Clutch device and steering device
A technology of clutch device and steering mechanism, which is applied to clutches, mechanically driven clutches, magnetically driven clutches, etc., to achieve the effect of improving steering control feeling
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment approach
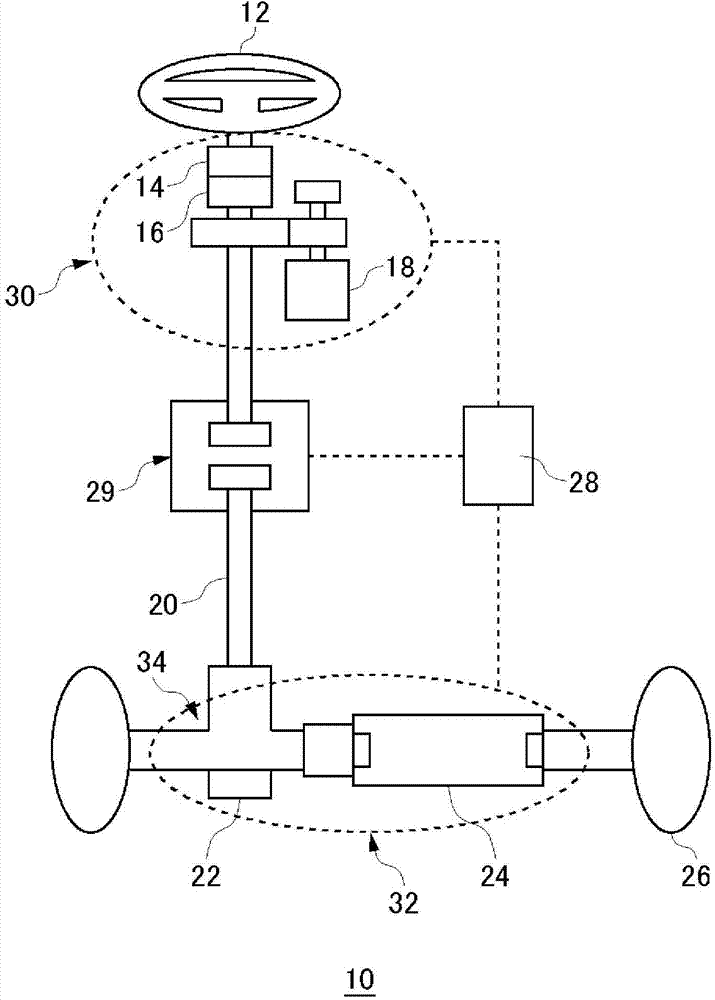
[0030] figure 1 It is a schematic diagram showing the schematic configuration of the vehicle steering device according to the first embodiment. The vehicle steering device 10 includes a steering wheel 12 , a steering angle sensor 14 , a torque sensor 16 , a steering reaction motor 18 , an intermediate shaft 20 , a steering angle sensor 22 , a steering motor 24 , tires 26 , an ECU 28 , and a clutch device 29 .
[0031] The steering actuator 30 is composed of a steering angle sensor 14 , a torque sensor 16 , and a steering reaction force motor 18 . In addition, the steering actuator 32 is constituted by the steering angle sensor 22 and the steering motor 24 . The ECU 28 controls the steering reaction motor 18 and the steering motor 24 based on various sensor information of the steering actuator 30 and the steering actuator 32 .
[0032] The steering wheel 12 is disposed on the driver's seat side in the vehicle compartment, and functions as a steering member that is rotated for...
no. 2 Embodiment approach
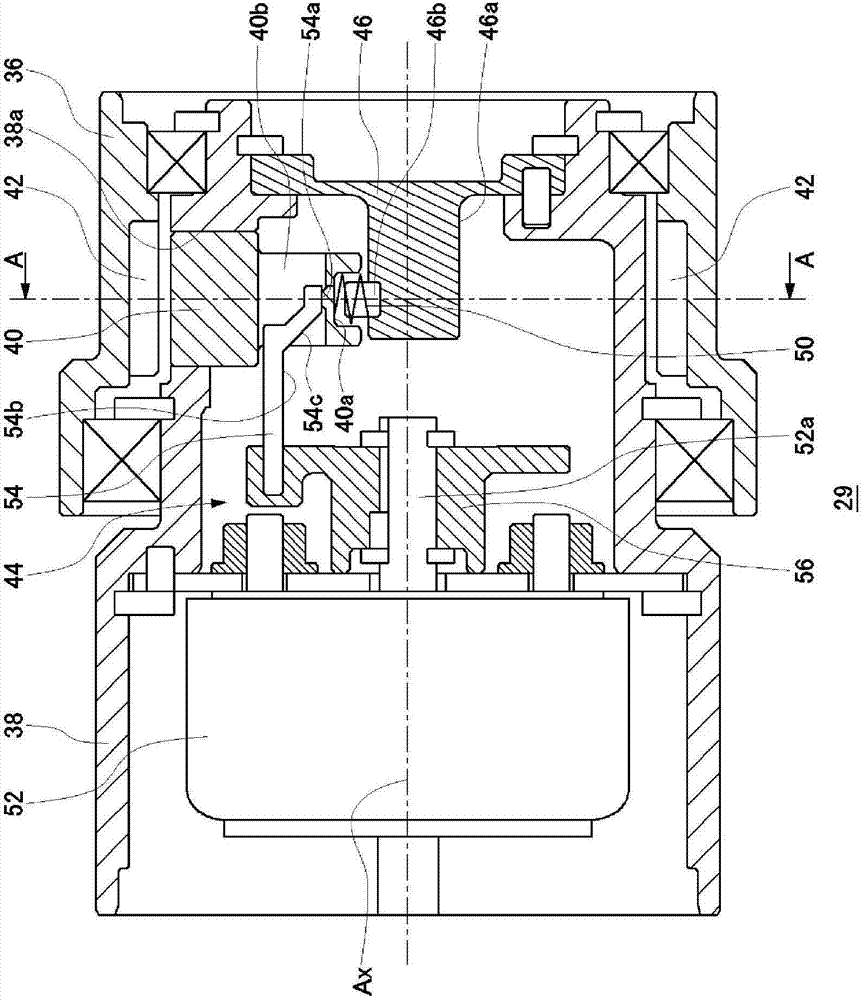
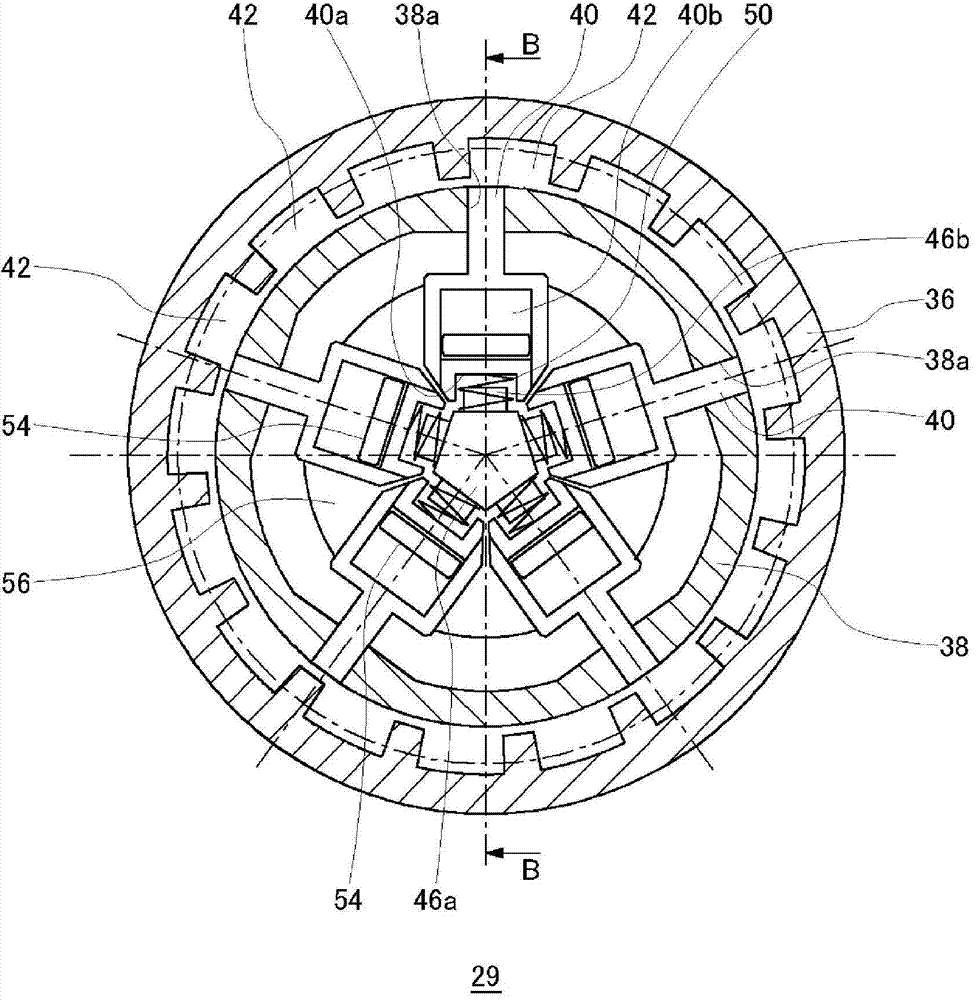
[0074] Figure 8 It is a cross-sectional view of the clutch device of the second embodiment. Figure 8 Compared with the clutch device 29 of the first embodiment, the illustrated clutch device 58 has a major feature that the sizes of the lock lever and the lock groove are different. The structure and operation of the clutch device 58 itself are substantially the same as those of the clutch device 29 of the first embodiment, and therefore description thereof will be appropriately omitted.
[0075] Various parameters of the lock bar 60 and the lock groove 62 in the clutch device 58 are as shown in Table 1. Compared with the clutch device 29, the width of the lock lever 40 of the clutch device 58 is widened, and the width of the lock groove 62 is narrowed. And, when the energization of the pulling solenoid 52 is cancelled, among the five lock levers 60, the number of lock levers that reliably enters any lock groove 62 is one (the clutch device 29 of the first embodiment in 2)....
no. 3 Embodiment approach
[0078] Figure 9 It is a cross-sectional view of the clutch device of the third embodiment. Figure 9 Compared with the clutch device 29 of the first embodiment and the clutch device 58 of the second embodiment, the illustrated clutch device 66 is characterized by a difference in the number of lock levers and lock grooves. The structure and operation of the clutch device 66 itself are substantially the same as those of the clutch device 29 of the first embodiment, and therefore description thereof will be appropriately omitted.
[0079] Various parameters of the lock bar 68 and the lock groove 70 in the clutch device 66 are as shown in Table 1. Compared with the clutch device 29 and the clutch device 58 , the clutch device 66 has fewer lock levers 68 and more lock grooves 70 . Furthermore, when the energization of the pulling solenoid 52 is cancelled, among the four lock levers 68, the number of lock levers that reliably enters any lock groove 70 is one (the clutch device 29...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com