Staring infrared imaging forest-fire prevention alarming system with wide field of view
An infrared imaging and forest fire prevention technology, applied in the optical field, can solve the problems of inaccurate positioning of the fire point, limited stability and precision, and limited monitoring coverage, so as to avoid full emission, prevent missing alarms, and improve the axis Effect of Outer Point Illumination
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
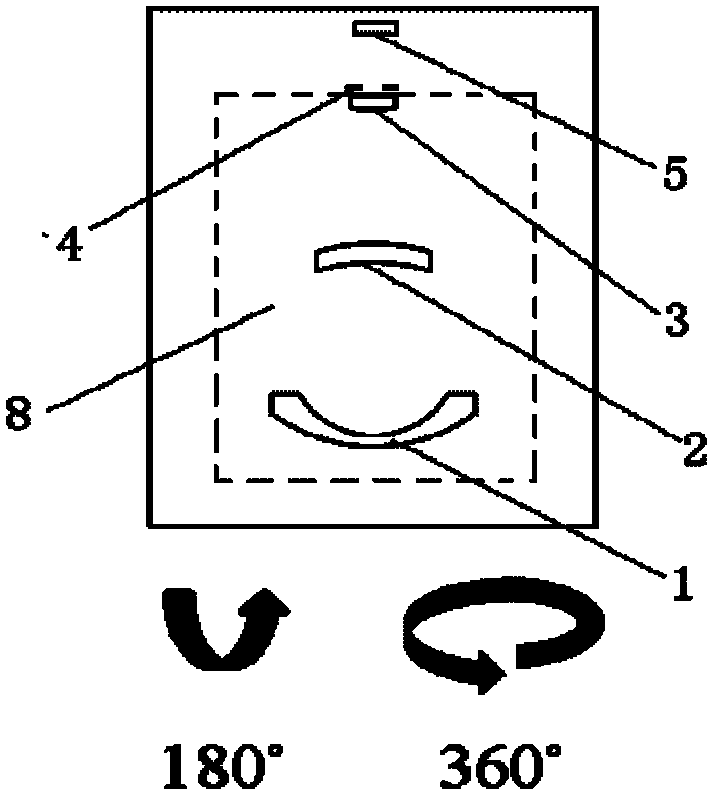
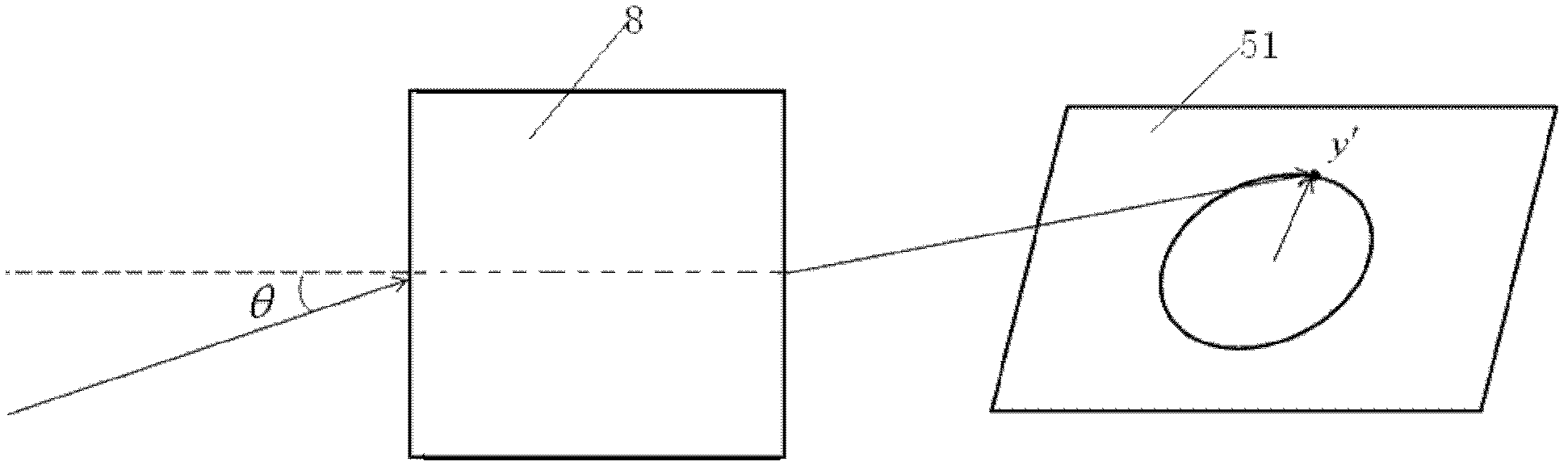
[0032] Such as image 3 As shown, the infrared imaging optical lens 8 includes a meniscus negative lens 1 , first and second positive lenses 2 and 3 , a cold diaphragm 4 and an infrared cooling detector 5 . The front surface 11 of the meniscus negative lens 1, the front surface 21 and the back surface 22 of the first positive lens, and the front surface 31 and the back surface 32 of the second positive lens are spherical; the back surface 12 of the meniscus negative lens 1 is Even-order aspheric surface, and add diffraction structure on the even-order aspheric surface. The position of the image point and the spatial orientation information of the object conform to the y′=fθ object-image relationship, and the object image points correspond one by one, and the image distance formed by the rays of the same angle of view on the focal plane array 51 is radial to the center of the focal plane array. equal distance. Where y' is the image height of the image formed by the object on ...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Such as Figure 4As shown, the infrared imaging optical lens 8 includes a meniscus negative lens 1 , first and second positive lenses 2 and 3 , a cold diaphragm 4 and an infrared cooling detector 5 . The front surface 11 of meniscus negative lens 1, the back surface 22 of the first positive lens and the front surface 31 of the second positive lens are spherical; The back surface 12 of meniscus negative lens 1, the front surface 21 of the first positive lens and the second The rear surfaces 32 of the two positive lenses are even-order aspheric surfaces.
[0040] The light passes through the meniscus negative lens 1, the first positive lens 2, and the second positive lens 3, and is finally imaged on the focal plane array 51 of the infrared cooling detector. The position of the imaging image point and the orientation information of the object space conform to the relationship of y′=fθ object image , where y′ is the image height of the image formed by the object on the inf...
Embodiment 3
[0048] Such as Figure 4 as shown in Figure 4 As shown, the infrared imaging optical lens 8 includes a meniscus negative lens 1 , first and second positive lenses 2 and 3 , a cold diaphragm 4 and an infrared cooling detector 5 . The front surface 11 of meniscus negative lens 1, the back surface 22 of the first positive lens and the front surface 31 of the second positive lens are spherical; The back surface 12 of meniscus negative lens 1, the front surface 21 of the first positive lens and the second The rear surfaces 32 of the two positive lenses are even-order aspheric surfaces. And a diffractive structure is added to the back surface 12 of the meniscus negative lens 1 .
[0049] The rear surface 12 of the meniscus negative lens 1, the second positive lens front surface 21, and the third positive lens rear surface 32 are selected from rotationally symmetrical even-order aspheric surfaces (even asphere), and the description equation is:
[0050] z ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com