Data protection method, data protection device and solid-state disk storage system
A solid-state hard disk, storage system technology, applied in the computer field, can solve the problem of unsolved write amplification, and achieve the effect of reducing modification, ensuring security, and avoiding frequent rewriting
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
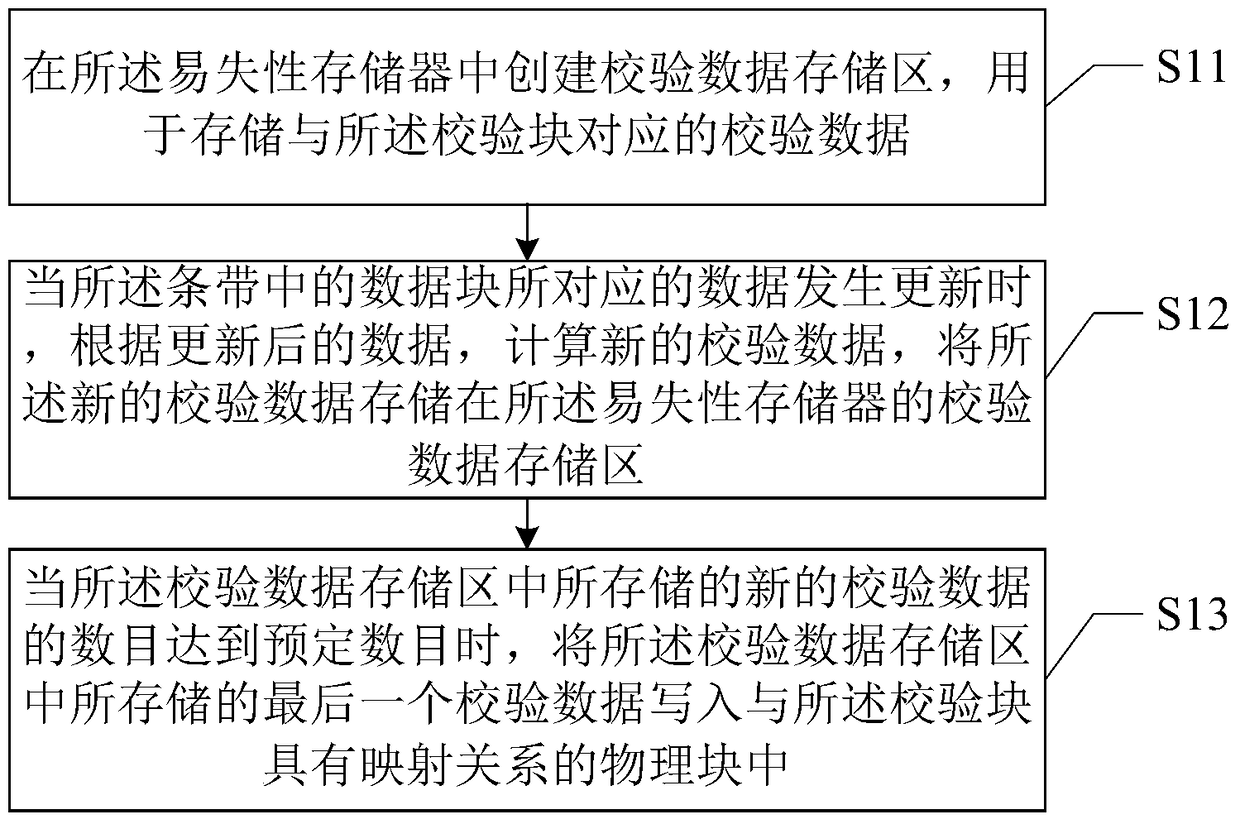
[0028] figure 2 is a flow chart of the data protection method in the first embodiment of the present invention. The method is applied to a solid-state hard disk storage system. In the embodiment of the present invention, the solid-state hard disk storage system at least includes a flash conversion layer, a volatile memory and a non-volatile memory.
[0029] In the embodiment of the present invention, the logic block layer in the flash translation layer is first striped in units of blocks, and each strip includes at least two data blocks corresponding to user data and one parity block. Wherein, the check blocks in each stripe correspond to the parity check values of other data blocks in the stripe. The parity blocks for each stripe are randomly distributed, depending on the flash translation layer. Each stripe is the same size. Here, the size of the stripe refers to the number of logical blocks included in the stripe. Preferably, each stripe includes 8 to 16 logical bloc...
no. 2 example
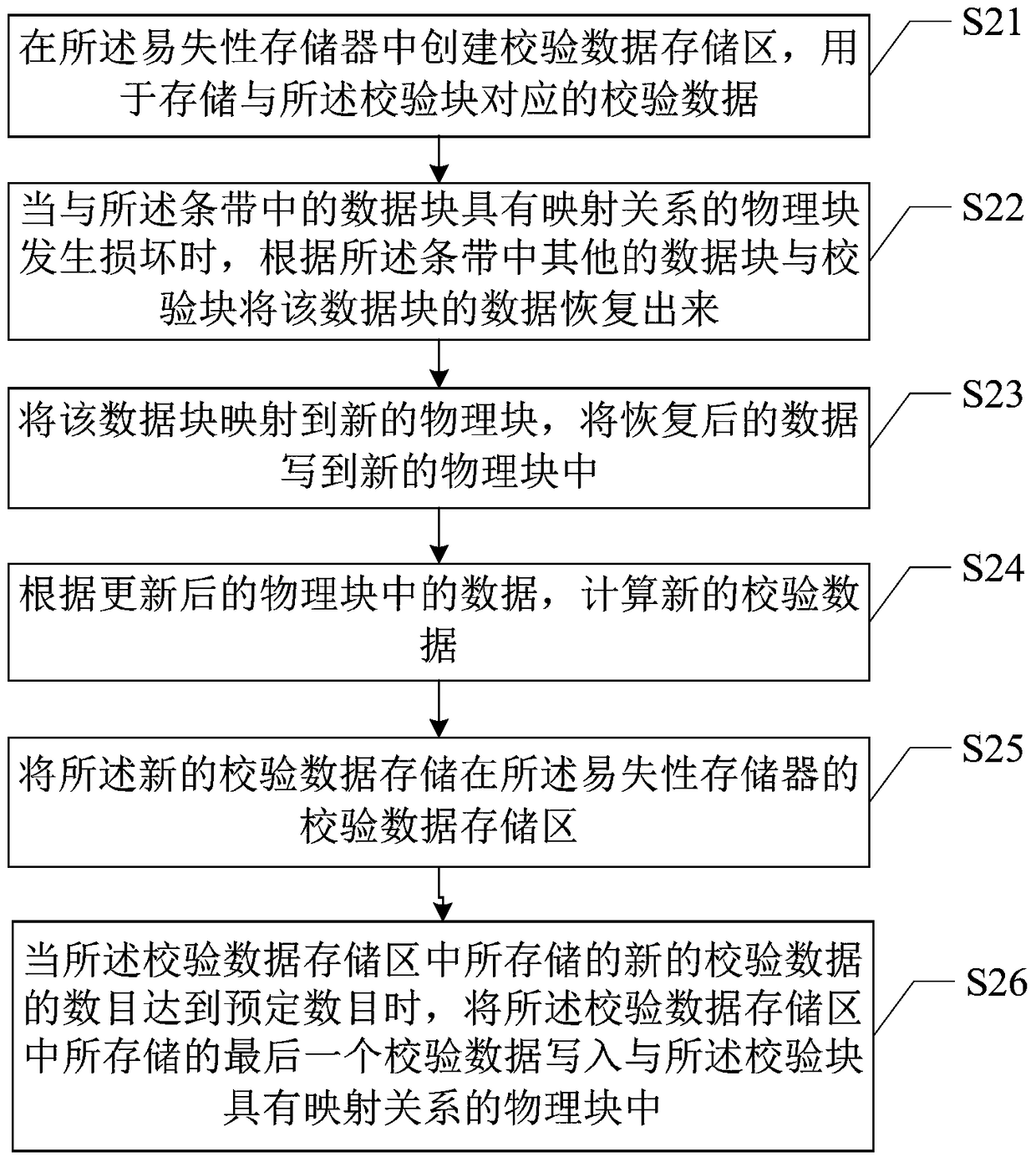
[0045] image 3 The above is a flow chart of the data protection method provided by the second embodiment of the present invention. Please refer to image 3 , the method may include:
[0046] Step S21, creating a check data storage area in the volatile memory for storing check data corresponding to the check block.
[0047] Step S22, when the physical block that has a mapping relationship with the data block in the stripe is damaged, recover the data of the data block according to other data blocks and parity blocks in the stripe.
[0048] Further, when a physical block that has a mapping relationship with a data block in the stripe is damaged, the damaged physical block can be marked as a special bad block, and the physical block marked as a special bad block does not enter recovery Process, when the number of new check data stored in the check data storage area reaches a predetermined number, mark the damaged physical block as a common bad block, and the physical block ma...
no. 3 example
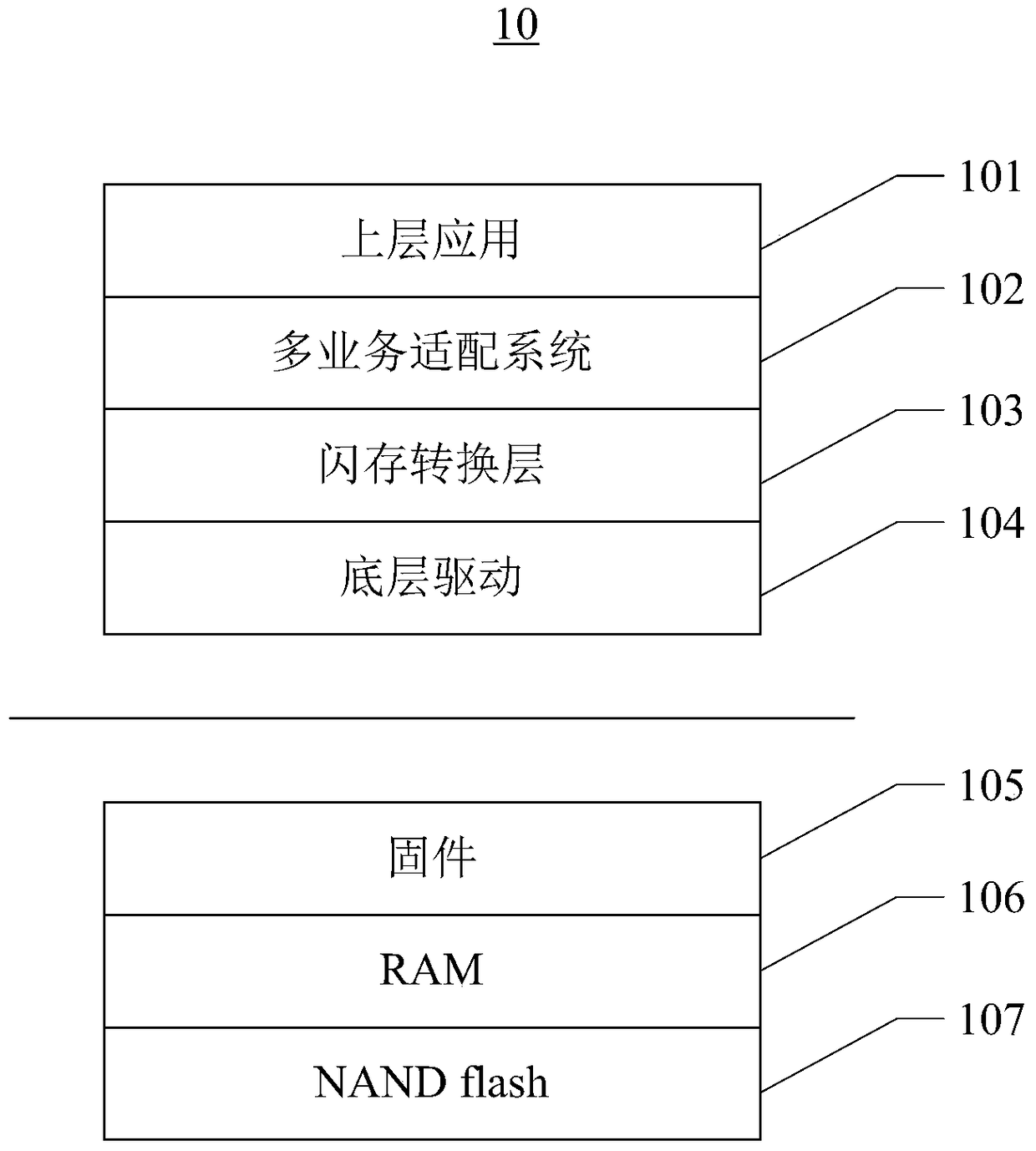
[0059] See Figure 5 , is a schematic structural diagram of a solid state disk storage system provided in the third embodiment of the present invention; please refer to Figure 5 , the solid state disk storage system 30 may at least include a flash conversion layer 31 , a volatile memory 32 , a nonvolatile memory 33 , and an energy storage element 34 .
[0060]The flash conversion layer 31 includes a striped logical block layer, each strip includes at least two data blocks and a parity block, and the non-volatile memory includes a mapping relationship with the logical block. physical block.
[0061] The flash conversion layer 31 is responsible for establishing and maintaining the logical block mapping table, realizing wear leveling, and garbage collection.
[0062] The energy storage element 34 stores electric energy when the solid-state hard disk is working normally, and it can be a capacitor or a battery element. When the solid-state hard disk loses power abnormally, the e...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com