Distributed load balancing method based on quantified unbiased broadcast Gossip algorithm
A load balancing and distributed technology, applied in wireless communication, network traffic/resource management, electrical components, etc., can solve the problem of lack of wireless channel broadcast characteristics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
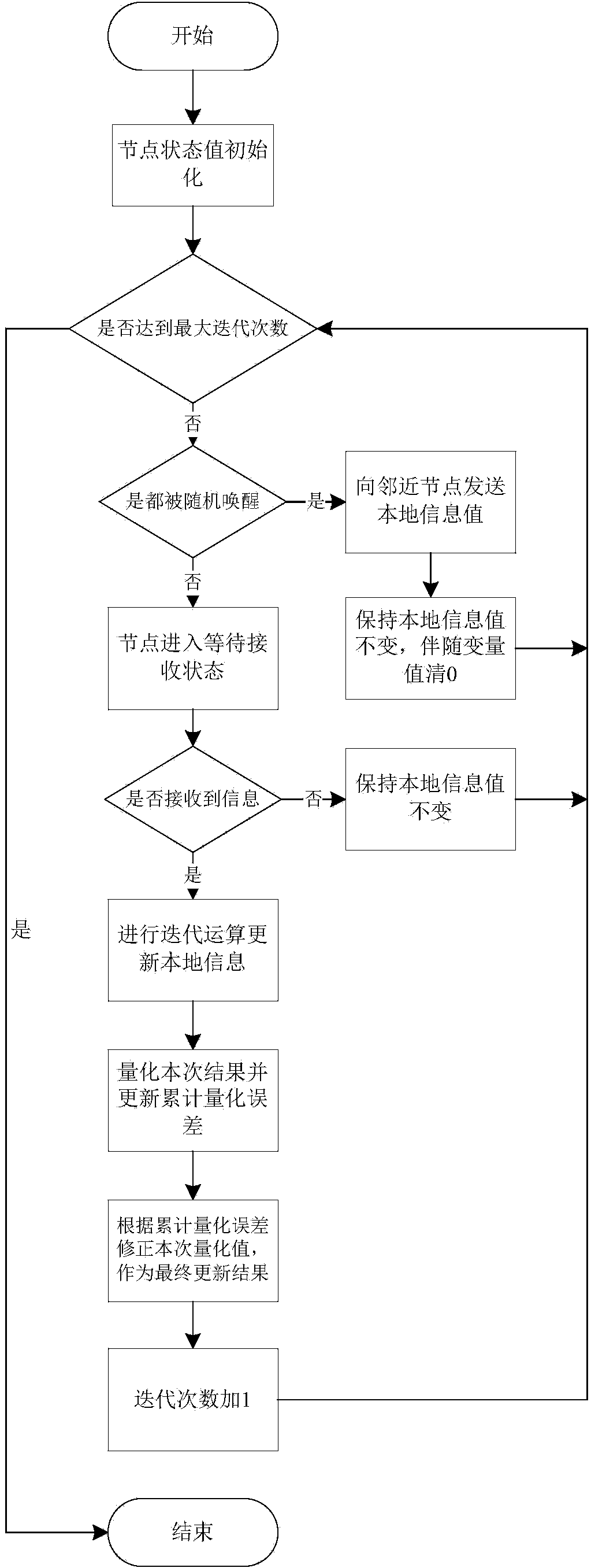
[0021] Specific embodiment one: the distributed load balancing method based on the quantitative unbiased broadcast Gossip algorithm of this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0022] 1. Initialize the node state value and set the synchronization clock and the maximum number of iterations of the wireless sensor network;
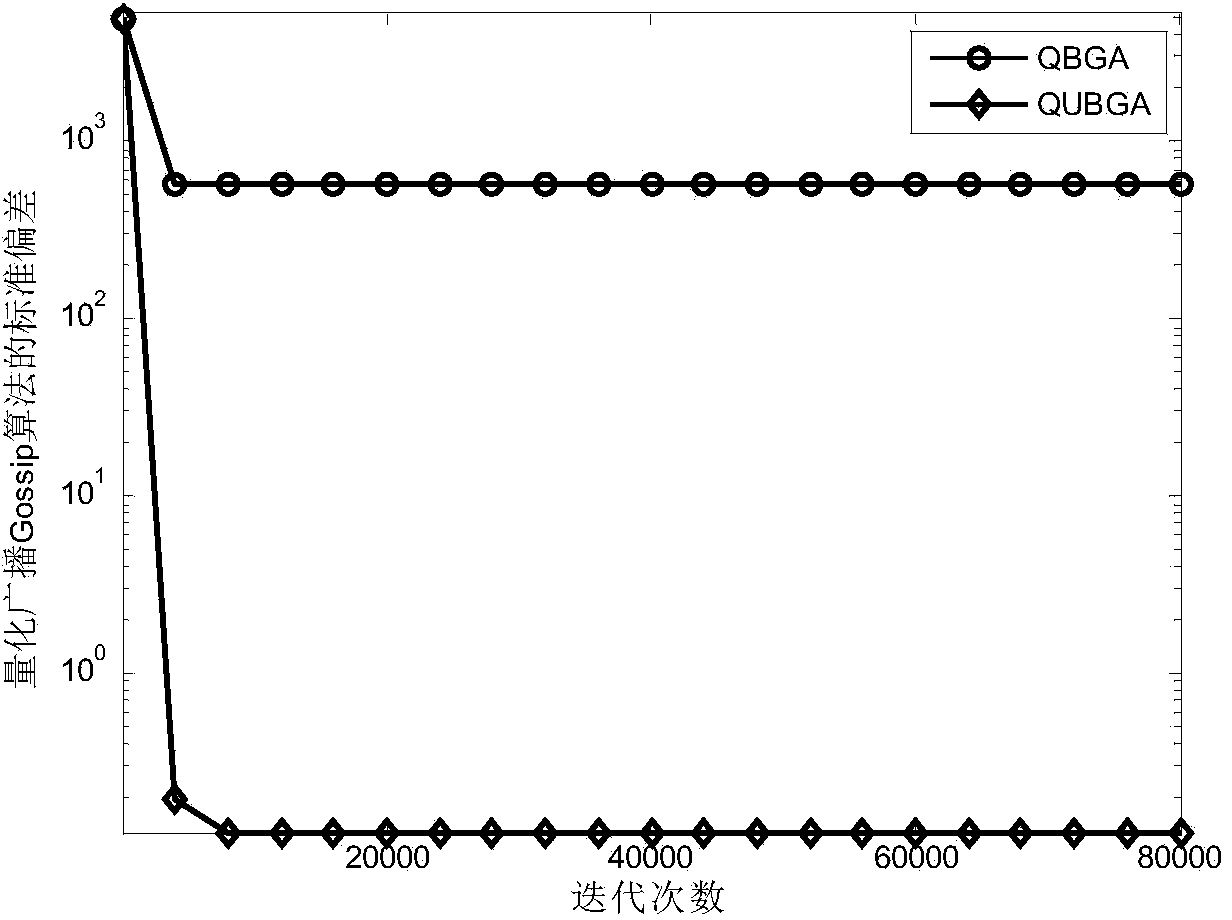
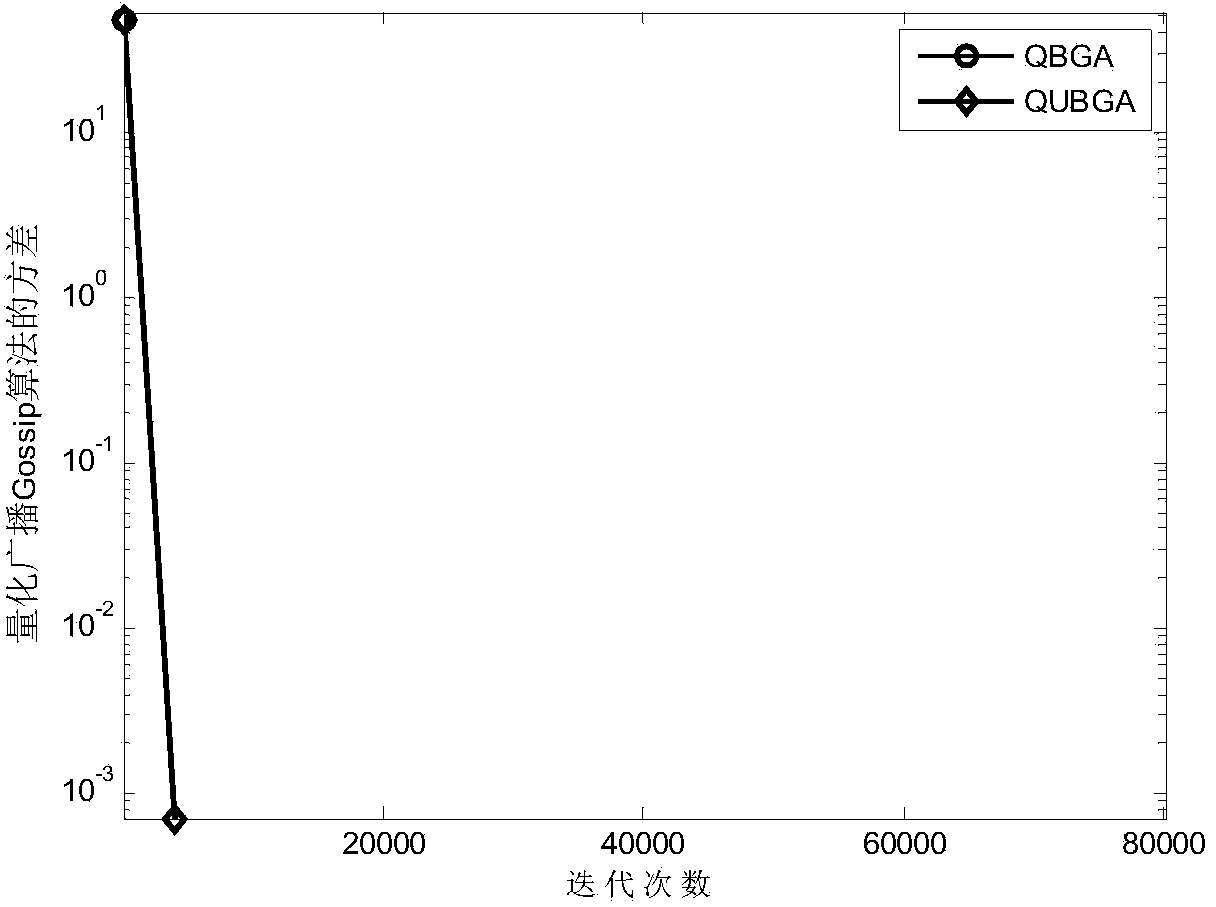
[0023] 2. The iteration and quantization process of the unbiased broadcast Gossip algorithm;
[0024] 3. When the number of iterations reaches the preset maximum number of iterations, the iteration ends; at this time, the loads of all nodes in the wireless sensor network are balanced, that is, the distributed load balancing method based on the quantized unbiased broadcast Gossip algorithm is completed.
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0025] Specific implementation mode two: the difference between this implementation mode and specific implementation mode one is that the step one is specifically:
[0026] (1) The wireless sensor network is regarded as a random geometric graph model G(N, R), N represents the number of sensor nodes, R is the connection radius, and N sensor nodes are evenly distributed in the network; the N sensor nodes The topology is represented by an N×N adjacent matrix A. If the Euclidean distance between two nodes i and j is less than the transmission radius R, the two nodes are considered to be adjacent to each other and can communicate directly. Let A ij = 1; otherwise, the two nodes are not adjacent and cannot communicate directly, then let A ij =0; when i=j, i and j represent the same node, then let A ij = 0; let N i ={j∈{1,2,…,N}:A ij ≠0} means all adjacent nodes of node i;
[0027] (2) Each node i in the wireless sensor network saves two variables, one is the estimated value x of...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0030] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one or two is: the iterative and quantization process of the unbiased broadcast Gossip algorithm in the step two is specifically:
[0031] 1) Start the timer and start timing: when the current round of iteration starts, judge whether the current iteration number has reached the maximum value, if not, enter the current round of iteration process; if it has reached the maximum value, then exit the iteration process;
[0032] 2) During the current round of iteration, judge whether the timer count value of the node is full: if the timing of node k expires at time t, the node will be awakened randomly, otherwise the node will not be awakened and enter the waiting state; The awakened node k broadcasts its current quantized state value to the whole network and quantified accompanying variable values At the same time, node k updates its final state value at time t+1 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com