Method, system and device for distributing contention resources
A technology of competing resources and allocation methods, applied in electrical components, wireless communication, etc., can solve the problem of how UE obtains competing resources without a corresponding technical solution, affecting applications, etc., and achieves the effect of satisfying the system state transition delay
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
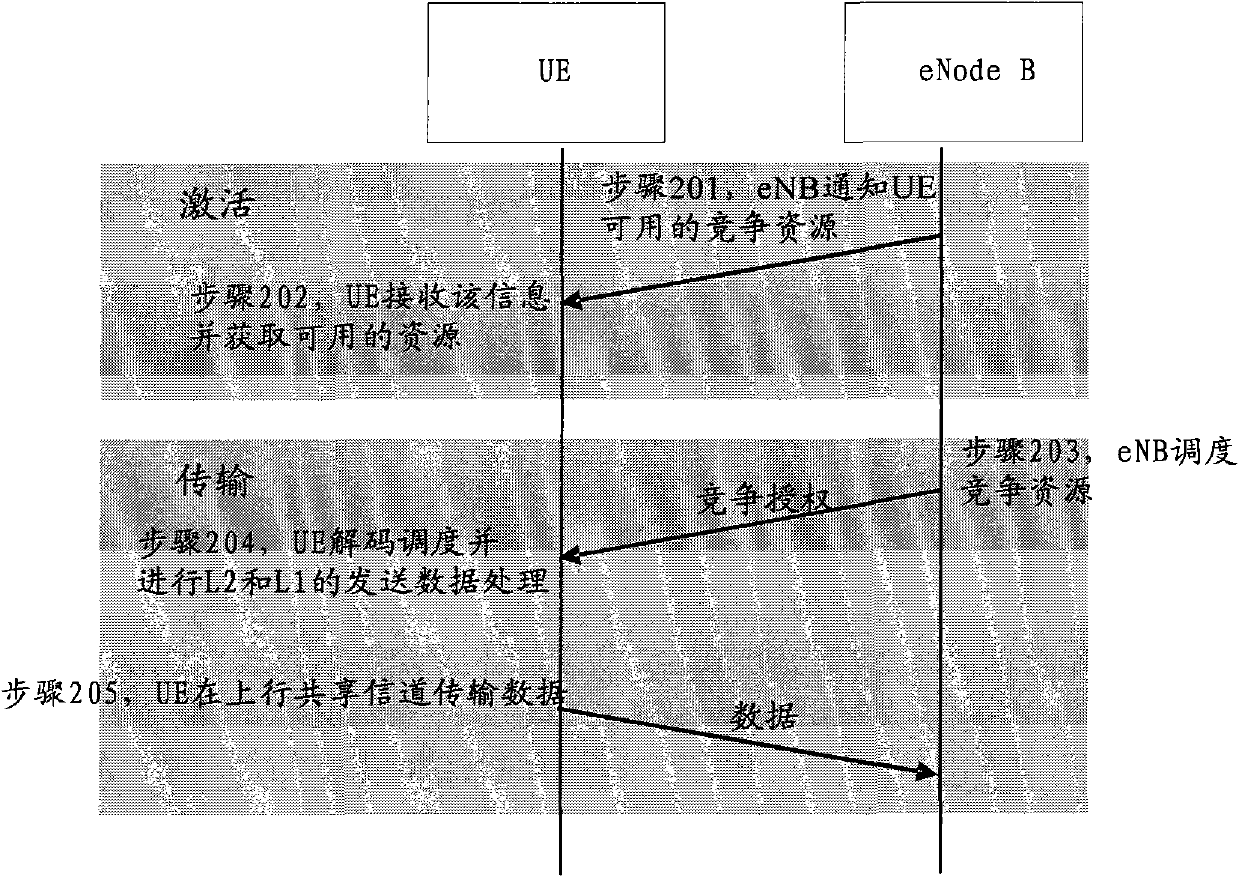
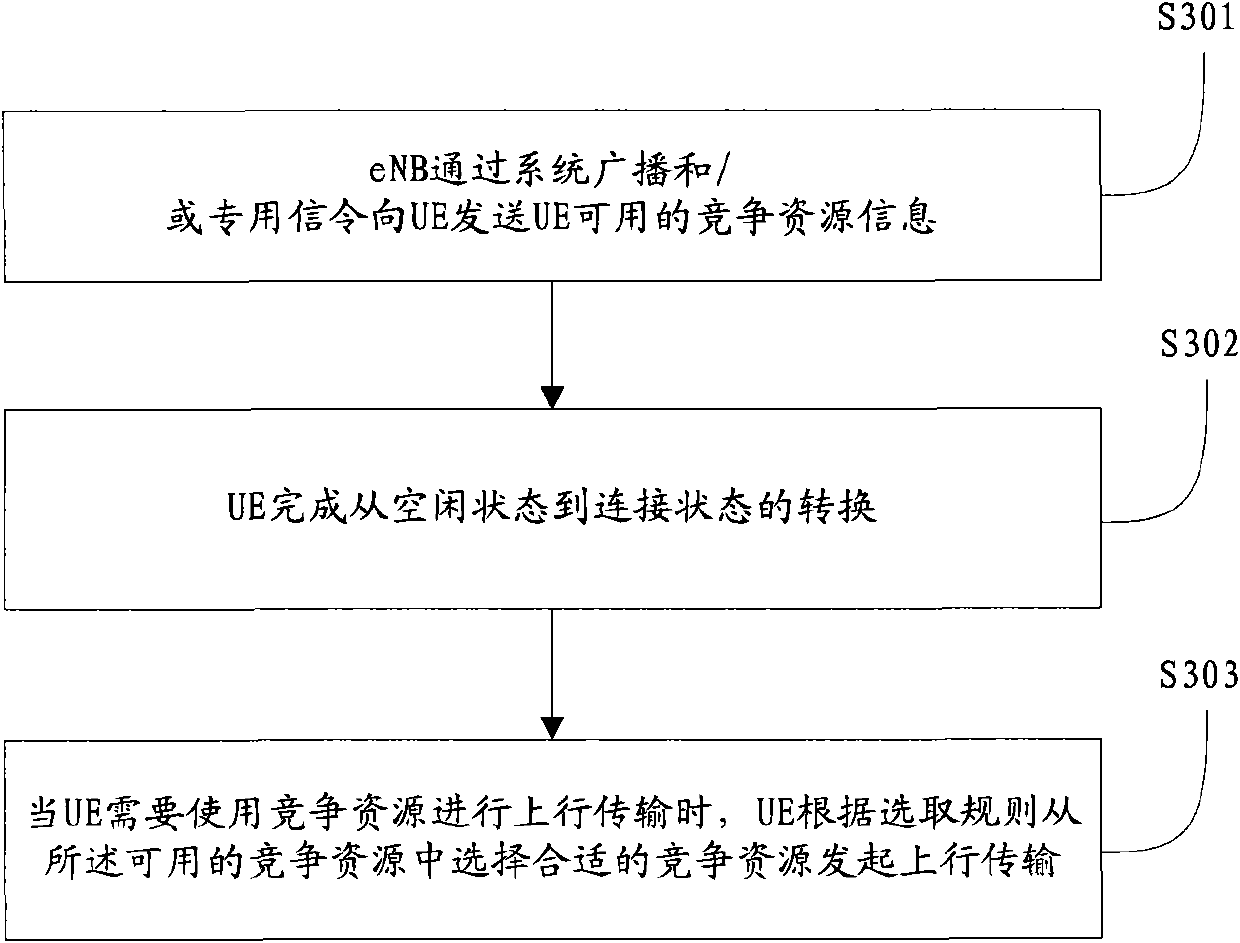
[0062] In this embodiment, a set of indicators can be specified, which can be used to indicate information such as different physical resource block frequency domain and time domain positions and their corresponding modulation and coding methods, and the network side publishes the available two Block contention resources and their corresponding indications, such as m and n, the steps for UE to use contention resources are as follows Figure 4 shown.
[0063] In step S401, the UE reads system broadcast information, and obtains information identifiers m and n related to contention resources therefrom.
[0064] In step S402, the UE completes the transition from the idle state to the connected state.
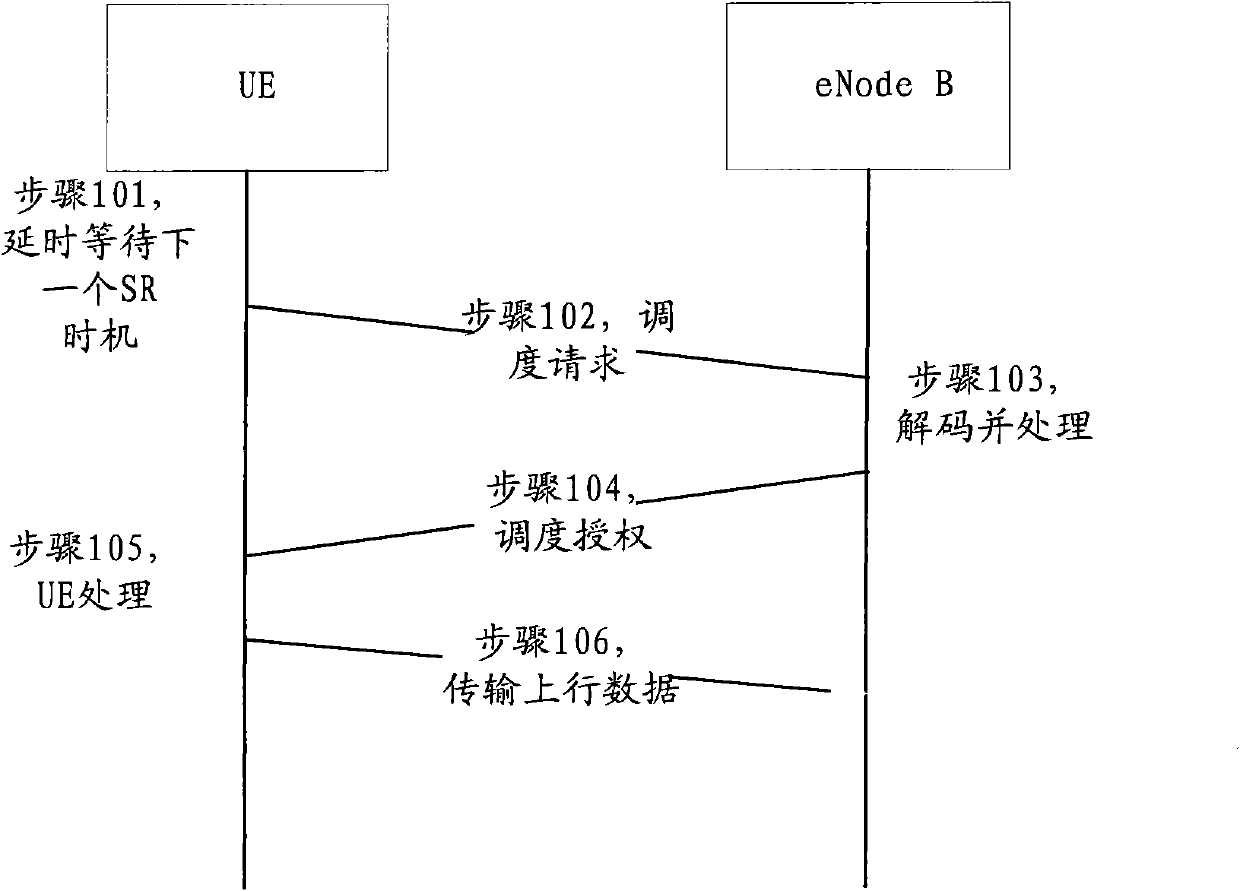
[0065] Step S403, the UE is in the synchronized state. When the UE needs to use contention resources for uplink transmission, such as meeting the sending Scheduling Request (SR) conditions or other situations where there is uplink data but no uplink resources are available for a pe...
Embodiment 2
[0068] In this embodiment, CB-RNTI is the default. The number of available CB-RNTI broadcast by eNB in the system information is 2, and the default CB-RNTI is the first two or last two of the reserved parts (FFF4-FFFD) in the current RNTI value, or other specified methods Obtain. As shown in Table 1, the distribution of RNTI values in R8 is as follows:
[0069] Table 1
[0070] value
RNTI
0000
N / A
0001-003C
RA-RNTI, C-RNTI, C-RNTI for semi-persistent scheduling, temporary
C-RNTI, TPC-PUCCH-RNTI and TPC-PUSCH-RNTI
003D-FFF3
C-RNTI, C-RNTI for semi-persistent scheduling, temporary C-RNTI,
TPC-PUCCH-RNTI and TPC-PUSCH-RNTI
FFF4-FFFD
reserve
[0071] FFFE
P-RNTI
FFFF
SI-RNTI
[0072] Such as Figure 5 As shown, it is a flow chart of UE initiating contention transmission in Embodiment 2, including the following steps:
[0073] In step S501, the UE reads the broad...
Embodiment 3
[0077] In this embodiment, the contention resource information also includes CB-RNTI grouping information, and the UE first selects a monitoring group according to its own situation, and then further selects a suitable contention resource from the selected group to initiate uplink transmission. The number of available CB-RNTIs broadcast by the eNB in the system information is 3, of which the number of CB-RNTIs belonging to group A is 2, and the remaining 1 CB-RNTI is group B. The specific CB-RNTIs corresponding to each The value can be directly broadcast by the system information, or selected in the reserved area of the RNTI space according to the default method, or other methods defined by the standard. Such as Figure 6 As shown, it is a flow chart of UE initiating contention transmission in Embodiment 3, including the following steps:
[0078] In step S601, the UE reads the broadcast information, obtains information about contention resources, obtains the currently ava...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com