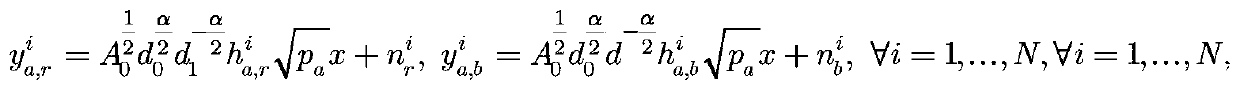Joint Path Selection and Power Allocation Method for Energy Harvesting Nodes in Wireless Sensor Networks
A wireless sensor network, energy harvesting technology, applied in power management, wireless communication, energy reduction and other directions, can solve the problem of insufficient consideration of energy harvesting factors, performance improvement, joint resource allocation performance optimization, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0073] The present invention is aimed at a special application scene, comes from practical application, and the scene setting is meticulous and reasonable, and has practical guiding significance. Specifically, a joint path selection and power allocation method for energy harvesting nodes in a wireless sensor network, comprising the following steps:
[0074] Step 1: System scenario analysis, problem description;
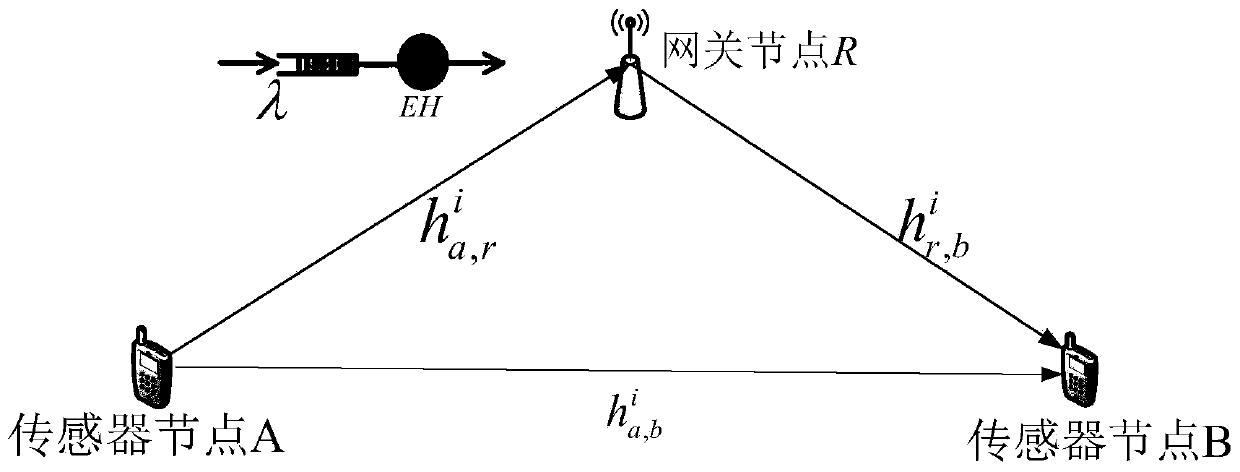
[0075] Consider a non-real-time data transmission scenario of a wireless sensor network based on energy harvesting. In the scenario, there is a sensor node A with stable power supply, a relay node R for energy harvesting and a target communication sensor node B. Consider sensor node A with stable power supply There is a direct path between the sensor node B and the target communication, and an energy harvesting relay node R can cooperate to forward information. The energy harvesting relay node R adopts the decoding and forwarding working mode. A transmission process i...
Embodiment 2
[0112] In order to make the algorithm closer to the actual application, it can better reflect the channel situation and be closer to the real channel. Further improvement on the basis of the foregoing embodiment one. Specifically, the use of the Bernoulli model is to simplify the calculation, which can better reflect the situation of the channel and is closer to the actual channel.
[0113] Said step 2 includes:
[0114] Step 2.1: Determine whether the decoding is successful
[0115]
[0116] In order to reduce the computational complexity, the Bernoulli process is used to describe whether the decoding is successful or not, where p is the parameter of the Bernoulli process, and D i Indicates whether the i-th transmission is successfully decoded, D i =1 means successful decoding, D i =0 means decoding failure, and the Bernoulli parameter p is expressed as:
[0117]
[0118] Step 2.2: We again define the link selection result
[0119] where r i = 1 means that the ...
Embodiment 3
[0128] In order to make the algorithm closer to practical application, we adopt a simplified energy harvesting curve, which can better reflect the real model of energy harvesting, simple and effective. It can be used on the basis of the foregoing embodiment one. The energy harvesting model uses a Bernoulli process, specifically,
[0129]
[0130] Among them: E represents the basic energy unit, Represents the energy collected in the i-th time slot, then the average energy collected in each time slot can be expressed as:
[0131]
[0132] Among them: ρ represents the parameters of the Bernoulli process, 2T p Indicates the length of a time slot; correspondingly, the energy causal constraint can be expressed as:
[0133]
[0134] For simplicity, let's assume that the battery capacity of the relay is large enough:
[0135]
[0136]
[0137] Among them, ε i+1 Indicates the remaining energy in the battery after the i+1th transmission slot, (x) + Indicates the fu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com