Mobility management method and mobile access gateway
A technology of a mobile access gateway and a management method, which is applied in the field of mobile access gateway and mobility management, and can solve problems such as packets cannot be forwarded smoothly
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
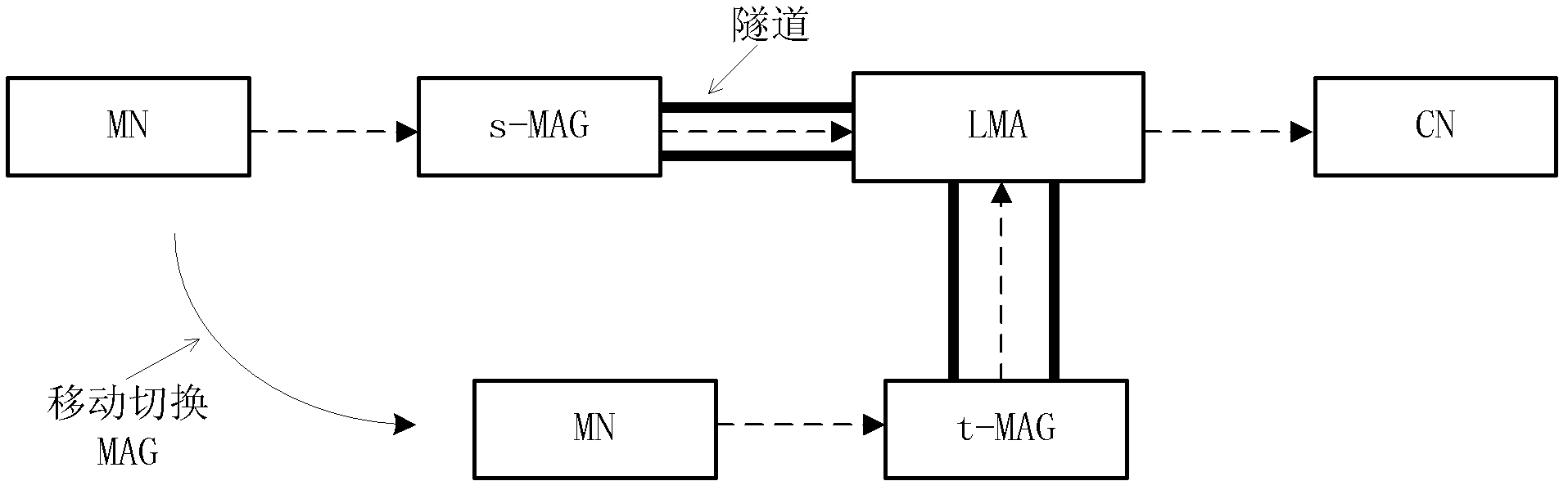
[0086] Figure 5 It is the first embodiment of the present invention. Embodiment 1 of the mobility management method provides a handover management mechanism, which specifically includes the following steps:
[0087] Step 501: During the moving process of the MN, according to the prior art, the process of switching the MN from sMAG to tMAG is triggered, for example, when the MN moves from the service area of sMAG to the service area of tMAG. At this time, the sMAG needs to obtain the address information of the tMAG (for example, the IP address of the tMAG), or the CoA allocated by the tMAG to the MN (called a new CoA), or obtain the above address and the new CoA at the same time.
[0088] Preferably, the sMAG can obtain the address information and the new CoA of the above-mentioned tMAG from the anchor point LMA (LMA-MN) of the MN or the tMAG.
[0089] Steps 502a-502c: the peer CN of the MN sends an IP message (called downlink data) to the MN, and the IP message first rea...
Embodiment 2
[0099] As mentioned above, in order to avoid path waste, the MAG-MN needs to know the address of the MAG-CN (or the CoA of the CN). When the MAG-MN does not have relevant information, it needs to query other external network elements.
[0100] In order to avoid frequent inquiries (you can't inquire once every time you receive an IP message sent to the CN by an MN), the present invention also proposes that the MAG-MN needs to cache the address of the above-mentioned MAG-CN or the CoA of the CN locally, At the same time, the HoA or HNP or ID of the CN is used as an index to form a mapping relationship of the peer node, such as the HoA or HNP or ID of the CN, which is mapped to the MAG-CN address or the CoA of the CN, referred to as the peer mapping relationship (Correspondent Node Relationship, CNR). It is worth noting that when the MN has more than one CN, the MAG-MN needs to cache multiple above-mentioned correspondences locally. At this time, a peer-to-peer mapping table (CN...
no. 3 example
[0115] Figure 8 It is the third embodiment of the present invention, specifically including the following steps:
[0116] Step 801: There is an established session between the MN and the CN, and the IP packets sent and received between the MN and the CN are forwarded through the MAG-MN (corresponding to the sMAG of the MN at this time) and the MAG-CN.
[0117] There is a bidirectional tunnel between the MAG-MN and the MAG-CN, which is used to forward the above IP message, and the data transmission path is expressed as MNsMAGMAG-CNCN.
[0118] Step 802: When the MN moves and needs to switch the currently connected MAG, the MN needs to trigger the process of changing the currently connected MAG, switching from sMAG to tMAG.
[0119] Step 803: When the MN moves to the range managed by the tMAG, the MN sends a Router Solicitation message to the tMAG.
[0120] Step 804a: tMAG finds the anchor point LMA (being LMA-MN) of MN according to the identification (being MN-ID) of MN, dis...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com