Low latency cacheable media streaming
A technology for media, media data, used in the field of low-latency cacheable media streaming
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
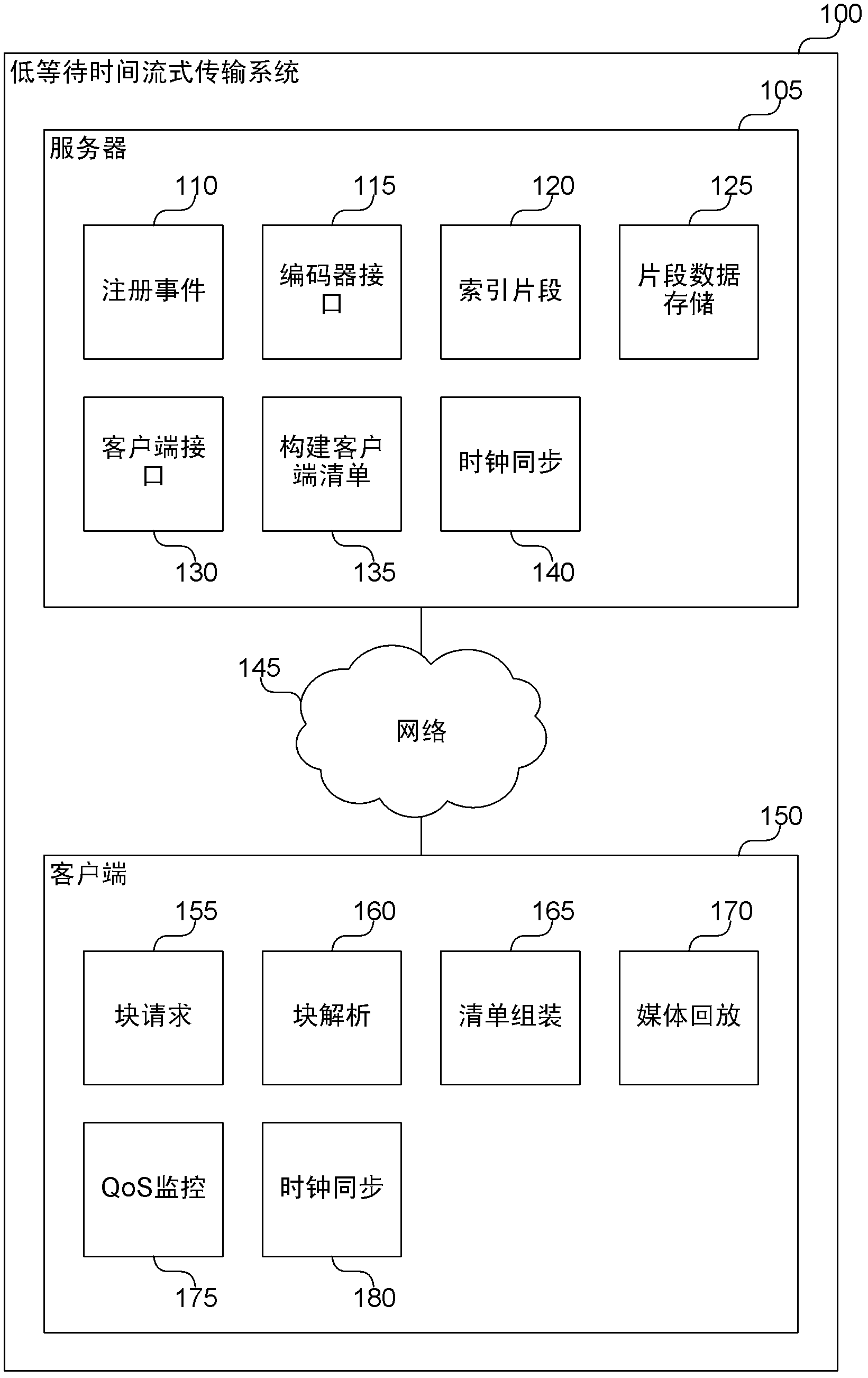
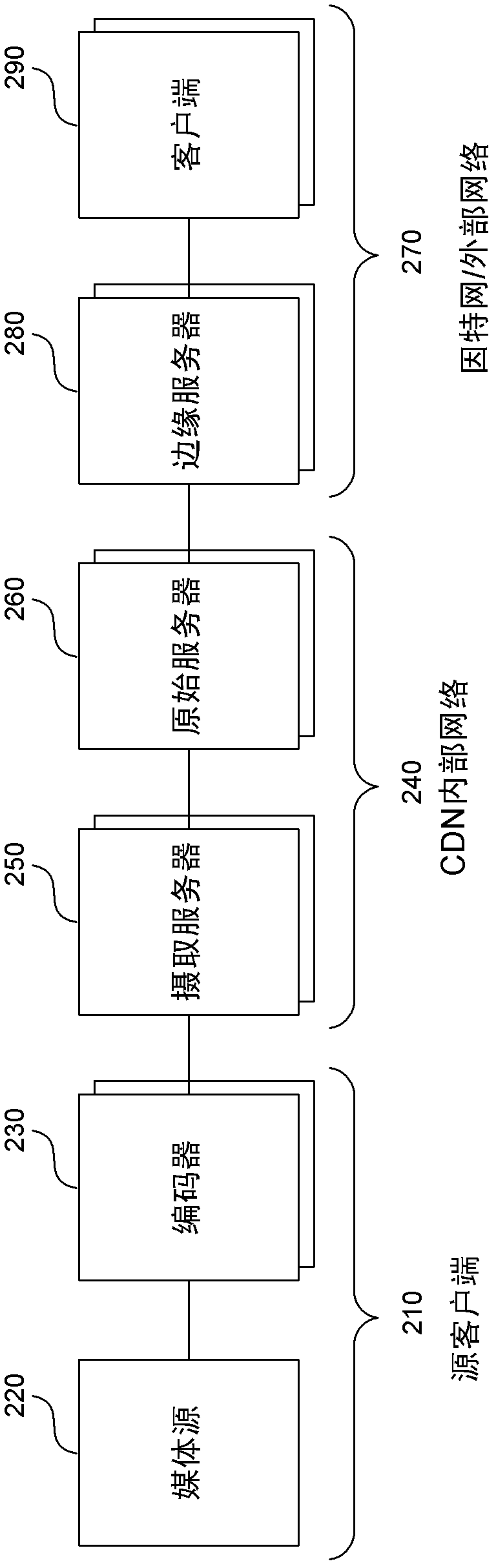
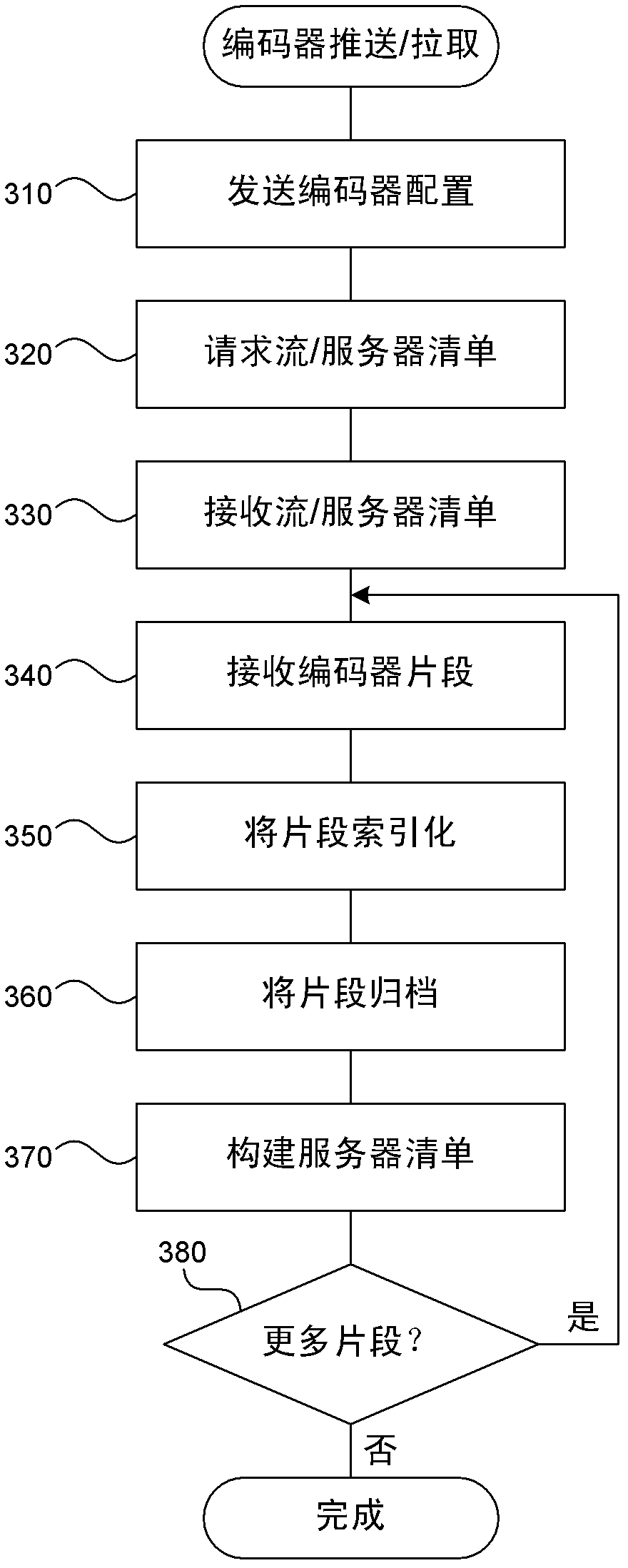
[0014] A low-latency streaming system is described herein that provides a stateless protocol between clients and servers with reduced latency compared to previous systems. The server embeds incremental information in media segments (eg, chunks) that eliminates the use of typical control channels. In addition, the server provides a uniform media segment response to media segment requests (ie, clients requesting the same segment get the same response), thereby allowing existing Internet caching infrastructures to cache streaming media data. Each segment has a distinct Uniform Resource Locator (URL) that allows the segment to be identified and cached by both the Internet caching server and the client's browser cache. Caching reduces the load on the server and allows more clients to view the same content at the same time. A low-latency streaming system receives media data in fragments from one or more encoders, creates an index for each fragment, and stores the fragments.
[001...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com