Adjusting measurements of the effects of acoustic radiation force for background motion effects
A technology of background movement and measurement results, applied in the field of medical diagnostic ultrasound systems, can solve problems such as large amplitude
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
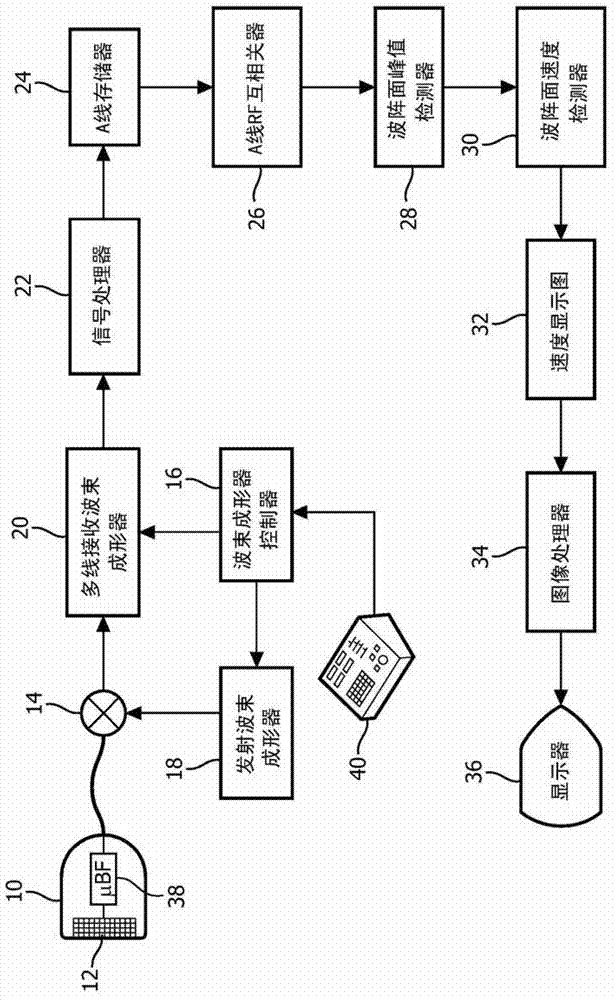
[0016] first reference figure 1 , showing in block diagram form an ultrasonic system for shear wave measurement constructed according to the principles of the present invention. The ultrasound probe 10 has a two-dimensional array 12 of transducer elements for transmitting and receiving ultrasound signals. Two-dimensional array transducers are capable of scanning a two-dimensional (2D) plane by transmitting a beam on a single plane of the body and receiving returned echo signals, and can also be used to pass through different directions in a volumetric (3D) area of the body. and / or emit beams in a plane to scan a volumetric area. The array elements are coupled to a microbeamformer 38 located in the probe, which controls the transmission of the elements and processes echo signals received from groups or subarrays of elements into partially beamformed signals . Through a transmit / receive (T / R) switch 14 , part of the beamformed signal is coupled from the probe to a multi-lin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com