Method of designing injection target point of Mars probe with optimal fuel
A technology of Mars probe and design method, which is applied in the direction of instruments, calculations, special data processing applications, etc., and can solve problems such as consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0017] Read the detailed description of non-limiting embodiments with reference to the following figures.
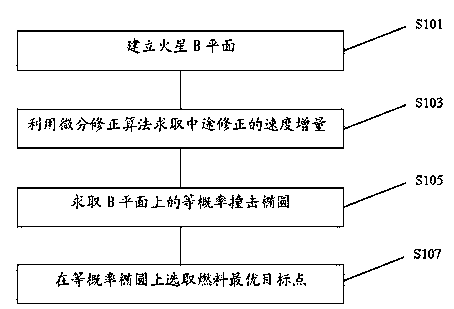
[0018] The present invention provides a method for designing the target point of the Mars probe with optimal fuel, the process of which is as follows figure 1 shown. The constraint parameter is the probability of the probe or the upper stage of the rocket hitting Mars, and the optimization parameter is the speed increment that needs to be corrected halfway to correct the probe to the final target point.
[0019] 1) Build the Mars B plane:
[0020] 1-1) Definition of B plane
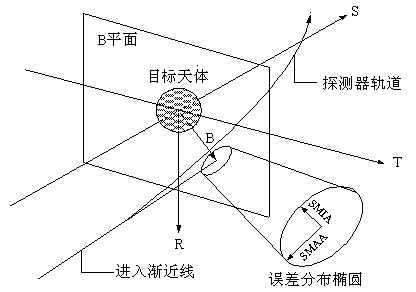
[0021] Before the probe reaches the vicinity of Mars and does not brake, its flight trajectory relative to Mars is a hyperbola. The so-called B plane refers to the plane passing through the center of Mars and perpendicular to the incident asymptote of the hyperbolic orbit of the probe, such as figure 2 shown.
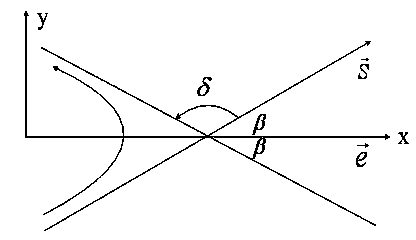
[0022] Suppose the vector of the incident asymptote of the hyperbolic orbit is , ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com