Method for preparing magnesium-neodymium master alloy by using neodymium-iron-boron magnet waste
The technology of magnesium-neodymium master alloy and NdFeB is applied in the fields of preparing magnesium-neodymium master alloy and rare earth resource recycling, which can solve the problems of high energy consumption and cost, and high price of rare-earth-containing magnesium alloy, so as to widen the recovery ways and reduce the Cost, simple process and stable effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] This embodiment relates to the direct preparation of Mg-Nd master alloys by using NdFeB industrial waste as raw material and adopting the process of diffusion reduction in high-temperature Mg liquid. The preparation process mainly includes the following three steps:
[0025] ①Pretreatment of NdFeB waste (cleaning and crushing). In order to remove the oil and dirt on the surface of NdFeB industrial waste, first put the waste block into a strong alkali solution tank (NaOH or KOH) and stir it for a certain cleaning effect, and soak it for 24 hours to clean thoroughly, and then rinse it repeatedly with clean water for 3 to 4 hours. Dry the water in an oven at 100-200°C; then use a pulverizer to crush the waste and sieve it to about 30-100 mesh or finer.
[0026] ②Diffusion reaction of NdFeB waste powder with high temperature pure Mg solution. According to a certain material ratio (mass ratio of NdFeB waste to magnesium liquid), here refers to NdFeB / Mg=0.25, slowly add NdFeB...
Embodiment 2~15
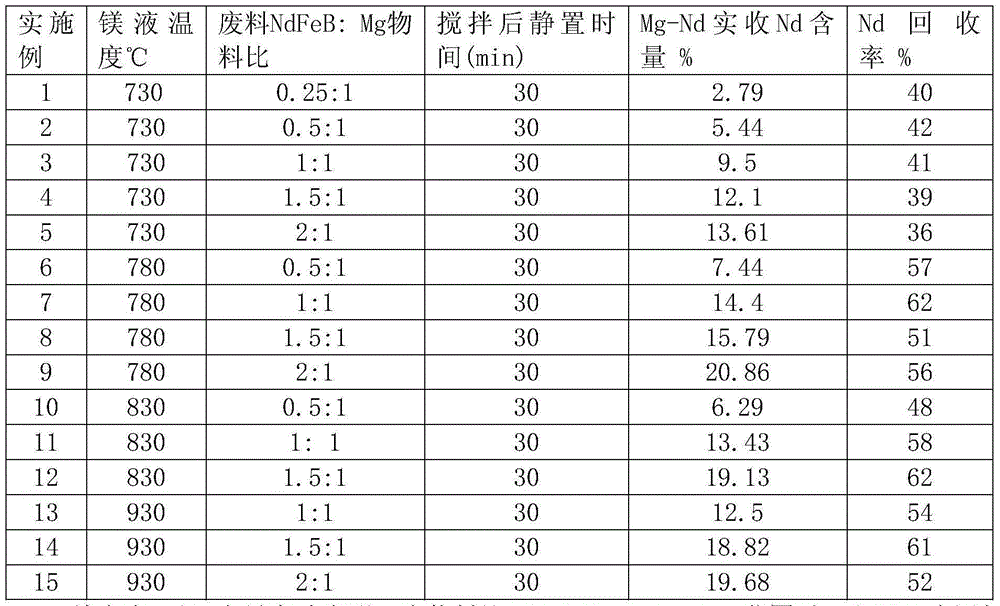
[0031] Embodiments 2 to 15 also relate to the direct preparation of Mg-Nd master alloys by using NdFeB industrial waste as raw material and adopting the process of diffusion reduction in high-temperature Mg liquid. The difference between the preparation method and Example 1 is that the temperature of the magnesium solution, the waste NdFeB:Mg material ratio (mass ratio), and the resting time after stirring are shown in Table 1 respectively. The Nd content of the prepared Mg-Nd is collected, the Nd recovery rate is shown in Table 1, the content of impurity elements Fe+B<1%, and there is no obvious oxidation inclusion.
[0032] Table 1
[0033]
[0034] Combining Table 1 and a large number of experiments show that: when the material ratio NdFeB / Mg=0.25~2.0 range, that is, when the Nd element addition amount is 7.0%~38%, (0.25×0.3 / (0.25×0.3+1)=7%, 2.0× 0.3 / (2.0×0.3+1)=38%), the Nd content of the prepared Mg-Nd alloy is in the range of 3%-21%, and the Nd recovery rate can be a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com