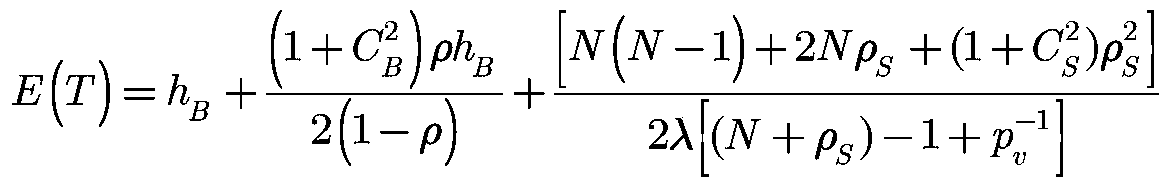Power control method of wireless sensor network gateway node based on n-policy
A wireless sensor network and gateway node technology, applied in the field of power control of wireless sensor network gateway nodes based on N strategy, can solve the practical problems of increasing node delay sleep, node delay start, and not fully considering node sleep and business Performance improvement, node delay, sleep node delay start and other issues, to achieve the effect of detailed scene setting, reasonable algorithm design, and easy implementation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0069] Step 1: Scenario description;
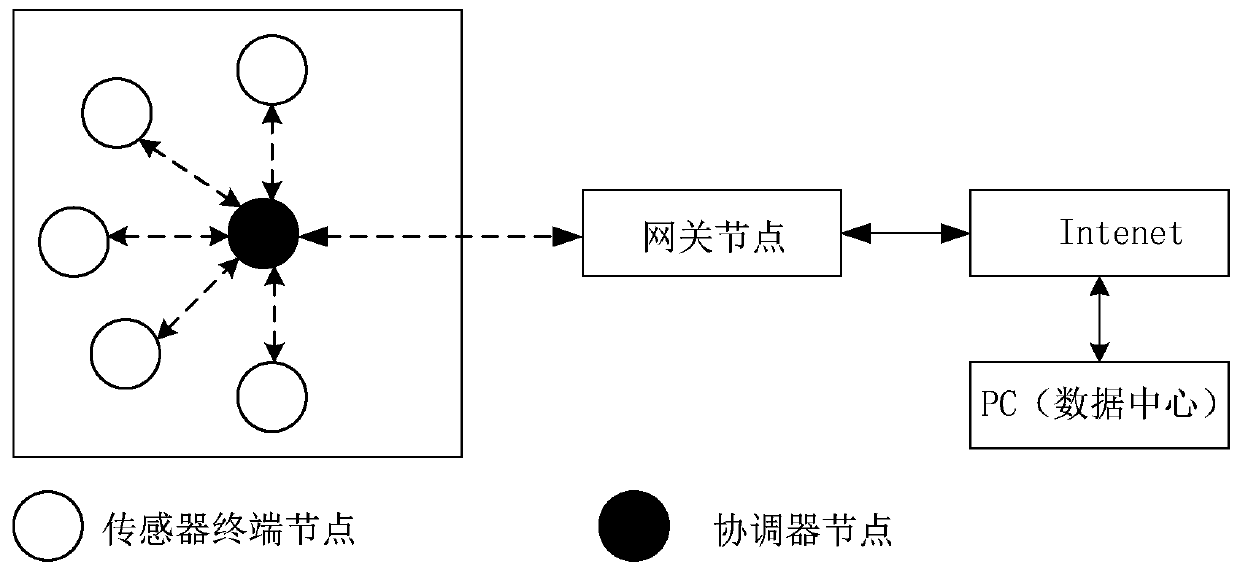
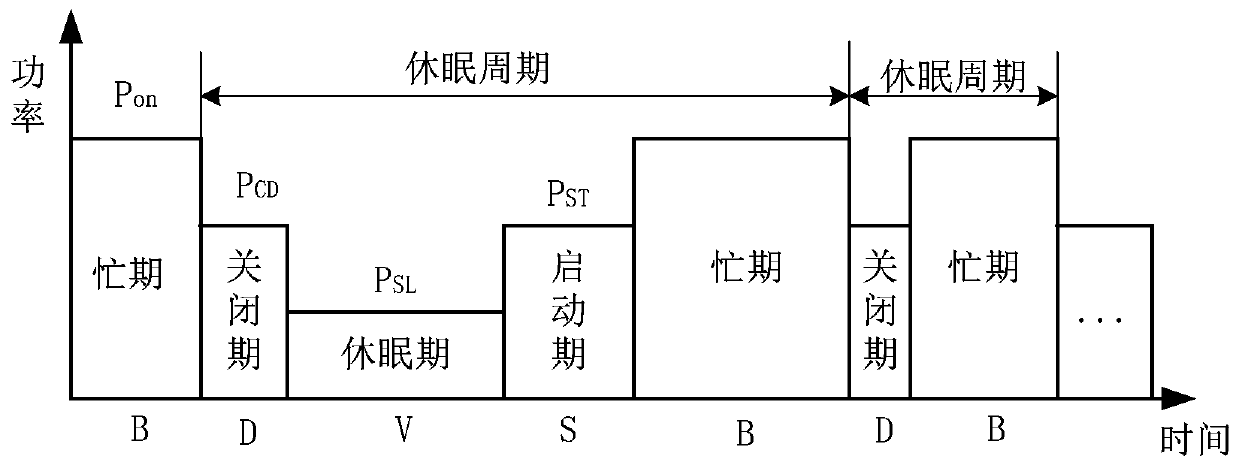
[0070] like figure 1 As shown, the wireless sensor network is composed of many nodes, the core of which is the gateway node. Therefore, to improve network performance and reduce system energy consumption, the most direct method is to study the sleep strategy of gateway nodes. However, node dormancy means that it will no longer work and no longer participate in cooperation during the dormancy period. Arrived data packets will accumulate in the cache of the node and stay for a long time until the node is woken up and put into work again, but this will increase virtually. The residence time of the data packet at this node will be affected, which in turn will affect the average delay of the entire system. The present invention differs from the previous method of extending the life cycle of nodes in wireless sensor networks, focuses on researching gateway nodes from reality, proposes an N-strategy gateway node sleep method, and comprehensivel...
Embodiment 2
[0113] This embodiment proposes a suboptimal method, which simplifies the mathematical expression and is more conducive to practical engineering applications.
[0114] Specifically, we set the shutdown period to 0, so that the dormancy probability p v =1. The N-strategy sleep method we proposed is equivalent to a 1-strategy sleep method. In this special case:
[0115] h S =E[S] / N (12)
[0116] We can derive the average power under this assumption:
[0117]
[0118] Likewise, we can derive the average length of stay under this assumption:
[0119]
[0120] Furthermore, we combine formula (13) and formula (14) to obtain the compromise relationship between the average stay time E(T) and the average node energy consumption E(P) under this assumption:
[0121]
[0122] in:
Embodiment 3
[0124] In the actual application process, we sometimes pay more attention to the maximum delay characteristic of the system, because it may greatly affect the data transmission effect. Therefore, this embodiment focuses on trying to derive the variance characteristic of the average stay time of nodes.
[0125] We use inverse Laplace transform to formula (4) to try to deduce the variance characteristics of the average stay time of nodes, but the exact mathematical expression cannot be given because it is too complicated. Fortunately, we can deduce the exact expression of the average stay time of nodes in the case of N=1, which can be used to judge the performance of nodes and guide practice.
[0126]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com