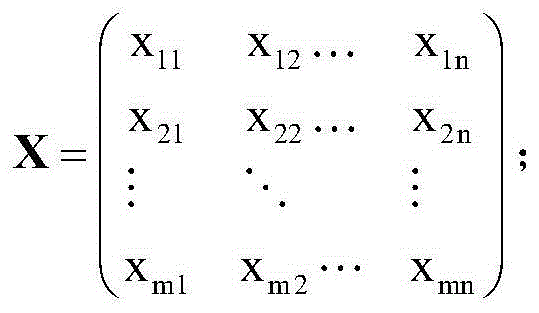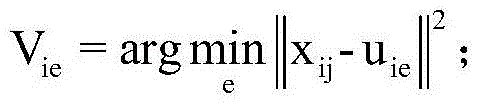Sleep scheduling method and system for energy acquisition sensor network
A sensor network and energy acquisition technology, applied in the field of sensor networks, can solve the problems of not considering the randomness of energy arrival, optimizing the use of energy, and not paying attention to node relationships
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0011] 1. The energy harvesting sensor network is randomly deployed in an area, and a total of n energy harvesting sensor nodes are thrown. Since the arrival of energy is discontinuous and random, the time of energy arrival is also intermittent, so the amount of energy EH obtained by each node is recorded every other time period, and 24 hours are divided into m time periods. The predicted energy EH obtained for each node in each time period mn , has the following formula: EH mn =(1-θ)EH mn '+θEH' mn . EH mn Indicates the predicted value of energy gain at the current moment m, EH′ mn Indicates the measured value of energy gain at the last m time, EH mn 'Indicates the predicted value at the last m time, θ is the weight, 0<θ≤1.
[0012] 2. Divide 24 hours a day into m segments on average, and the matrix X can be obtained, as follows:
[0013]
[0014] where: x ij is the element in the matrix X of m×n, 1≤i≤m, 1≤j≤n, n is the total number of nodes in the sensor network,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com