Human-derived anti-human CD146 monoclonal antibody with efficient neutralizing activity
A monoclonal antibody and humanized technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problems of rejection, weak ADCC effect, short half-life, etc., and achieve the effect of high-efficiency neutralization activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] Humanization strategy of anti-human CD146 human-mouse chimeric antibody
[0041] The best-fit CDR construction technology was used to humanize the anti-human CD146 human-mouse chimeric antibody. The murine CDRs are grafted into a human-acceptable framework with high sequence homology to the framework region of the chimeric antibody. The best matching FR frameworks of graftable CDRs were searched in the human germline sequence database. Antibody primary structural sequences and 3D structural data were used to identify key framework residues required to maintain the correct conformation of the murine CDRs to preserve binding affinity and specificity. In order to maintain the affinity of the antibody, back mutations are carried out in different humanized molecular frameworks, and finally a highly humanized monoclonal antibody is obtained.
[0042] By BLAST analysis of the human V region gene database, human IGHV3-33 and anti-human CD146 human-mouse chimeric antibody heav...
Embodiment 2
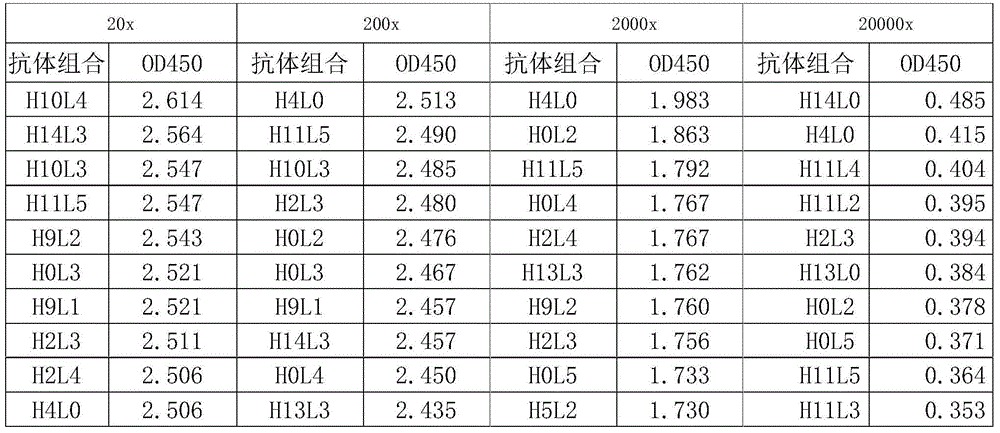
[0045] Figure 1 shows the ELISA results of the binding of anti-CD146 murine antibody to CD146. Determination of specificity of humanized designed antibody binding to human CD146 receptor by ELISA
[0046] Synthesize the VH domain and VL domain according to the results of computer simulation humanization design, and clone the synthetic VH domain and VL domain into a mammalian expression vector, which enables the corresponding domains to be placed on the complete human IgG backbone in the expression. Humanized antibodies are produced in small batches by co-transfecting the heavy chain construct with the light chain construct into mammalian cells. Transient transfection supernatants were subjected to ELISA detection. IgG is purified to homogeneity by protein A or G resin for detection in cell-based assays.
[0047] To determine the specificity of humanized antibodies binding to CD146, ELISA was performed against CD146 and control protein. The above-mentioned transient transfe...
Embodiment 3
[0071] BIACORE analysis of binding of humanized antibody series to CD146
[0072] The purpose of this example is to use BIACORE to analyze the binding affinity of the humanized engineered antibody to human CD146. The humanized engineered antibody is an H5L0 antibody, and the H5L0 antibody comprises the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 14 and SEQ ID NO: 24); the H10L2 antibody comprises the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 19 and SEQ ID NO: 26; H14L0 The antibody comprises the amino acid sequences of SEQ ID NO: 23 and SEQ ID NO: 24; the H11L3 antibody comprises the amino acid sequences of SEQ ID NO: 20 and SEQ ID NO: 27; the H11L4 antibody comprises the amino acid sequences of SEQ ID NO: 20 and SEQ ID NO: 28; The H13L0 antibody comprises the amino acid sequences of SEQ ID NO: 22 and SEQ ID NO: 24; the H0L2 antibody comprises the amino acid sequences of SEQ ID NO: 9 and SEQ ID NO: 26; the H11L2 antibody comprises the amino acid sequences of SEQ ID NO: 20 and SEQ ID NO: 26 The...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap