Deadlock-free adaptive routing method
An adaptive, deadlock-free technology, applied in digital transmission systems, electrical components, transmission systems, etc., can solve problems such as deadlock-free and livelock-free routing solutions are invalid and performance degradation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0025] The specific implementation manners of the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments. The following examples are used to illustrate the present invention, but are not intended to limit the scope of the present invention.
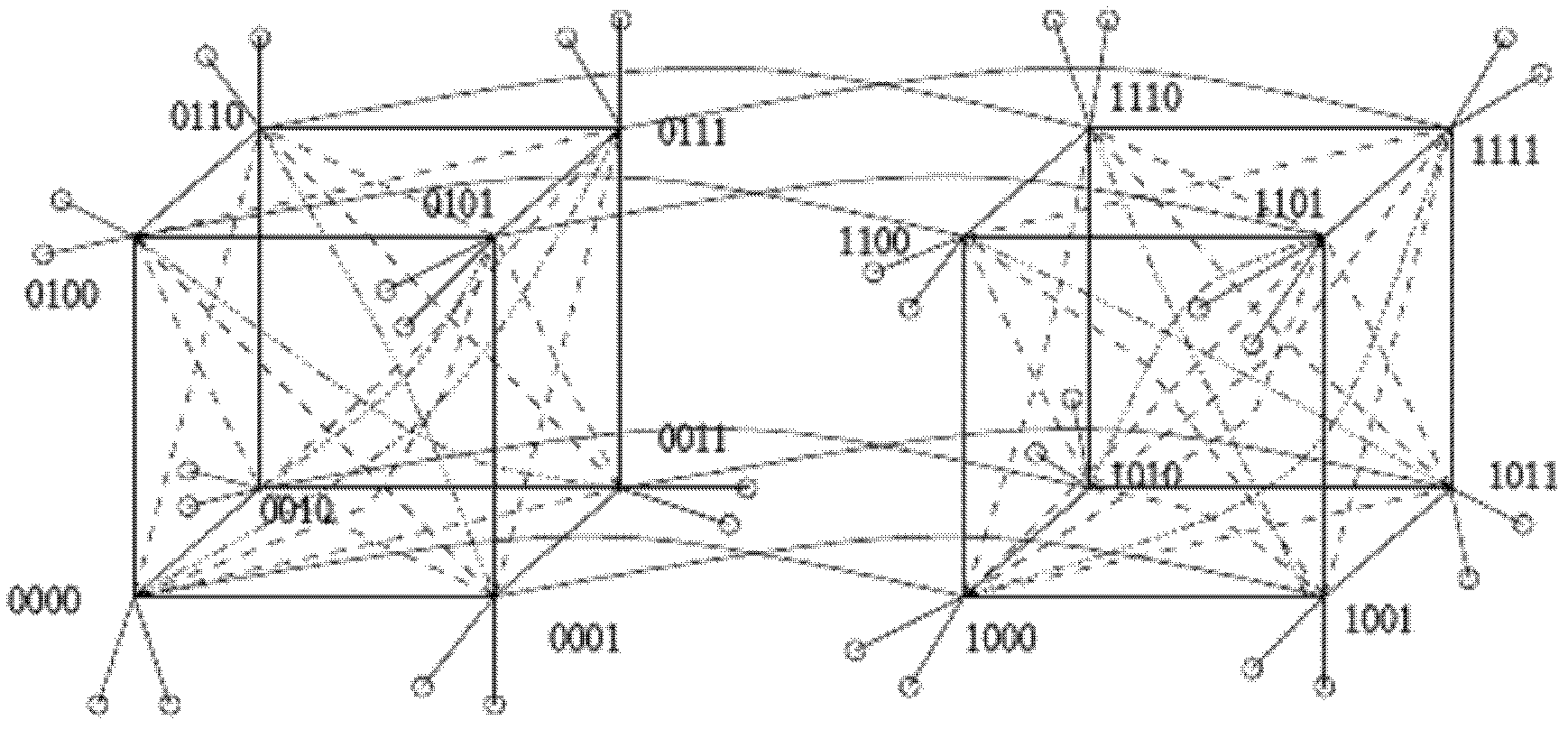
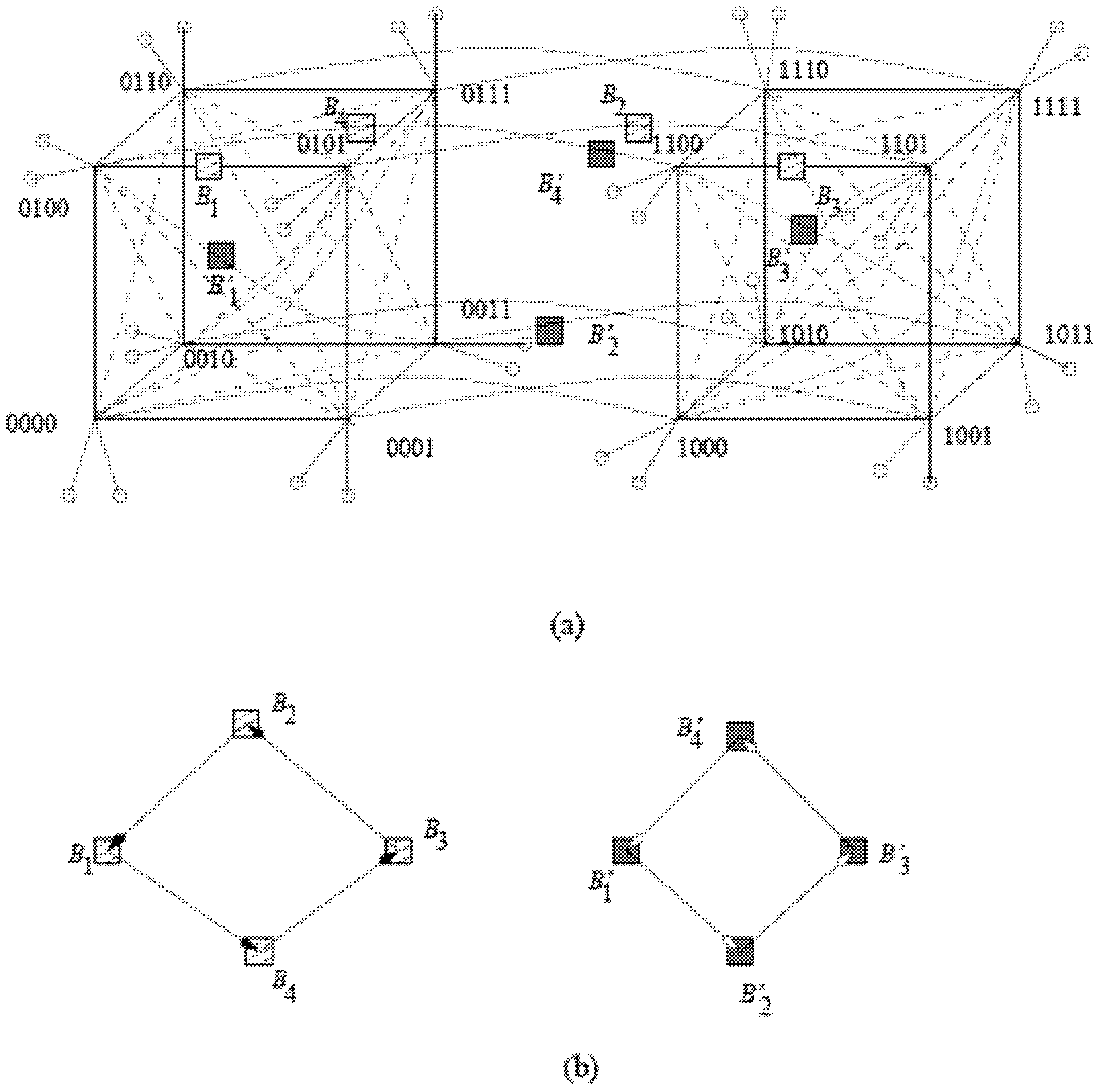
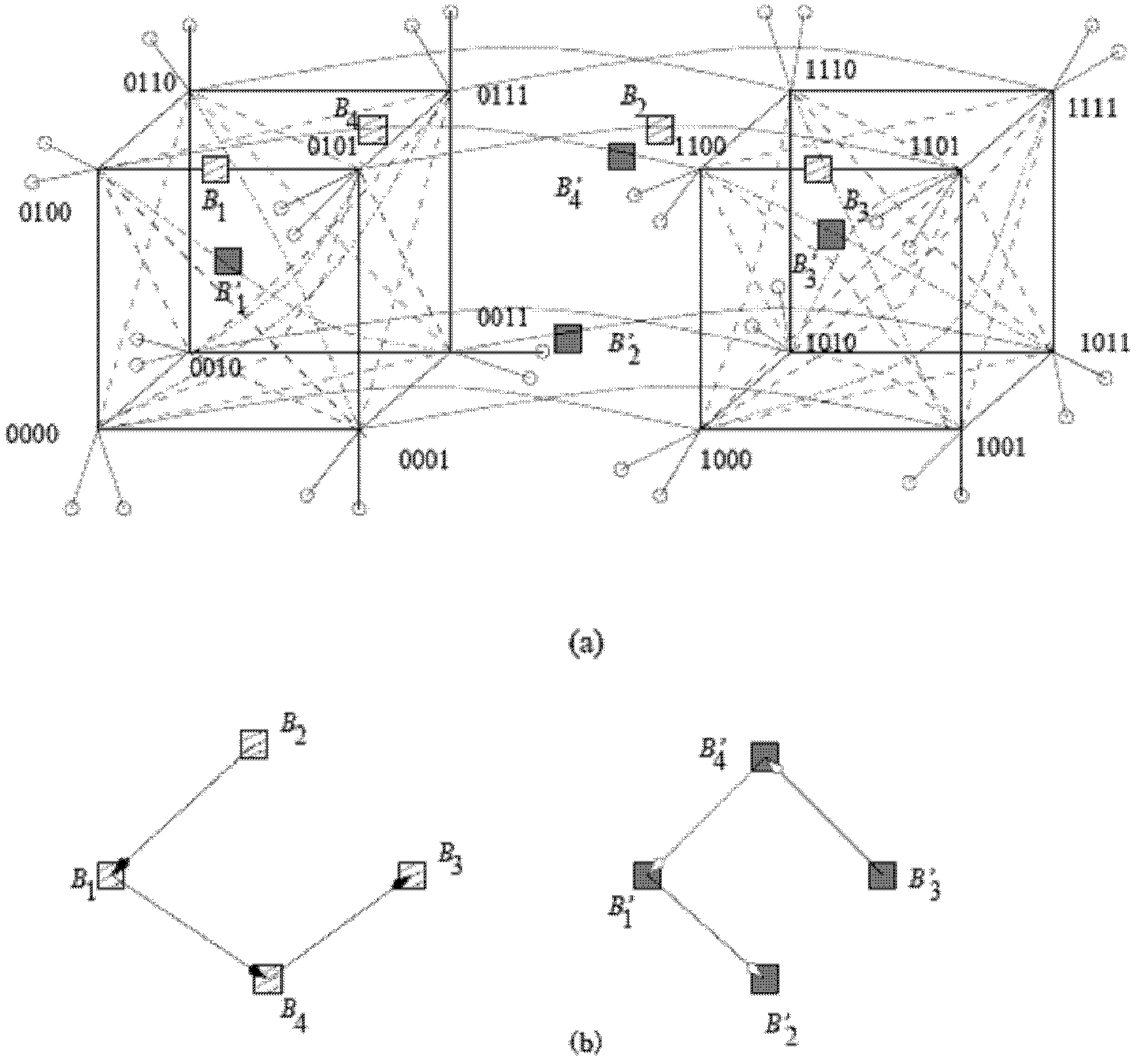
[0026] The N switches in the first subnet of the fault-tolerant network are numbered from 0 to N-1, and the N switches in the second subnet are numbered from N to 2N-1. If the value of the node number modulo N is the same, there is a link between the two switches on different networks.
[0027] Taking 8 switches in each sub-network as an example, all the switches in the two sub-networks in the fault-tolerant network are represented by a binary number (also can be represented by other base numbers), the first sub-network structure is represented by the following 8 switches constitute: 0000, 0001, 0010, 0011, 0100, 0101, 0110, 0111; the serial numbers of switches in the sec...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com