Liquid-crystalline medium
A technology of liquid crystal media and compounds, which is applied in the field of liquid crystal displays and can solve problems such as high rotational viscosity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0307] The following examples are intended to illustrate the invention without limiting it.
[0308] In this context, percentage data represent percentages by weight. All temperatures are expressed in degrees Celsius. m.p. means melting point, cl.p. = clearing point. Furthermore, C=crystalline state, N=nematic phase, S=smectic phase and I=isotropic phase. The data between these symbols represent the transition temperature. also,
[0309] V о Indicates threshold voltage, capacitive at 20°C [V]
[0310] Δn represents the optical anisotropy measured at 20 °C and 589 nm
[0311] Δε represents the dielectric anisotropy at 20 °C and 1 kHz
[0312] cp. means clearing point [°C]
[0313] K 1 Indicates the elastic constant, the "slope" deformation at 20°C, [pN]
[0314] K 3 Indicates the elastic constant, "bending" deformation at 20°C, [pN]
[0315] gamma 1 Indicates the rotational viscosity [mPa·s] measured at 20°C, measured in a magnetic field by the rotational method
...
Embodiment 1
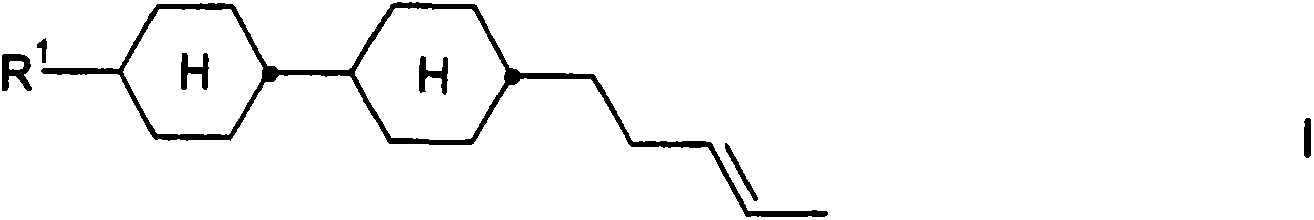
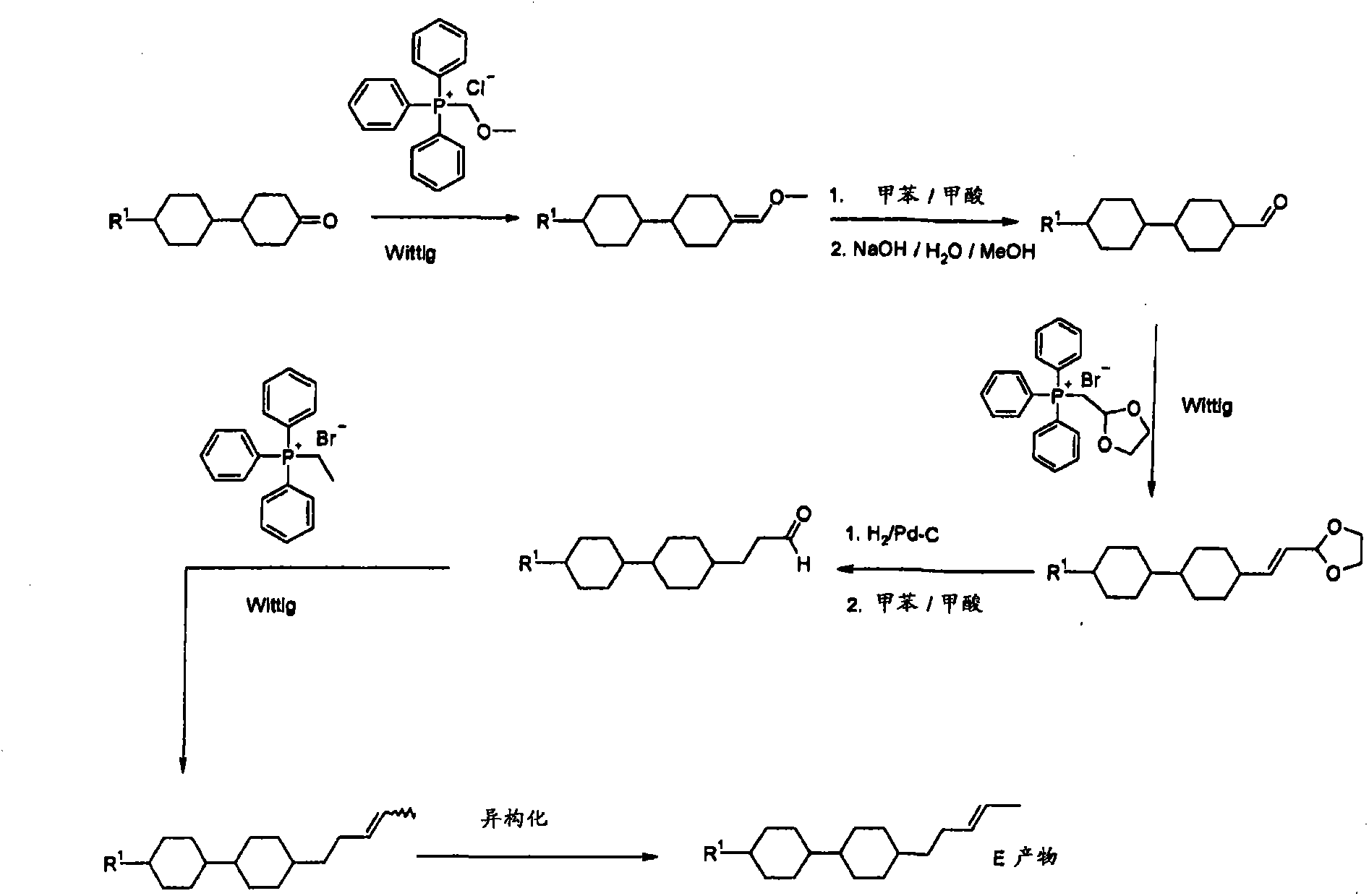
[0320] Mode The compound of is prepared according to the following scheme:
[0321]
[0322] C43S B 75N96.2I; Δn=0.0594; Δε=0.1; γ 1 =43mpa s;
[0323] K 1 =15.78; K 3 =19.56
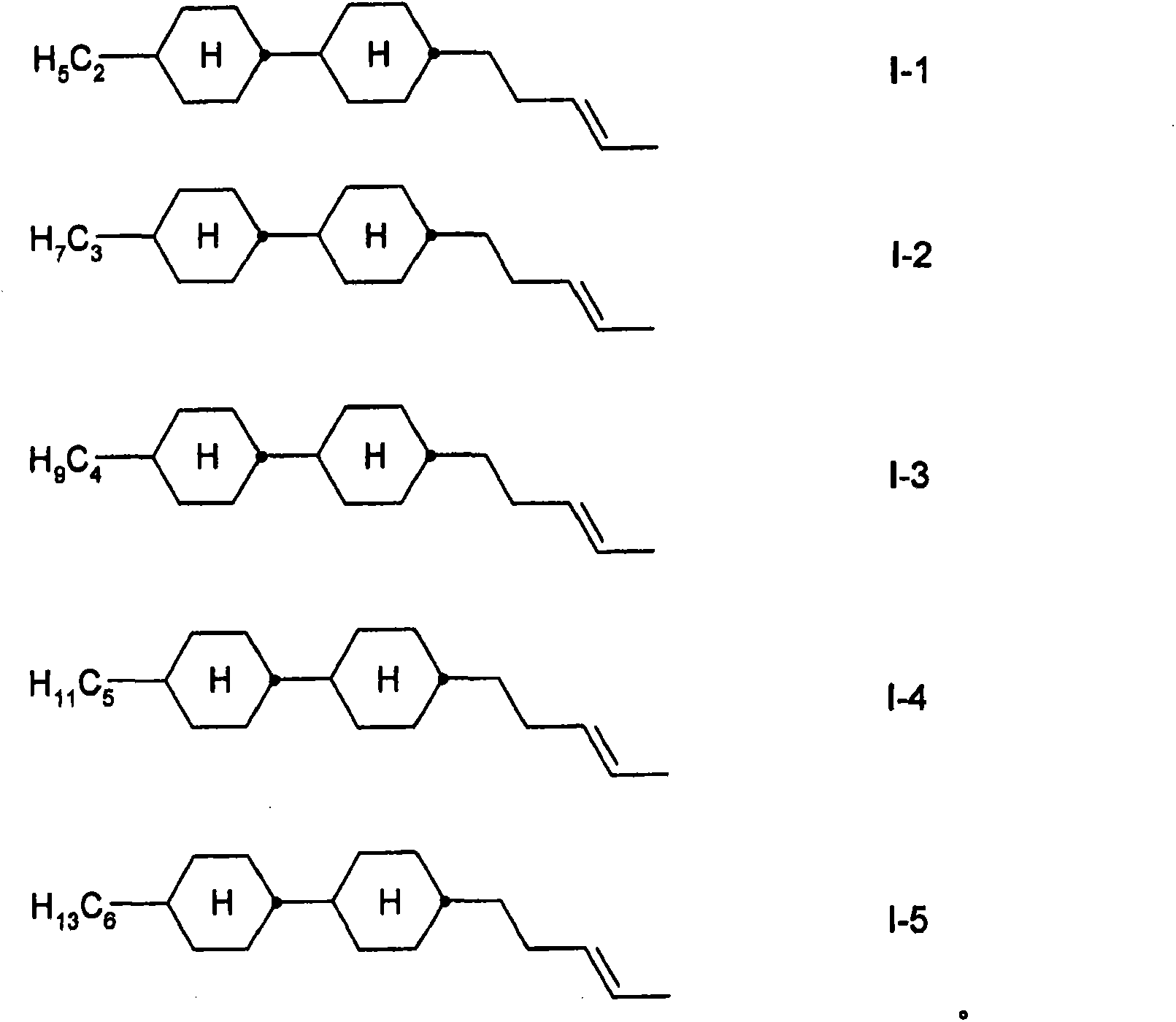
[0324] The following compounds were similarly prepared
[0325]
[0326] Mixture Example
[0327] Unless explicitly stated otherwise, electro-optical data were determined in a TN cell at 20°C at the first minimum (ie d·Δn value of 0.5 μm). Optical data are determined at 20°C unless expressly stated otherwise. All physical properties were determined according to "Merck Liquid Crystals, Physical Properties of Liquid Crystals", Status Nov. 1997, Merck KGaA, Germany and applied at a temperature of 20°C, unless expressly stated otherwise.
Embodiment M1
[0329]
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| refractive index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com