Crosslapper
A cross-lapper and web-laying technology, which is applied to roll-forming mechanisms, textiles and papermaking, fiber processing, etc., can solve problems such as uneven surface shape of non-woven fabrics and non-straight laying of fiber webs.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
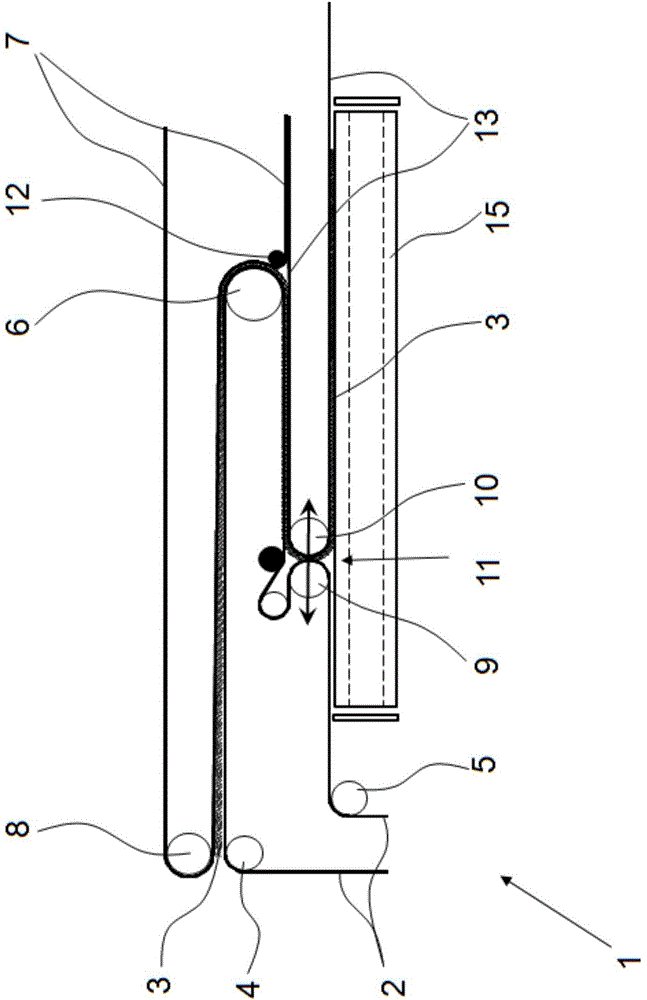
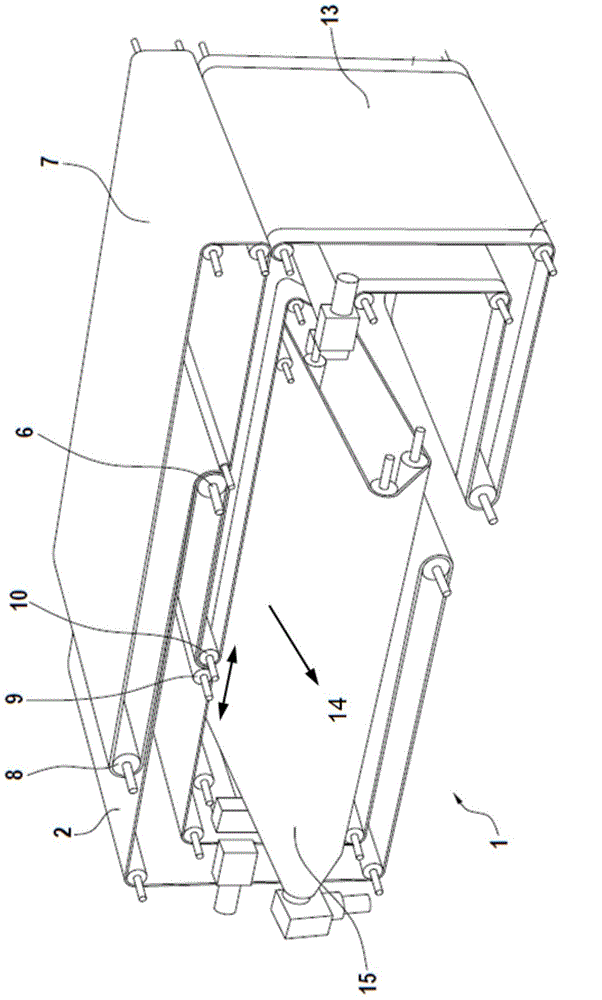
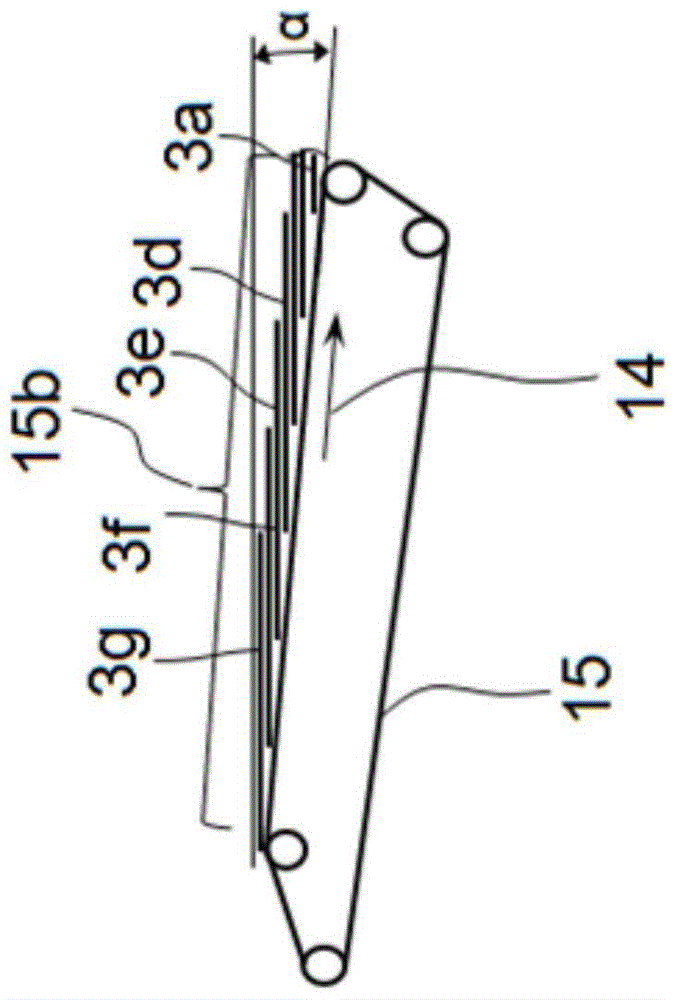
[0023] exist figure 1 and 2 The principle of the crosslapper 1 is shown by way of example and only schematically. Triggered by a card not shown, the fiber web 3 is conveyed onto the input belt 2 of the crosslapper 1 . Inside the crosslapper 1 is arranged an upper trolley, in which only the deflection rollers 6 can be seen in this view. Furthermore, the crosslapper 1 has a laying trolley, of which a laying roller 10 for the matching belt 13 and a laying roller 9 for the infeed belt 2 are shown. Between the laying roller 10 of the mating belt 13 and the laying roller 9 of the infeed belt 2 a so-called laying gap 11 is arranged, from which the fiber web 3 emerges and is laid on Output belt 15 on. Depending on the direction of travel, the two laying rollers 9 , 10 take over the task of laying the fiber web 3 perpendicular to the preceding direction of travel on a delivery belt 15 arranged below the laying carriage and simultaneously folding it. For this purpose, the laying tr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com