Motion-based localization method based on magnetic gradient tensor and geomagnetic vector measurement
A technology of magnetic gradient tensor and positioning method, which is applied in the field of magnetic measurement, can solve the problems that the three-dimensional coordinate system of the magnetic target cannot be dynamically determined in real time, and the lack of research on the three-dimensional positioning of the moving type can achieve the effect of avoiding the inaccuracy of the geomagnetic vector
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
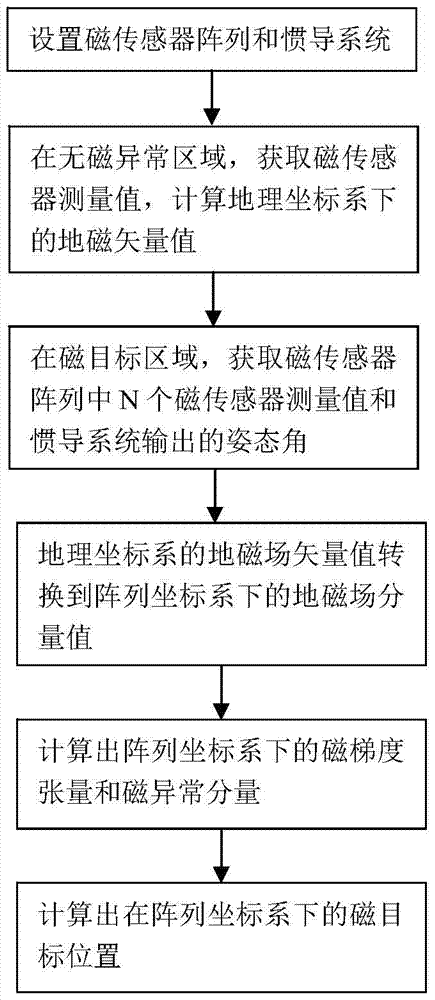
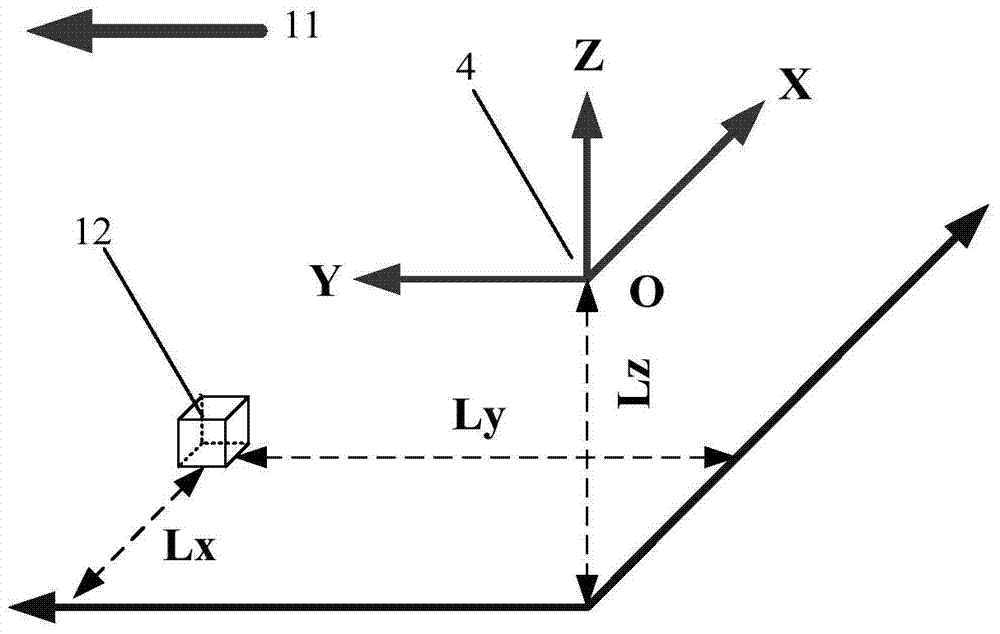
[0042] Below, the present invention will be further described in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments. In order to better understand the technical solution of the present invention, its principles and calculation formulas will now be deduced in detail in conjunction with specific embodiments and described in detail as follows:
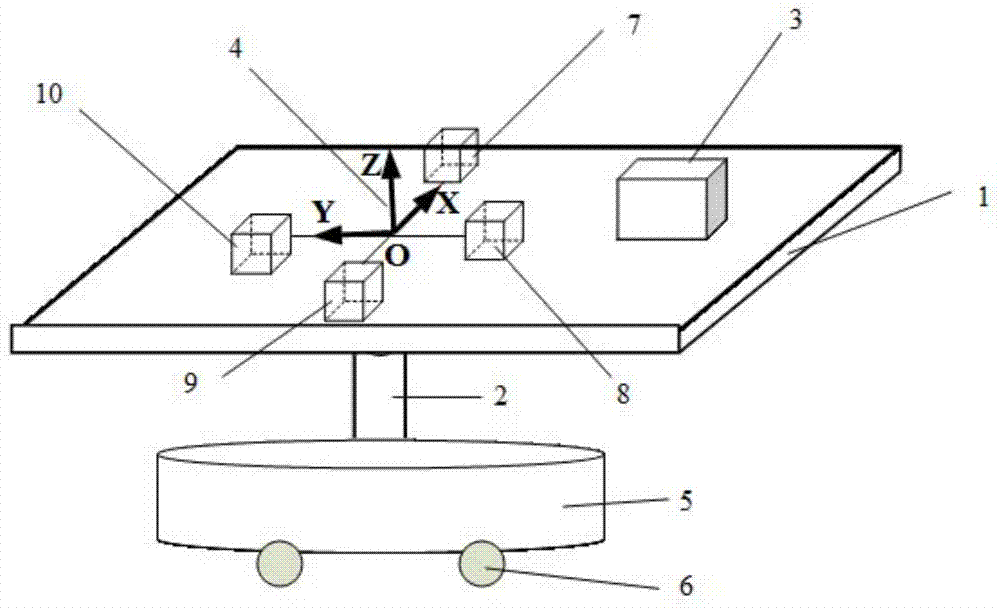
[0043] Such as figure 2 As shown, the non-magnetic moving device includes a non-magnetic platform 1, a platform support shaft 2, a non-magnetic base 5 and a moving pulley 6, the platform support shaft 2 is installed on the non-magnetic base 5, and the platform support shaft 2 is connected to the non-magnetic The magnetic platform 1 is connected to and supports the non-magnetic platform 1, and the moving pulley 6 is installed on the bottom of the non-magnetic base 5 to facilitate the movement of the non-magnetic moving device.
[0044] In this embodiment, the number N of magnetic sensors is taken as 4.
[0045] The 4 mag...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com