A Method for Obtaining Evaluation Index of Physical Hardening Performance of Asphalt Material
A technology of asphalt material and hardening performance, which is applied in the direction of testing the strength of the material by applying a stable bending force, and can solve the problems of being unable to objectively and accurately evaluate the physical hardening performance of asphalt materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0019] A method for obtaining an evaluation index of asphalt material physical hardening performance, comprising the following steps:
[0020] Step 1. Prepare the test piece: heat the asphalt to the state of glue and pour it into the specimen mold of the bending beam rheometer. The specimens are divided into two groups, and one group is denoted as specimen a 0 , and the other group is denoted as specimen b 0 ;
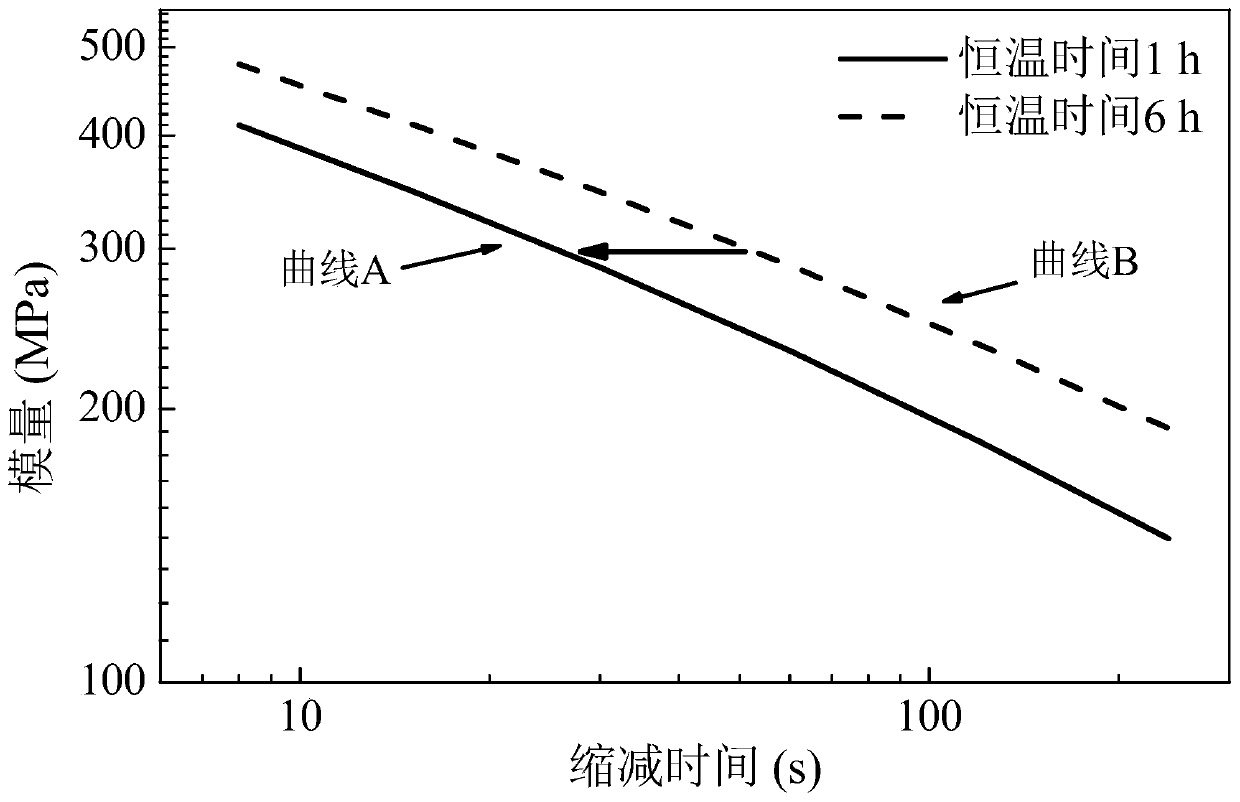
[0021] Step 2, the specimen a prepared in step 1 0 Put it into the bending beam rheometer and keep the constant temperature for 1 hour. The constant temperature is the temperature T℃ required by the product to be evaluated. After the constant temperature is completed, the test piece a 1 , for specimen a 1 Carry out the creep test to obtain the stiffness modulus curve A of the material as the asphalt material modulus curve under the reference condition; carry out at least two sets of parallel tests, and select the data with consistent results of the two sets of para...
specific Embodiment approach 2
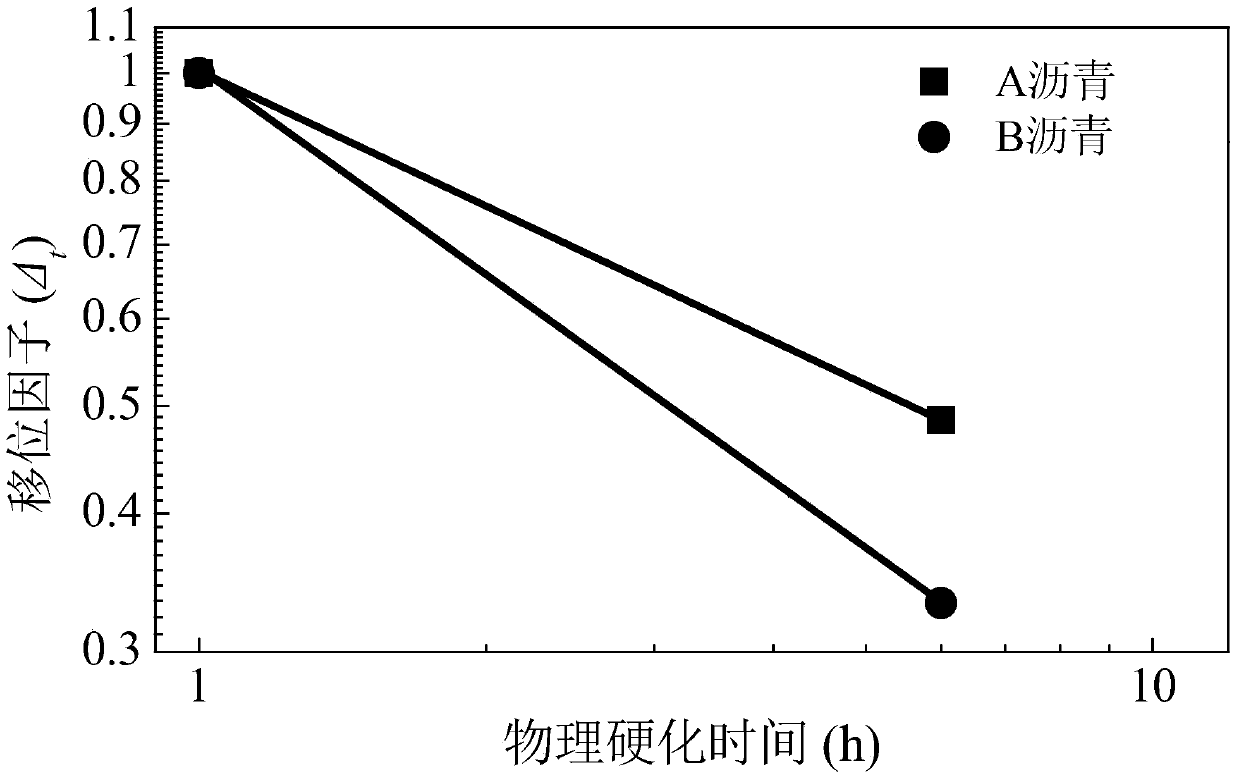
[0029] The steps of drawing the time-shift factor relationship curve C of the asphalt material in step five of the present embodiment are as follows:
[0030] Record the shift factor and time corresponding to the stiffness modulus curve A, and record the corresponding point as α; the shift factor of the stiffness modulus curve A is 1, and the time is 1 hour, which is the coordinate of α (1,1);
[0031] Record the displacement factor and time corresponding to the stiffness modulus curve B, and record the corresponding point as β; the displacement factor of the stiffness modulus curve B is Δ t , the time is t 2 hours, that is, the coordinates of β (Δ t ,t 2 );
[0032] In the logarithmic coordinate system, with time as the abscissa and the displacement factor as the ordinate, mark points α and β, and connect the two points as the time-displacement factor relationship curve C.
[0033] Other steps and parameters are the same as those in the first embodiment.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0035] In this embodiment, t 2 From 6 hours to 24 hours.
[0036] Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1 or 2.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com