Improved methods of cell culture for adoptive cell therapy
A cell culture and cell technology, applied in the field of cell culture, can solve problems such as the complexity of T cell methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0085] Example 1: Demonstration of the limitations of conventional methods.
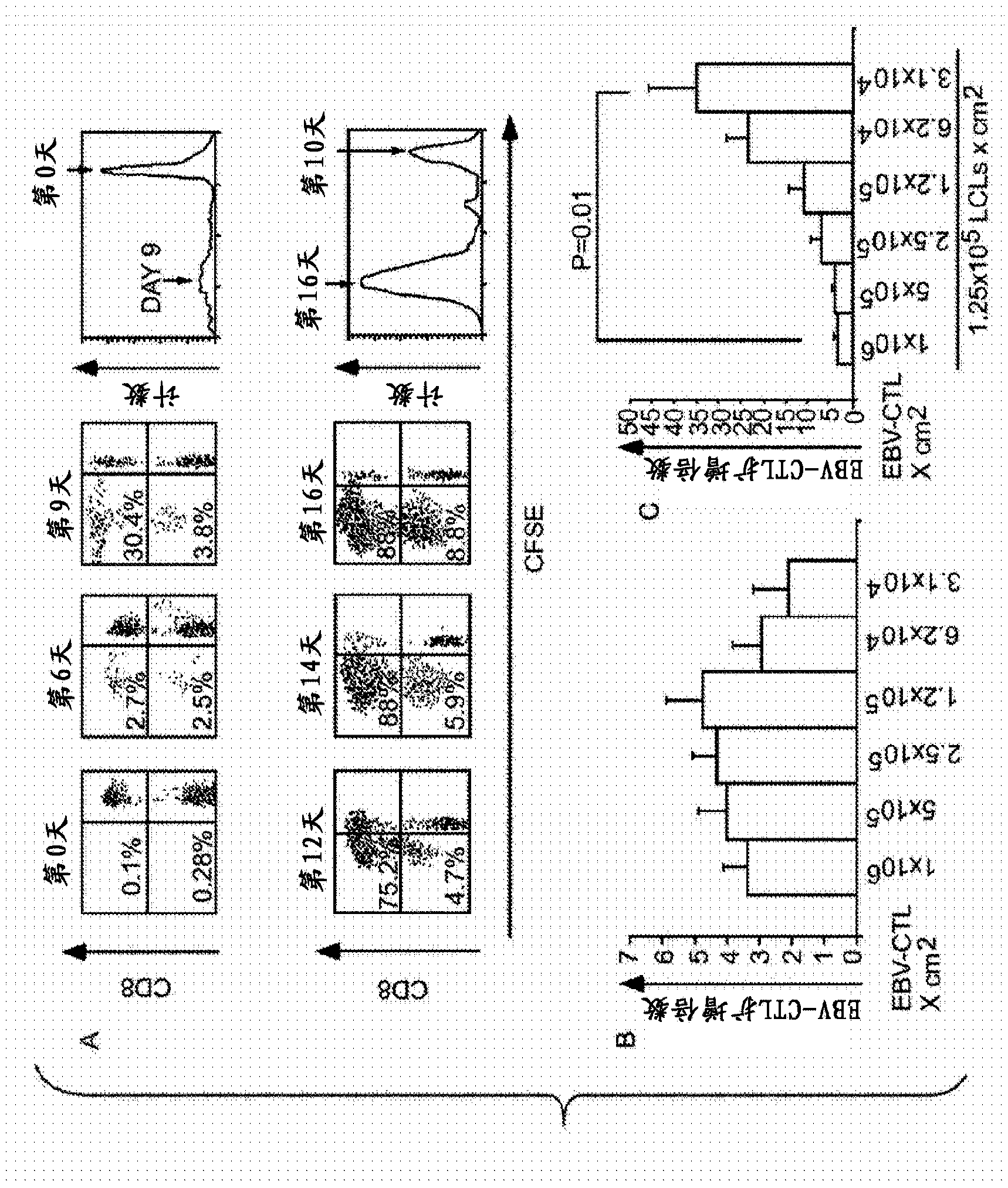
[0086] The data in this example demonstrates that when using 2ml medium volume per well (i.e., medium height is 1.0cm, medium volume to surface area ratio is 1ml / cm 2 ) standard 24-well tissue culture plate (that is, each well has a surface area of 2 cm 2 ) in the limitations of conventional culture methods for preparing EBV-CTL.
[0087] Stage 1 of culture, day 0: γ-irradiated (40Gy) antigen-presenting autologous EBV-LCL at a ratio of 40:1 (PBMC:LCL) and 1 ml / cm 2 The ratio of medium volume to growth surface for cell composition from normal donor PBMC (approximately 1×10 6 cells / ml) were cultured to initiate expansion of the EBV-CTL population, whereby 45% Click medium (Irvine Scientific, Santa Ana, CA), 2mM GlutaMAX-I, and 10% FBS supplemented RPMI 1640 built in approximately 1×10 6 cells / cm 2 surface density of the cell composition.
[0088] Stage 2 of culture, days 9-16: On day 9, EBV-CTL...
Embodiment 2
[0100] Example 2: At any given stage or at the beginning of each stage of culture, a reduction in the amount of time required to increase a target cell population can be achieved by reducing the cell surface density of the target cell population.
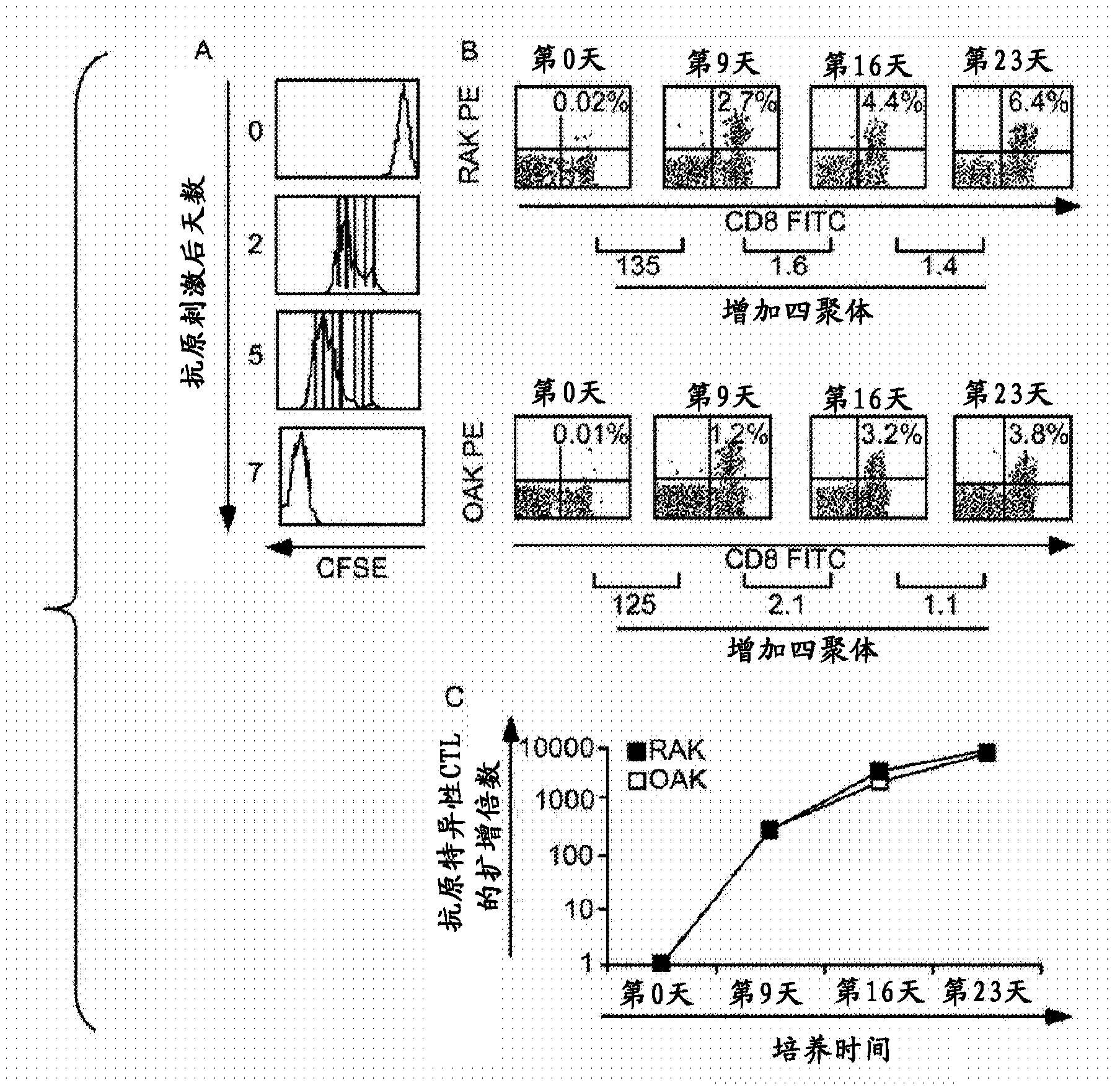
[0101] We hypothesized that the reduced expansion rate of the target cell population after the second T cell stimulation compared to the first stimulation is due to restrictive cell culture conditions leading to activation-induced cell death (AICD). For example, refer to image 3 A, At first stimulation, the EBV antigen-specific T cell component of PBMCs constituted at most 2% of the population, and thus antigen-specific responsive T cells were seeded at a density of less than 2 × 10 4 / cm 2 , the remaining PBMC acted as non-proliferative feeder cells (shown as image 3 CFSE-positive cells in A), these feeder cells maintain optimal cell-cell contacts that enable the proliferation of antigen-specific CTLs. In contrast, at the seco...
Embodiment 3
[0105] Example 3: Minimum Surface Density of Cell Populations Comprising Target Cells and / or Antigen Presenting Cells can allow growth of target cell populations seeded at very low surface densities.
[0106] Figure 4 shows when continuing image 3 The work described in is an example of the results we have obtained, which further demonstrates that when the target cells need the support of other cells, as long as the target cells are provided with sufficient feeder cells and / or antigen presenting cells, unconventional low The target cell surface density can then initiate population expansion. In these experiments, we went on to demonstrate that with an R:S ratio of about 1.0×10 6 target cells / cm 2 Compared to only about 3900 target cells / cm at an R:S ratio of 1 to 32 2 We stopped testing how the total cell composition at a surface density and R:S ratio between the target cells greatly expanded beyond 50-fold the starting surface density.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Inoculation density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Surface density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com