A method of computing a collision-free velocity for an agent in a crowd simulation environment
A crowd simulation and intelligent body technology, applied in computing, 3D modeling, instruments, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
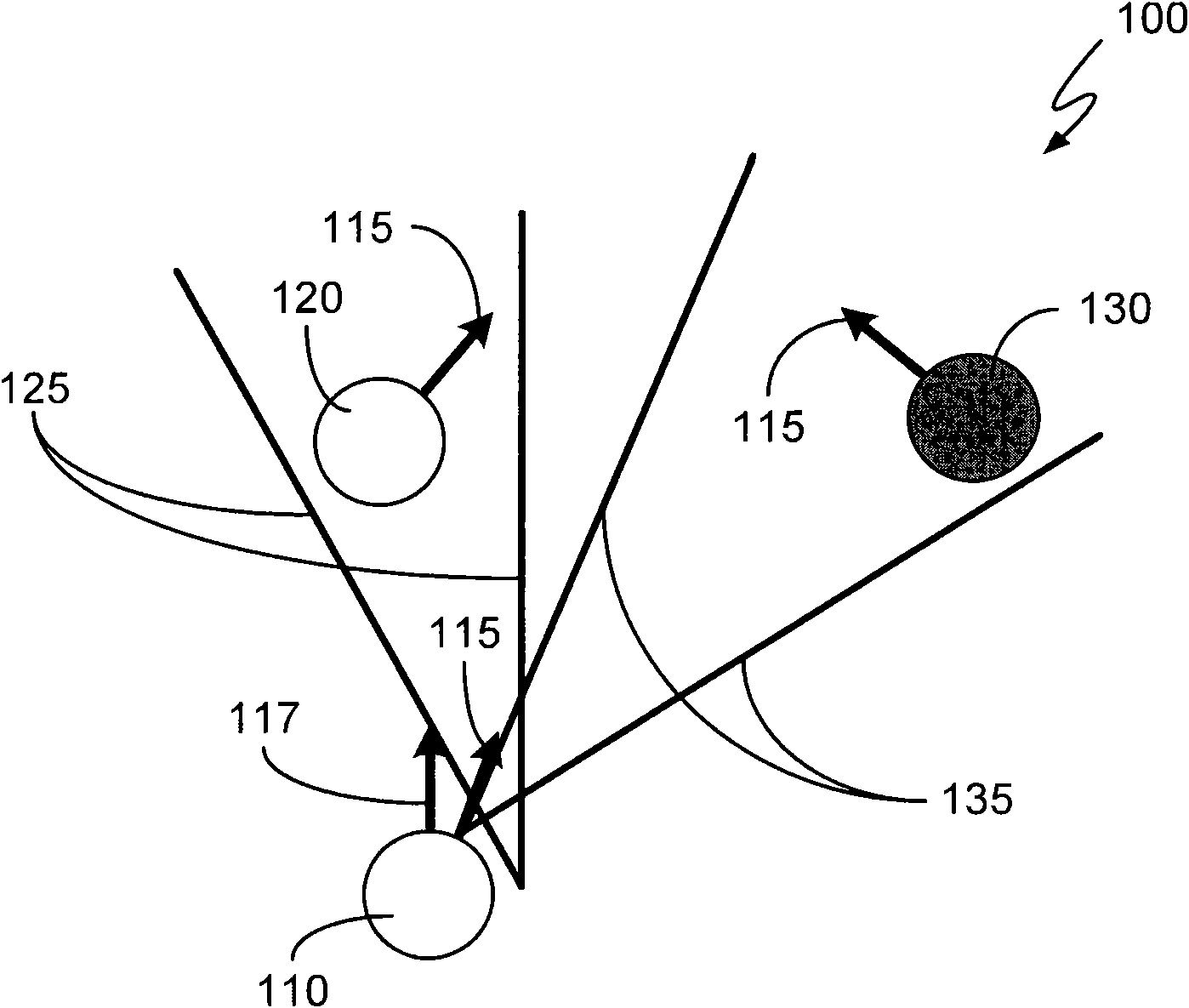
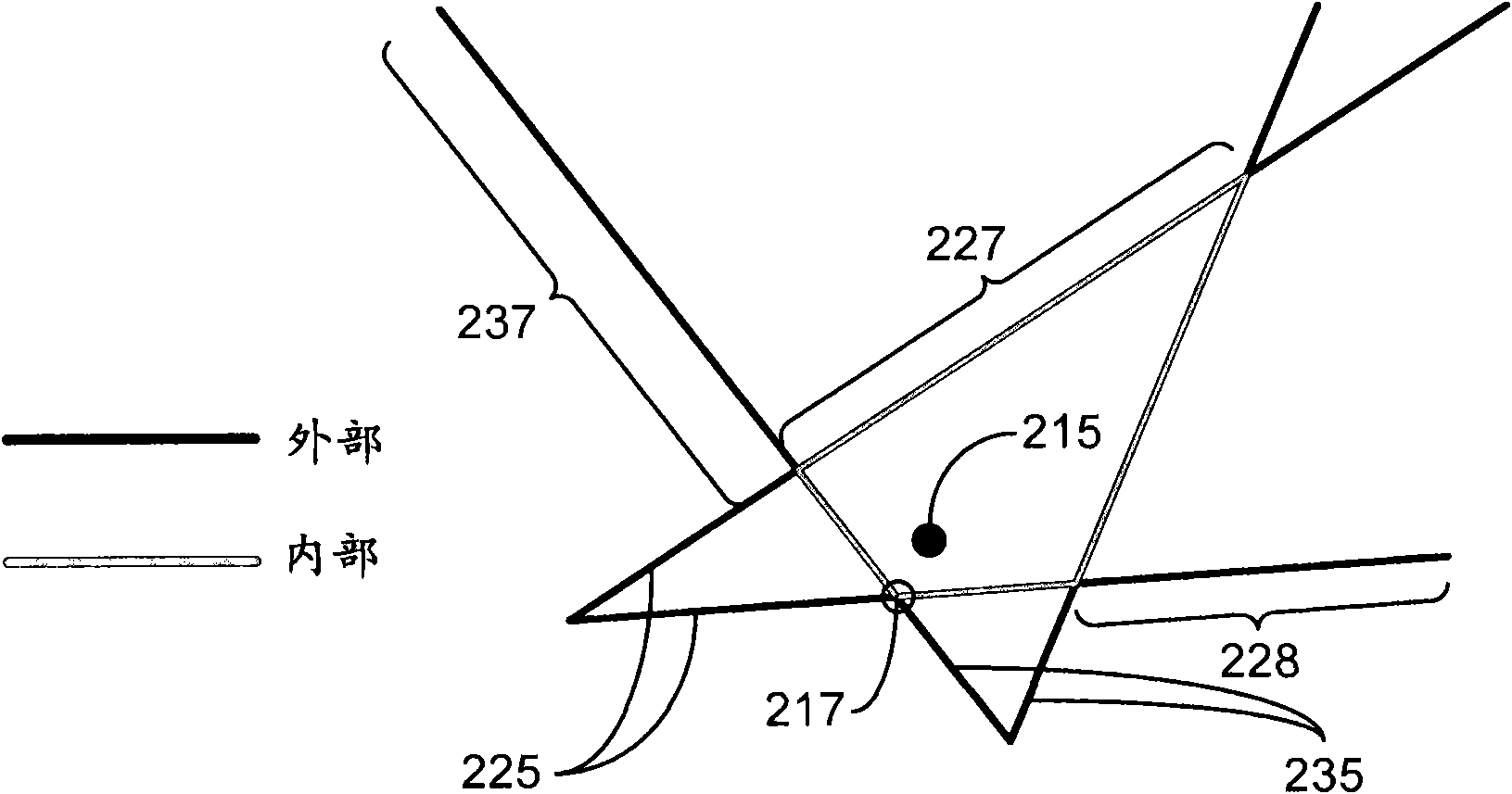
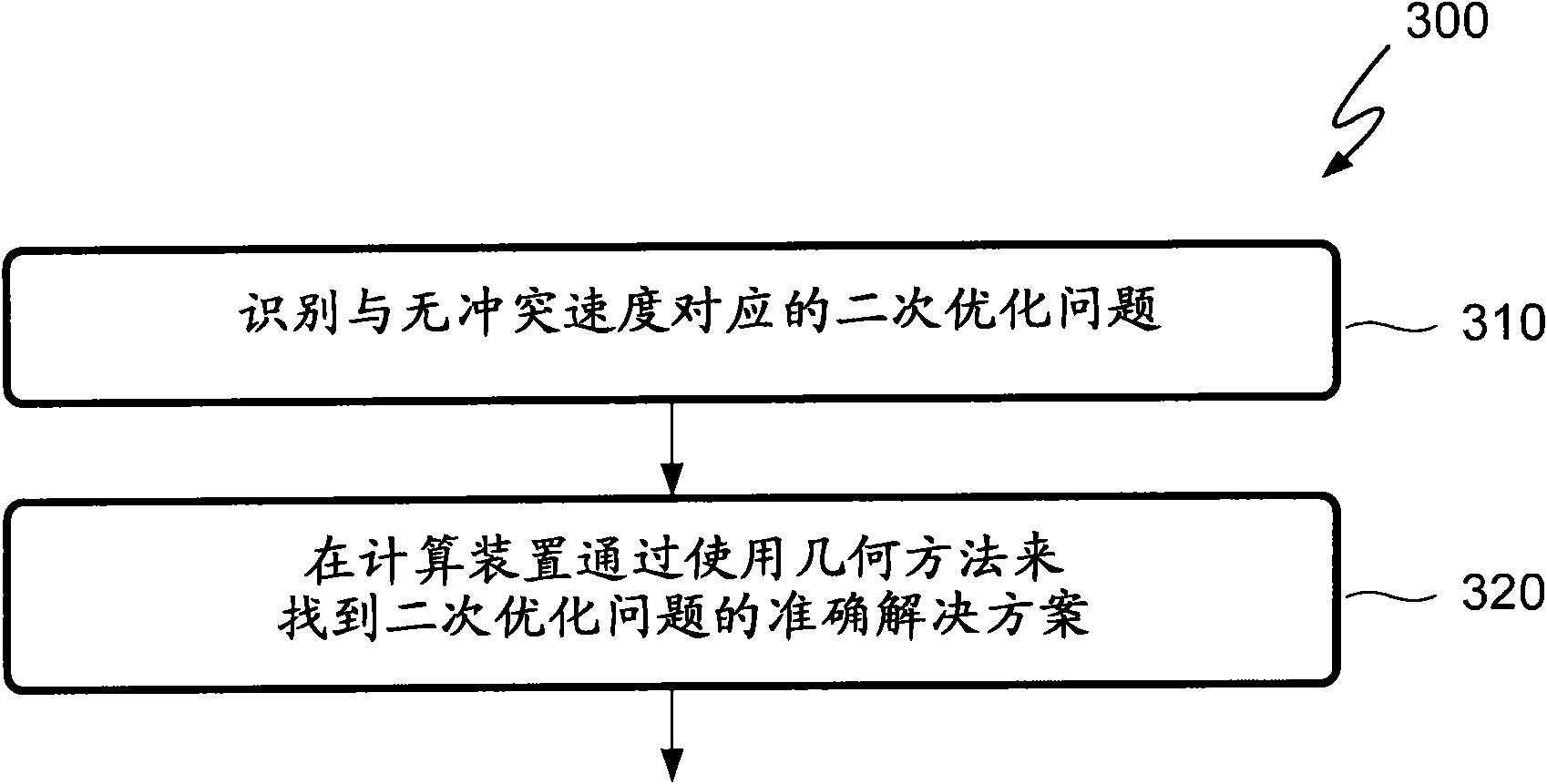
[0011] For simplicity and clarity of illustration, the drawings illustrate the general manner of construction, and descriptions and details of well-known features and techniques may be omitted so as not to unnecessarily obscure the discussion of the described embodiments of the invention. Additionally, elements in the drawings are not necessarily drawn to scale. For example, the dimensions of some of the elements in the figures are exaggerated relative to other elements to help to improve understanding of embodiments of the present invention. The same reference numbers in different drawings denote the same elements, while similar reference numbers may, but do not necessarily, denote similar elements.
[0012] The terms "first," "second," "third," "fourth," etc., if present, in the description and claims are used to distinguish similar elements, but not necessarily to describe a particular sequential or temporal order. It is to be understood that the terms so used are intercha...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com