A Distributed Passive Radar Target Detection Method in the Condition of No Direct Arrival Wave
A technology for passive radar and target detection, applied in radio wave measurement systems, radio wave reflection/reradiation, measurement devices, etc. To achieve the effect of avoiding ambiguous positioning and target matching problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0026] The present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
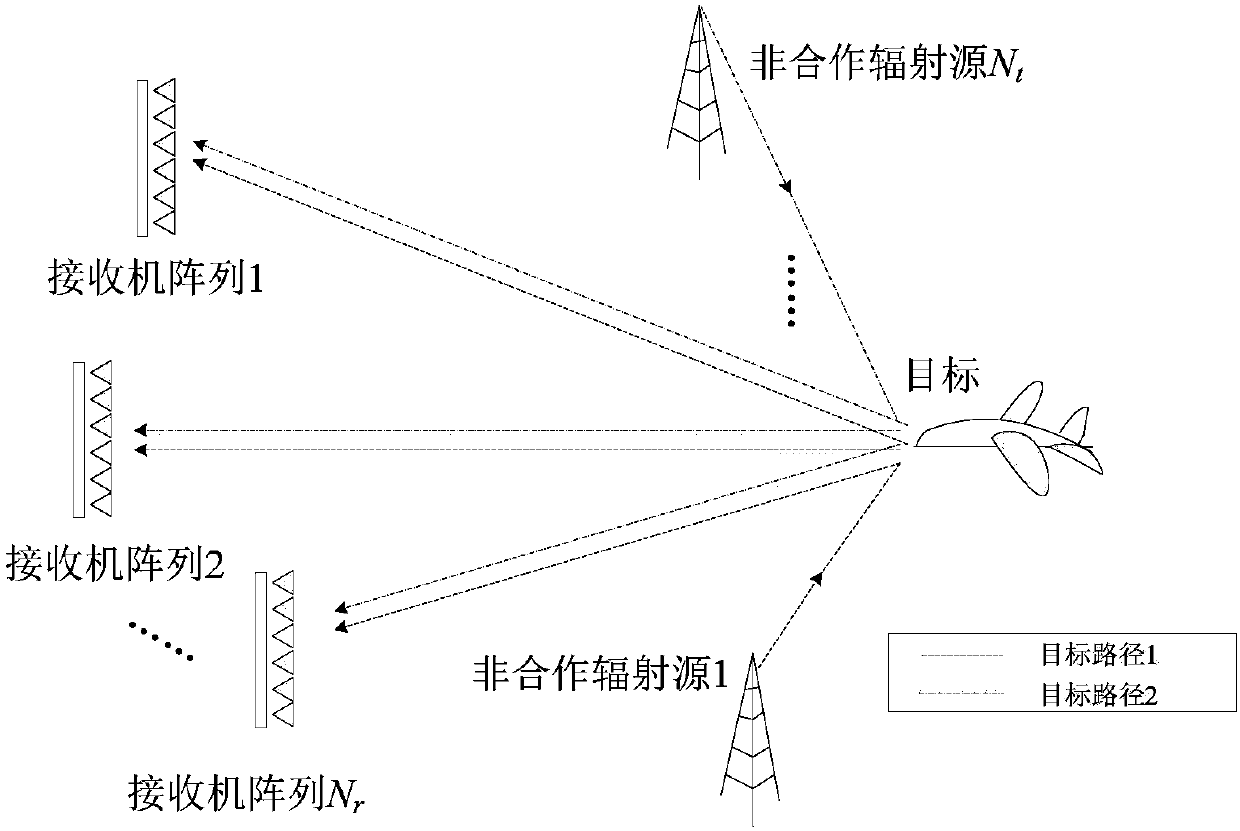
[0027] Such as figure 1 As shown, the distributed passive radar system includes N t transmitters, which are also called non-cooperative radiation sources in the field of passive radar, N r receiver array, 1 target, where N t ≥2,N r ≥2.
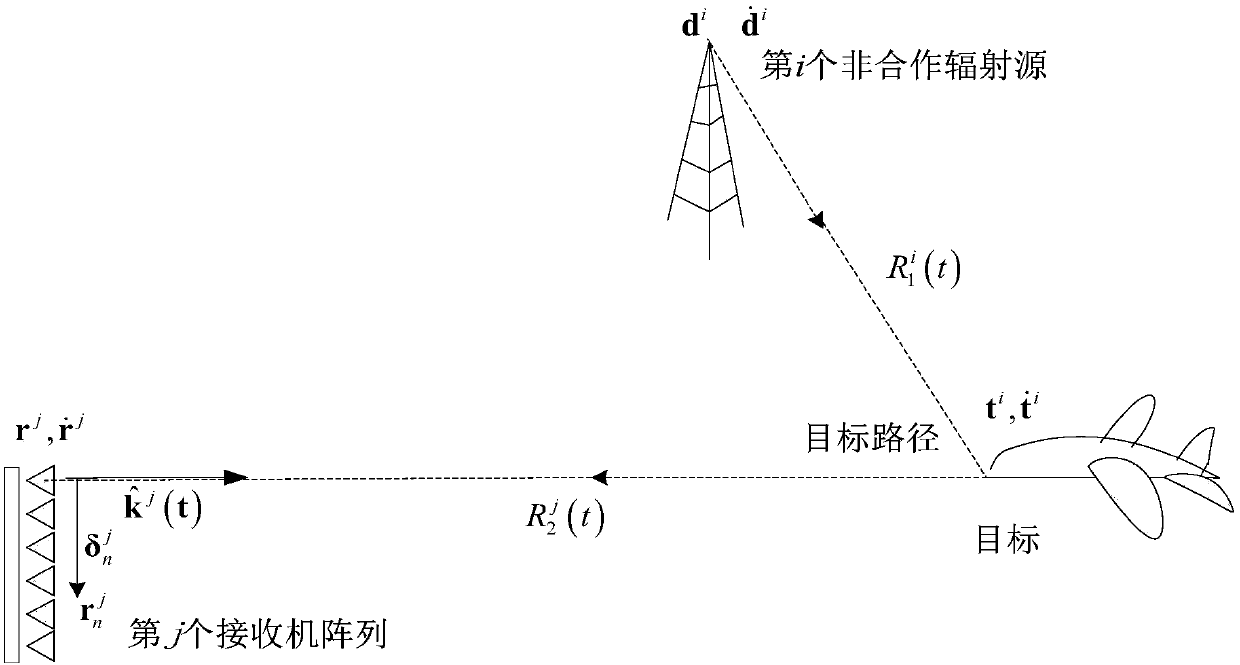
[0028] Such as figure 2 As shown, the geometric relationship and signal environment of the ij-th bistatic pair, the position and velocity of the i-th transmitter are denoted as d i with i=1,...,N t , the position and velocity of the jth receiver array are denoted as r j with j=1,...,N r , while the position and velocity of the target are denoted as t and where d i , r j , t, are all functions of time. In general, the transmitter and receiver, and the target are moving. The distance from the i-th transmitter to the j-th receiver is Similarly, with represent the distance from the i-th transmitter ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com