Mesenchymal stem cells from meniscus tissues as well as preparation method and identification thereof
A mesenchymal stem cell and meniscus technology, applied in the field of mesenchymal stem cells and its preparation, can solve the problems of limited number of meniscus cells, inaccuracy of meniscus cells, poor repair effect, etc., and achieve good clinical application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
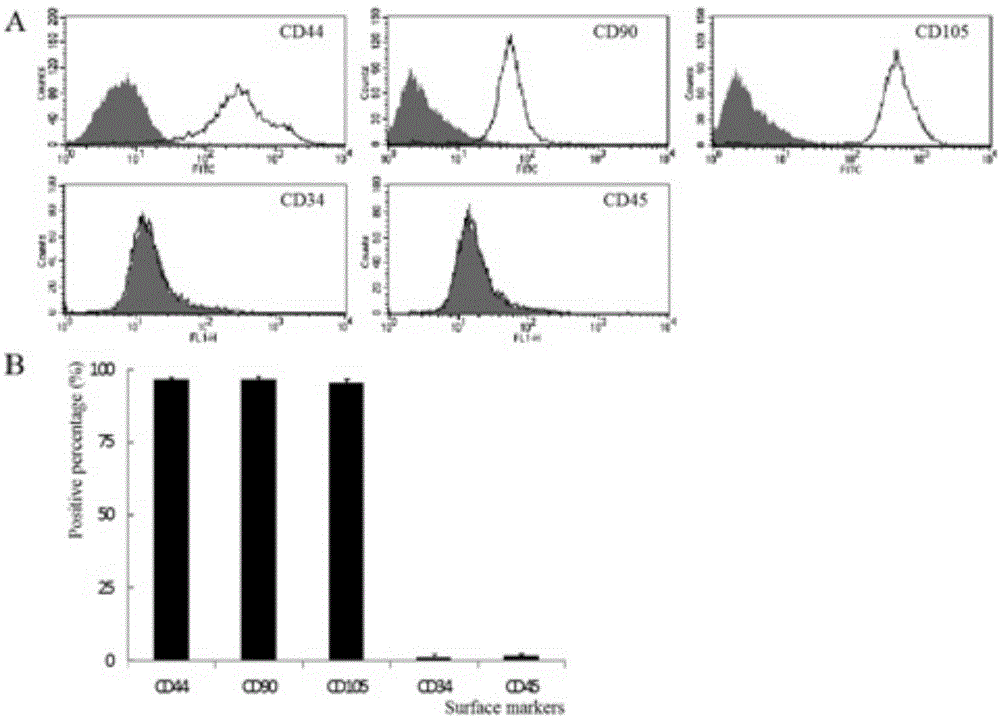
[0033] Example 1 Isolation and detection of mesenchymal stem cells derived from meniscus tissue of the present invention
[0034] 1. Separation and detection method
[0035] 1. Collection of meniscus fragments
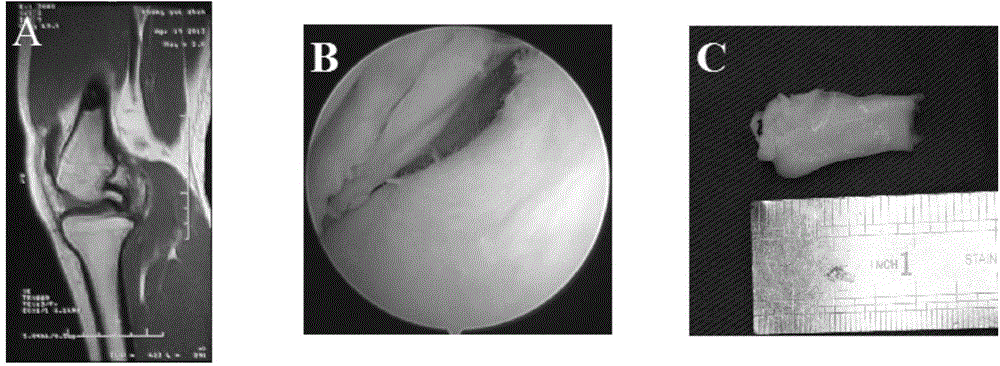
[0036] The diagnosis of meniscus injury was diagnosed comprehensively based on the patient's clinical manifestations, positive findings under MRI and arthroscopy (see figure 1 ). Arthroscopically removed meniscal fragments with nucleus forceps (see figure 1 ). The tissues with blood vessels, the surrounding synovium and ligaments were excised under a microscope, and rinsed 3 times in PBS containing double antibodies.
[0037] 2. Isolation and culture of tissue-specific mesenchymal stem cells derived from meniscus fragments
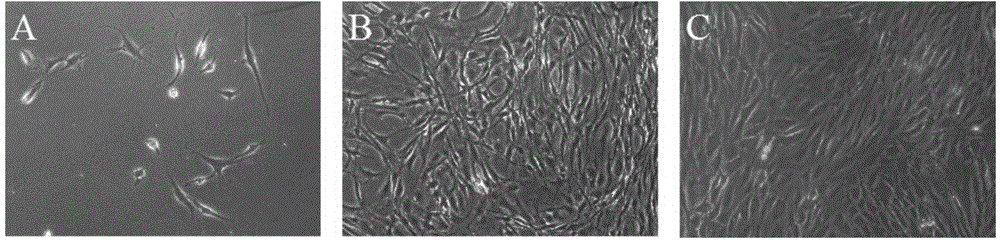
[0038] Use ophthalmic scissors to cut the collected meniscus fragments into about 1-5mm 3 Tissue fragments of different sizes were then shaken in a 0.2% type I, 0.2% type II mixed collagenase (concentrations of both type I and type II collage...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Example 2 Isolation and detection of mesenchymal stem cells derived from meniscus tissue of the present invention
[0040]1. Separation and detection method
[0041] 1. Collection of meniscus fragments
[0042] The diagnosis of meniscus injury was diagnosed comprehensively based on the patient's clinical manifestations, positive findings under MRI and arthroscopy (see figure 1 ). Arthroscopically removed meniscal fragments with nucleus forceps (see figure 1 ). The tissues with blood vessels, the surrounding synovium and ligaments were excised under a microscope, and rinsed 3 times in PBS containing double antibodies.
[0043] 2. Isolation and culture of tissue-specific mesenchymal stem cells derived from meniscus fragments
[0044] Use ophthalmic scissors to cut the collected meniscus fragments into about 1-5mm 3 Tissue fragments of different sizes were then shaken in a 0.1% type I and 0.1% type II mixed collagenase (concentrations of both type I and type II colla...
Embodiment 3
[0045] Example 3 Isolation and detection of mesenchymal stem cells derived from meniscus tissue of the present invention
[0046] 1. Separation and detection method
[0047] 1. Collection of meniscus fragments
[0048] The diagnosis of meniscus injury was diagnosed comprehensively based on the patient's clinical manifestations, positive findings under MRI and arthroscopy (see figure 1 ). Arthroscopically removed meniscal fragments with nucleus forceps (see figure 1 ). The tissues with blood vessels, the surrounding synovium and ligaments were excised under a microscope, and rinsed 3 times in PBS containing double antibodies.
[0049] 2. Isolation and culture of tissue-specific mesenchymal stem cells derived from meniscus fragments
[0050] Use ophthalmic scissors to cut the collected meniscus fragments into about 1-5mm 3 Tissue fragments of different sizes were then shaken in a 0.5% type I, 0.5% type II mixed collagenase (concentrations of both type I and type II collage...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com