The mmedco Ⅰ gene of Braconis schneidi and its application
A technology of wasp and gene, which is applied in the field of MmedCOⅠ gene of the medium red side wasp, can solve the problems of abnormal death of host larvae, increase the time and cost of investigation, and affect the statistical results, so as to shorten the detection time and avoid statistical errors. , the effect of improving the accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Example 1 Obtaining CO Ⅰ Gene of Zhonghong Sidegou Cocoon Peak
[0033] Log in to the NCBI website to download the registered nucleic acid sequence of the CO Ⅰ gene of Hymenoptera insects, use this sequence as the "Query" sequence, and use the local BLAST function of the BioEdit software to search for the transcriptome of the Braconis spp. The homologous sequence of the CO Ⅰ gene was obtained from the database, named Mmed CO Ⅰ.
[0034] The target gene sequence was compared with the NCBI non-redundant protein database, and it was found that the target gene had a high sequence similarity with insect CO Ⅰ family members, and the amino acid sequence identity with Cotesia vestalis CO Ⅰ was 79%. Therefore, the Mmed CO Ⅰ gene was judged to be the CO Ⅰ gene.
Embodiment 2
[0035] Example 2 Specific primers for amplifying the Mmed CO Ⅰ gene
[0036] The specific primers were designed by downloading the COI gene homologous sequences of host and non-host insects such as cotton bollworm, armyworm, and beet armyworm, and using the clustalx2.0 software to perform homologous comparison, and search for more than 2 bases according to the comparison results. The region with different bases is used as the 3' end sequence of the forward and reverse primers. In order to increase the specificity of the primer, the primer length should be more than 20 bases, the Tm value should be higher than 55°C, and the size of the amplified product fragment should be controlled at about 100-300bp. A total of 3 pairs of primers were designed according to the above principles, and only one pair of primers was found to be specific by PCR detection:
[0037] MmedCOI-F: 5'-ATTCGTTTGGAATTAGGTATACCAGGTAG-3';
[0038] MmedCOI-R: 5'-ACAGTTCATCCAGTTCCAAACACCAAC-3'.
[0039] Only u...
Embodiment 3
[0040] Example 3 Specificity and Sensitivity Test of Specific Primers
[0041] Specific detection:
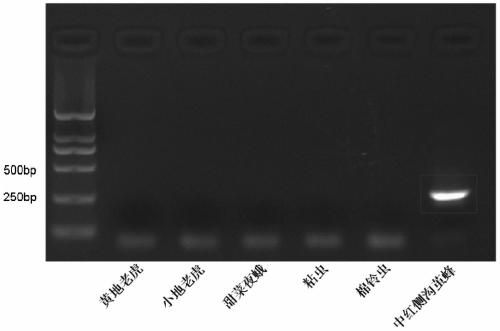
[0042] The genomic DNAs of cutworm, yellow cutworm, armyworm, cotton bollworm, beet armyworm, and red cutworm were extracted respectively, and whether there were non-specific bands were detected by PCR method, such as figure 1 shown. The results showed that only the DNA sample of Brachia schrenzo had a specific band, and the sequencing results showed that the band was the target sequence.
[0043] Sensitivity test:
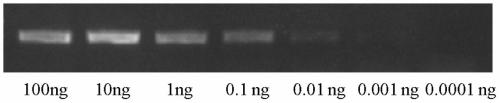
[0044] Dilute the DNA samples of Braconis sclerosus to different concentrations, and detect the PCR products of DNA samples at different concentrations, such as figure 2 shown. The results showed that the target sequence could be effectively detected even if the DNA sample content of Brachia schrenzia was 0.01ng.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com