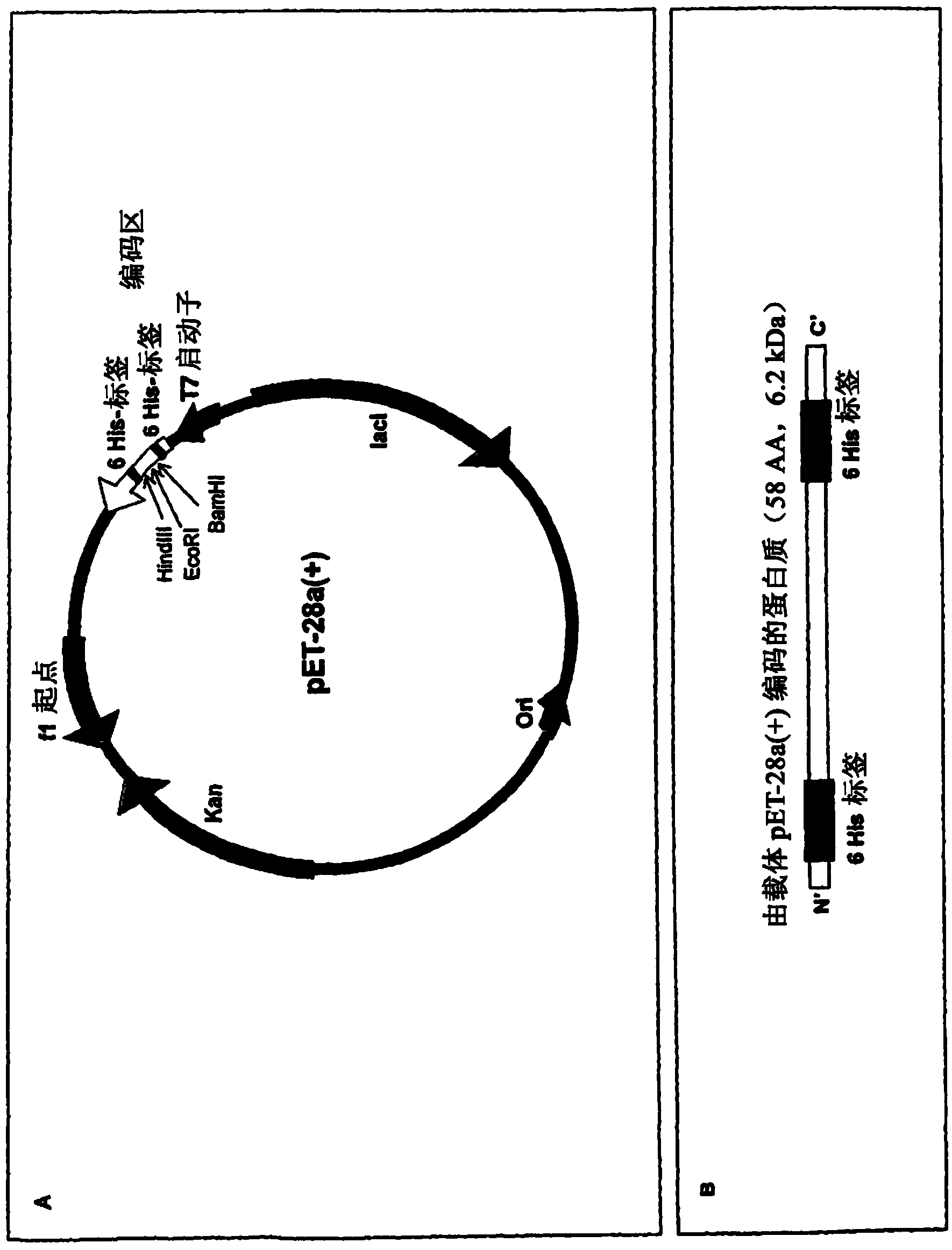
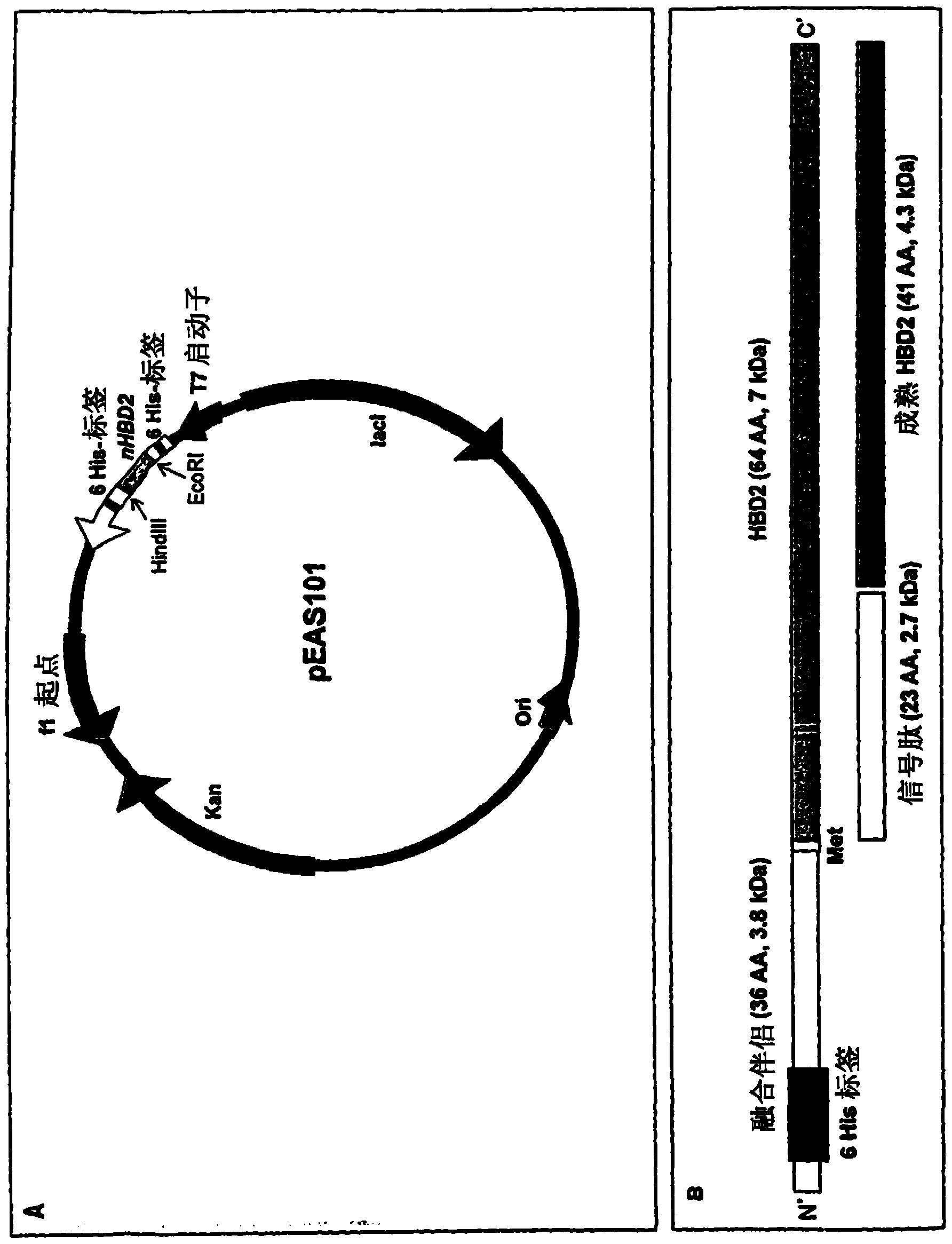
Recombinant escherichia coli strains
A technology for recombining Escherichia coli and Escherichia coli, which is applied in the direction of bacteria, cationic antimicrobial peptides, and medical raw materials derived from bacteria, etc. It can solve the problems of inactivity of fusion products, increased production of soluble products, and insolubility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0011] According to a first aspect, the present invention relates to recombinant Escherichia coli (E. coli) Nissle 1917 cells transformed with a nucleic acid encoding a defensin protein or a derivative thereof.
[0012] In the context of the present invention, the term "nucleic acid sequence" refers to a heteropolymer of nucleotides or a sequence of these nucleotides. The term "nucleic acid" includes RNA as well as DNA, including cDNA, genomic DNA, and synthetic (eg, chemically synthesized) nucleic acids, and the like.
[0013] As used herein, the term "derivative" refers to a nucleic acid derivative encoding a defensin protein, which comprises one or more substitutions, insertions and / or deletions compared to the original defensin nucleic acid sequence. Preferably, these derivatives have 1, 2, 3, 4 or more nucleotides deleted at the 5'-end or 3'-end or within the nucleic acid sequence, or these nucleotides are replaced by other core Nucleotide replacement.
[0014] The term...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com