M2M (machine to machine) user access control method in LTE (long term evolution) system
A control method and user technology, applied in electrical components, wireless communication, etc., can solve problems such as community system paralysis and increased channel access conflict probability in the community
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
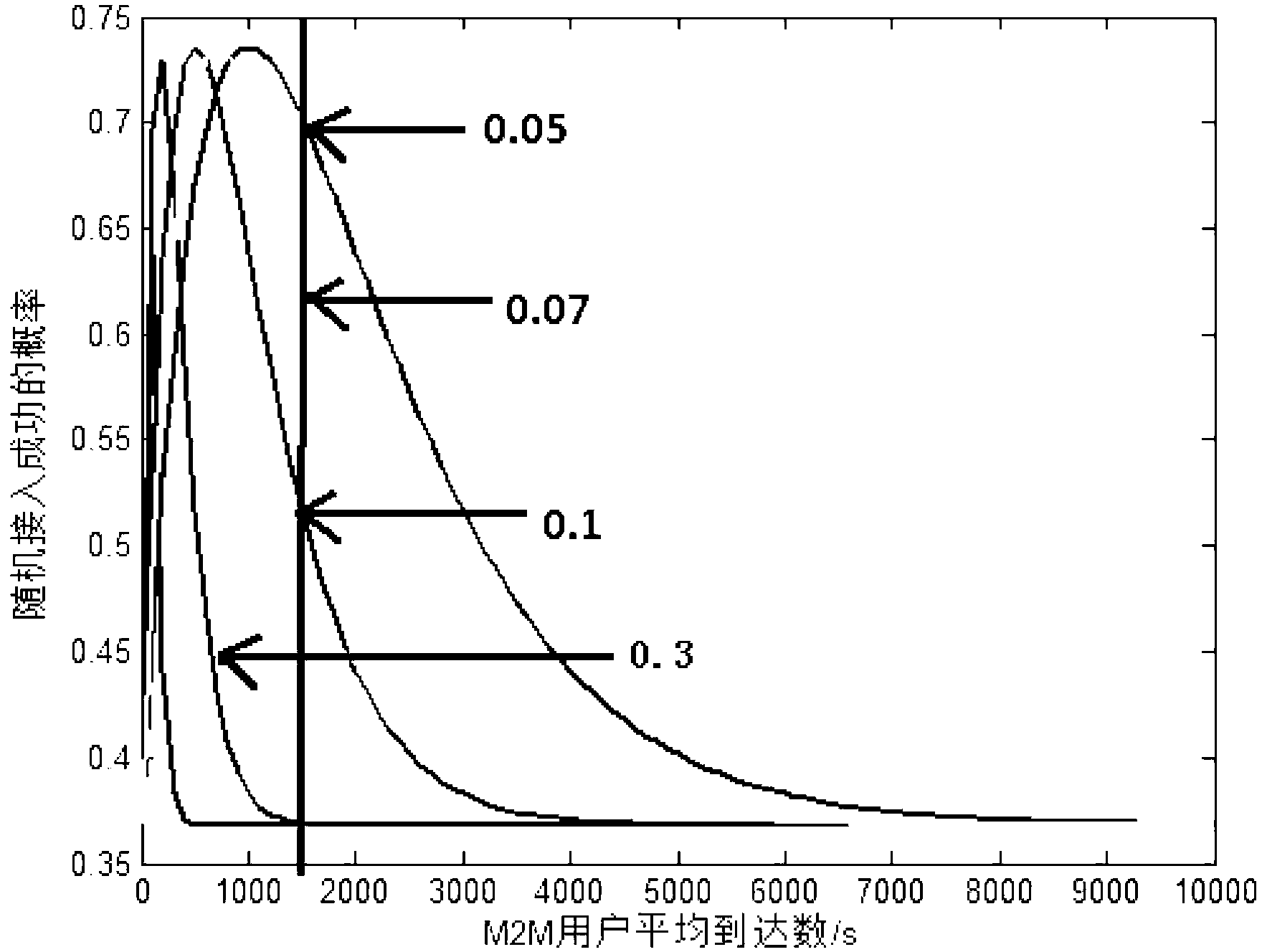
[0100] When a large number of M2M users perform random access together with H2H, set the average number of H2H users arriving per second as a fixed value, and the value range of M2M users is 0≤λ M ≤10000, at this time, different M2M access ratios are set, and the graph of the relationship between the number of M2M users and the random access success probability can be obtained, as shown in figure 1 shown.
[0101] Depend on figure 1 It can be seen that when a large number of M2M users and H2H users perform random access together, setting the random access ratio for the M2M users can increase the success probability of random access in the case of the same number of users.
Embodiment 2
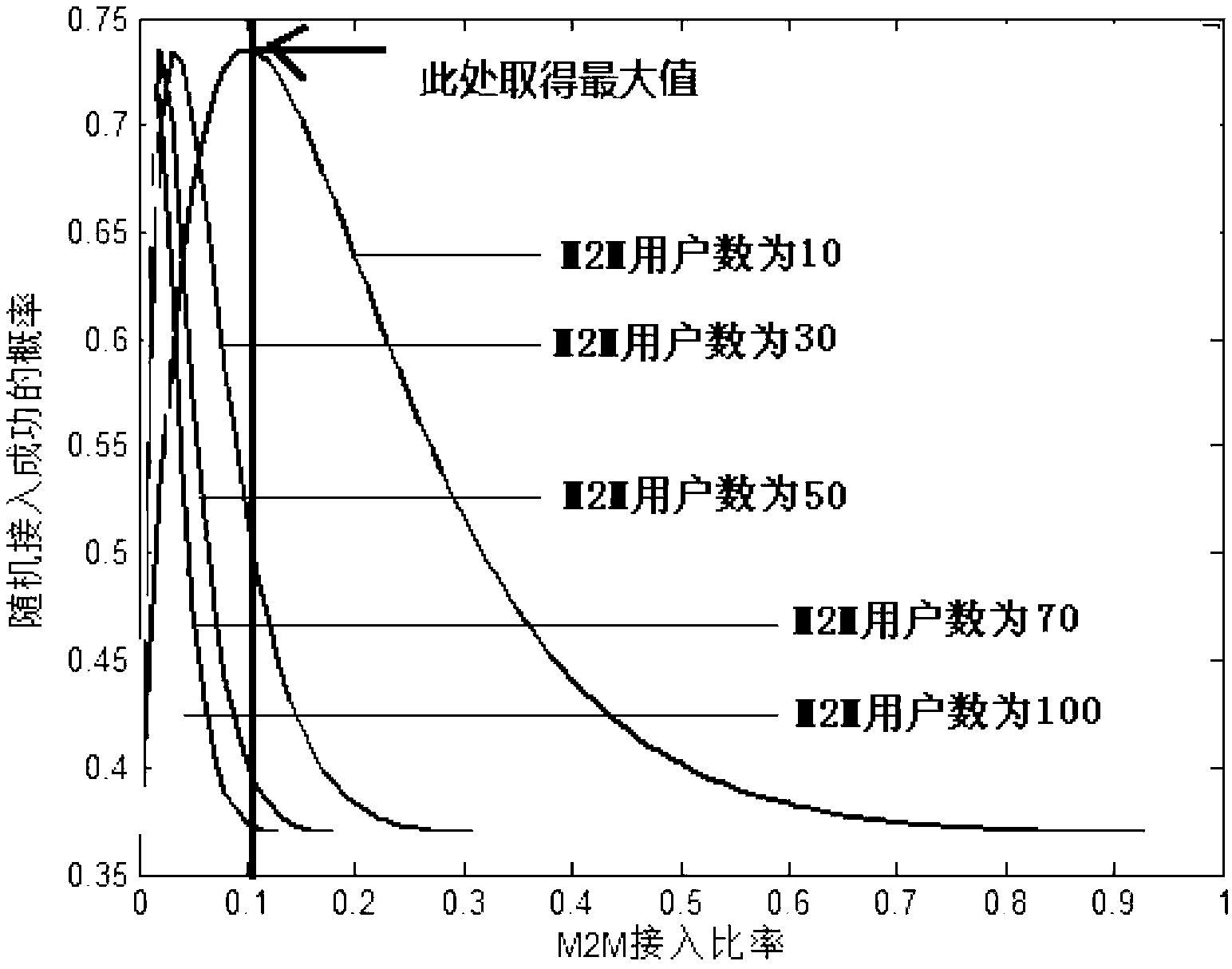
[0103] When the average number of H2H users arriving per second is set to be the same as the average number of M2M users arriving per second, and the random access ratios of M2M users are set to different values, the ratio between the M2M access ratio and random access success probability can be obtained The relationship diagram between, such as figure 2 shown.
[0104] Such as figure 2 It can be seen that no matter what value the M2M user random access ratio α takes, it can be The maximum value of random access success probability is obtained at the place.
[0105] The present invention also provides another M2M user access control method in the LTE system. When there are primary users, secondary users, and tertiary users in the LTE system, the control method is as follows:
[0106] 1) The time tolerance of the first-level users is set to be the lowest, the time tolerance of the second-level users is next, and the time tolerance of the third-level users is the highest; ...
Embodiment 3
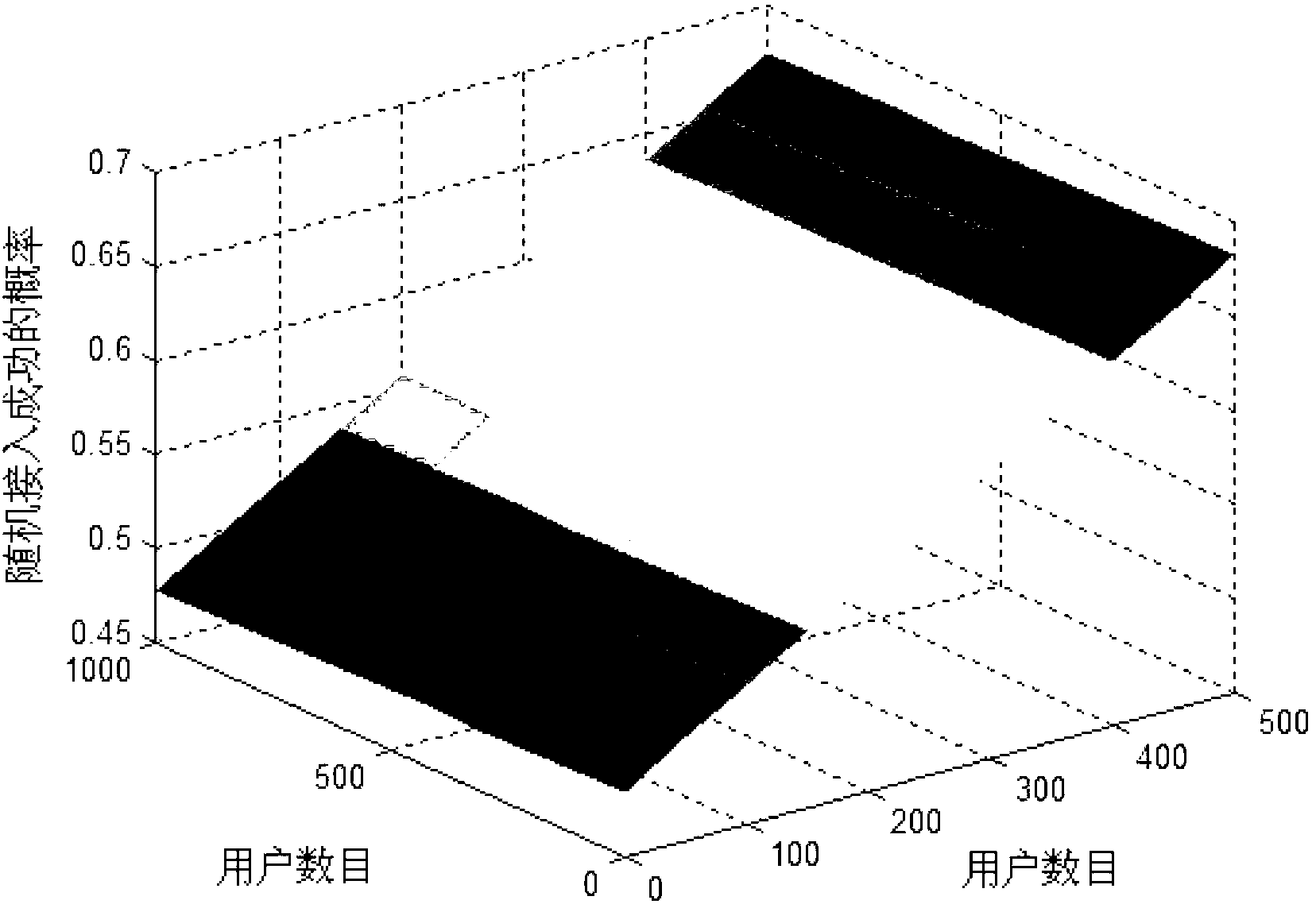
[0154] In the LTE system, there are first-level users, second-level users, and third-level users accessing, and when the access ratio of the second-level and third-level users is controlled to a very small value, the image 3 It can be seen that as the number of users increases, the success rate of channel access increases.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com