Novel application of neutral extracellular polysaccharides of paecilomyces hepiali
A technology of Paecilomyces spp. and Paecilomyces spp. applied in the field of neutral exopolysaccharides of P. spp. can solve problems such as increasing the production of short-chain fatty acids and lactic acid
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Preparation of neutral exopolysaccharide from Paecilomyces basilisk moth:
[0027] (1) From the parent species of Paecilomyceshepiali (Paecilomyceshepiali) HN1 strain preserved in potato slant medium, excavate a piece of mycelium with a size of about 0.5cm×0.5cm, and inoculate it in a capacity of 100mL seed medium In a 250mL Erlenmeyer flask, after static culture at 20°C for 12 hours, shake culture at 120rpm for 72 hours to obtain seed liquid. The composition of the seed medium is: glucose 30.00g / L, yeast extract 6.00g / L, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 1.50g / L, magnesium sulfate 0.50g / L, wort juice 10.00g / L, potato juice 10.00g / L, pH6 .5;
[0028] (2) Get the seed liquid in the step (1) and inoculate it into a 500 mL Erlenmeyer flask with a capacity of 200 mL of fermentation medium, insert the seed liquid by 2% of the volume of the fermentation medium, and cultivate it statically for 12 hours at 20° C. Then, shake culture at 120 rpm for 120 hours, centrifuge the ferme...
Embodiment 2
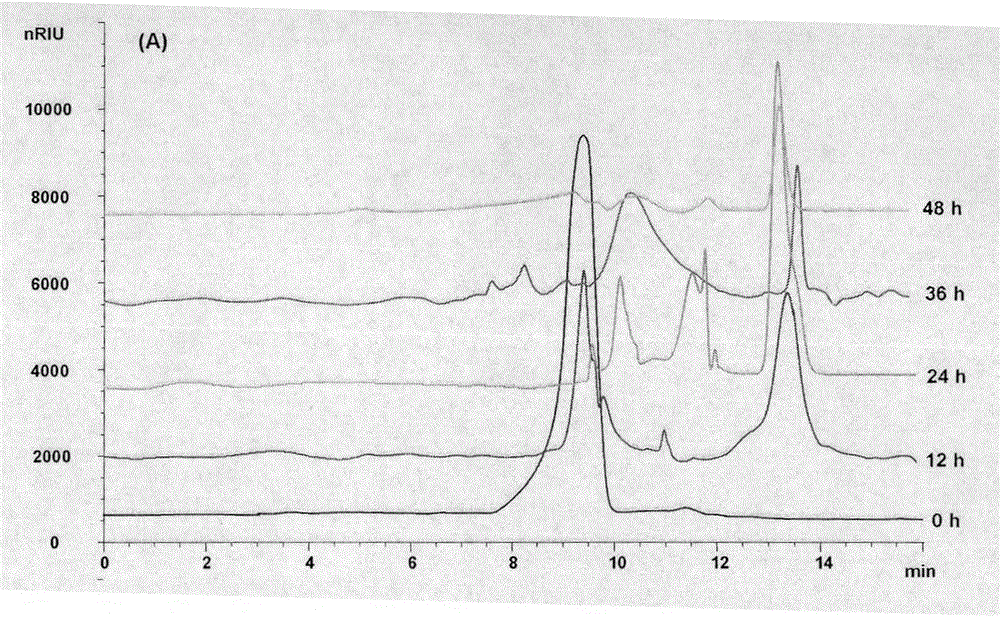
[0033] Metabolic Changes of Neutral Exopolysaccharides from Paecilomyces spp. in Anaerobic System
[0034] Depend on figure 1 It can be seen that the neutral exopolysaccharide components of Paecilomyces bat mothi can be better decomposed and utilized by intestinal microorganisms in the anaerobic fermentation system of human feces samples. At 12 hours of anaerobic fermentation, part of the polysaccharide components had been hydrolyzed into small molecular sugars, and at 24 hours, most of the polysaccharides had been hydrolyzed. As the fermentation time prolongs, it can be seen that the content of polysaccharides and small molecule sugars after hydrolysis gradually decreases, and at 48 hours after the end of fermentation, almost all the neutral exopolysaccharides of Paecilomyces hematilis are absorbed by the intestinal tract in the fermentation system. Microorganisms are exhausted.
Embodiment 3
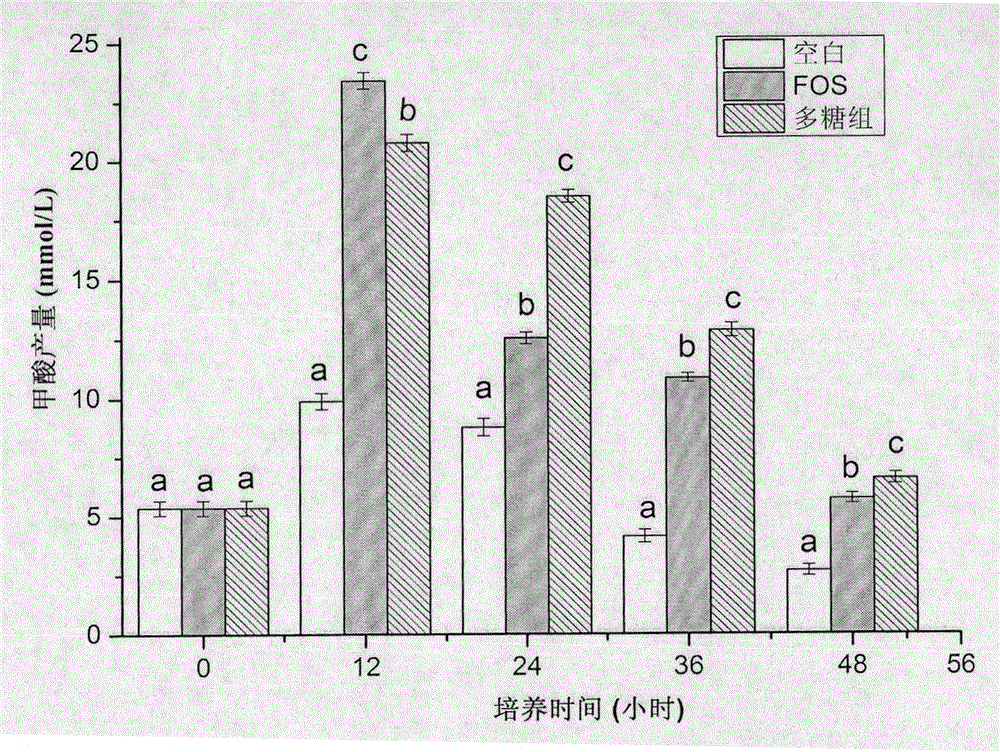
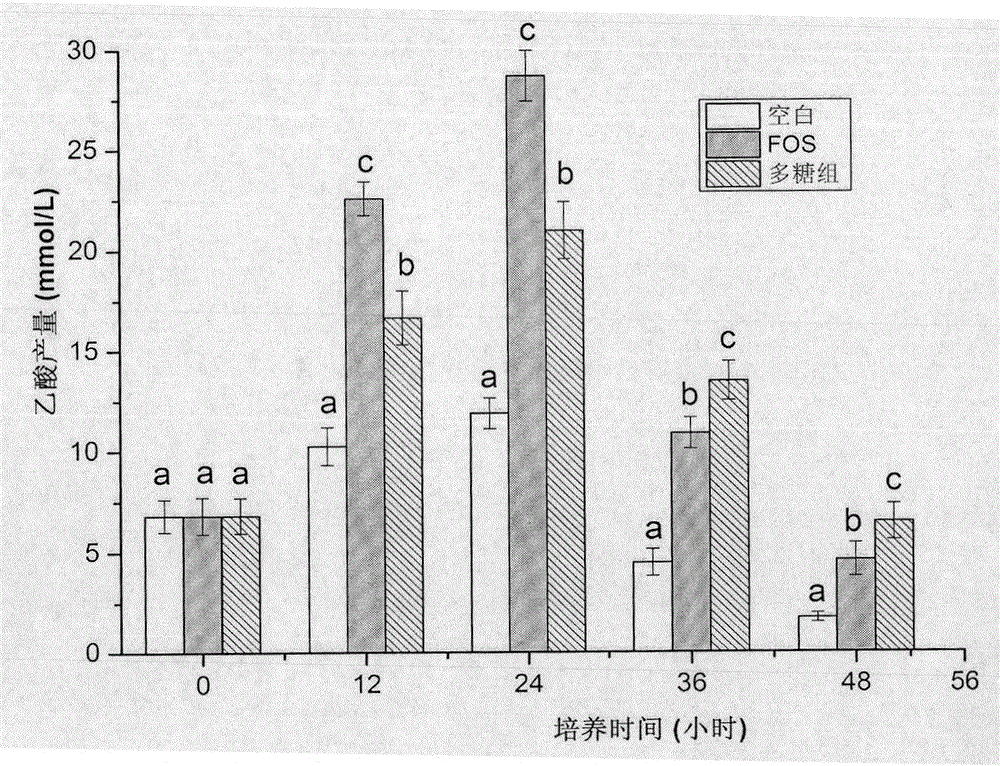
[0036] Effects of polysaccharides from Paecilomyces hematodes on intestinal flora
[0037] Studies have shown that some functional polysaccharides can affect the structure of intestinal flora, and then have beneficial effects on the body. To this end, we selected and monitored the proliferation of five genera of microorganisms that are closely related to intestinal health to evaluate the effects of adding different polysaccharide components on the intestinal flora in the in vitro fermentation system. The results are shown in Table 1.
[0038] Table 1 Changes of the bacterial flora of Paecilomyces bat moth in vitro anaerobic fermentation process of neutral exopolysaccharide
[0039]
[0040] * Different lowercase letters in each group indicate significant differences in experimental results (p<0.05).
[0041] It can be seen from Table 4-2 that, compared with the blank control group, adding the prebiotic fructo-oligosaccharide (FOS) significantly increased the two probiotics...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com