Inertial drive actuator
An inertial drive and actuator technology, applied in the direction of generator/motor, piezoelectric effect/electrostrictive or magnetostrictive motor, electrical components, etc., can solve the problem of lack of friction and long-term stability and other problems to achieve the effect of preventing circuit breakage, stabilizing driving, and reducing wear and tear
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment approach )
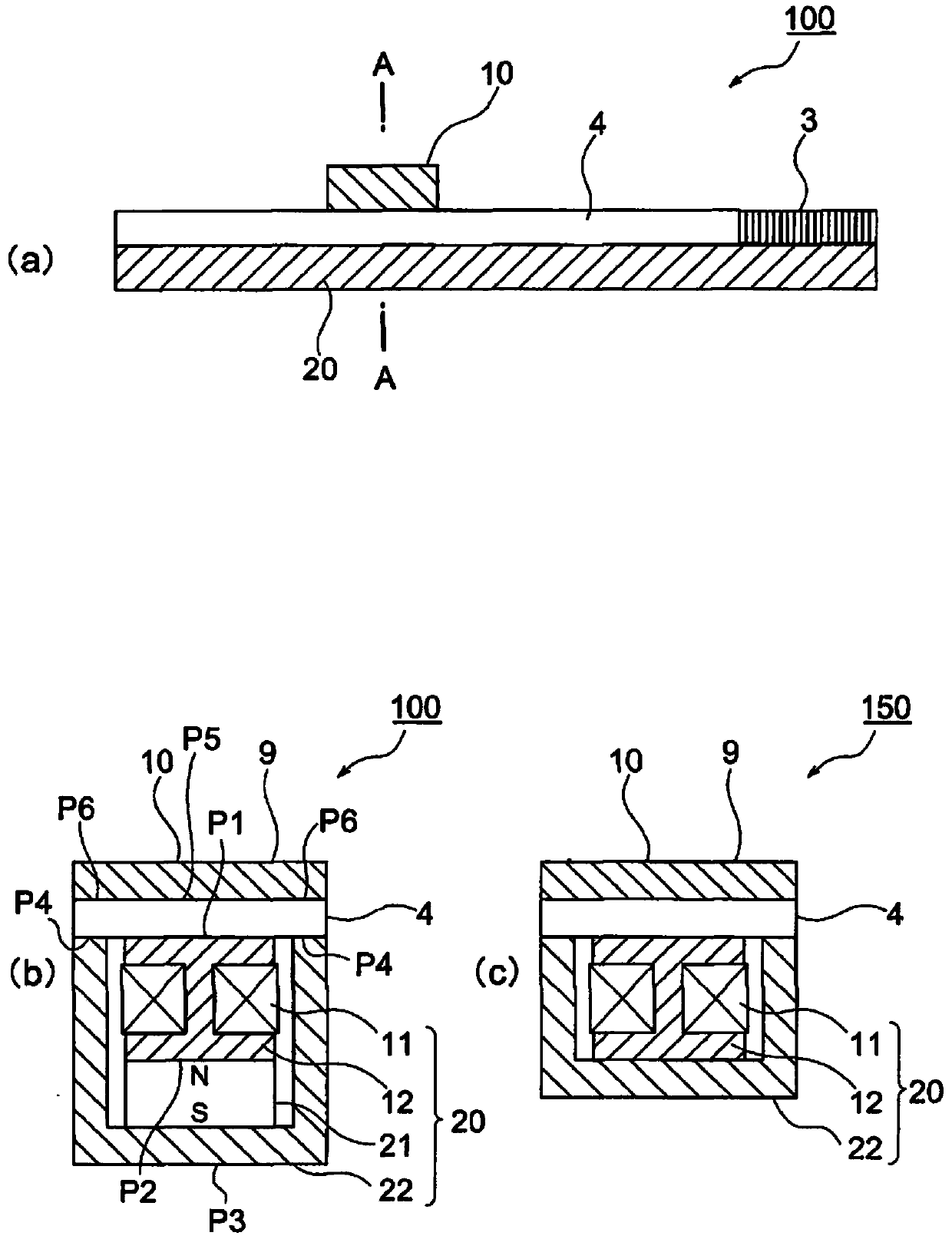
[0054] The inertial drive actuator of the first embodiment is shown in figure 1 . figure 1 (a) is the side view of the inertial drive actuator, figure 1 (b) is figure 1 Cross-sectional view at the position indicated by A-A in (a).
[0055] The inertial drive actuator 100 of the first embodiment is constituted by a piezoelectric element (displacement mechanism) 3 , a vibrating substrate 4 , a moving element 10 , and a stationary element 20 . The piezoelectric element 3 and the vibrating substrate 4 are located on the upper part of the fixed part 20 , and the moving part 10 is located on the upper part of the vibrating substrate 4 . The moving part 10 has the function of the first yoke 9 .
[0056] Both the piezoelectric element 3 and the vibrating substrate 4 are plate-shaped members. Here, a non-magnetic material is used for the vibrating substrate 4 . One end of the piezoelectric element 3 is mechanically connected to one end of the vibrating substrate 4 . In addit...
no. 2 Embodiment approach )
[0084] Next, an inertial drive actuator according to a second embodiment will be described.
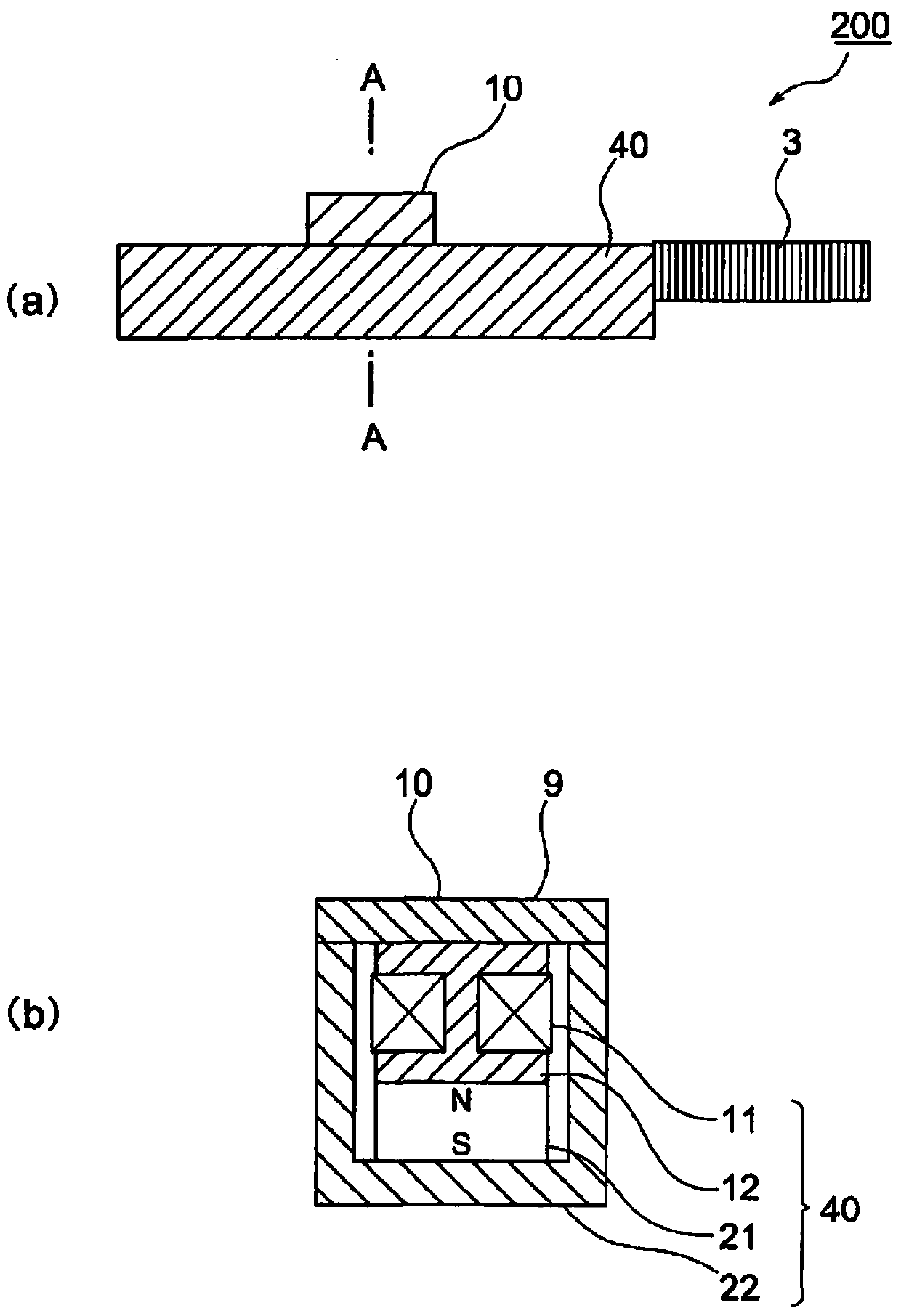
[0085] figure 2 (a) is a side view of the inertial drive actuator 200, figure 2 (b) is figure 2 Cross-sectional view at the position indicated by A-A in (a). The same reference numerals are assigned to the same configurations as those of the inertial drive actuator 100 of the first embodiment, and description thereof will be omitted.
[0086] The inertial drive actuator 200 of the second embodiment is constituted by the piezoelectric element 3 , the moving element 10 and the vibrating substrate 40 . The moving part 10 is located on the upper part of the vibrating substrate 40 . In addition, one end of the piezoelectric element 3 is mechanically connected to one end of the vibrating substrate 40 .
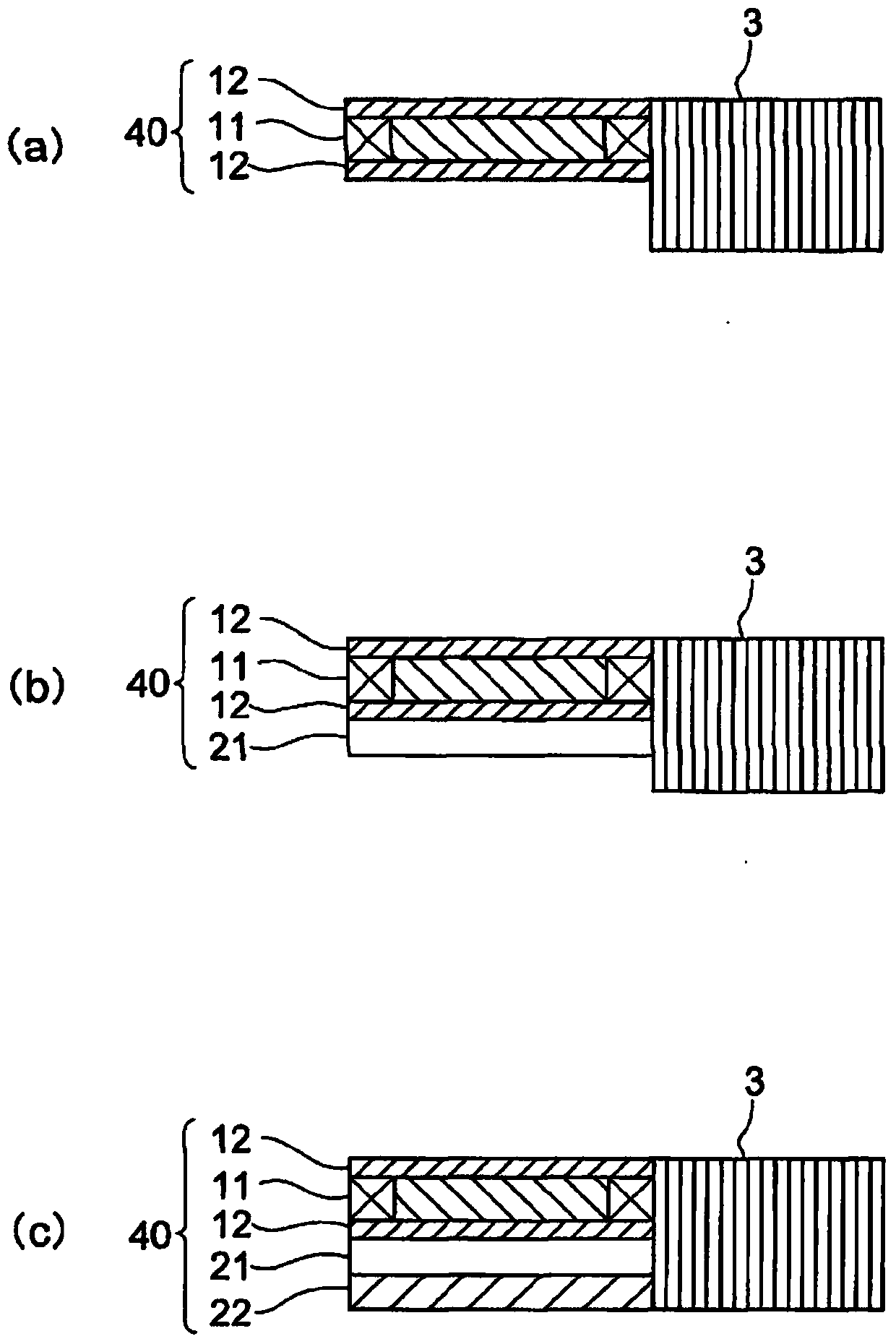
[0087] In addition, details of a configuration example in which the piezoelectric element 3 and the vibrating substrate 40 are connected will be described later.
[0088] The movin...
no. 3 Embodiment approach )
[0101] Next, an inertial drive actuator 300 according to a third embodiment will be described.
[0102] Figure 4 With figure 1 (b) Cross-sectional view of the same inertial drive actuator 300 . The same reference numerals are attached to the same components as those of the inertial drive actuator of the first embodiment, and description thereof will be omitted.
[0103] The inertial drive actuator 300 of the third embodiment is constituted by a piezoelectric element 3 (not shown), a vibrating substrate 4 , a moving element 10 , and a stationary element 20 . The piezoelectric element 3 and the vibrating substrate 4 are located on the upper part of the fixed part 20 , and the moving part 10 is located on the upper part of the vibrating substrate 4 .
[0104] The movable body 10 is composed of a first yoke 12d and a permanent magnet 13 . That is, the movable body 10 has a permanent magnet 13 .
[0105] On the other hand, the fixture 20 has the coil 11 and the second yokes ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com