Method in microprocessor
A microprocessor and micro-instruction technology, applied in electrical digital data processing, digital data processing components, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of high cost of FMA hardware setup, increased power consumption, and complexity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
other Embodiment approach
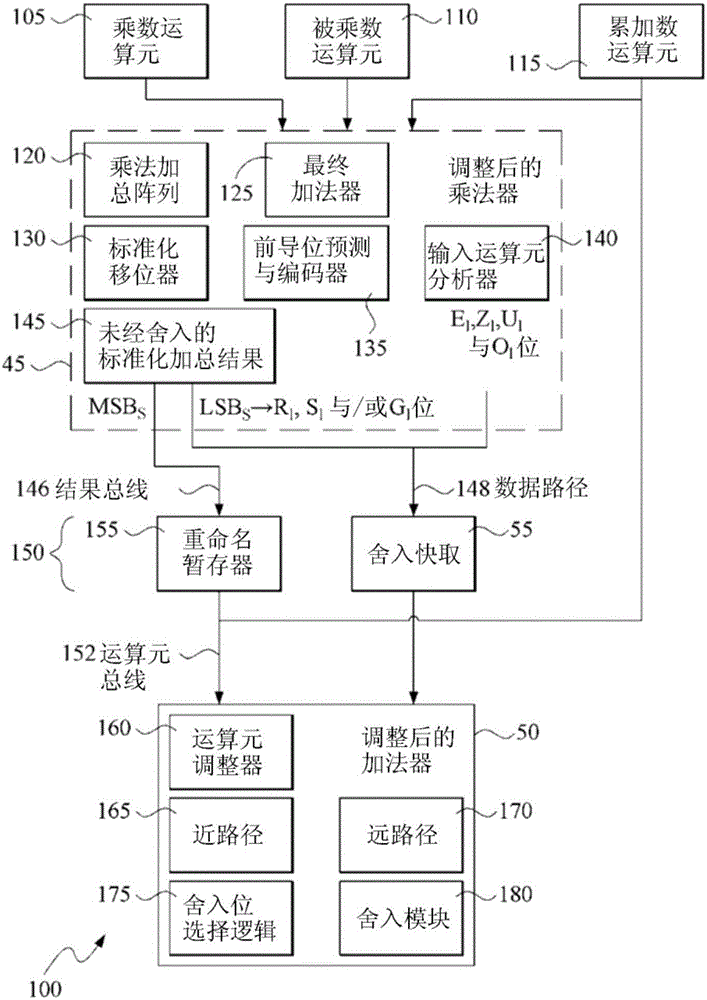
[0256] In other implementations, the rounding cache can be an addressable register bit, a content-accessible memory, a queue storage space, or a mapping function.
other Embodiment approach
[0257] Other embodiments may provide multiple independent hardware or execution units to execute the first microinstruction, and / or provide multiple independent hardware or execution units to execute the second microinstruction. Likewise, these embodiments may also provide multiple round caches for different source code instruction streams or data streams, or various embodiments of multi-core computer processors, if advantageous.
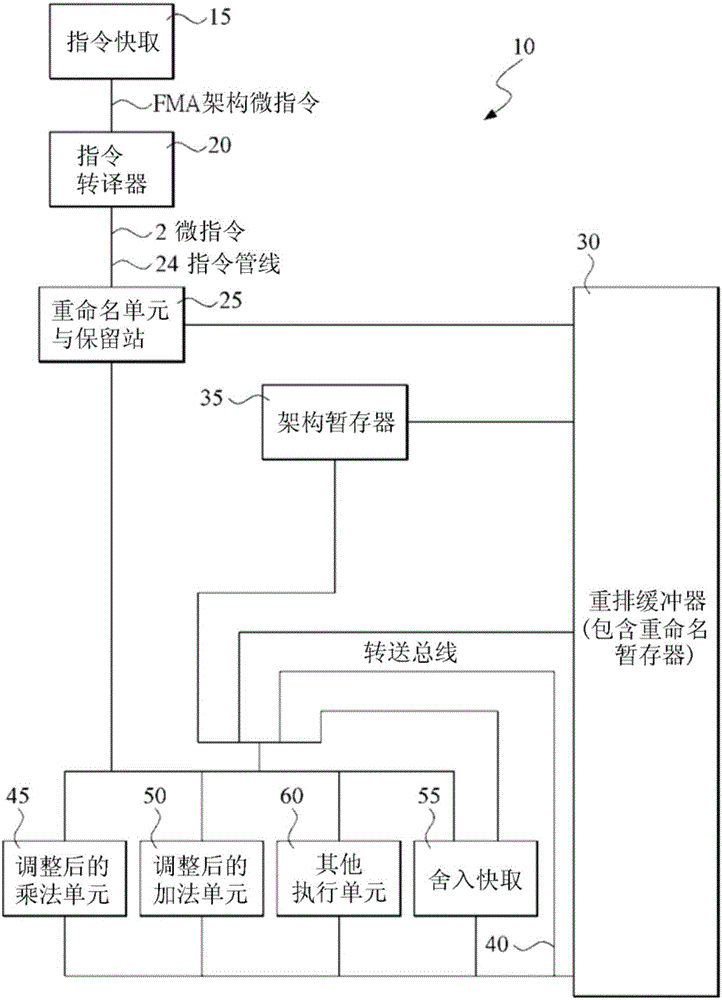
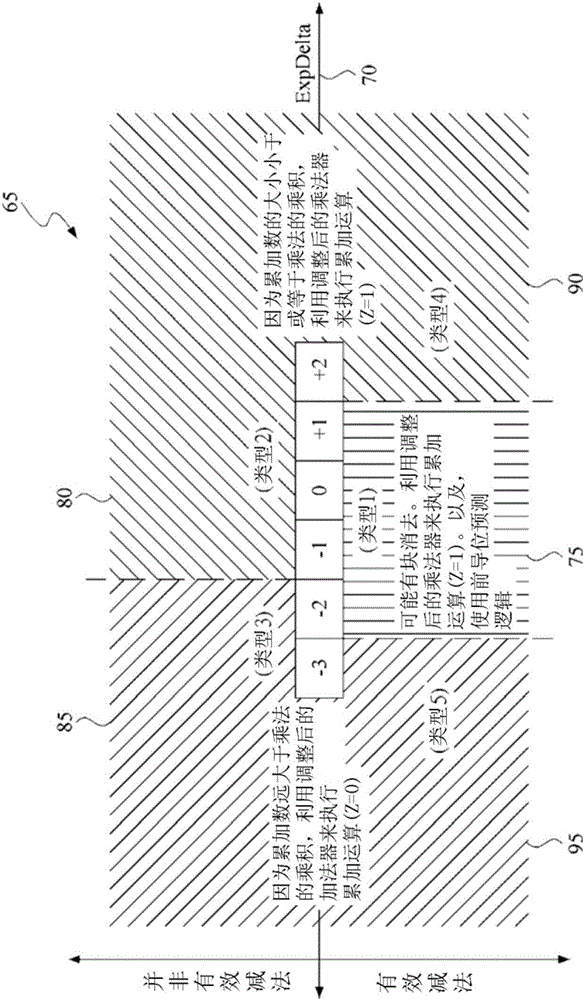
[0258] This implementation is for superscalar, non-sequential instruction dispatch, but other implementations can also be used for in-order instruction dispatch, for example, by removing instructions from the instruction cache and providing them to the data forwarding network. Distributed from the provided multiplication unit to a separate addition unit. The instantiation of the classification of FMA operations by the present invention, and the minimal amount of hardware adjustments required by the present invention, also have advantages in sequenti...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com