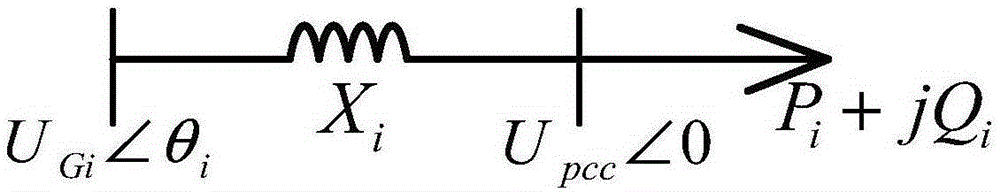Complex optimal control method for reactive power of wind power system in grid voltage sag fault
A grid voltage and wind power system technology, applied in reactive power adjustment/elimination/compensation, flexible AC transmission system, wind power generation, etc., can solve the problem of high cost, failure to meet low voltage ride-through requirements, slow response speed and difficult to meet grid operation Questions such as requirements
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
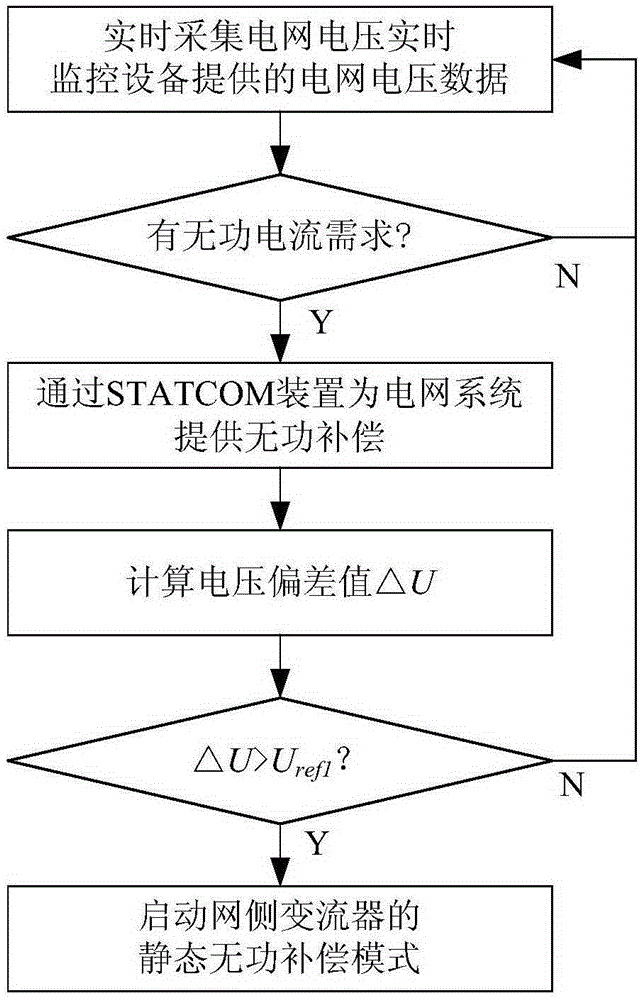
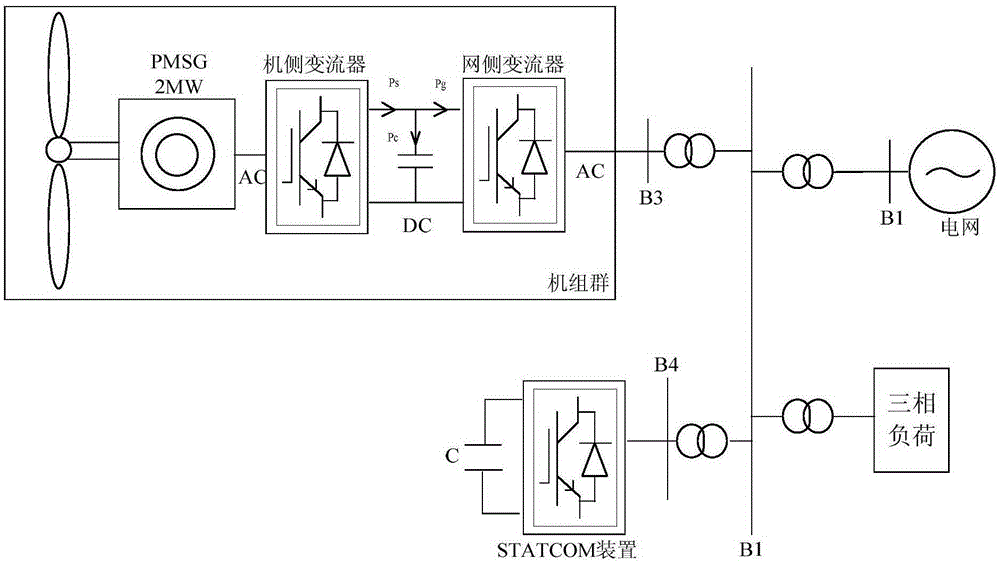
[0051] Such as figure 1 As shown, the steps of the wind power system reactive power comprehensive optimization control method in this embodiment include:
[0052] 1) Real-time collection of grid voltage data provided by grid voltage real-time monitoring equipment;
[0053] 2) According to the grid voltage data, it is judged whether the wind turbine itself has a reactive current demand, if there is a reactive current demand, skip to step 3), otherwise skip to step 1);
[0054] 3) Provide reactive power compensation for the grid system through the static synchronous compensator;
[0055] 4) Change the grid voltage U pcc with a preset reference voltage U pccref The voltage deviation value ΔU between, judge that the voltage deviation value ΔU is greater than the first preset threshold value U ref1 Whether it is true, if true, start the static reactive power compensation mode of the grid-side converter, so that the grid-side converter and the static synchronous compensator prov...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com