Fault line selection method of low current grounding system using time-frequency atom decomposition theory
A technology of time-frequency atomic decomposition and small current grounding, which is applied to the fault location and other directions, can solve problems such as low reliability, long training time, and poor convergence
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
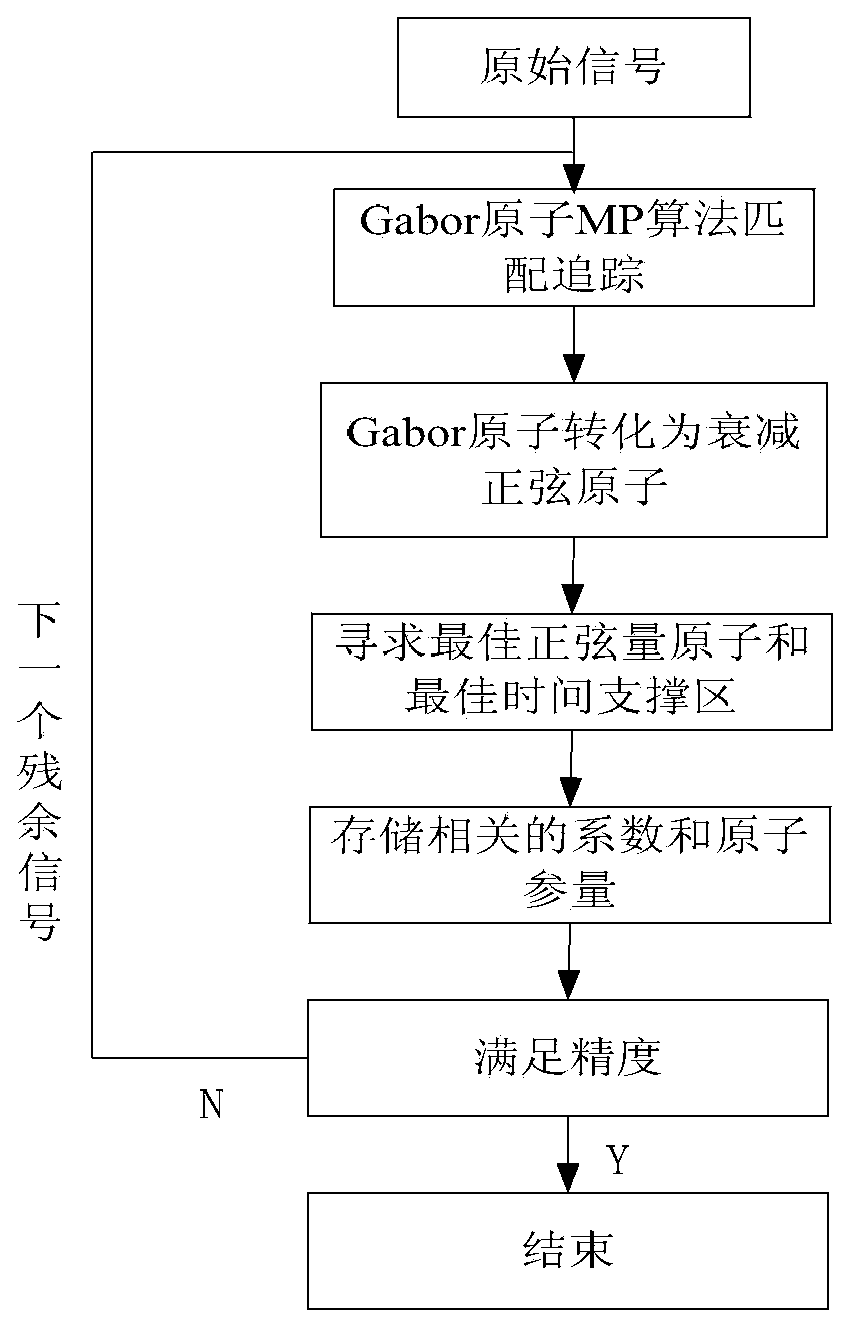
[0128] The present invention proposes a distribution network fault line selection method using the time-frequency atomic decomposition method, and its implementation flow chart is as follows Figure 8 shown.
[0129] Concrete realization of the present invention comprises the following steps:
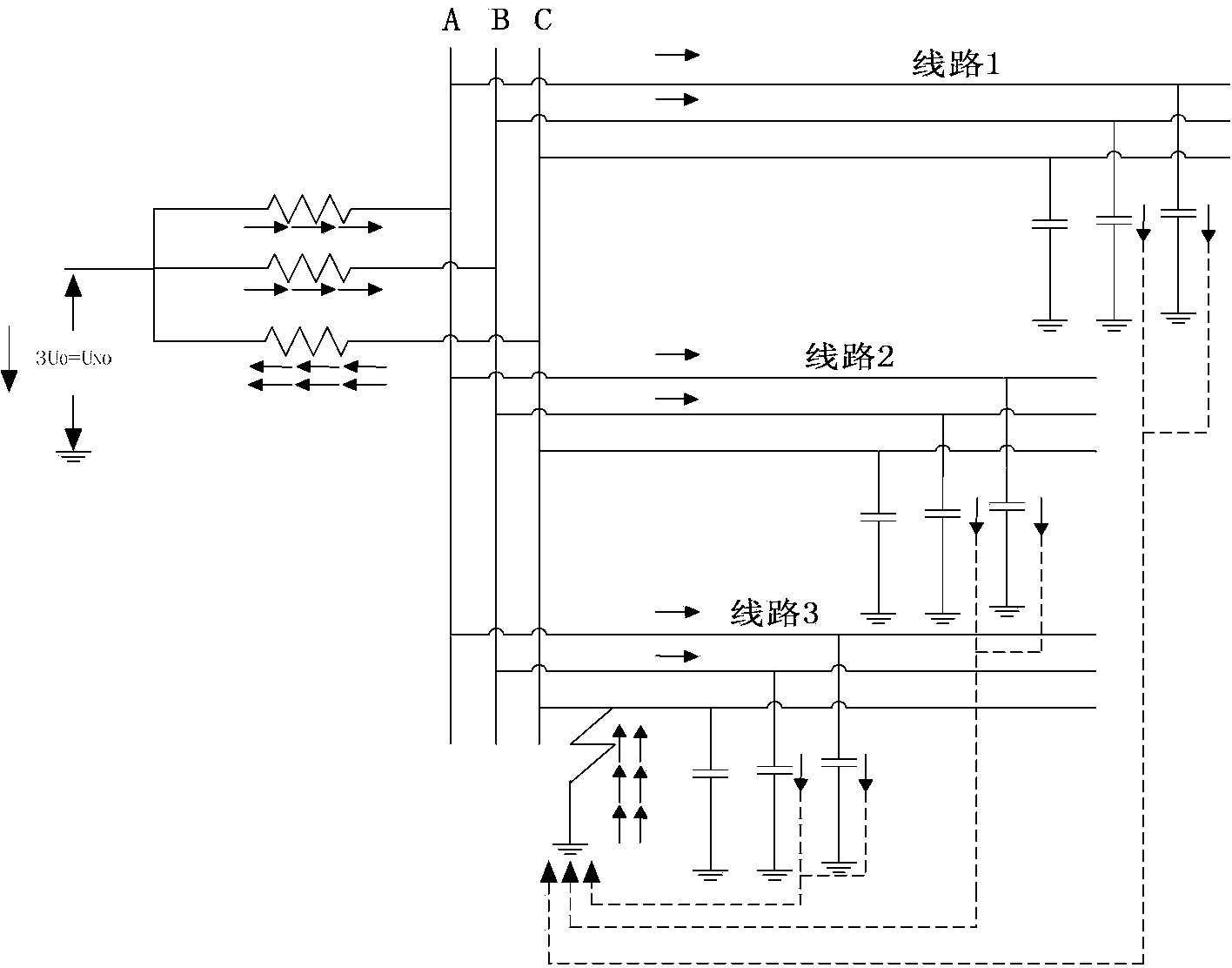
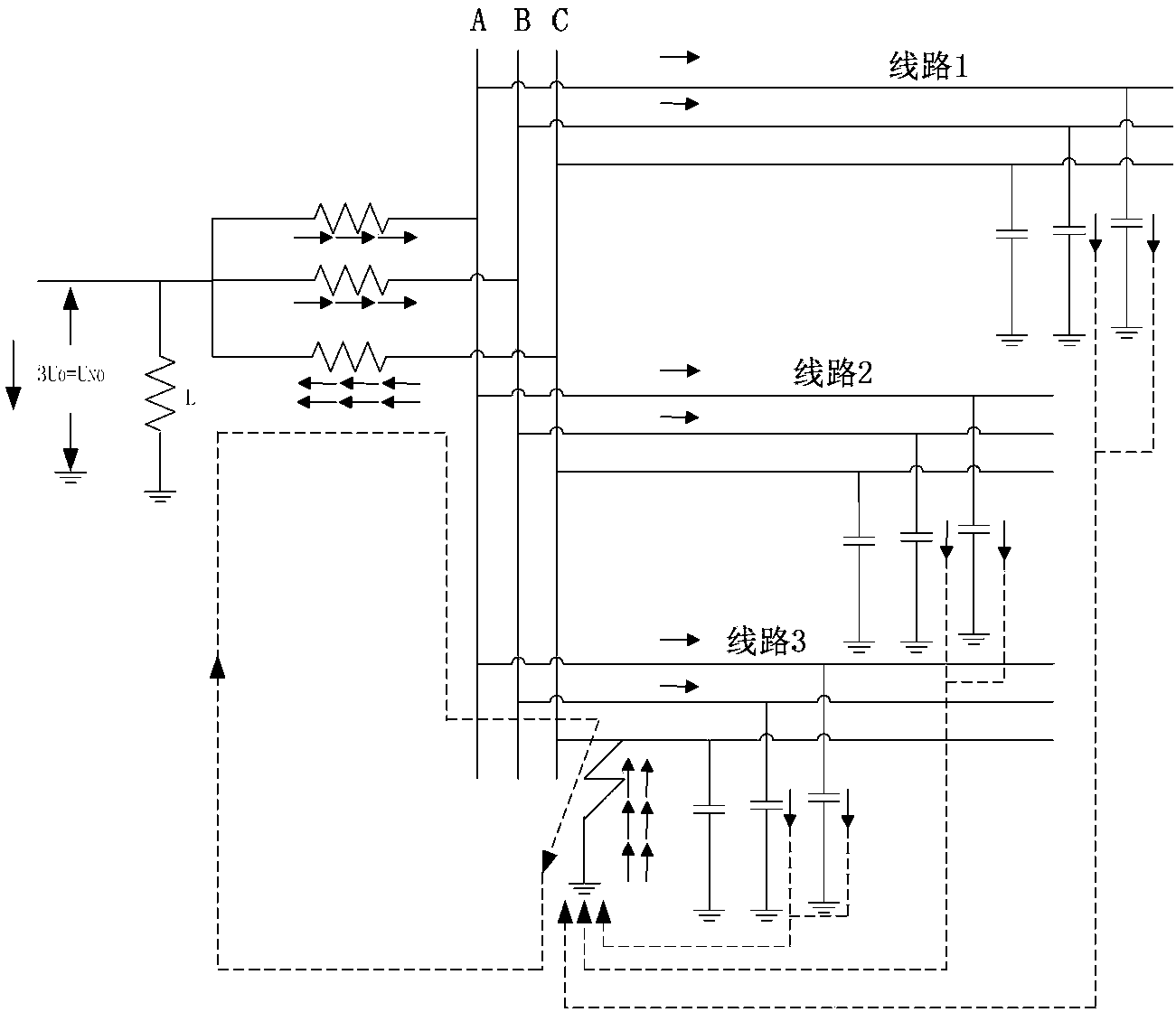
[0130] S1 establishes the zero-sequence current database when a small current ground fault occurs in the power distribution system:
[0131] The instantaneous value u(t) of the zero-sequence voltage of the bus is greater than K u u n As a fault start condition, where K u The value is 0.15, U n For the rated voltage of the busbar, record the zero-sequence current of each feeder for 2 cycles before and after the fault start through the line selection device, and establish a zero-sequence current database;
[0132] S2 conducts time-frequency atomic decomposition on the zero-sequence current database data, and selects characteristic quantity atoms:
[0133] Applying the matching pursuit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com