Cutting method of semiconductor wafer
A cutting method and semiconductor technology, applied in the fields of semiconductor devices, semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of increased cost, cost increase, slow laser cutting speed, etc., and achieve the effect of improving production speed and reducing cost.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0039] A method for dicing a semiconductor wafer according to a preferred embodiment of the present invention will be described below with reference to related drawings.
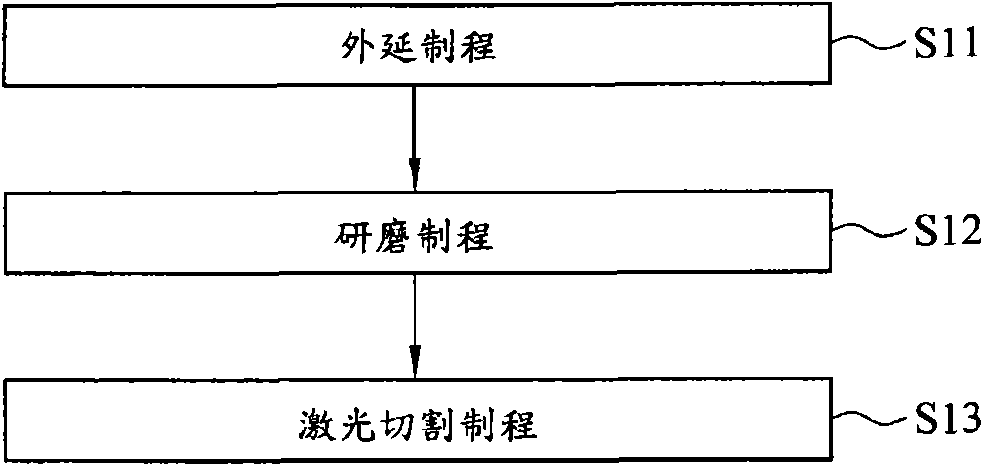
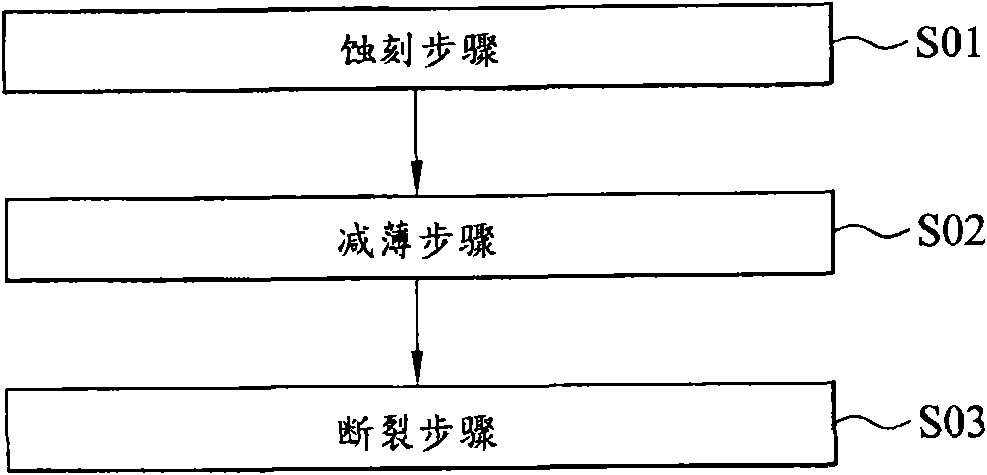
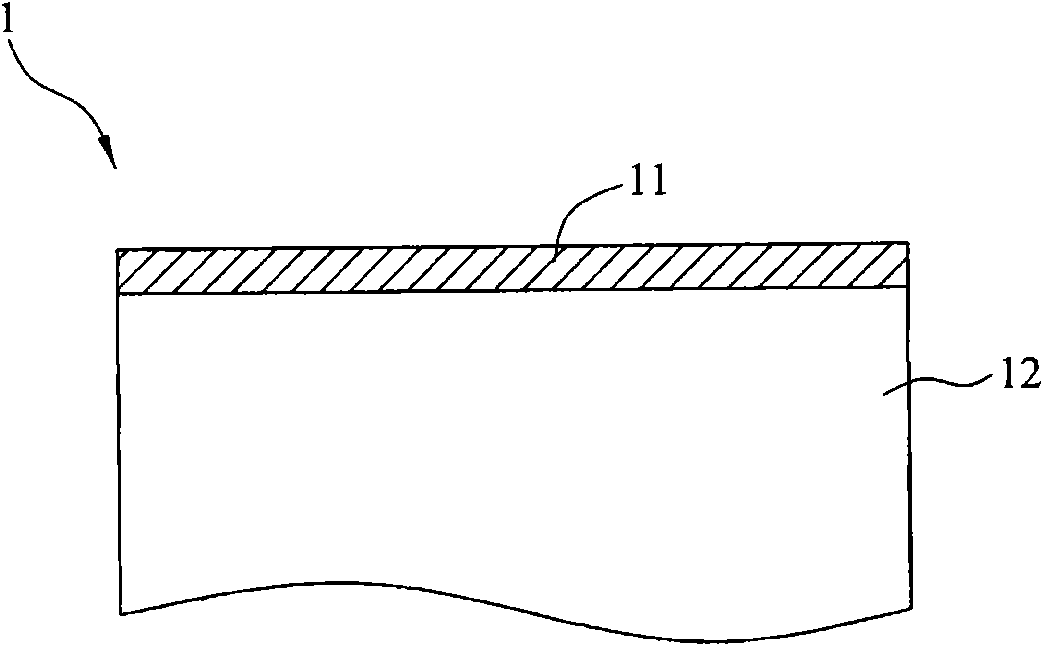
[0040] Please refer to figure 2 As shown, a method for cutting a semiconductor wafer according to a preferred embodiment of the present invention includes steps S01 to S03. Please refer to the semiconductor wafer 1 of the present embodiment Figure 3A As shown, the semiconductor wafer 1 has an active layer 11 and a substrate 12 . Wherein, the active layer 11 may include semiconductor circuits with any functions, and is not limited here, such as functions such as light emission, calculation, switching, sensing, and power generation. In addition, the present invention does not limit the material and shape of the substrate 12 , and the material of the substrate 12 may include, for example, glass, ceramics, metal, plastic, resin, or sapphire. In this embodiment, the semiconductor wafer 1 is an example of a l...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap