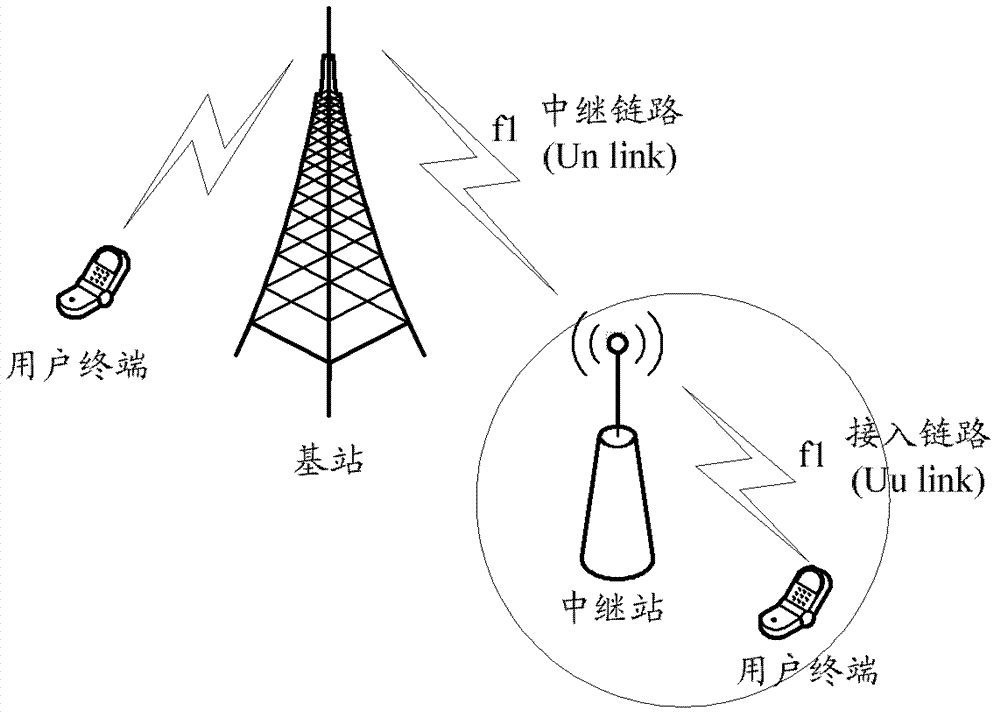
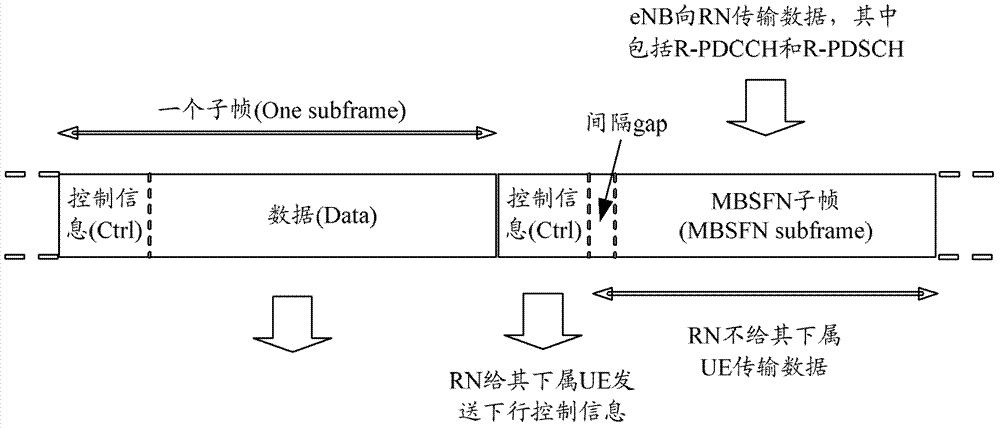
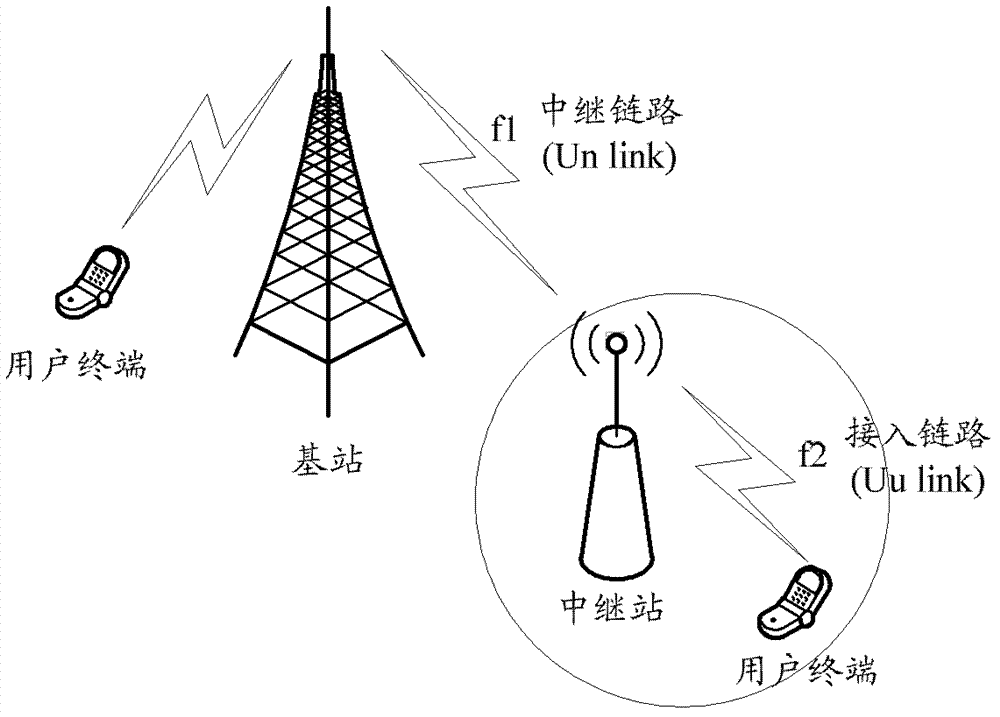
A method and device for determining a search space
A technology for searching space and determining units, which is applied in wireless communication, access restriction, network topology, etc., and can solve the problems of difficulty for users to receive data, starting position of search space, change of blind detection times of large and small mobile relays, and channel coherence time problems such as shortening
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
[0097] In the first embodiment, in-band non-interleaving is the case where the starting positions of each search space are the same. In this embodiment, it is assumed that the mobile relay belongs to the in-band relay, and the R-PDCCHs of the mobile relays covered by the same base station are non-interleaved. The base station pre-configures 40 VRB pairs semi-statically for the mobile relay to carry the R-PDCCH by using high-level signaling, and the numbers are VRB0, VRB1, ..., VRB39 respectively. The 40 VRB pairs are logically continuous, but physically, they may be continuous or discrete depending on the way VRBs are mapped to PRBs.
[0098] The determination of each mobile relay search space includes:
[0099] If the value of Λ configured by the base station is {1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32}, the number of corresponding R-PDCCH candidates is {6 or 8 or 10, 6 or 8 or 10, 2 or 3 or 4, 2 or 3 or 4, 1 or 2, 1}.
[0100] The starting positions of the search spaces corresponding to diffe...
no. 2 example
[0115] In the second embodiment, in-band non-interleaving is the case where the starting positions of each search space are different. In this embodiment, if the base station configures Λ to be {4, 8, 16, 32}, the numbers of corresponding R-PDCCH candidates are {2, 2, 1, 1}. The starting positions of the search spaces corresponding to different Λ are different, for example, the starting positions of the search spaces corresponding to Λ=4 are VRB28; the starting positions of the search spaces corresponding to Λ=8 are all VRB24; Λ=16 The starting position of the corresponding search space is VRB16; the starting position of the corresponding search space of Λ=32 is VRB0;
[0116] The specific blind inspection process is as follows:
[0117] The mobile relay performs detection in a group of 4-VRBs starting from Λ=4, and the corresponding R-PDCCH candidates are 2, that is, 2 detections in total;
[0118] The search spaces are: {{VRB28, VRB29, VRB30, VRB31}, {VRB32, VRB33, VRB34, ...
no. 3 example
[0126] The third embodiment, in-band interleaving. In this embodiment, it is assumed that the mobile relay belongs to the in-band relay, and the R-PDCCHs of the mobile relays covered by the same base station are interleaved with each other. At this time, the method for determining the search space is basically the same as the method for determining the search space of the UE in the current LTE / LTE-A. The difference is that the number of R-PDCCH candidates corresponding to L=16 is 1 or 2, and when L=32, the corresponding number of R-PDCCH candidates is 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com