Testing method and apparatus for supporting state, dynamic balancing state and non-centering state of rotating machine
A technology of rotating machines and testing methods, applied in the field of reliability and safety of mechanical equipment, can solve the problems of inability to identify the blind area of machine support stiffness state and alignment state, and inability to comprehensively and correctly guide debugging, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
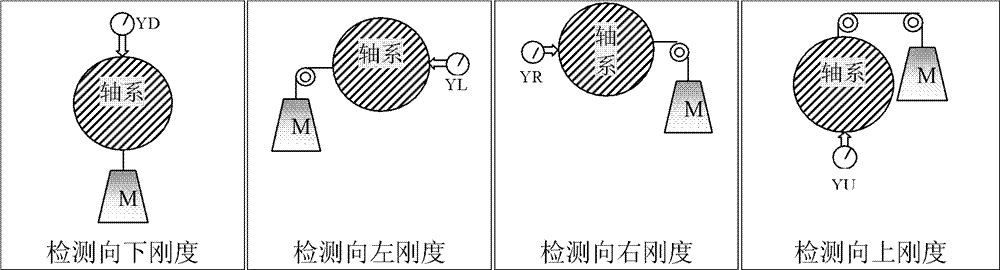
[0217] Example 1: Measurement of the low stiffness function of the machine 1 support.
[0218] For N(0)~N(i), the vibration value of the first order at i+1 rotation speed is divided by the corresponding vibration value X11(0) and Y11(0) at the first lowest rotation speed to get the return A unified transfer function value containing (possibly multiple) resonance factors:
[0219] XC11(0~i)=X11(0~i) / X11(0), YC11(0~i)=Y11(0~i) / Y11(0),
[0220] Then divide the corresponding first-order vibration magnitude and second-order vibration magnitude by the above transfer function value to get the implicit, original vibration function that removes the (possibly multiple) resonance factors expressed by the transfer function value:
[0221] Original vibration function XG11(0~i), YG11(0~i),
[0222] Then, use the following formula to calculate the low-rigidity direction angle and the low-rigidity vibration value at different speeds Ni=N(0)~N(i):
[0223] The low stiffness vibration value of machine 1 ...
Embodiment 2
[0229] Example 2: Measurement of the misalignment function of machine 1
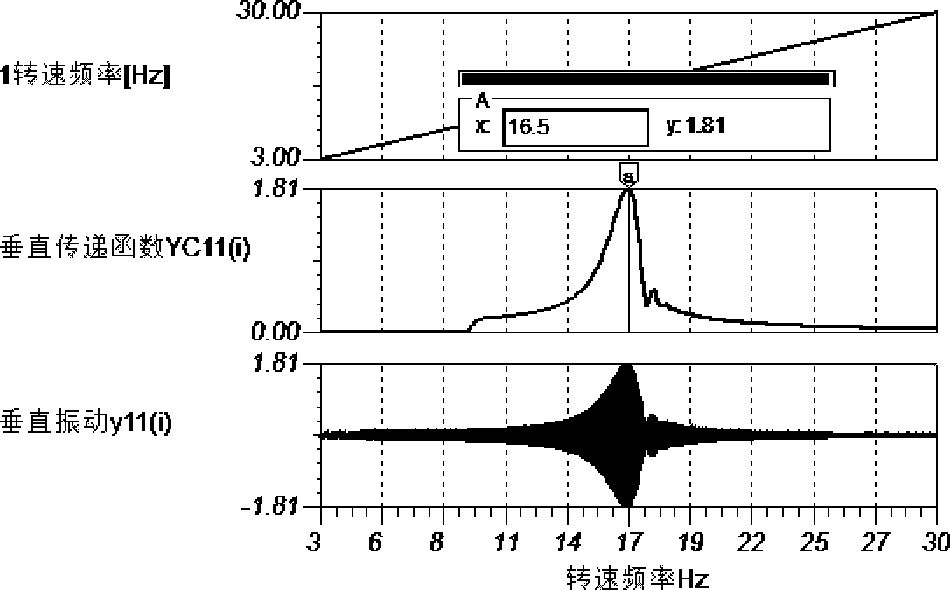
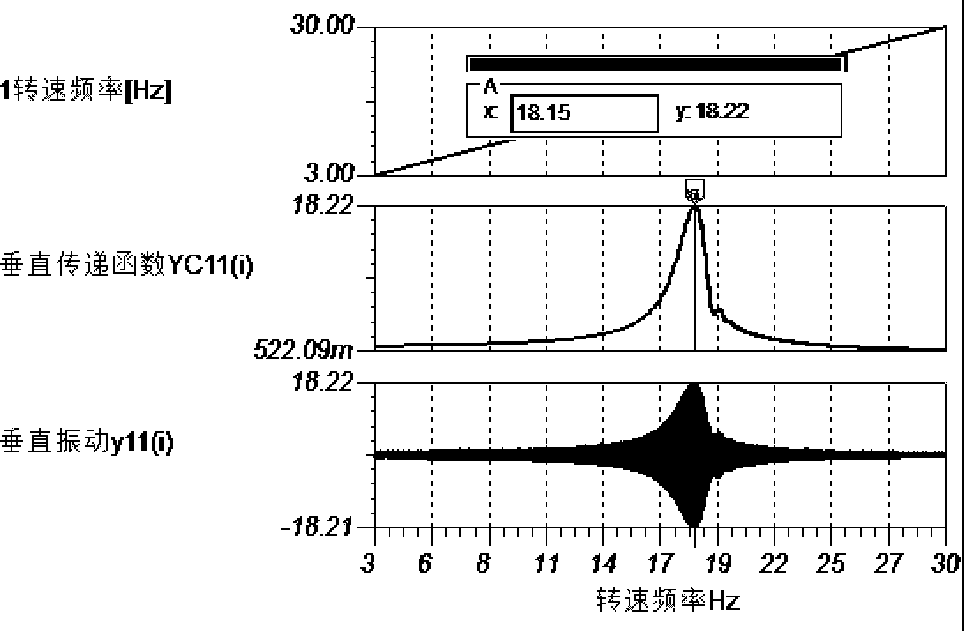
[0230] The support stiffness and misalignment dynamic test and diagnosis software contained in the computer 37 of the support stiffness and misalignment dynamic tester, through the vibration measurement of the machine from the low speed to the highest test speed, or from the low speed to the highest test speed. Several constant speed vibration measurements of N(0)~N(i) (i+1) quasi-full speed test speed data and their corresponding vibration data samples N(0~i) and x1(0~i) ), y1(0~i); analyze and process the above 2(i+1) vibration data samples separately, separate the horizontal and vertical first-order vibration of one of the machines, and obtain the first-order vibration magnitude of the quasi-full speed range: X11(0~i), Y11(0~i).
[0231] Analyze and process the above 2(i+1) vibration data samples separately, separate the horizontal and vertical second-order vibration of one of the machines, and obtain the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com