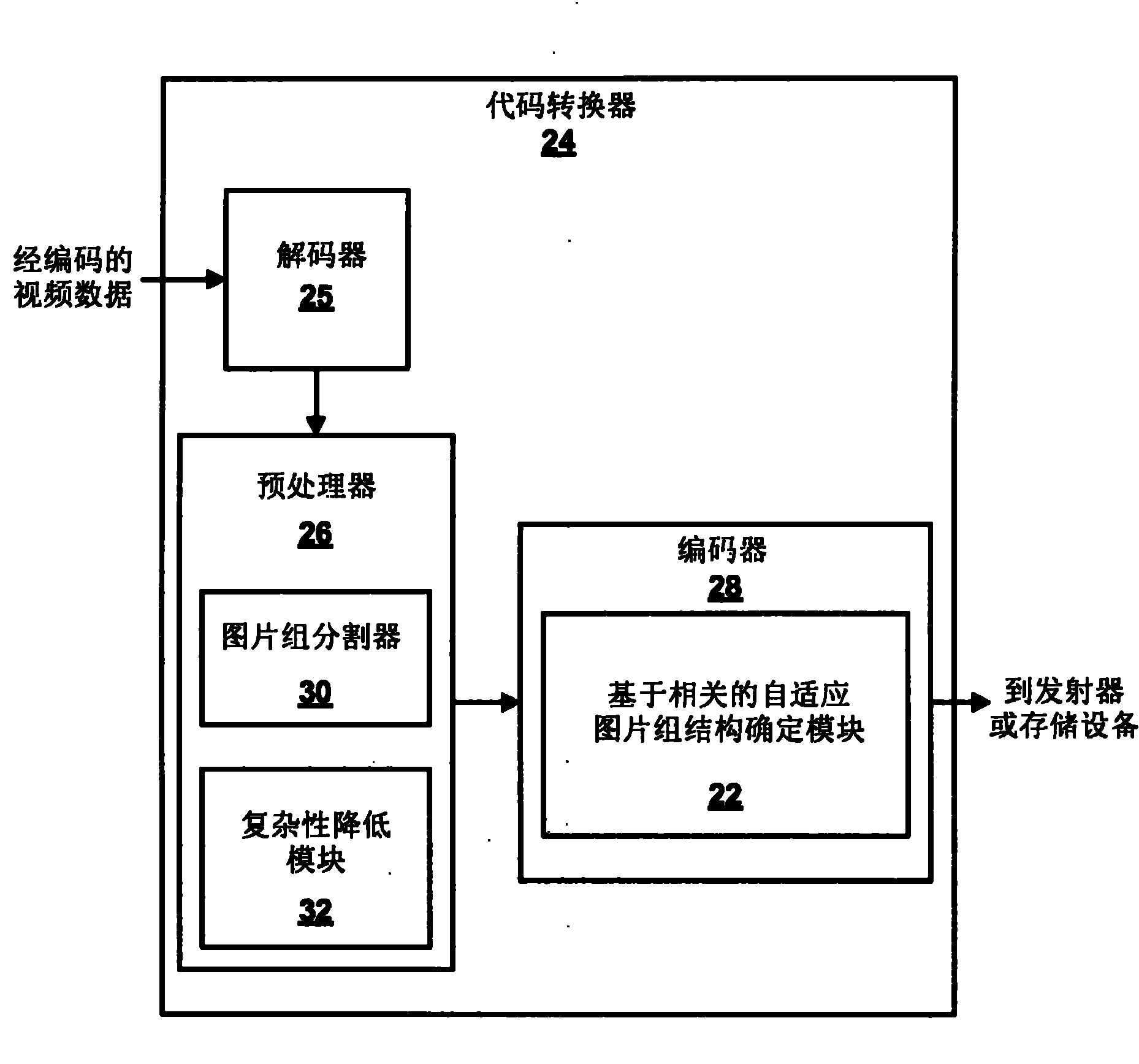
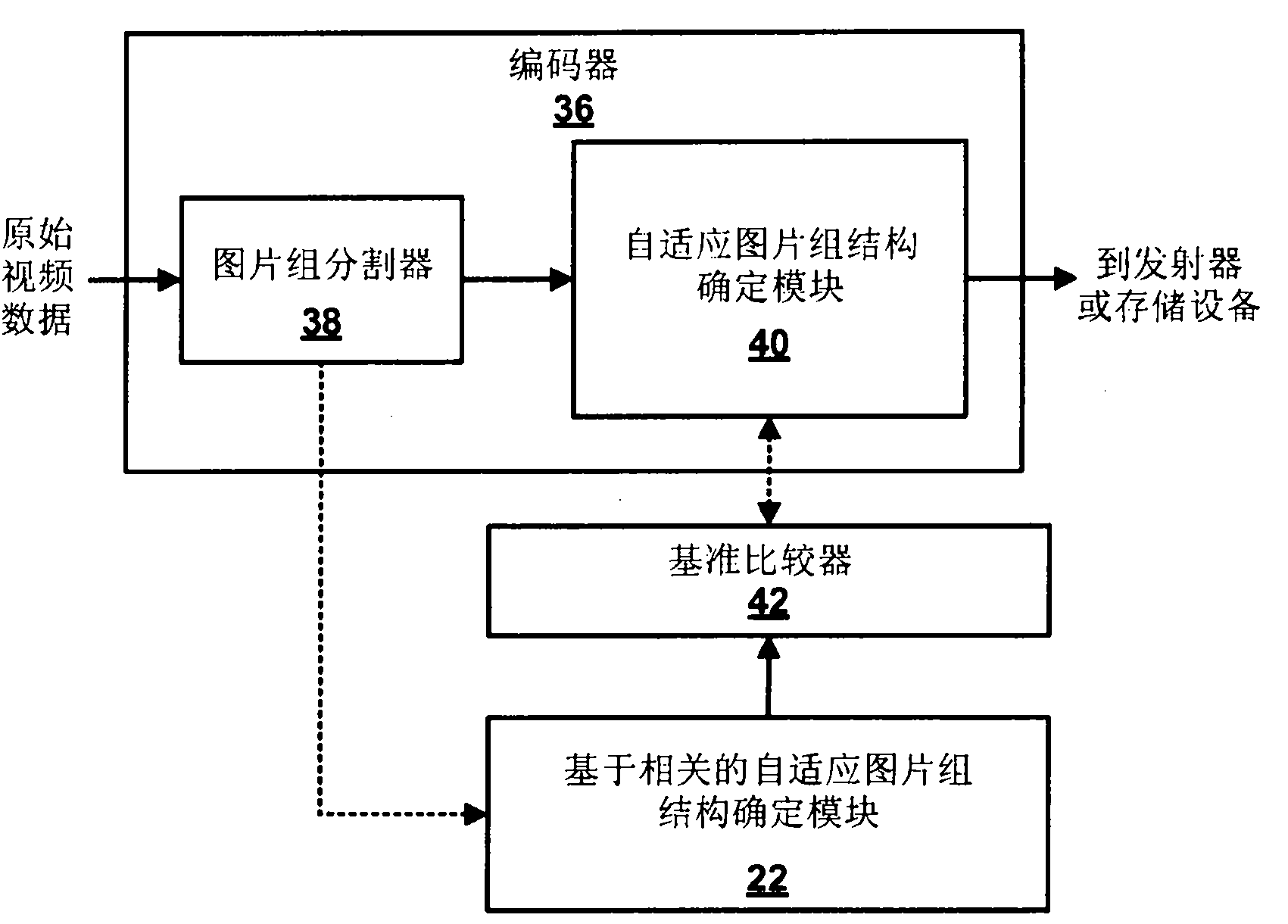
[0040] This disclosure describes techniques for determining a picture type for each of multiple frames included in a video sequence based on a cross-correlation between the frames. The cross-correlation includes a first-order cross-correlation between several pairs of image information in a frame included in the video sequence and a second-order cross-correlation between several pairs of the first-order cross-correlation. The first order cross-correlations can be analyzed to detect video transition effects between the frames, such as cut scene changes, flash frames, crossfades, and camera pans and rolls. The first order cross-correlations and the second order cross-correlations may be analyzed comparatively to determine temporal similarity between the frames. Accordingly, the correlation-based determination technique determines the picture type of the frame based on the video transition effect and the temporal similarity. The correlation-based determination technique may comp...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com