Patents
Literature
138 results about "Ubiquitous computing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
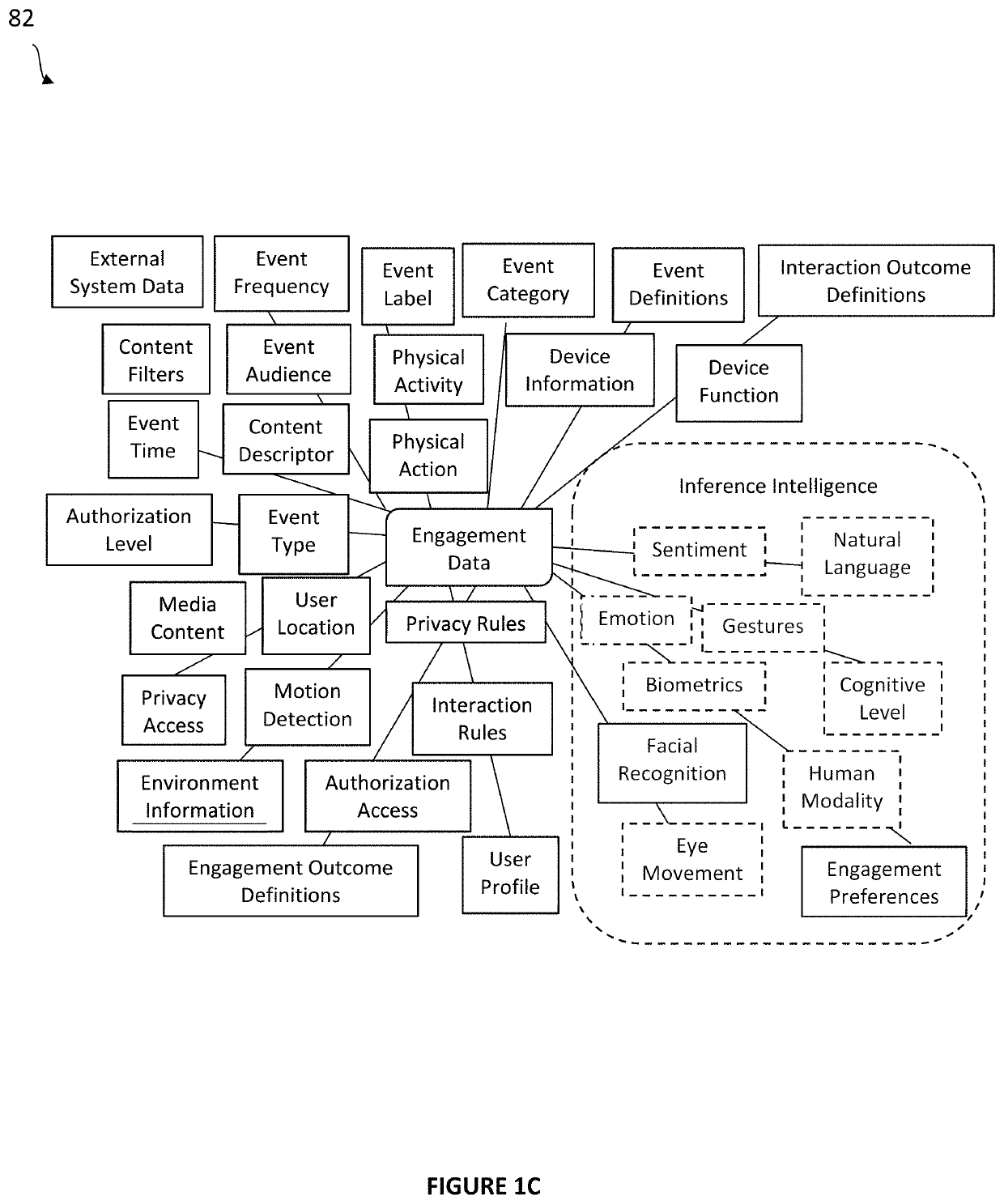
Ubiquitous computing (or "ubicomp") is a concept in software engineering and computer science where computing is made to appear anytime and everywhere. In contrast to desktop computing, ubiquitous computing can occur using any device, in any location, and in any format. A user interacts with the computer, which can exist in many different forms, including laptop computers, tablets and terminals in everyday objects such as a refrigerator or a pair of glasses. The underlying technologies to support ubiquitous computing include Internet, advanced middleware, operating system, mobile code, sensors, microprocessors, new I/O and user interfaces, computer networks, mobile protocols, location and positioning, and new materials.
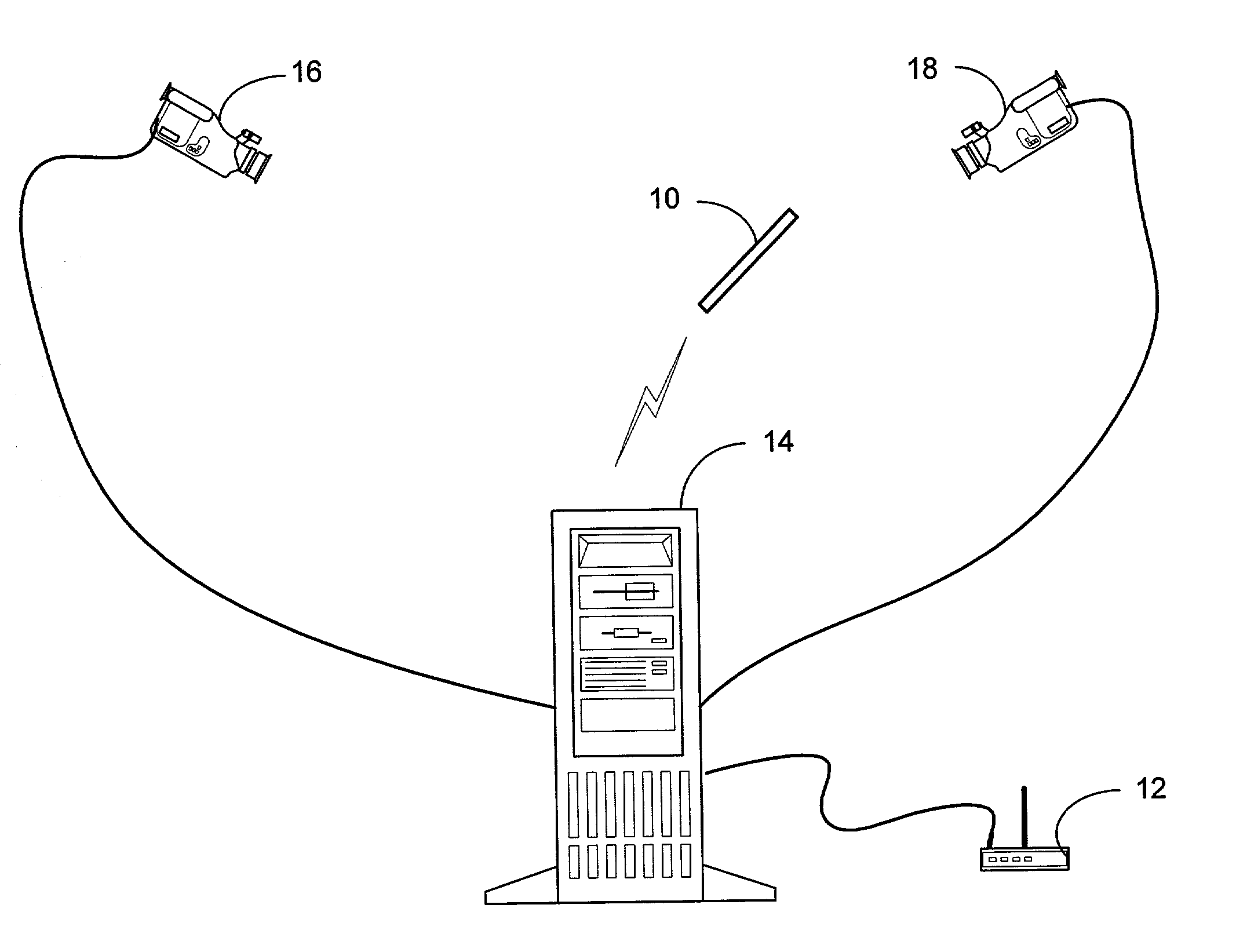
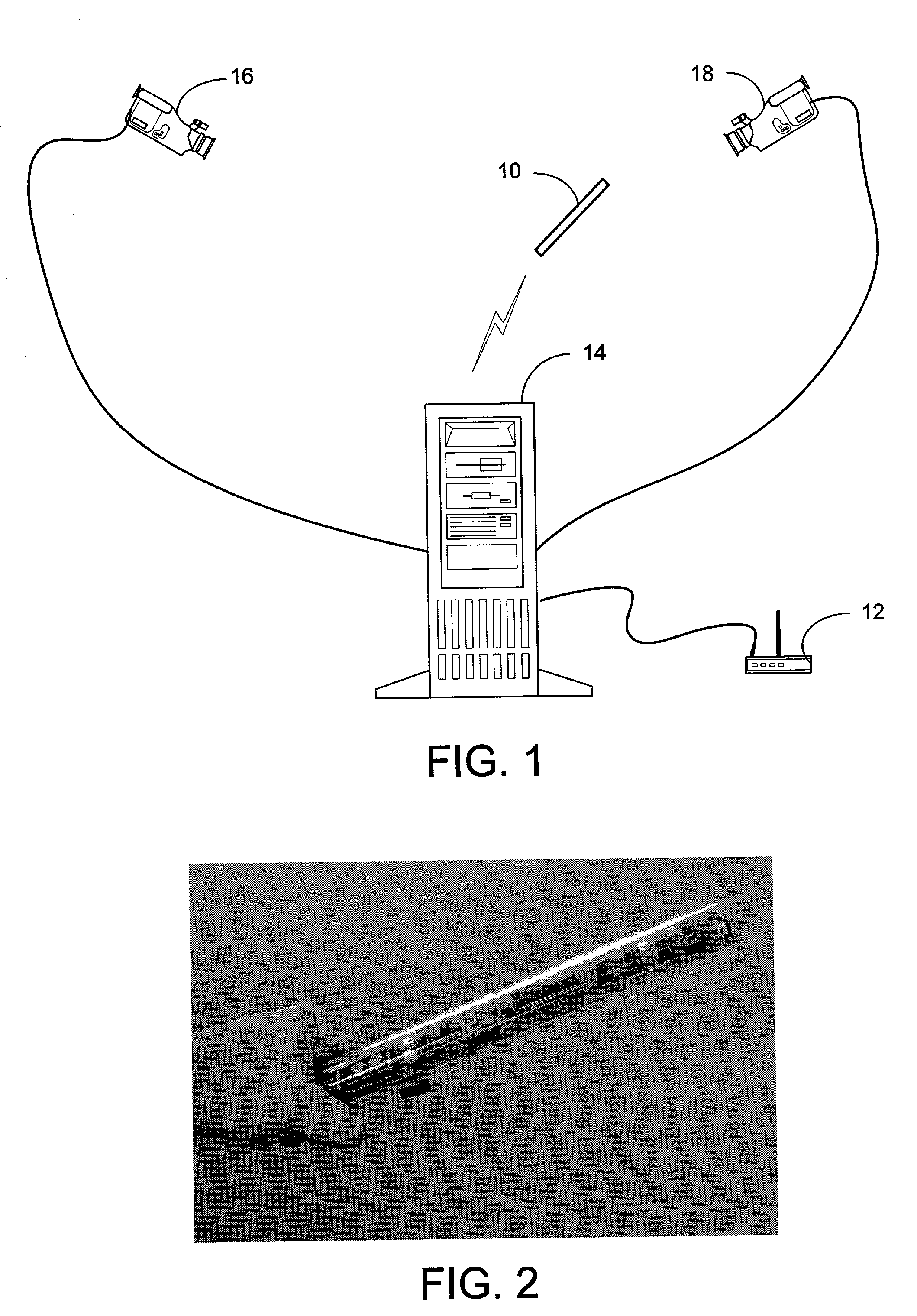
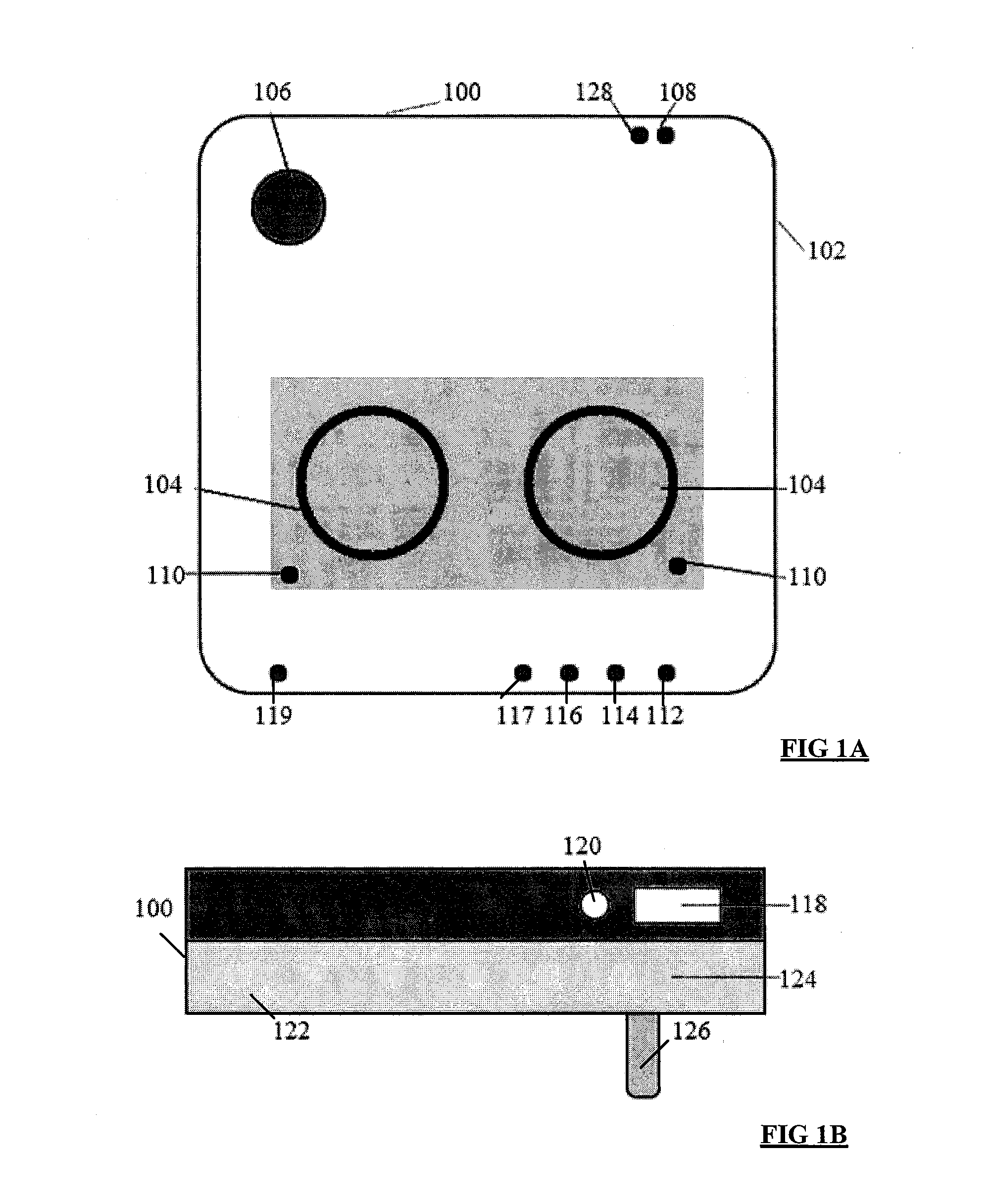
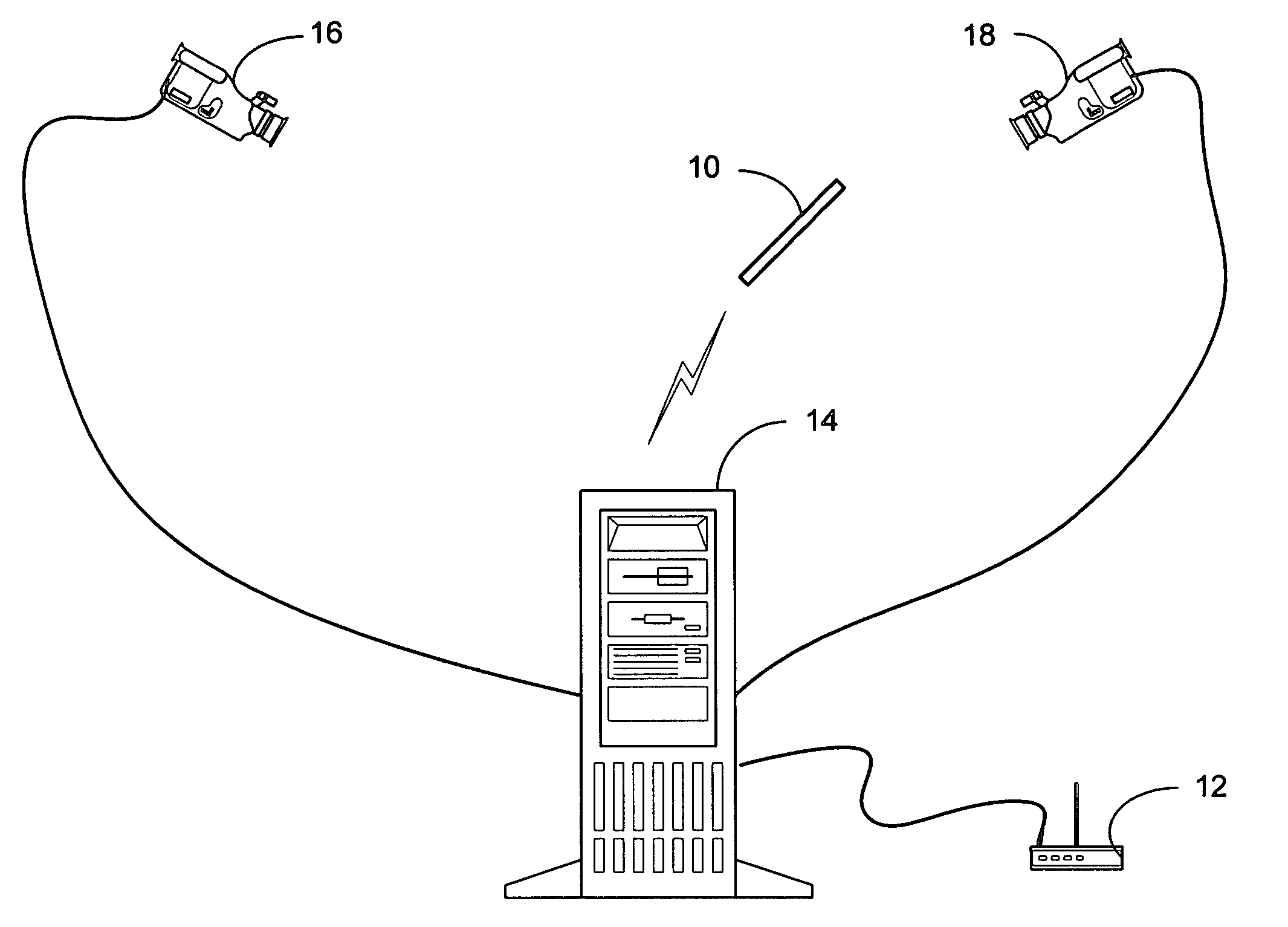
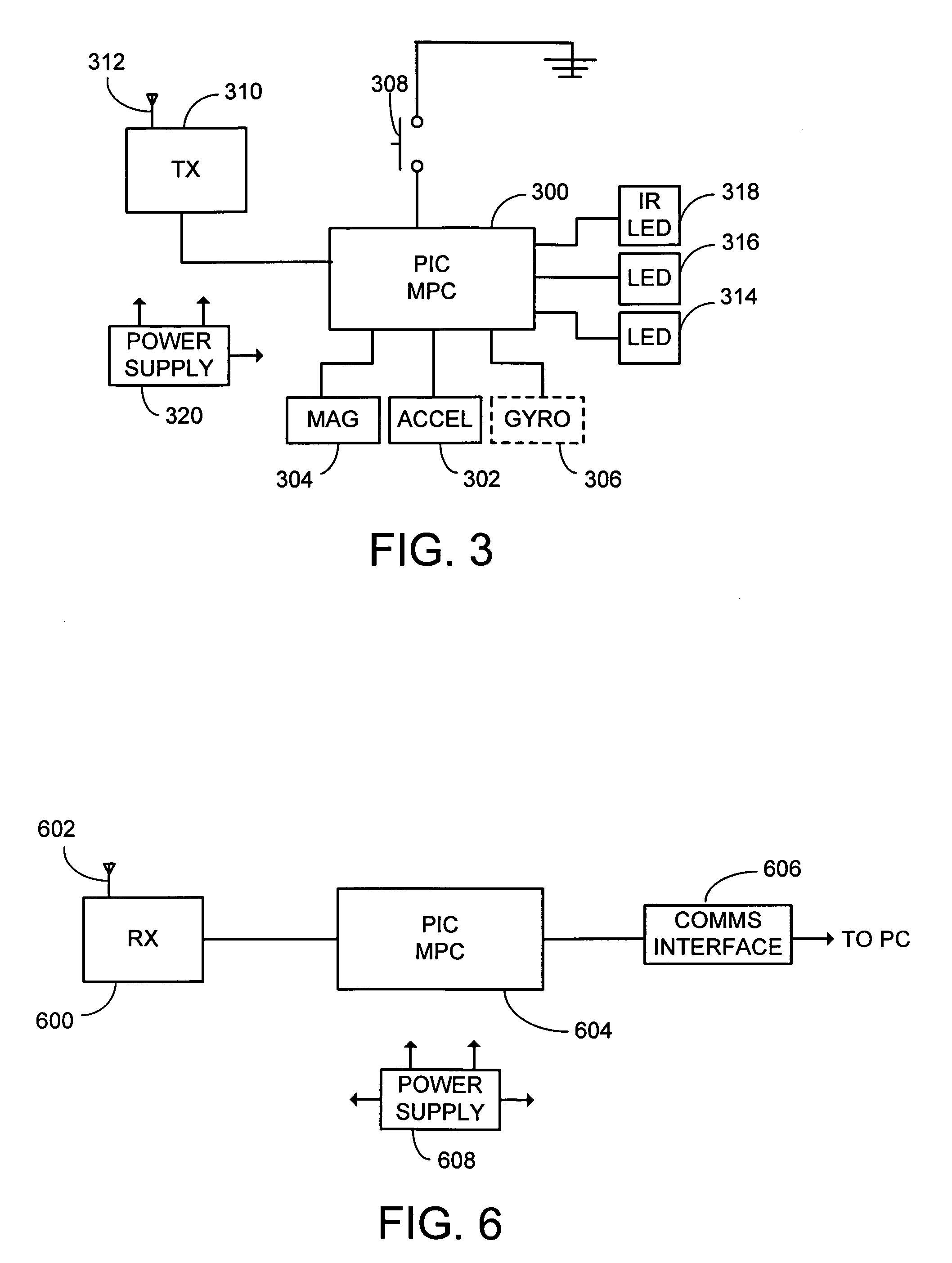
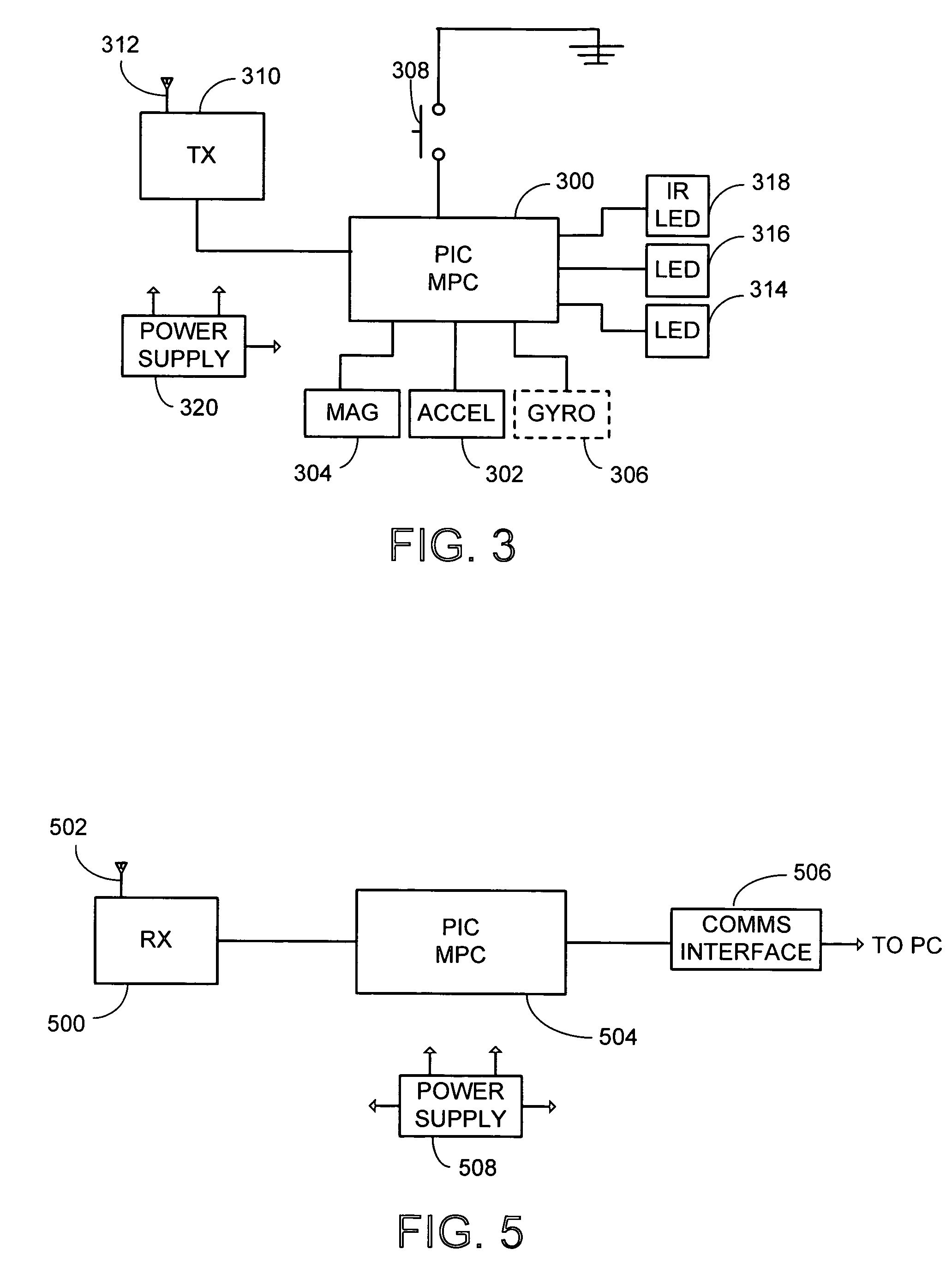
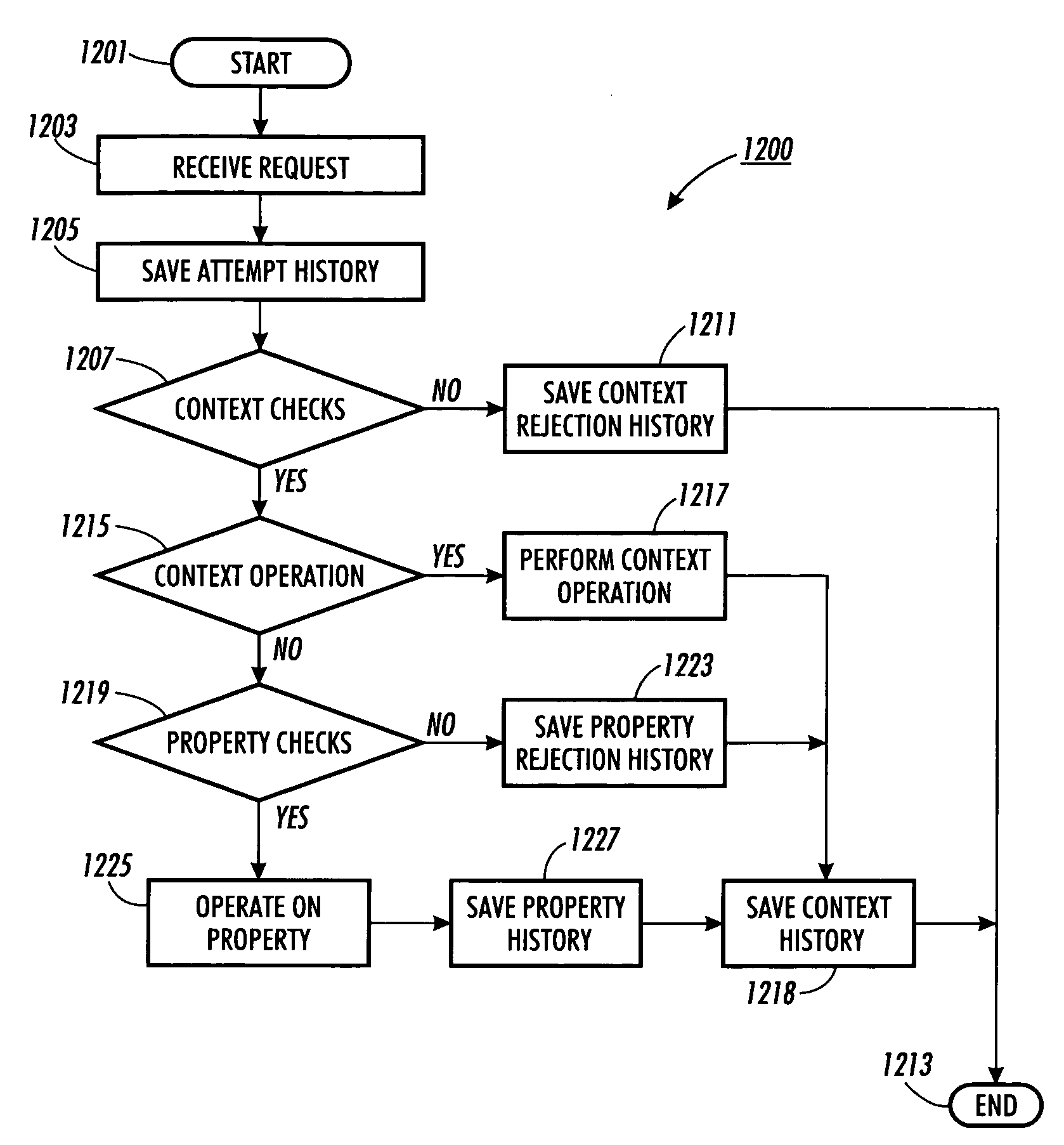
System and process for controlling electronic components in a ubiquitous computing environment using multimodal integration
ActiveUS6990639B2Increase choiceMade robustTransmission systemsCathode-ray tube indicatorsPointing deviceElectronic component
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
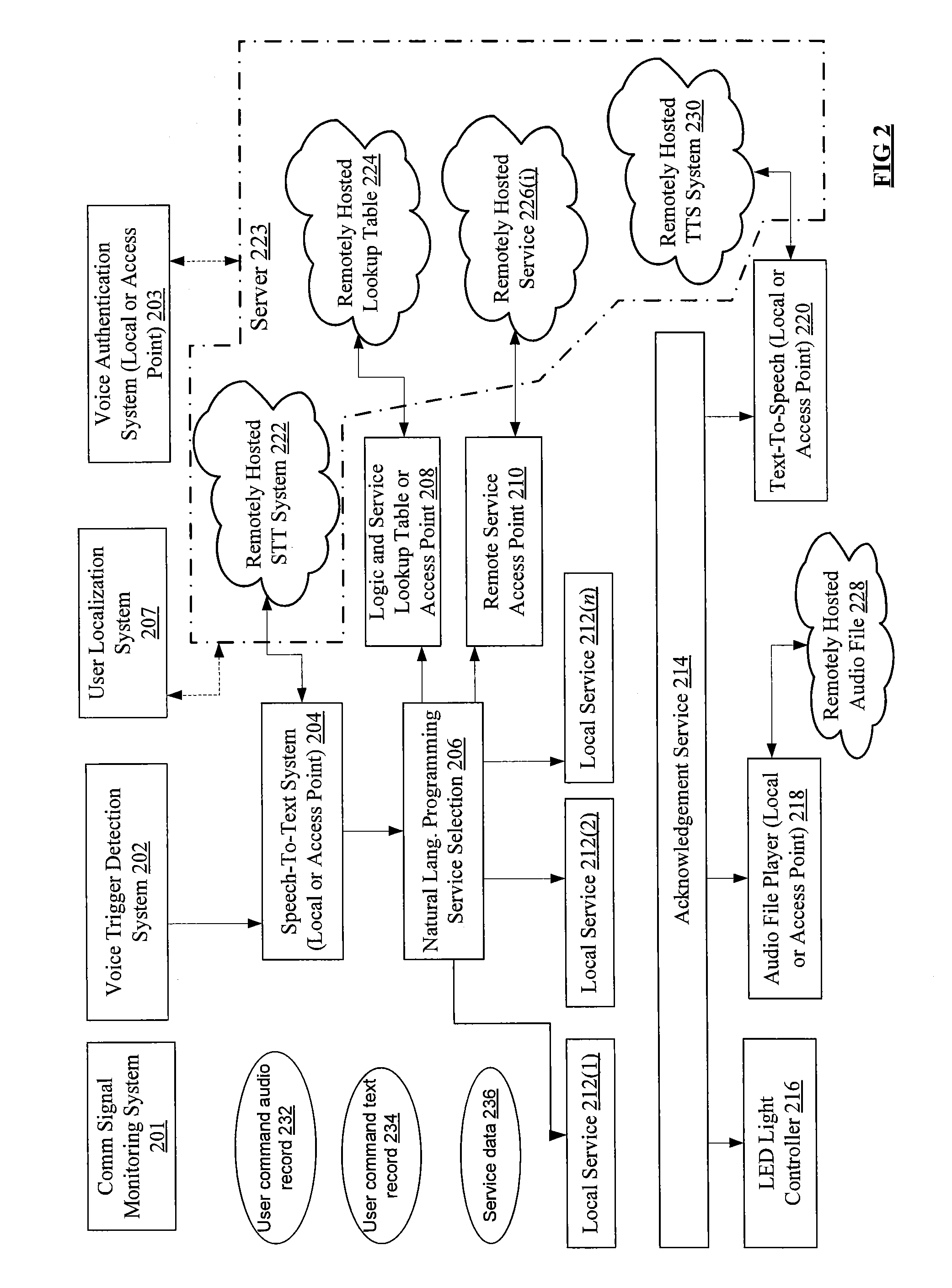
Voice-Operated Internet-Ready Ubiquitous Computing Device and Method Thereof
InactiveUS20140136195A1Special service for subscribersSpeech recognitionComputer networkThe Internet
In one aspect of this disclosure, a voice-operated internet-ready ubiquitous computing device and a method implemented by the computing device are disclosed. A sound input associated with a user is received at the first computing device, and in response to receiving the sound input, the first computing device establishes a voice session associated with the user. The first computing device then determines a session quality associated with the voice input, and sends the session quality to a further computing device such as a second computing device or a server. The first computing device will receive a request to transfer the voice session to a second computing device; and in response to receiving the request, transfers the voice session to the second computing device.
Owner:UNIFIED COMP INTELLIGENCE
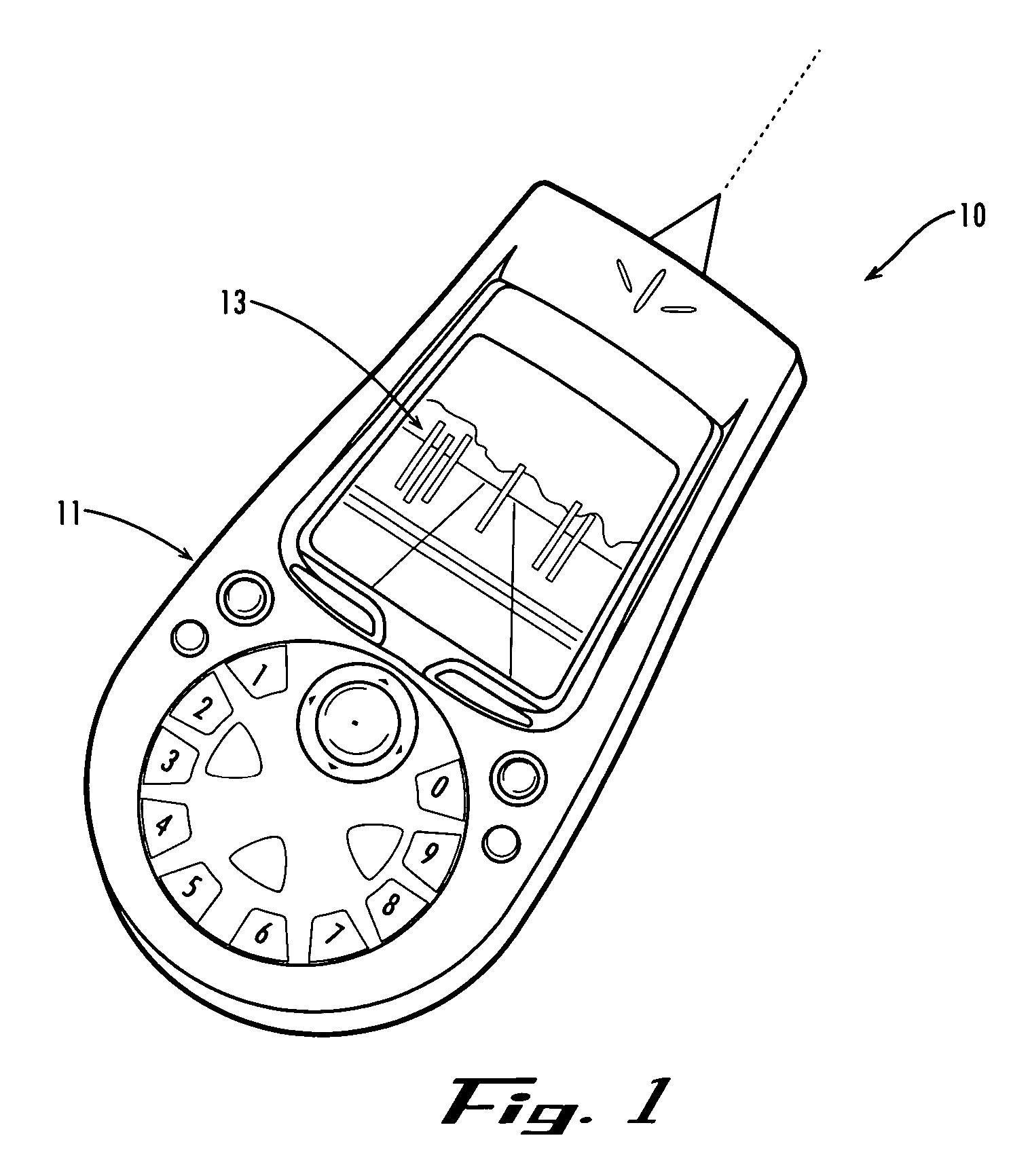
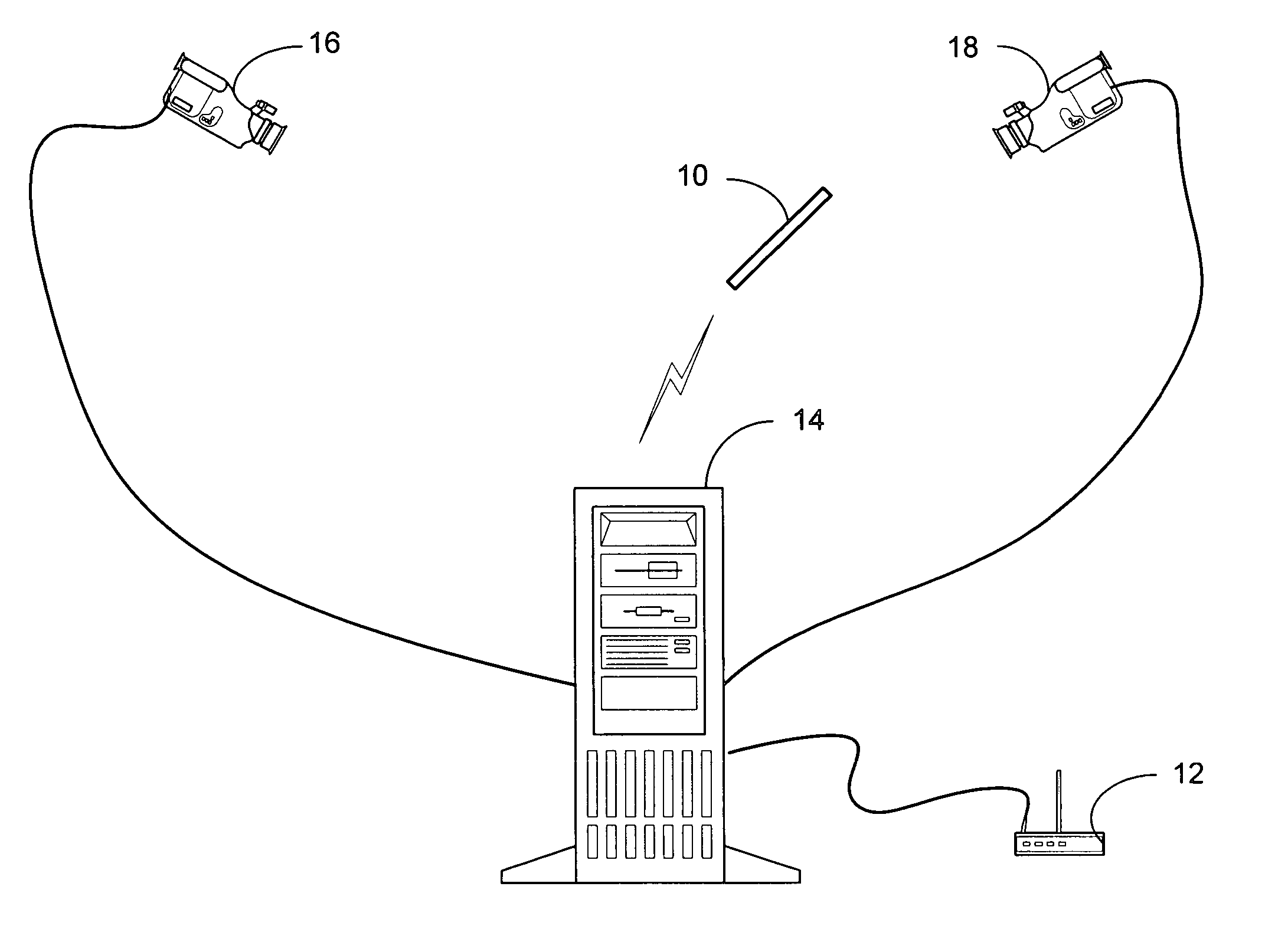
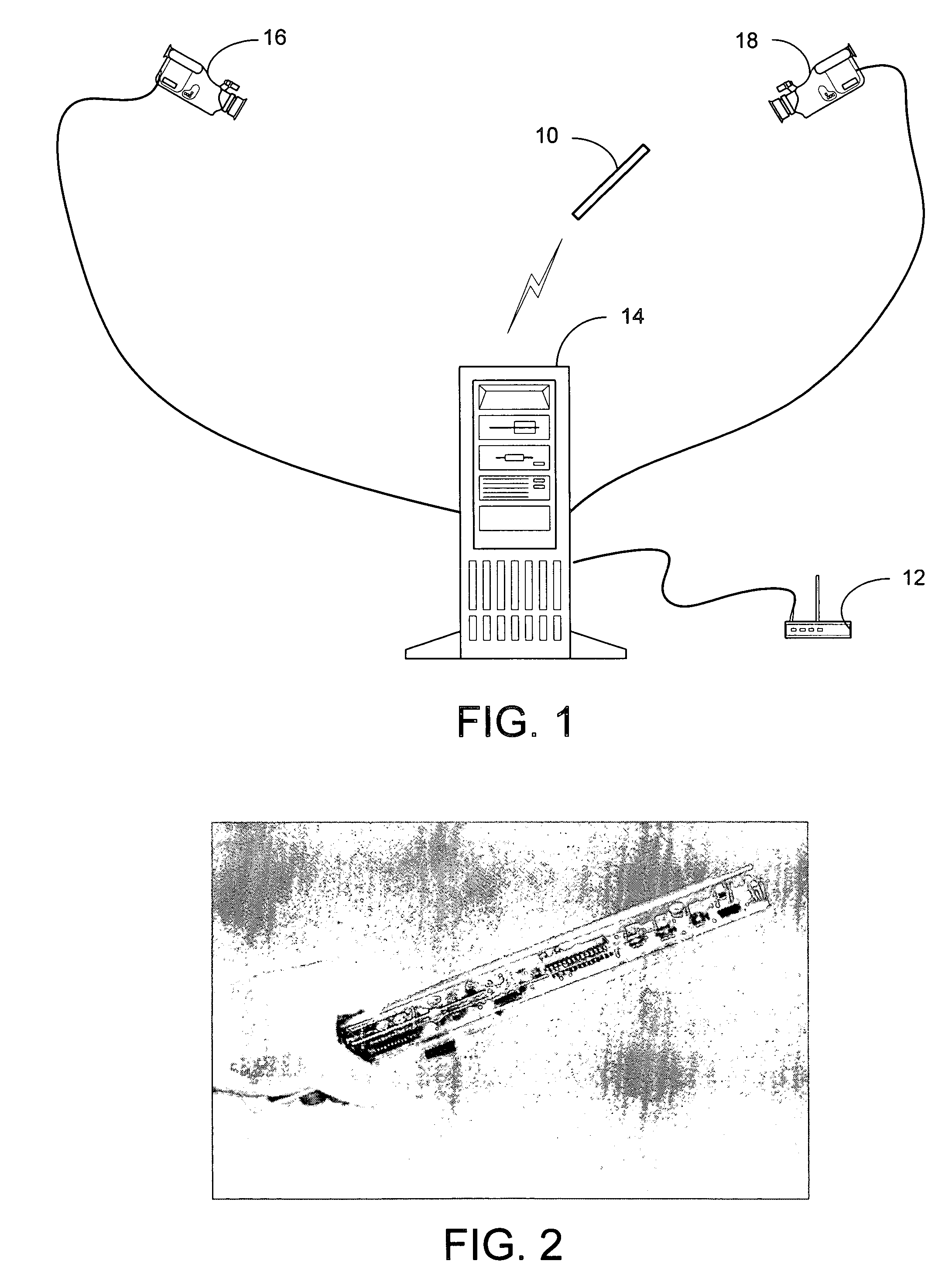
Method and apparatus for point-and-send data transfer within an ubiquitous computing environment
A point-and-send user interface is disclosed wherein a user can point a handheld unit at one of a plurality of electronic devices in a physical environment to select the electronic device and send data to it. Physical feedback can be provided to inform the user of the success and / or other status of the selection and data transfer process. A computer implemented method includes providing a handheld unit adapted to be contacted and moved by a user within a ubiquitous computing environment; receiving sensor data indicating whether the handheld unit is substantially pointed at an electronic device within a ubiquitous computing environment; determining whether an electronic device within the ubiquitous computing environment has been selected by a user based at least in part on the sensor data; and providing the user with physical feedback through the handheld unit upon determining that an electronic device within the ubiquitous computing has been selected.
Owner:OUTLAND RES
System and Method for Pervasive Computing
ActiveUS20110055317A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsUbiquitous computingCloud computing
A method and system for pervasive computing are disclosed. According to one embodiment, a computer implemented method comprises a server communicating with a first device in a cloud computing environment, wherein the first device can detect surrounding devices, and an application program executable by the server, wherein the application program is controlled by the first device and the output of the application program is directed by the server to one of the devices detected by the first device.
Owner:AMAZON TECH INC +11
System and process for selecting objects in a ubiquitous computing environment
InactiveUS20050156883A1Input/output for user-computer interactionTransmission systemsTransceiverNetwork connection
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
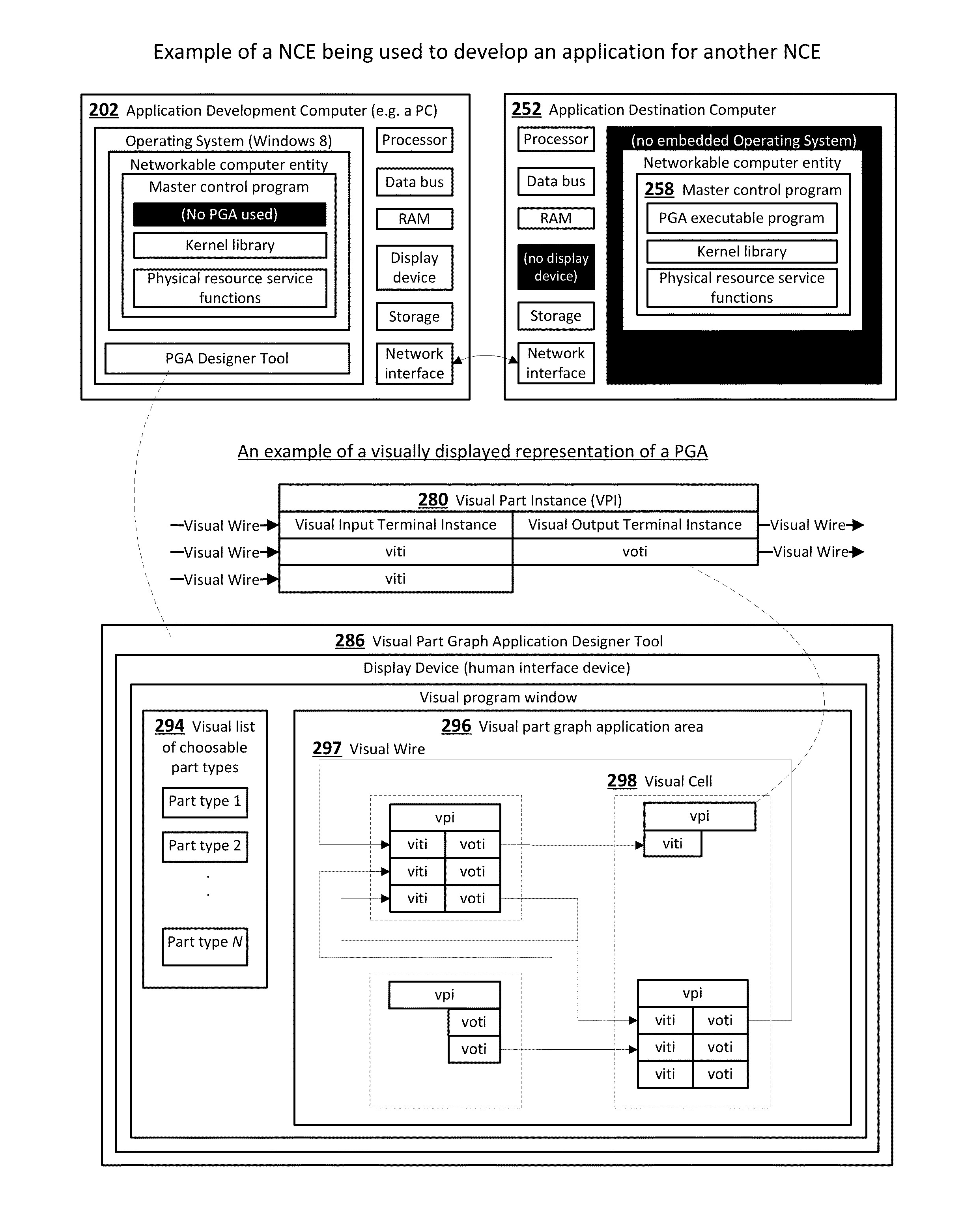
System and methods for end-users to graphically program and manage computers and devices
InactiveUS20140359558A1Reduce needReduce testingSoftware designVisual/graphical programmingInformation processingGraphics
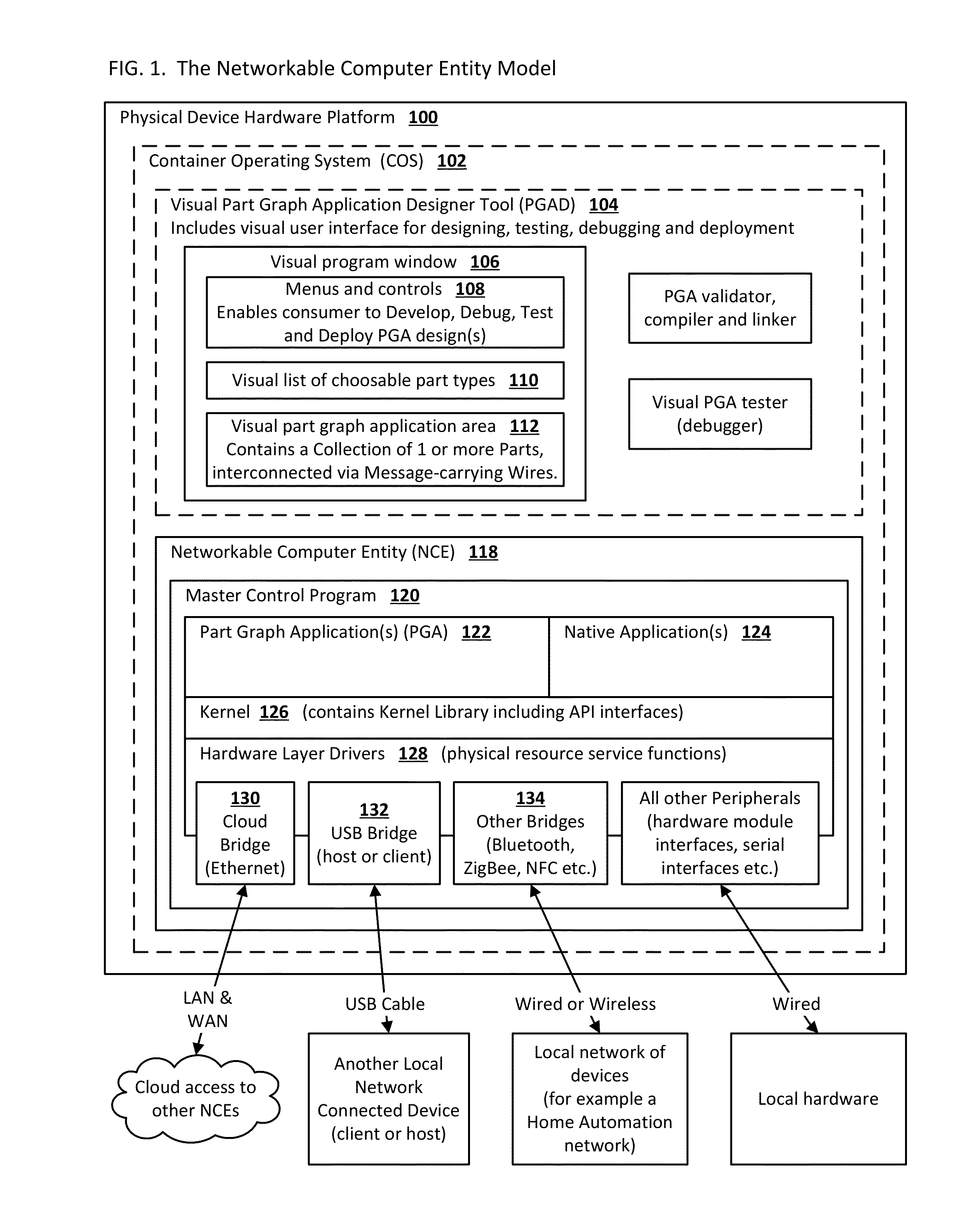
A system that enables end-users who are not skilled in the art of traditional computer programming to intuitively program, configure and manage computers and devices and / or systems that contain many computers and devices. End-users connect graphical parts using graphical wires using a graphical user interface. The timing of the messages that are carried in the wires that connect the parts is deterministic, consistent and intuitive to the end-user. Parts and their user-configurable features are typically designed, fully tested and certified by the original equipment manufacturer or independent software vendor. This invention relates to ubiquitous computing, a model of human-computer interaction in which information processing has been thoroughly integrated into everyday objects and activities associated with those objects.
Owner:CHAMBERLAIN MARK SPENCER
System and process for selecting objects in a ubiquitous computing environment
ActiveUS20050110751A1Input/output for user-computer interactionTransmission systemsTransceiverNetwork connection
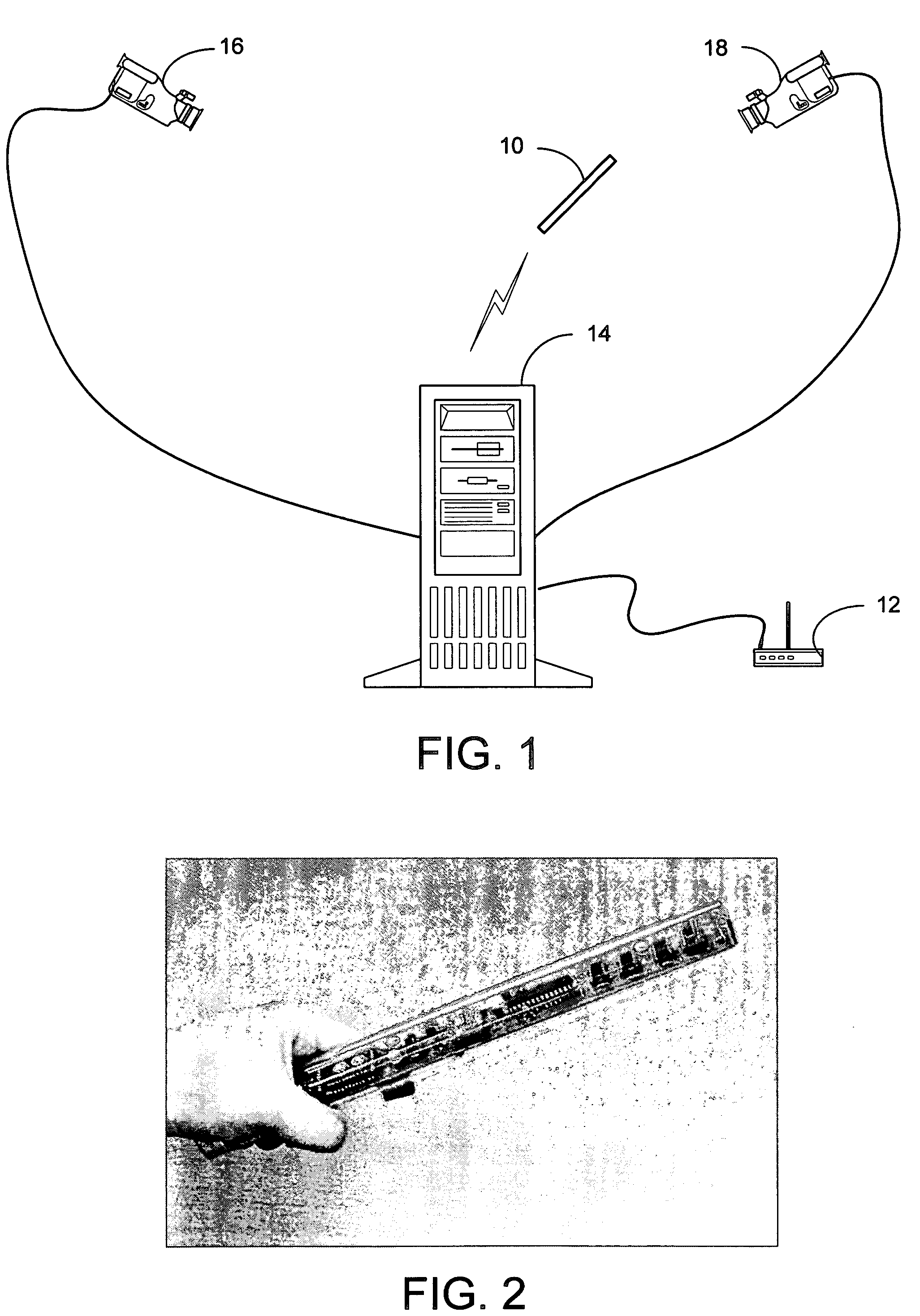
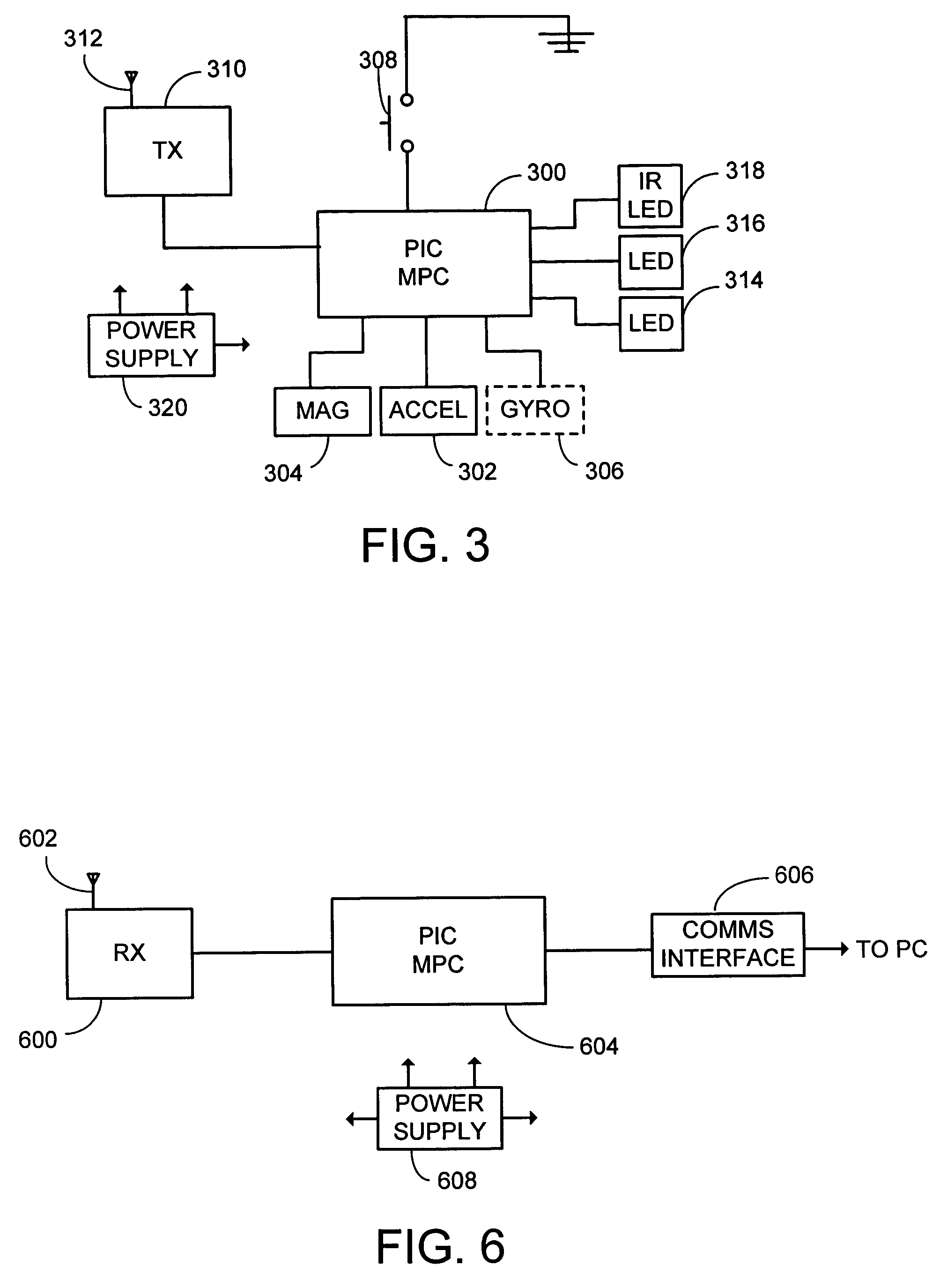
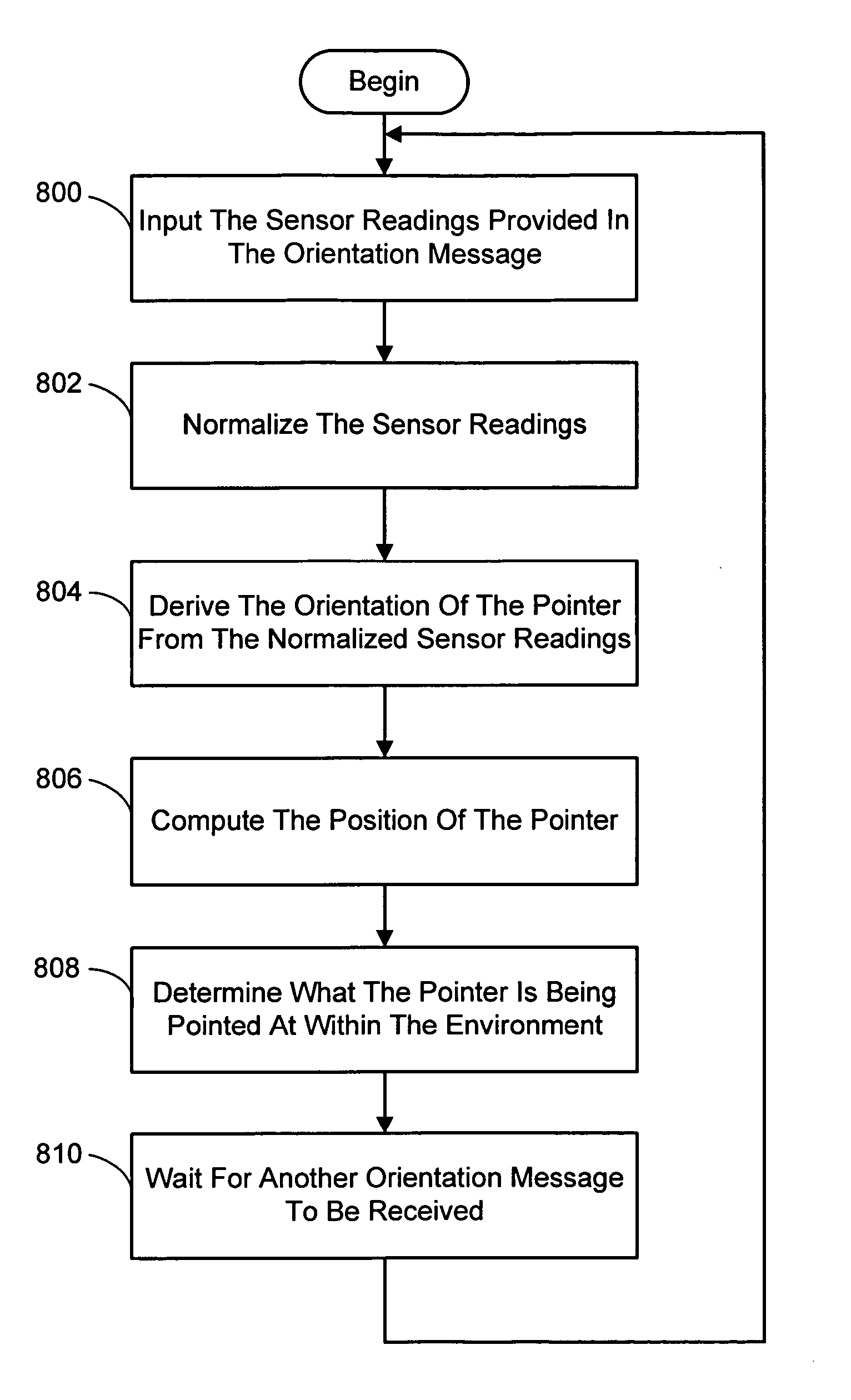
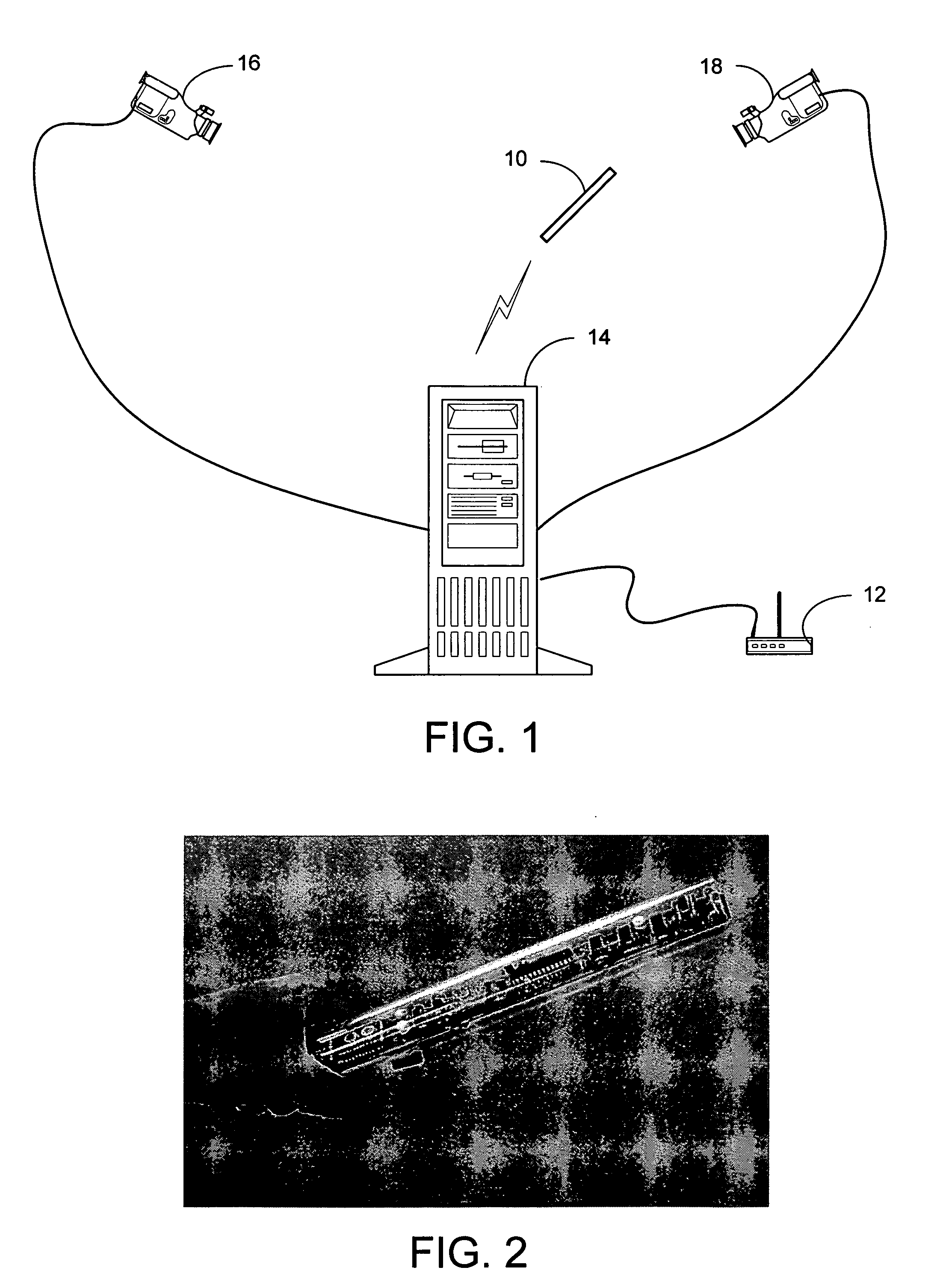
A system and process for selecting objects in an ubiquitous computing environment where various electronic devices are controlled by a computer via a network connection and the objects are selected by a user pointing to them with a wireless RF pointer. By a combination of electronic sensors onboard the pointer and external calibrated cameras, a host computer equipped with an RF transceiver decodes the orientation sensor values transmitted to it by the pointer and computes the orientation and 3D position of the pointer. This information, along with a model defining the locations of each object in the environment that is associated with a controllable electronic component, is used to determine what object a user is pointing at so as to select that object for further control actions.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
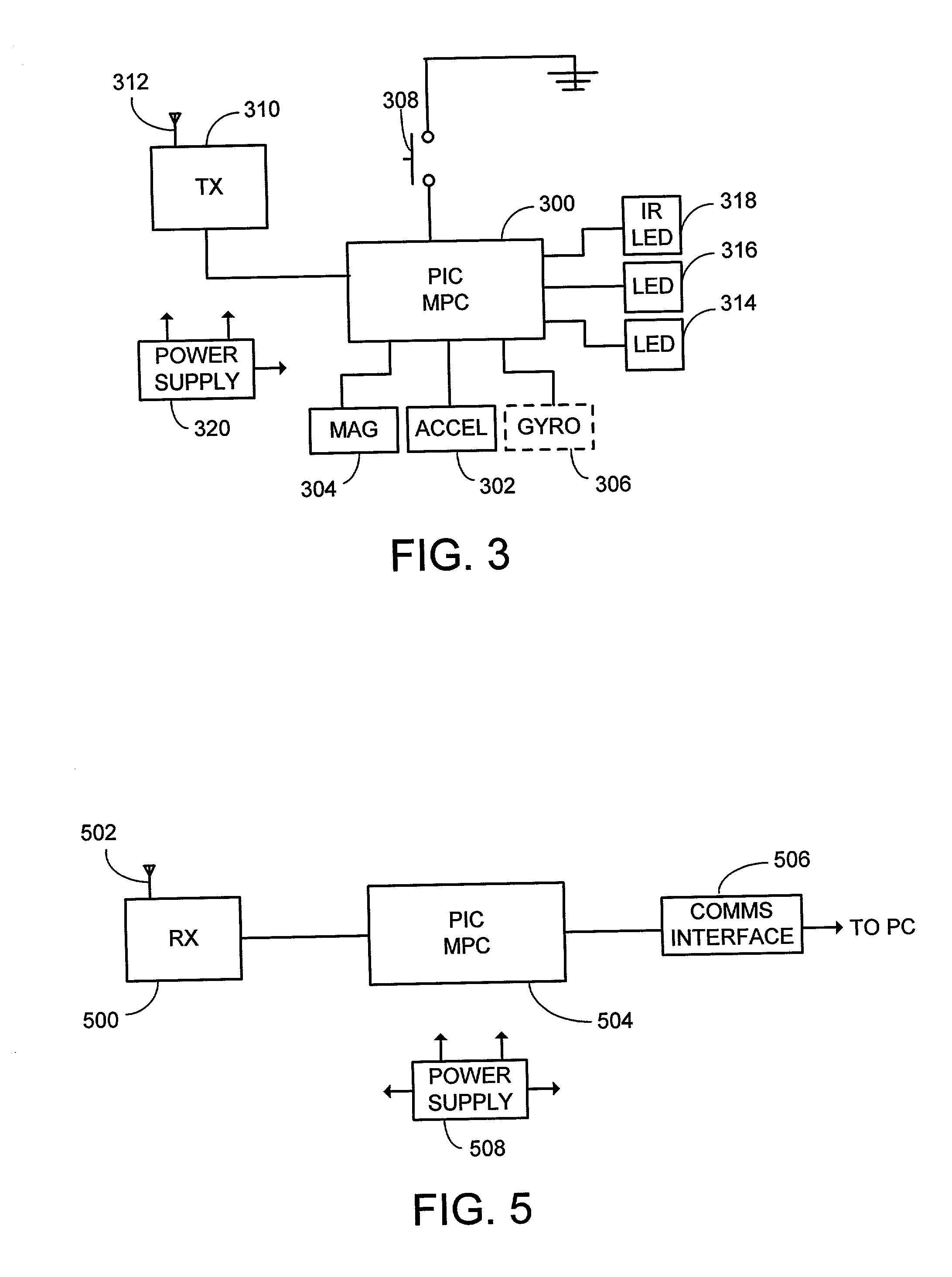
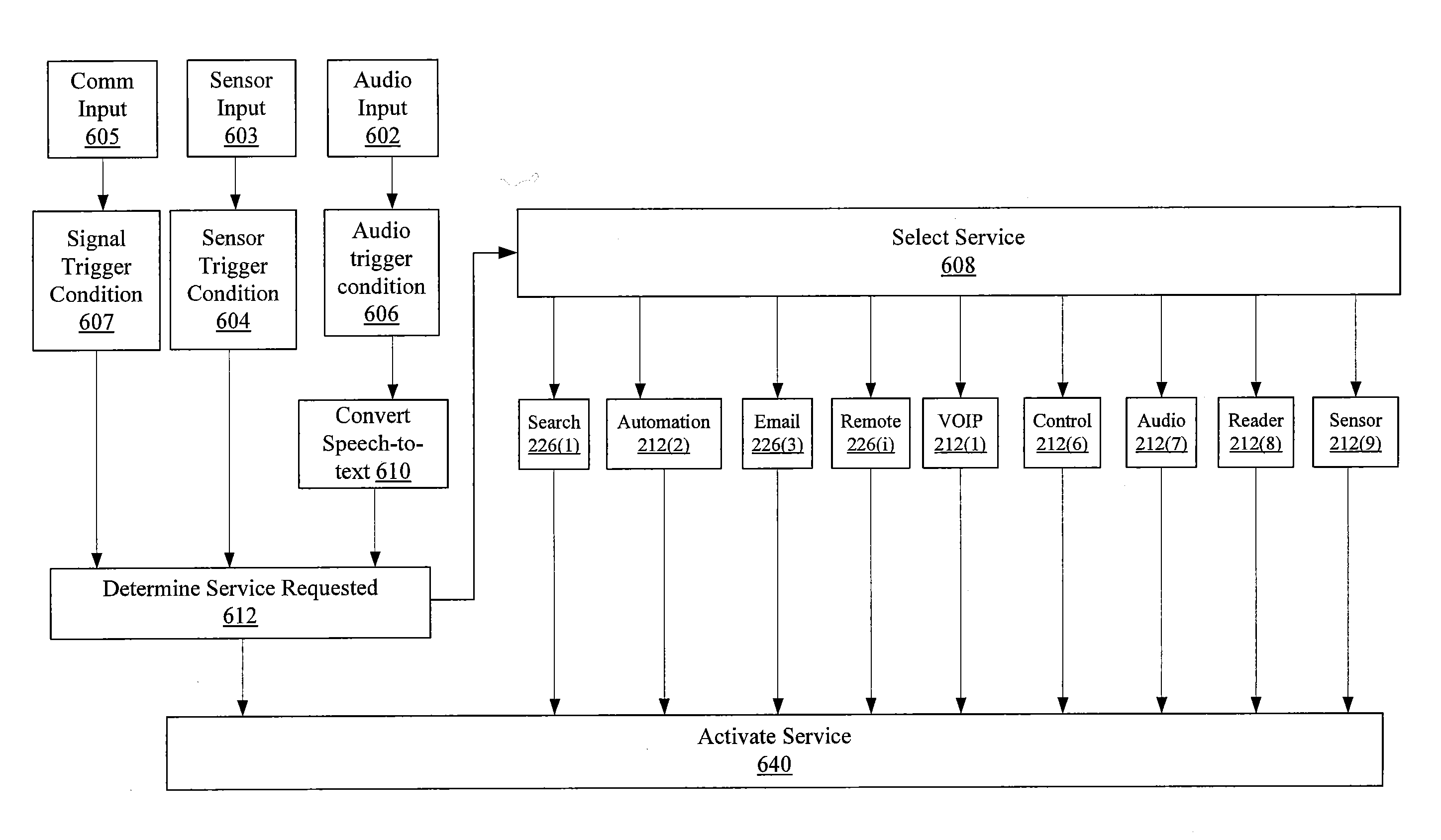
System and process for controlling electronic components in a ubiquitous computing environment using multimodal integration
InactiveUS20050257174A1Increase choiceMade robustTransmission systemsSpeech recognitionEngineeringSystem combination
The present invention is directed toward a system and process that controls a group of networked electronic components using a multimodal integration scheme in which inputs from a speech recognition subsystem, gesture recognition subsystem employing a wireless pointing device and pointing analysis subsystem also employing the pointing device, are combined to determine what component a user wants to control and what control action is desired. In this multimodal integration scheme, the desired action concerning an electronic component is decomposed into a command and a referent pair. The referent can be identified using the pointing device to identify the component by pointing at the component or an object associated with it, by using speech recognition, or both. The command may be specified by pressing a button on the pointing device, by a gesture performed with the pointing device, by a speech recognition event, or by any combination of these inputs.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
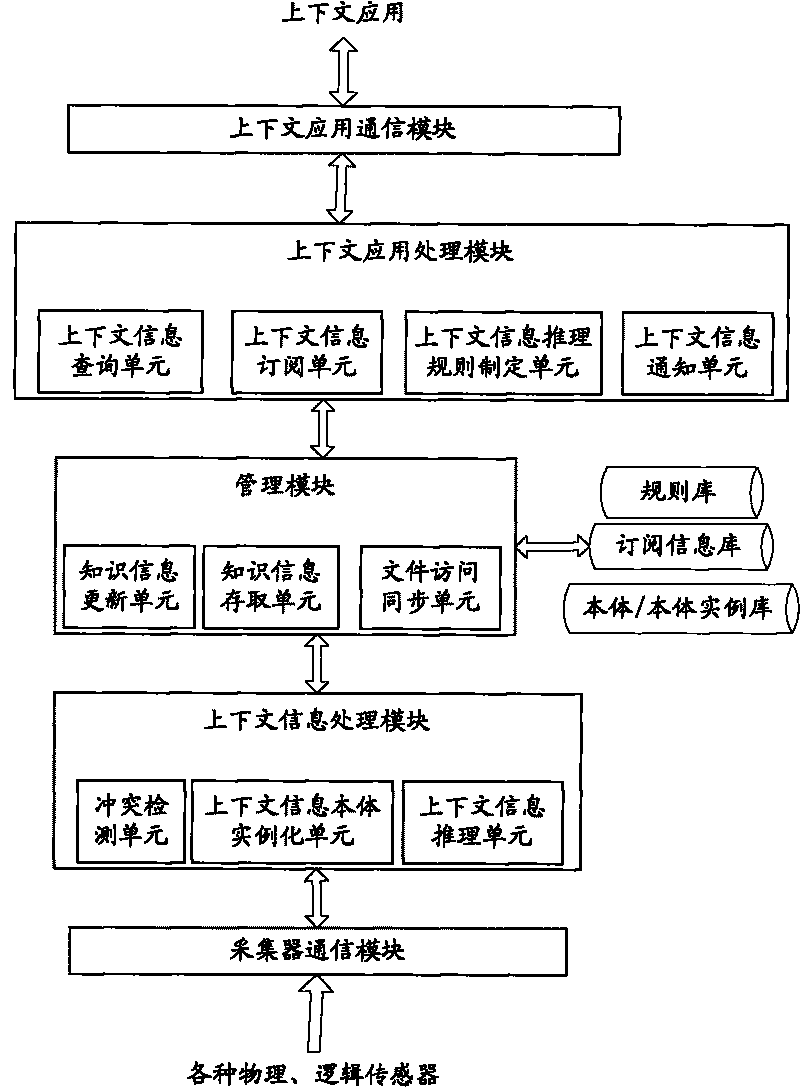
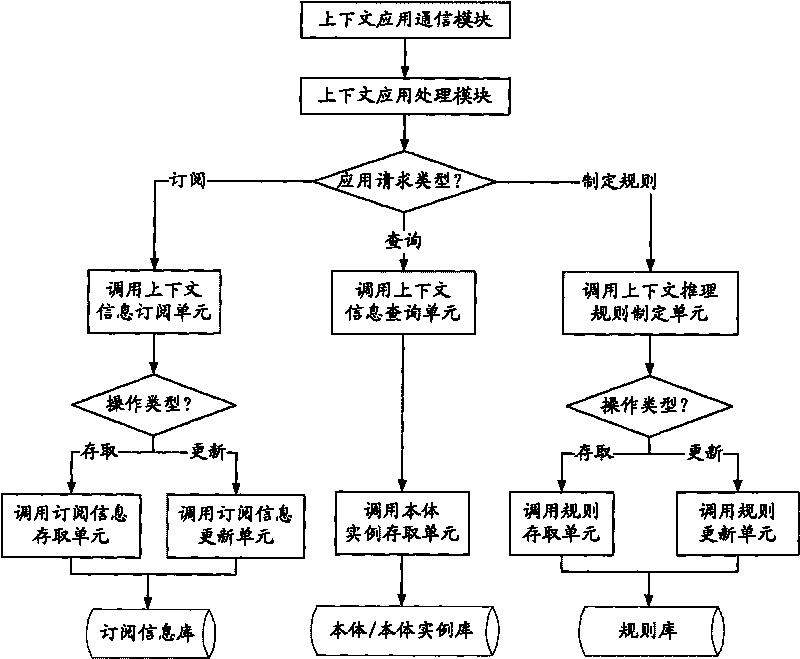
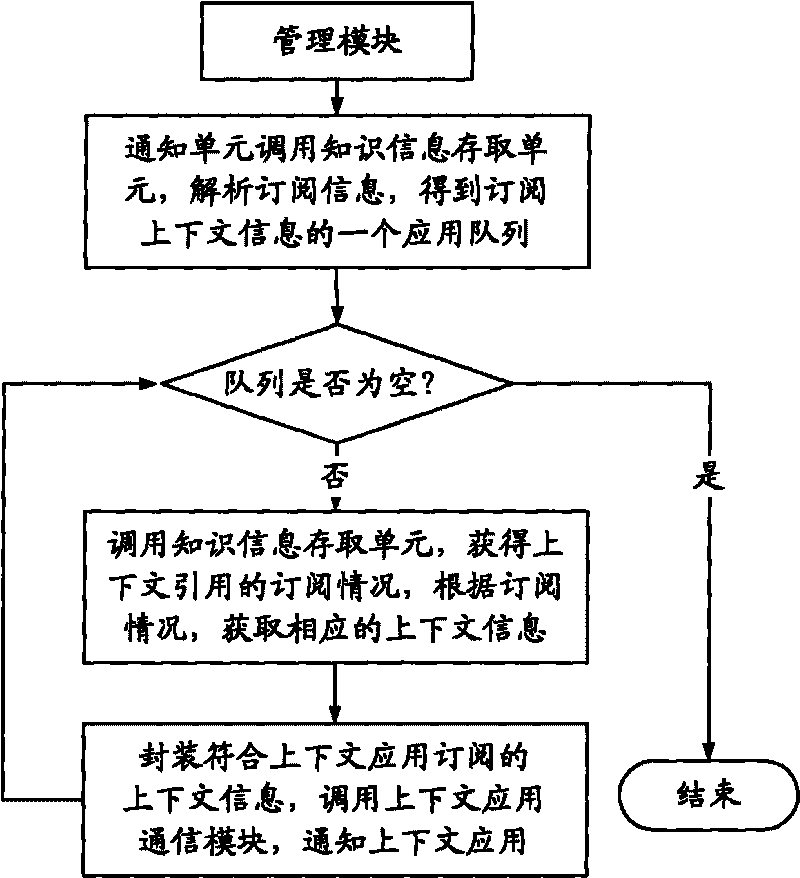
Context sensing application platform based on main body and work method thereof
InactiveCN101694629AAchieve mutual transparencyMultiprogramming arrangementsSpecial data processing applicationsInformation repositoryInformation processing
Disclosed is a context sensing application platform based on main body and a work method thereof, wherein the creation core of the invention is to supply a general-purpose processing model for obtaining context information, wherein the processing model comprises a gatherer communication module, a context information processing module, a management module, a knowledge information base, a context application processing module and a context sensing application platform of the context application processing module, when the application platform is supplied for sensing the context application, two mutually-independent and mutually-coordinated context information processing flows are proposed on how to use the context information processing steps, are mutually transparent, and share knowledge information through a synchronous control mechanism. The two processing flows are both on the basis of the context sensing and application platform of the invention, cover each flow of the context information processing, and reach knowledge sharing. The invention uses a main body to describe the context information, and reaches the universal share of knowledge information in the calculating field.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
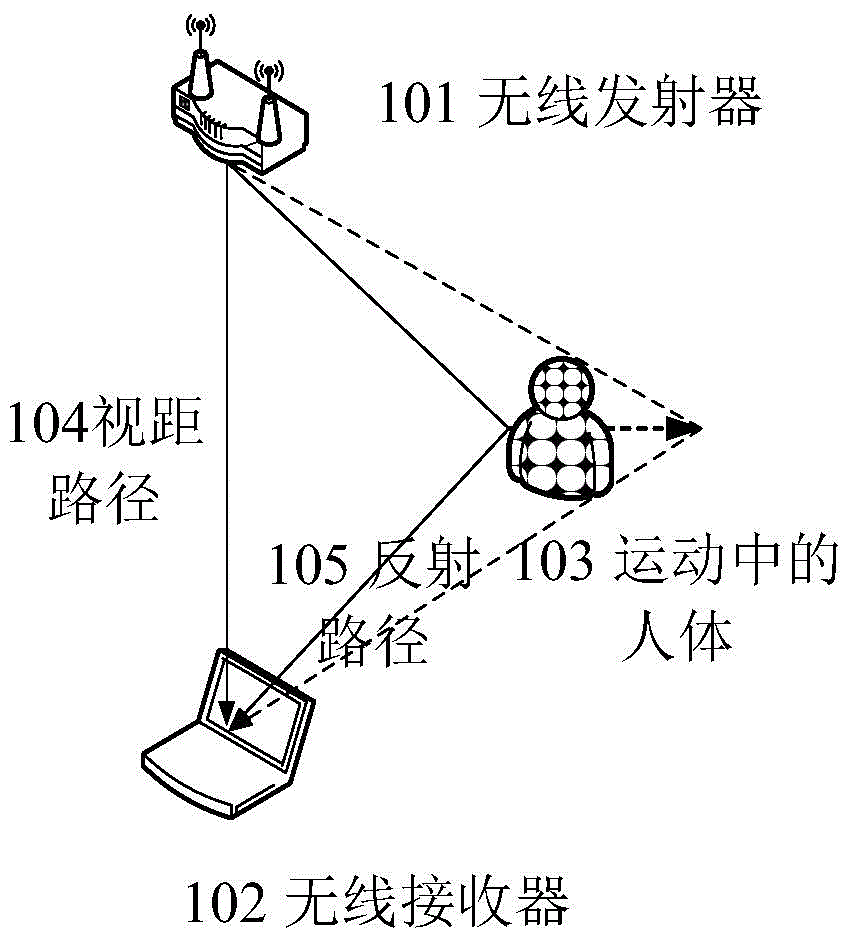
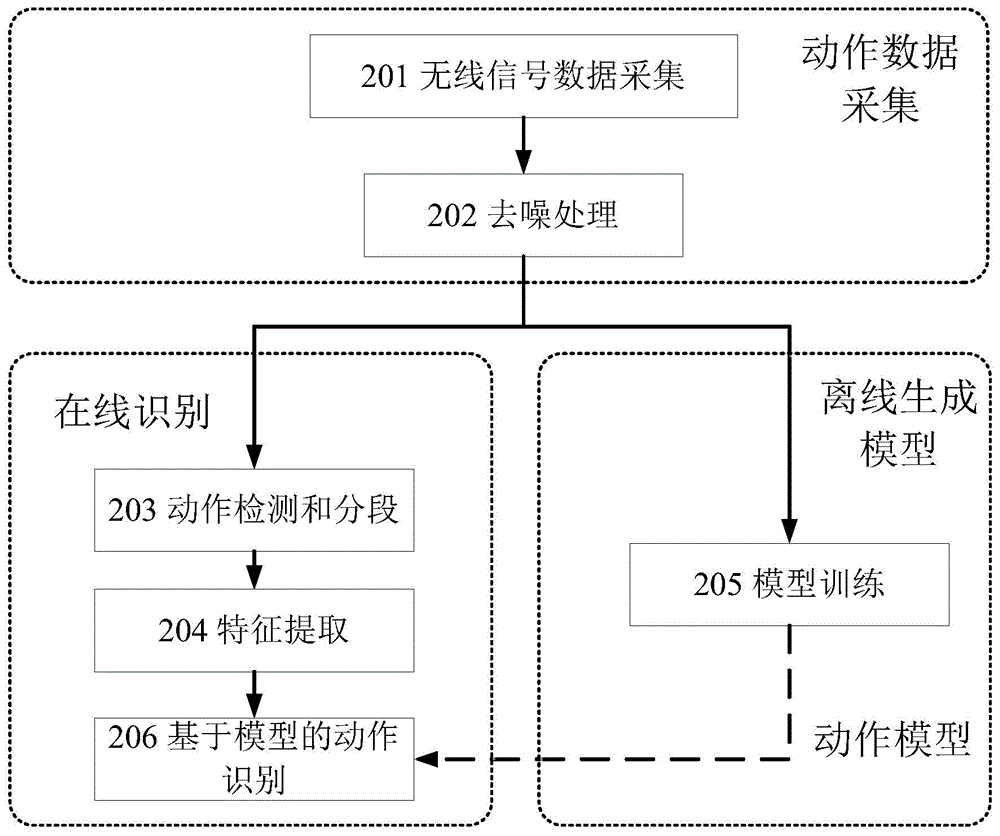
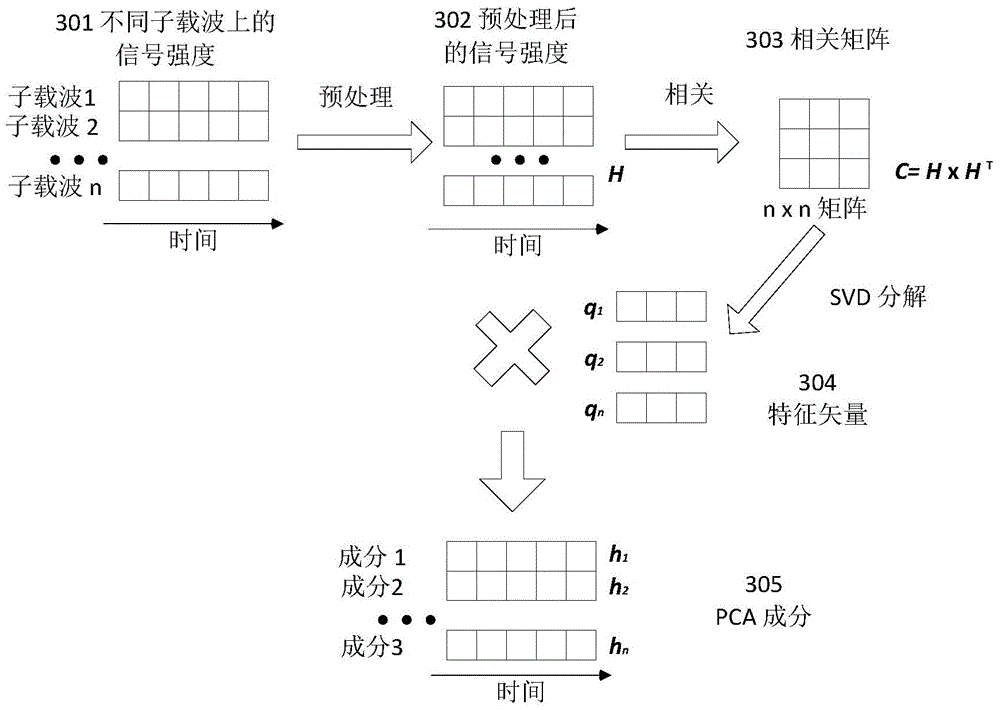
Action detecting and identifying method based on radio signals
ActiveCN104951757AEasy to identifyImprove anti-interference abilityCharacter and pattern recognitionRadio networksFeature extraction
The invention discloses an action detecting and identifying method based on radio signals and relates to the field of radio network and pervasive computing, in particular to an action detecting and identifying method based on radio signals. Radio signals are interfered by means of human actions, a universal radio device acquires radio signal data, and data is subjected to noise removal and characteristic extraction correlated with action speed to identify action. The radio signal data is acquired via one or more universal radio devices, radio data is subjected to noise removal by means of multichannel radio signal data, and characteristics correlated to human action speed can be extracted from the radio data so as to detect and identify the actions. The action detecting and identifying method includes steps of data acquisition, data denoising, data segmenting, characteristic extraction, model training and action identifying.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
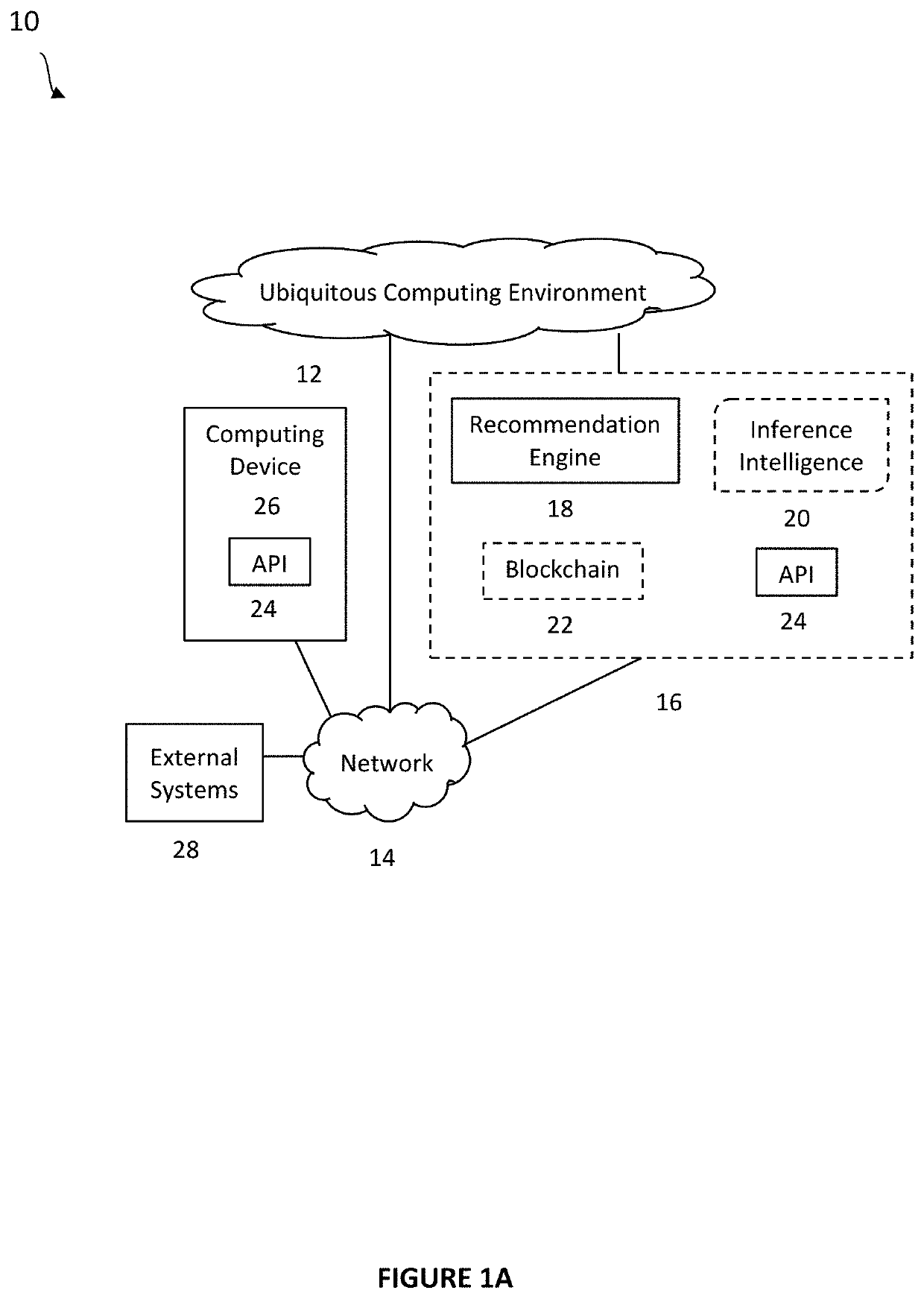
System and method for recommendations in ubiquituous computing environments
ActiveUS20200364588A1Particular environment based servicesCharacter and pattern recognitionEngineeringBehavioral data
Systems and methods for creating an ad hoc pervasive computing environment comprised of an inference recommendation engine coupled to commodity devices and sensors that passively collect human activity and behavioral data. Methods include machine learning and deep learning applications that analyze data to generate preference based recommendations to assist, inform, and guide subjects interacting with a connected living space and their connected social network.
Owner:KNOX GREGORY
Safety equipment, multi-application system and safety method for ubiquitous networks
InactiveCN103269326AEliminate reliability issues with unstable coverageAddress access security issuesClimate change adaptationTransmissionThe InternetAccess technology
The invention provides a mobile payment multi-application system, which uses an intelligent terminal as a platform, a safety module as a carrier and an e-commerce platform as a supporter, builds the ubiquitous computing environment for smart cities and realizes the seamless joint with the existing system. The mobile payment multi-application system has the advantages that the NFC (near field communication), UHF(ultra high frequency), Zigbee and WiFi (wireless fidelity) converged access technology, the distributed key technology, the embedded middleware technology and the multi-interface adapting technology are adopted, a mobile communication network, a wireless sensing network and the Internet are organically merged, an multi-application access platform is built, a special safety module and PKI (public key infrastructure) combining mechanism is adopted, and the safety of the system is improved through the multi-factor cross combination checking; multipath automatic selection and mutual backup are provided for ensuring the reliability, the safety and the robustness of the system transmission; and the perfect matching of a mobile terminal is realized through the cross-platform middleware technology, and the seamless integration with the existing system is realized through the technology of digital signature, biometric feature recognition and the like, so the existing system realizes the stable transition.
Owner:潘铁军
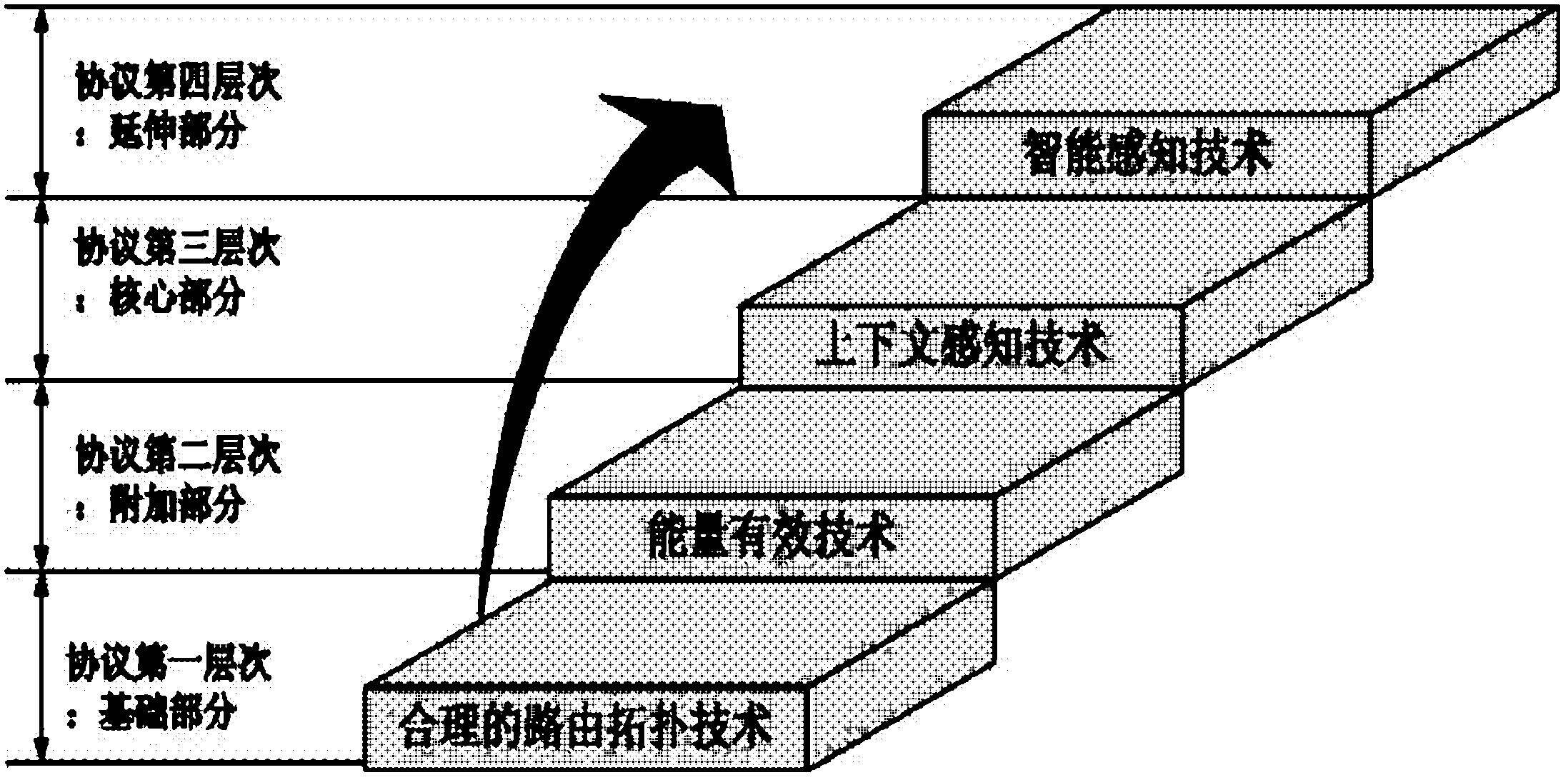
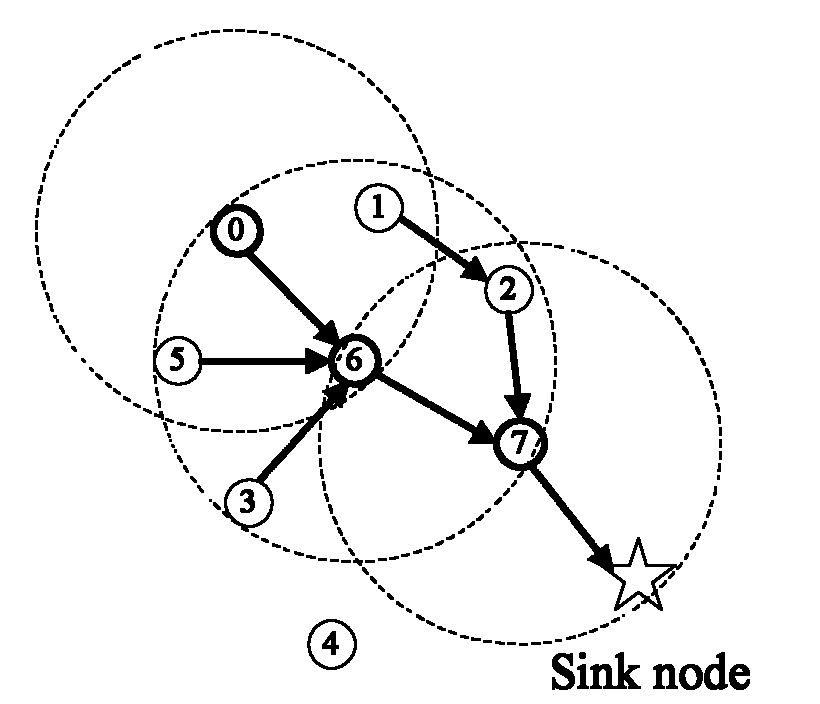
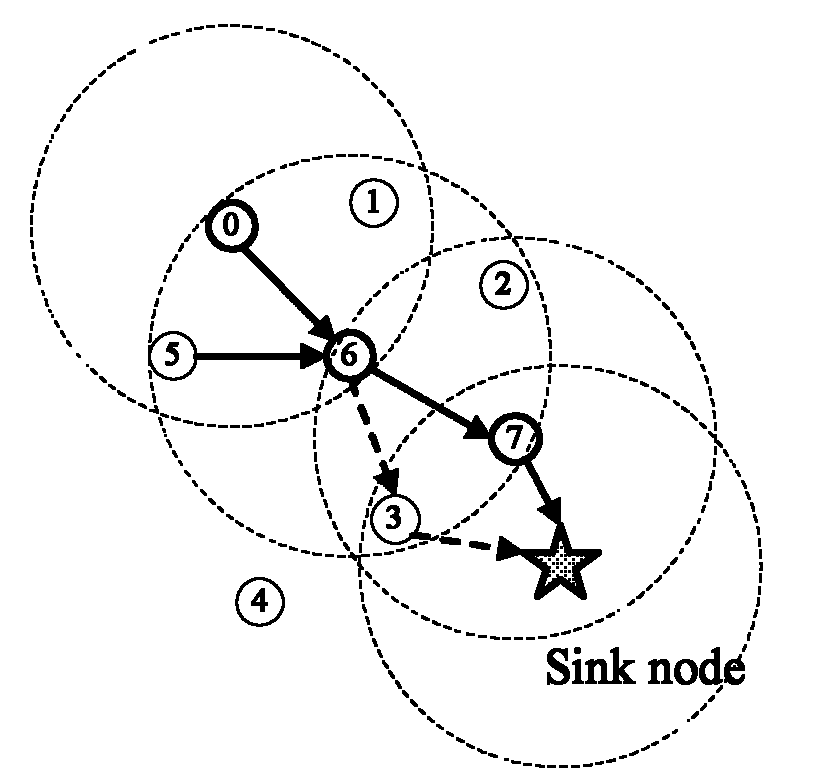
An energy-saving routing method for IoT nodes based on context-aware technology
InactiveCN102271379AGood forecastGood energy saving effectEnergy efficient ICTPower managementThe InternetContext based
The invention discloses an energy-saving routing method of nodes of an energy effective based on a context-aware technology. A CATRP (Context-Aware Technology Routing Protocol) is used as a routing work way of nodes in an internet of things environment, so as to achieve an established energy saving goal. The method disclosed by the invention belongs to the technical field of the internet of things. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the context-aware technology is applied to communicational nodes which work in the internet of things as a core technology for an energy-saving purpose of the invention, and composition modules of the protocol are designed comprehensively from the perspectives of working process, data structure, quantitative algorithm design, and the like. Due to application of the patent, a good foundation for realization of a universal computing service in the whole society in the near future can be laid, right development of the internet of things technology in the future is guided, theoretical basis enrichment and certain contribution for transformation of a wireless sensor network technology at the present stage are made, and the method has important meaning to enhancement of energy saving technology level of the internet of things in the industry, to acceleration of schedule of a national energy-saving routing research subject for nodes of the internet of things, to promotion of domestic demand, and to promotion of development of related industries.
Owner:陈实 +3
System and method for pervasive computing
ActiveUS8060560B2Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsUbiquitous computingCloud computing
A method and system for pervasive computing are disclosed. According to one embodiment, a computer implemented method comprises a server communicating with a first device in a cloud computing environment, wherein the first device can detect surrounding devices, and an application program executable by the server, wherein the application program is controlled by the first device and the output of the application program is directed by the server to one of the devices detected by the first device.
Owner:AMAZON TECH INC +11
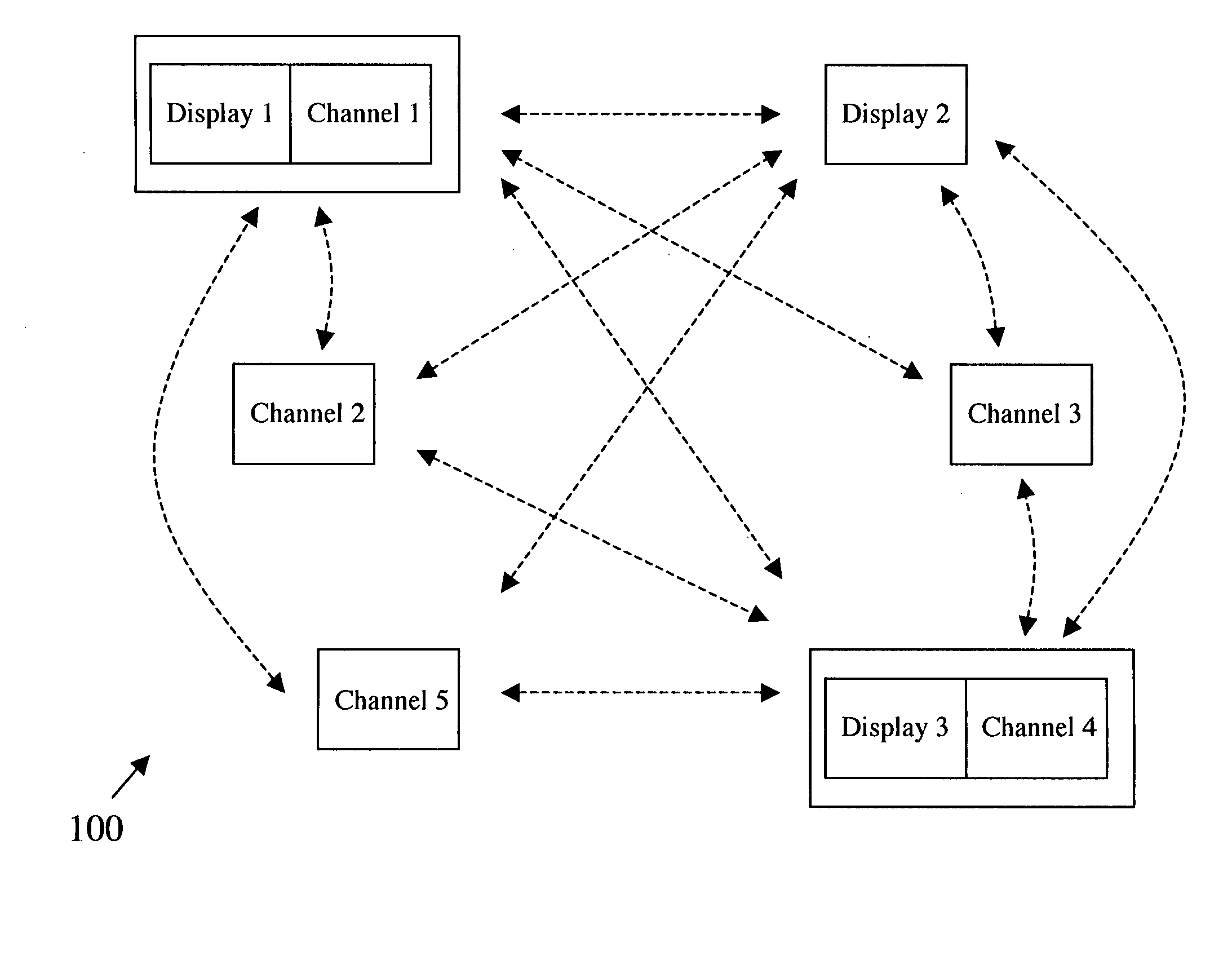
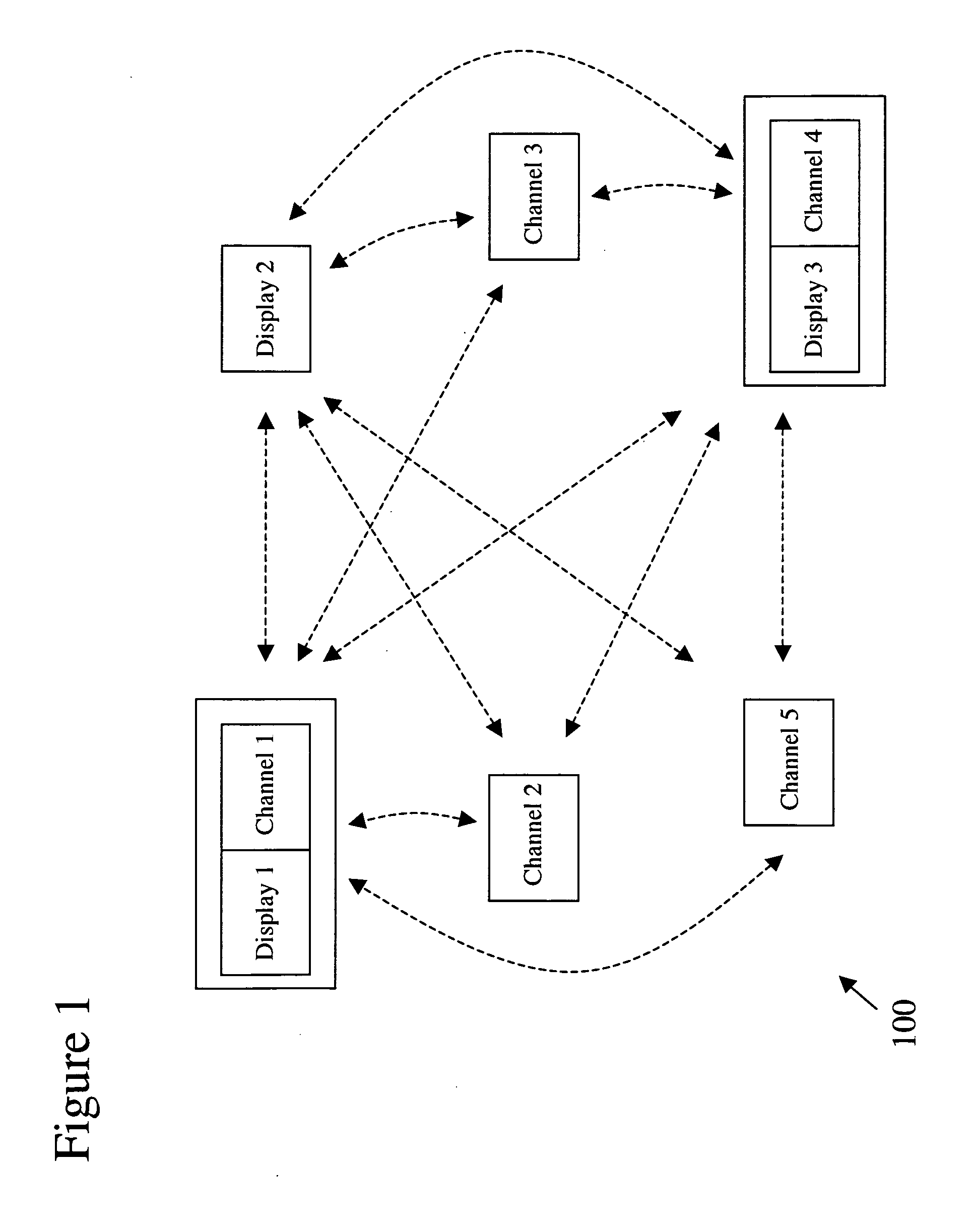
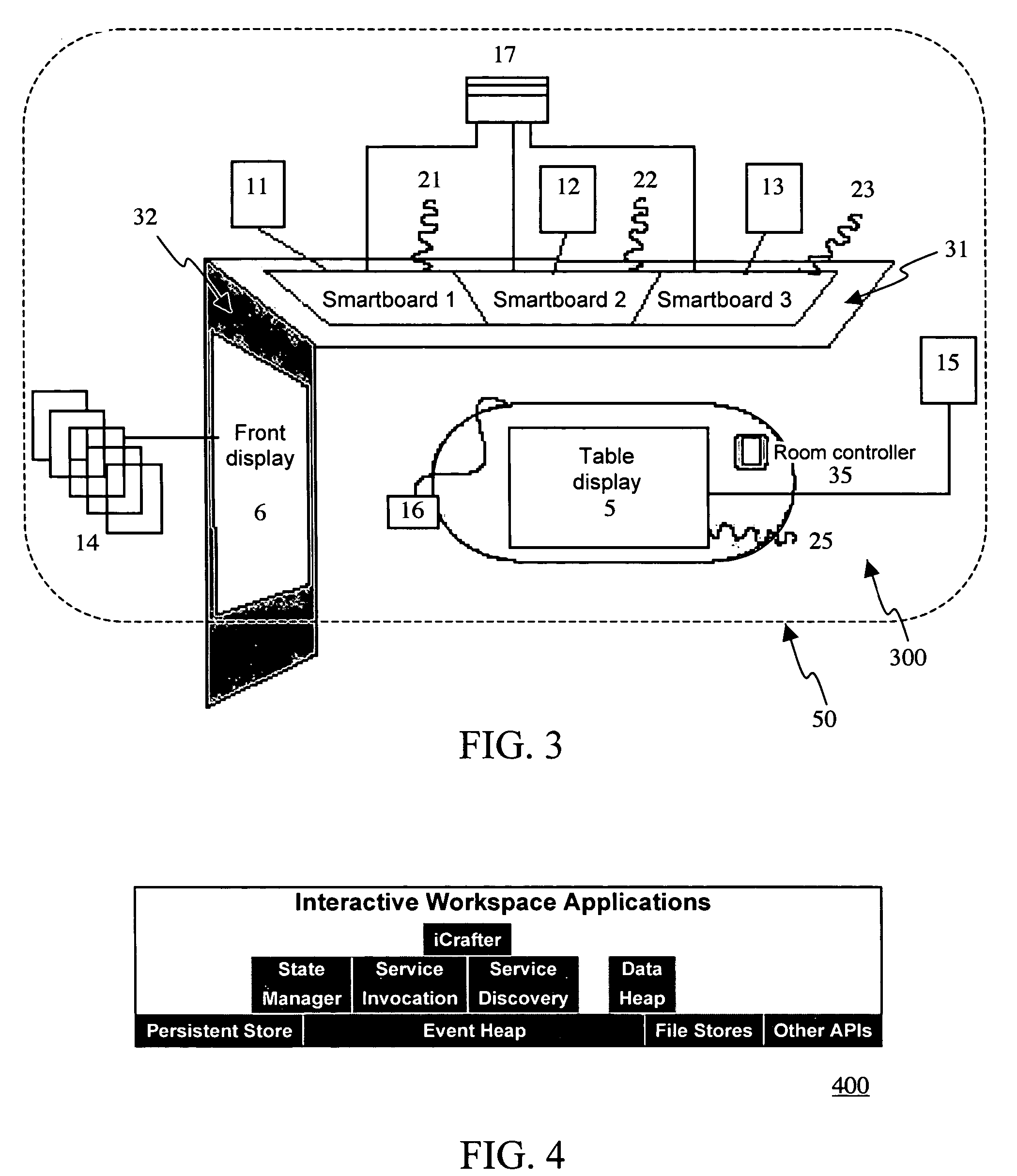
Heterogeneous content channel manager for ubiquitous computer software systems
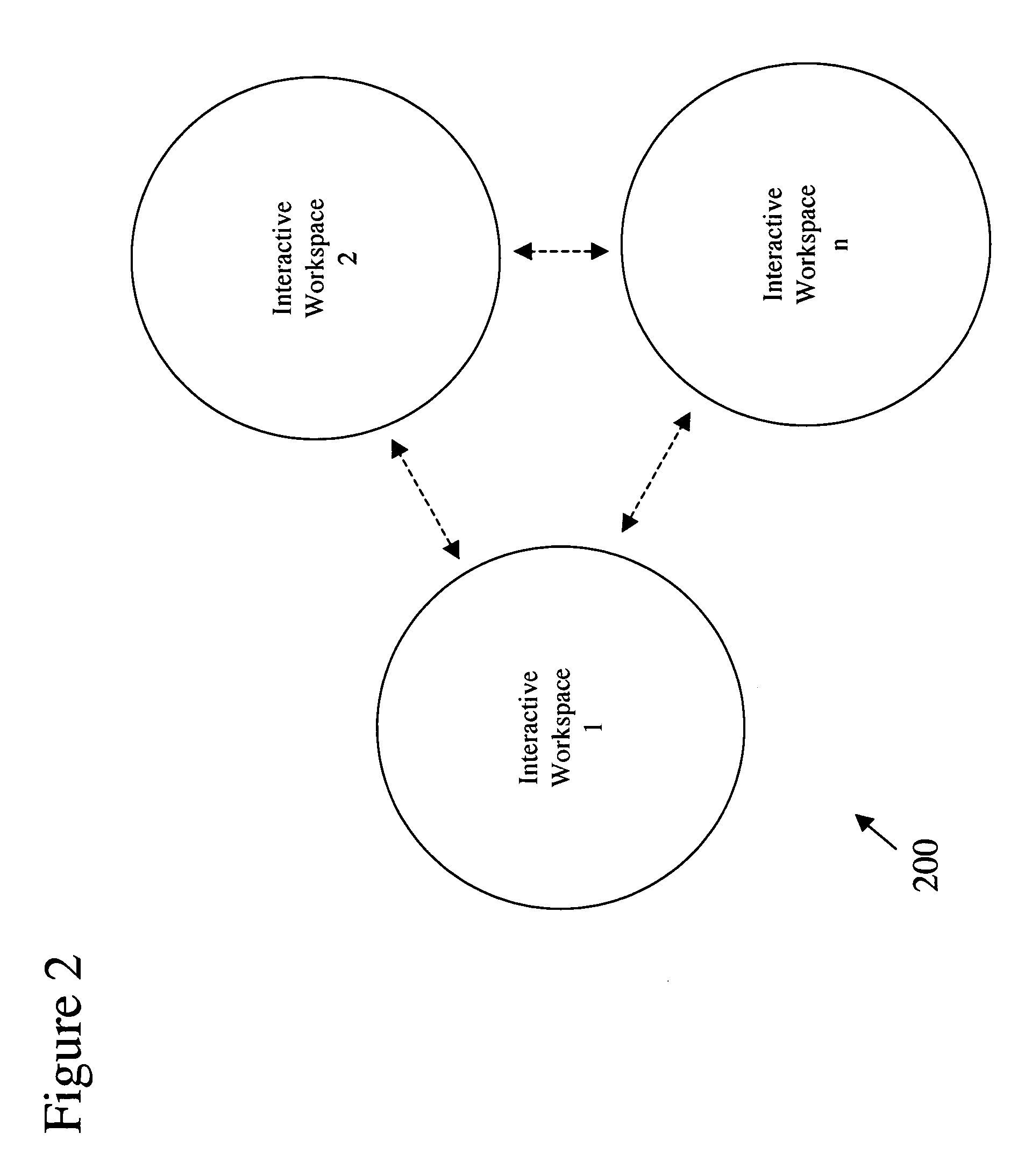
InactiveUS20060242584A1Minimizing interruptionComputer controlTelevision conference systemsSoftware systemWorkspace
A heterogeneous content channel manager is provided for content management and collaboration within and across interactive workspaces. A content channel bar, available on each of the displays in the workspace(s), contains two or more unique representations of respectively two or more different channels available in the interactive workspace(s). Within the set of available channels on each channel bar two or more different channel types are represented. Furthermore, each one of the unique representations in the content channel bar represents different and unique content supported by their respective channels and their types. Channel selection on the channel bar initiates display, on the display where the channel selection was made, of the content represented by the selected representation and channel in a manner appropriate for the channel's type.
Owner:TIDEBREAK
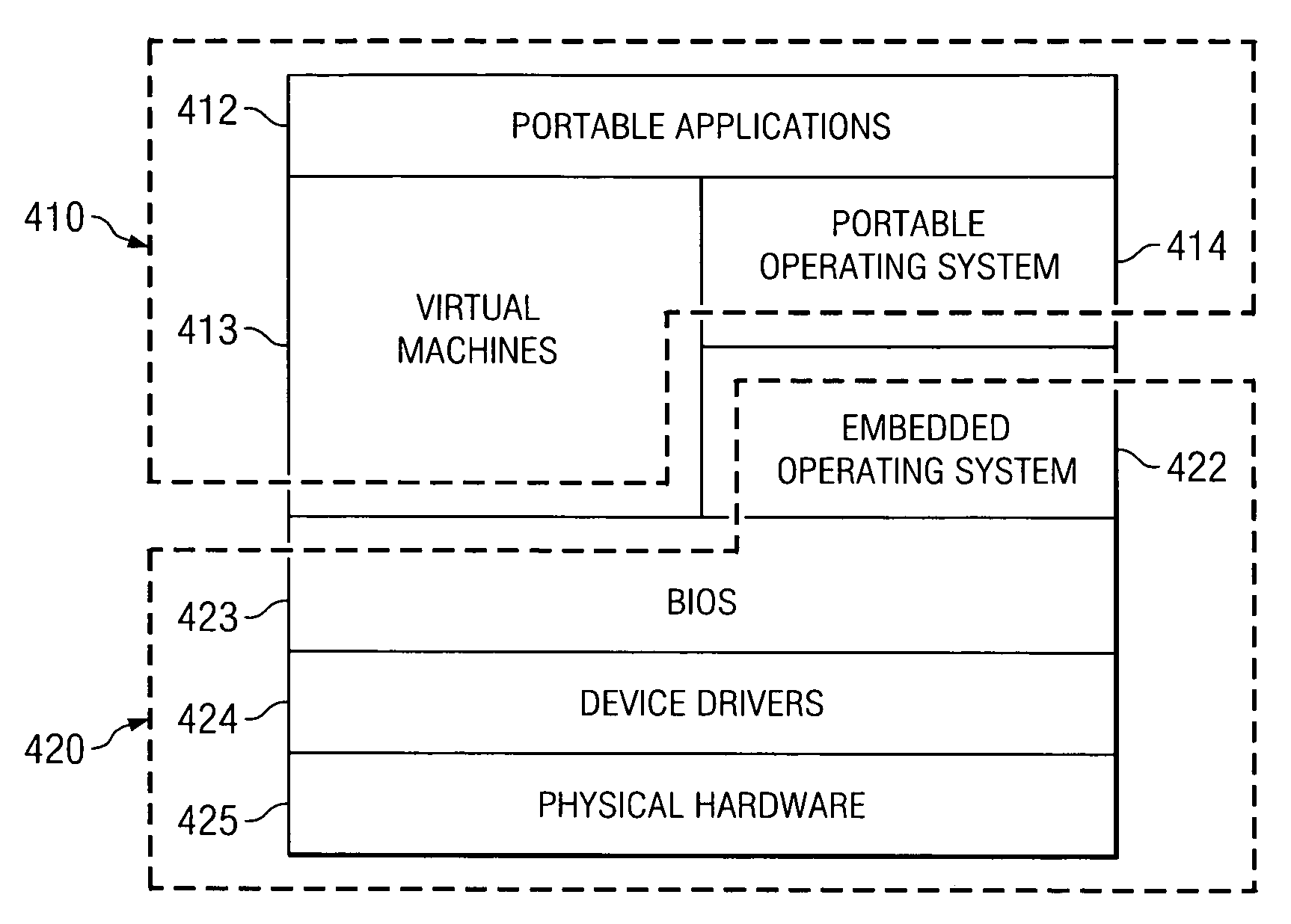
System and method for pervasive computing with a portable non-volatile memory device
ActiveUS20060070085A1Multiprogramming arrangementsMemory systemsData processing systemOperational system
A method, computer program product, and a data processing system for providing pervasive computing with a removable non-volatile memory device is provided. A portable operating system receives a command for removal of a portable memory device from a first host. A running application that is stored on the portable memory device is identified. Application state data of the application is saved in a data structure stored on the portable memory device. The portable memory device may then be removed from the first host and connected with a second host. A determination is made of whether the second host is adapted to run the application. The saved state data is retrieved responsive to determining that the second host is adapted to run the application, and the application is restored to an application state at which the state data was saved.
Owner:KYNDRYL INC
Hybrid implementation game system based on pervasive computing, and method thereof
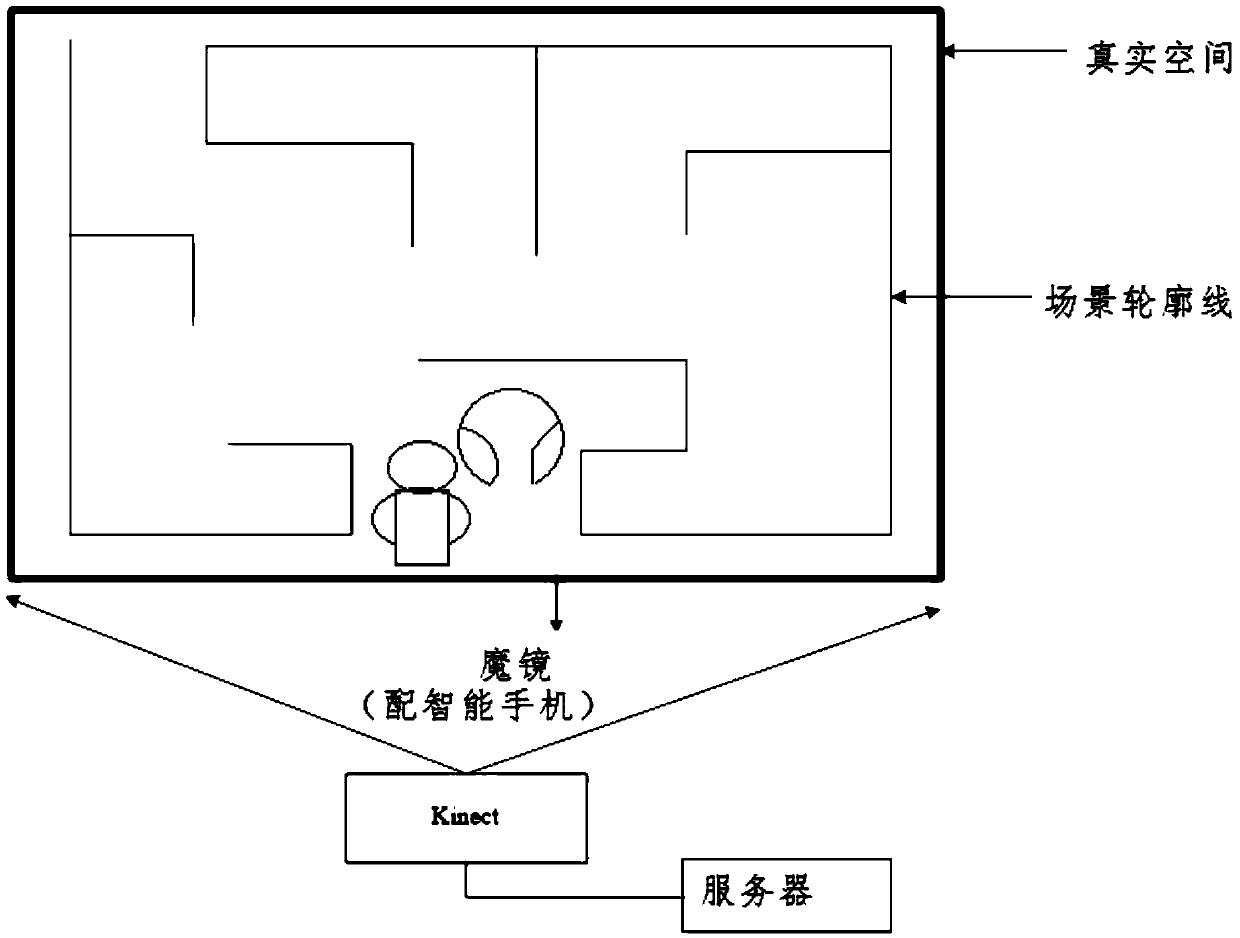
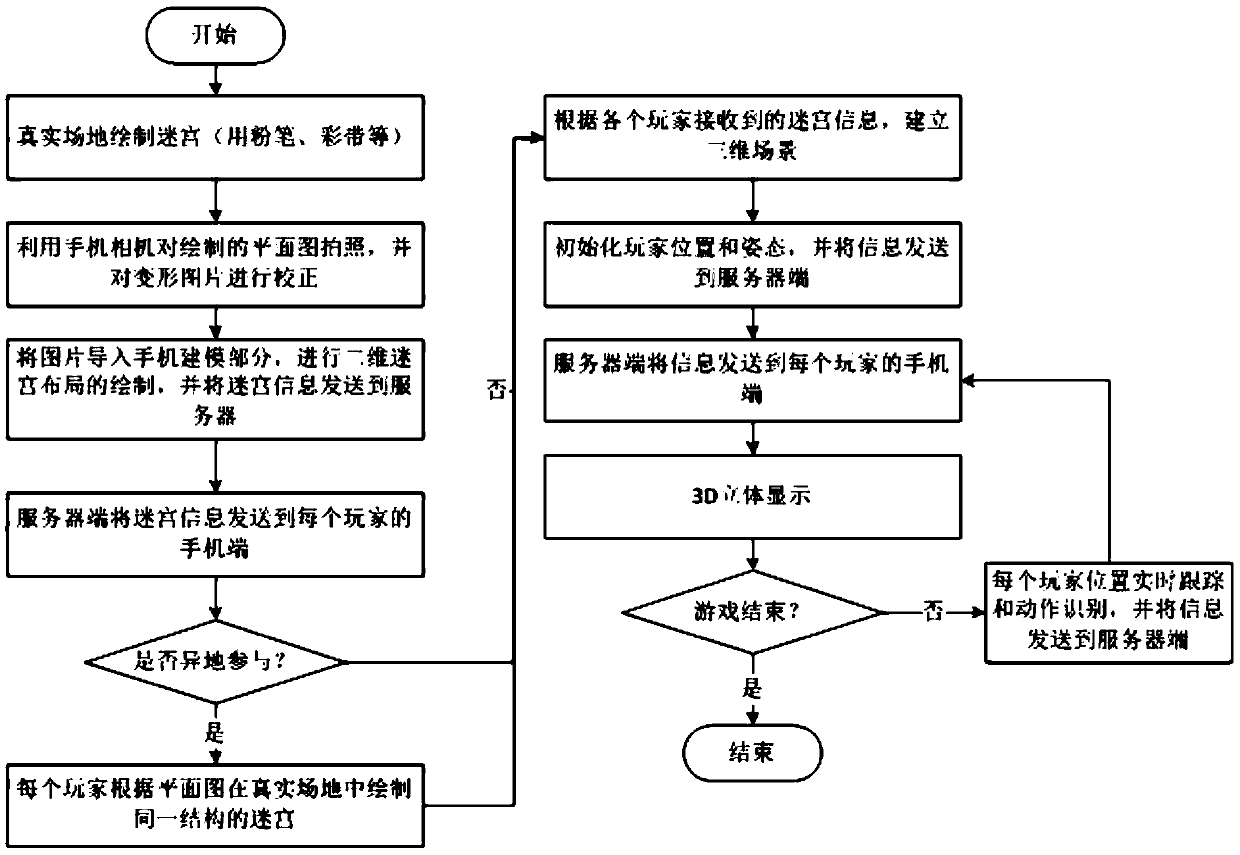
ActiveCN105373224AEasy to useEasy to operateInput/output for user-computer interactionVideo gamesPhysical spaceMixed reality
The invention discloses a hybrid implementation game system based on pervasive computing, and a method thereof. The system allows a player to design maze layout anytime and anywhere in any free space and draw a maze planar graph through a drawing tool; a corresponding three-dimensional virtual scene is built quickly through photographing by a mobile phone; by a virtual reality glasses, the player can enjoy immersive experience through real rotation of the head of the player; and by means of tracking and identifying real posture of the player through a motion sensing device, mobile input control and natural interaction to the virtual scene by the player is realized. The system has no need of special physical space and expensive virtual reality devices, and users are not required to be trained and can play games anytime and anywhere.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
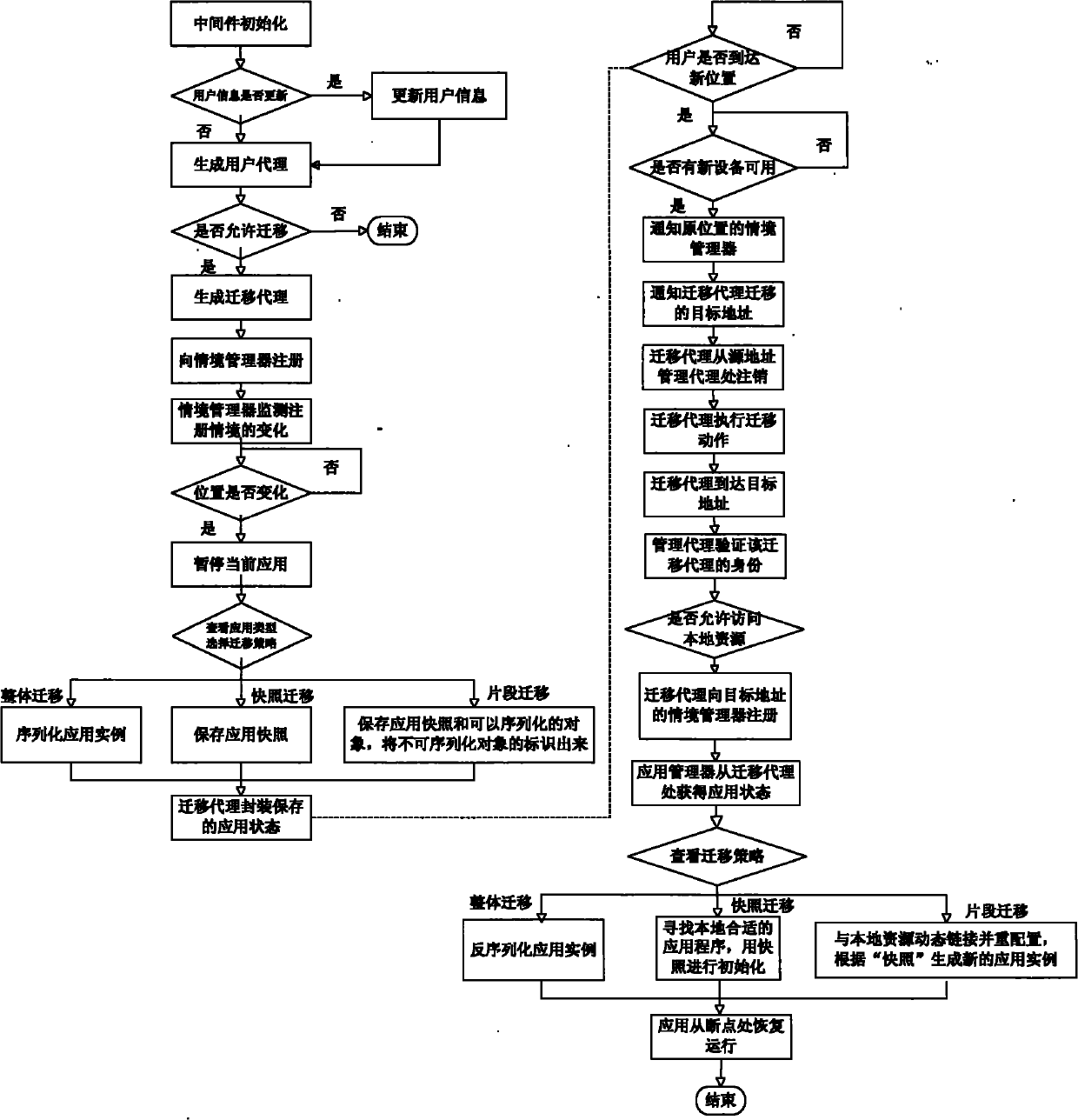
Mobile agent-based application seamless migration method
InactiveCN101907989AEasy to integrateProtection securitySpecific program execution arrangementsSemanticsSoftware agent
The invention discloses a mobile agent-based application seamless migration method, which comprises the following steps of: constructing a middleware system supporting application seamless migration, configuring the personal information of a user, defining the structure and semantics of a software agent supporting the application migration, formulating three different migration strategies according to the different characteristics of application, and providing a method for application reconfiguration after the migration. The method has the advantages of overcoming the defects of difficult application migration, low migration efficiency and the like in the prior art, reducing network load, shortening migration delay, and improving the degree of satisfaction of the user on an application migration service under a ubiquitous computing environment.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
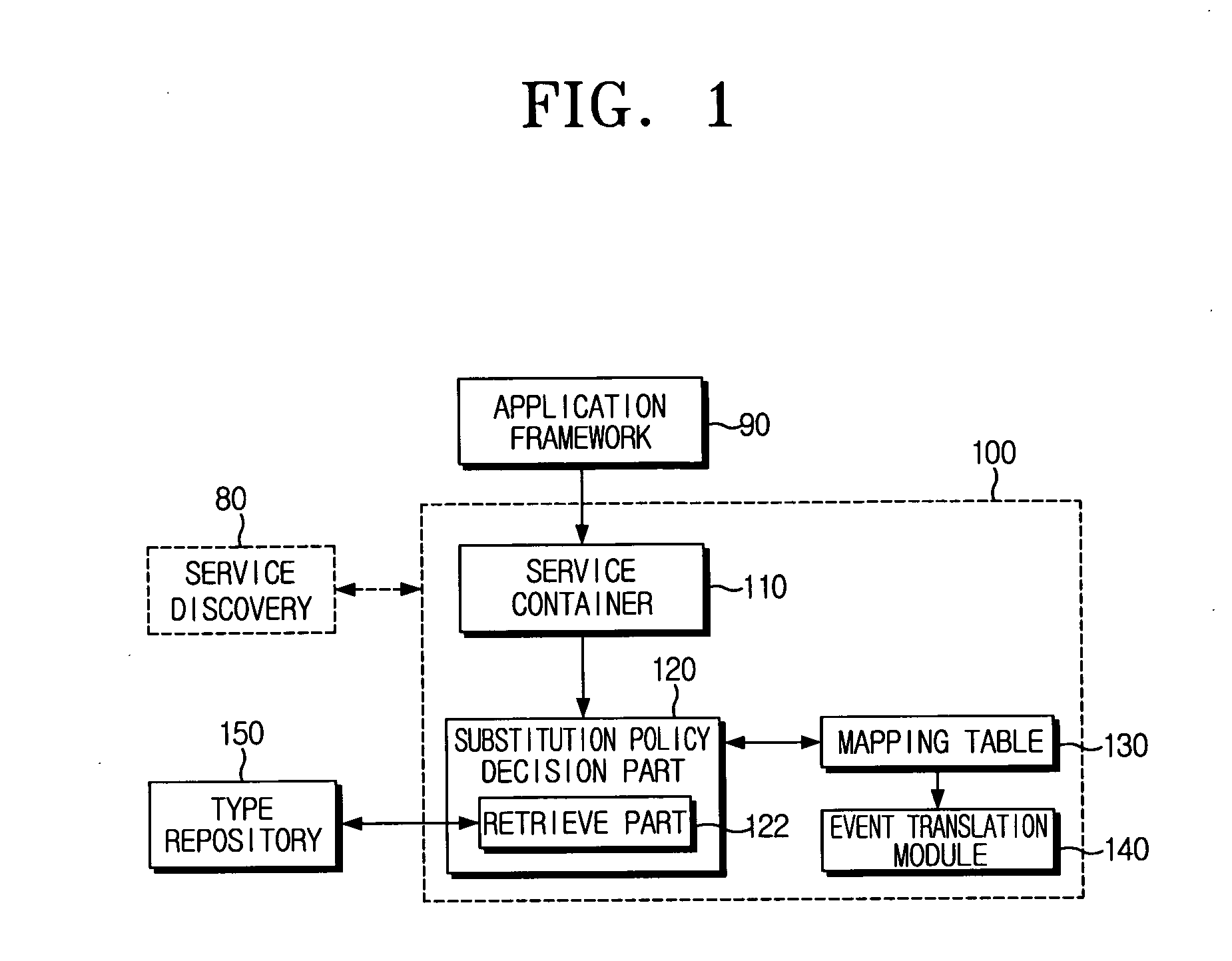
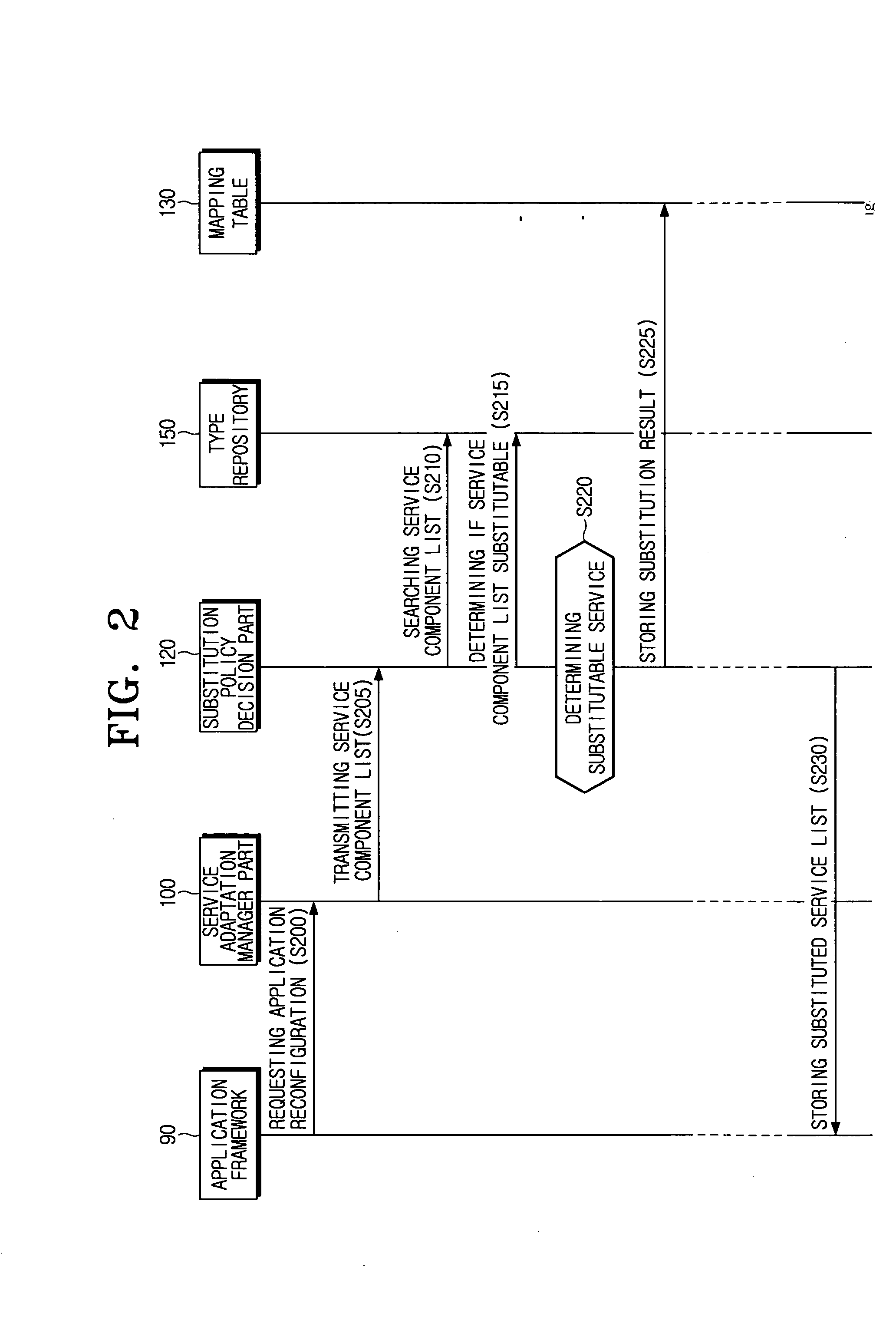
Method for reconfiguring application using subtyping-based flexible service adaptation in pervasive computing environment and system thereof
InactiveUS20060212878A1Multiprogramming arrangementsProgram loading/initiatingService adaptationUbiquitous computing
A method for reconfiguring an application in a pervasive computing environment, includes receiving a request for a reconfiguration of a predetermined application reconfiguration according to a change in a context, searching a service in response to the change in the context with respect to each of at least one service component configuring the predetermined application, and reconfiguring the predetermined application based on the searched service.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Electrical wiring schedule information management system
InactiveCN101247532ACo-operative working arrangementsSelection arrangementsStructure of Management InformationNetwork management
The present invention belongs to the technique field of the network management and wireless communication, and in particular relates to an electric wiring table information management system. The most bothersome and complex part in the network management is the management to the wiring information, especially the wiring information of the convergence layer and the access layer. The invention totally realizes the electric storing and management of the network wiring information with the techniques of IC, ID, ubiquitous computing and the like. The IC or ID card is used for replacing the paper label at the network site. The mobile terminal is used for replacing the paper and pen for reading, amending, seeking and searching various wiring information of the network. The wiring and topological structure drawing of the whole network can be quickly obtained in the office and the important equipment is real-time monitored. The network maintaining personnel can be facilitated to execute real-time and accurate management to the whole network with the informationized facility at any place relevant to the network.
Owner:SHANGHAI GOKEI INFORMATION TECH
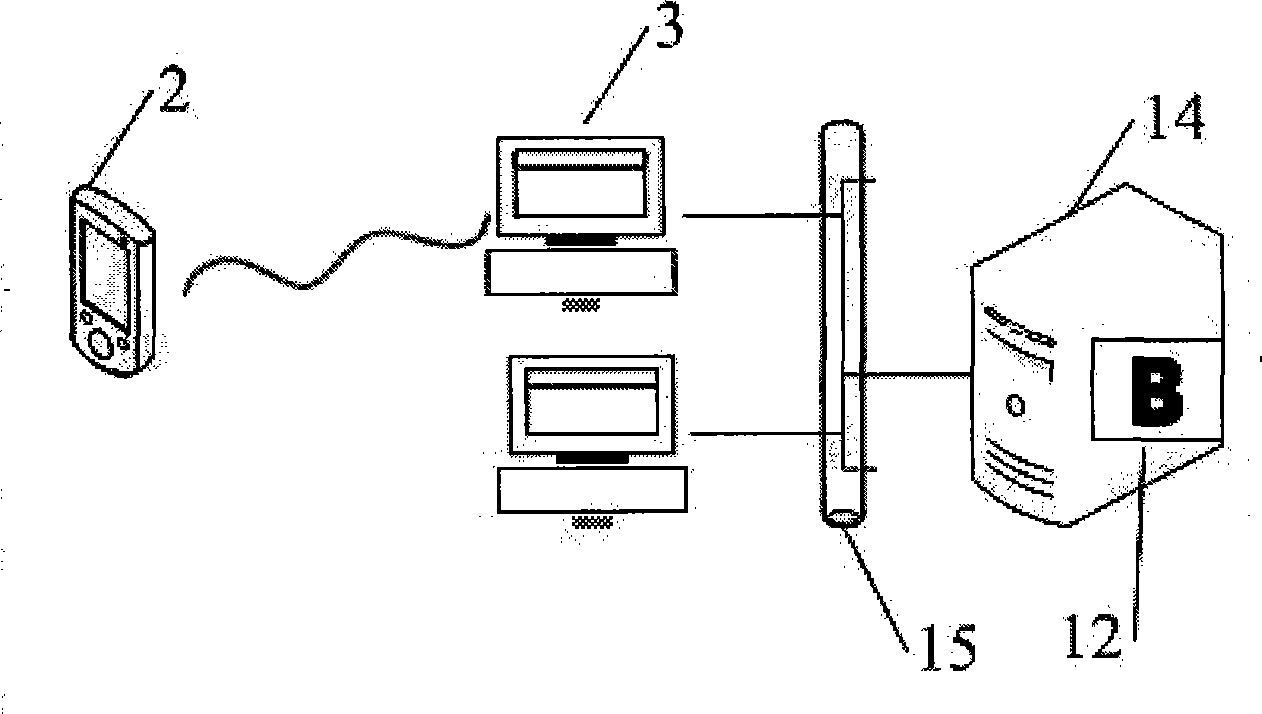
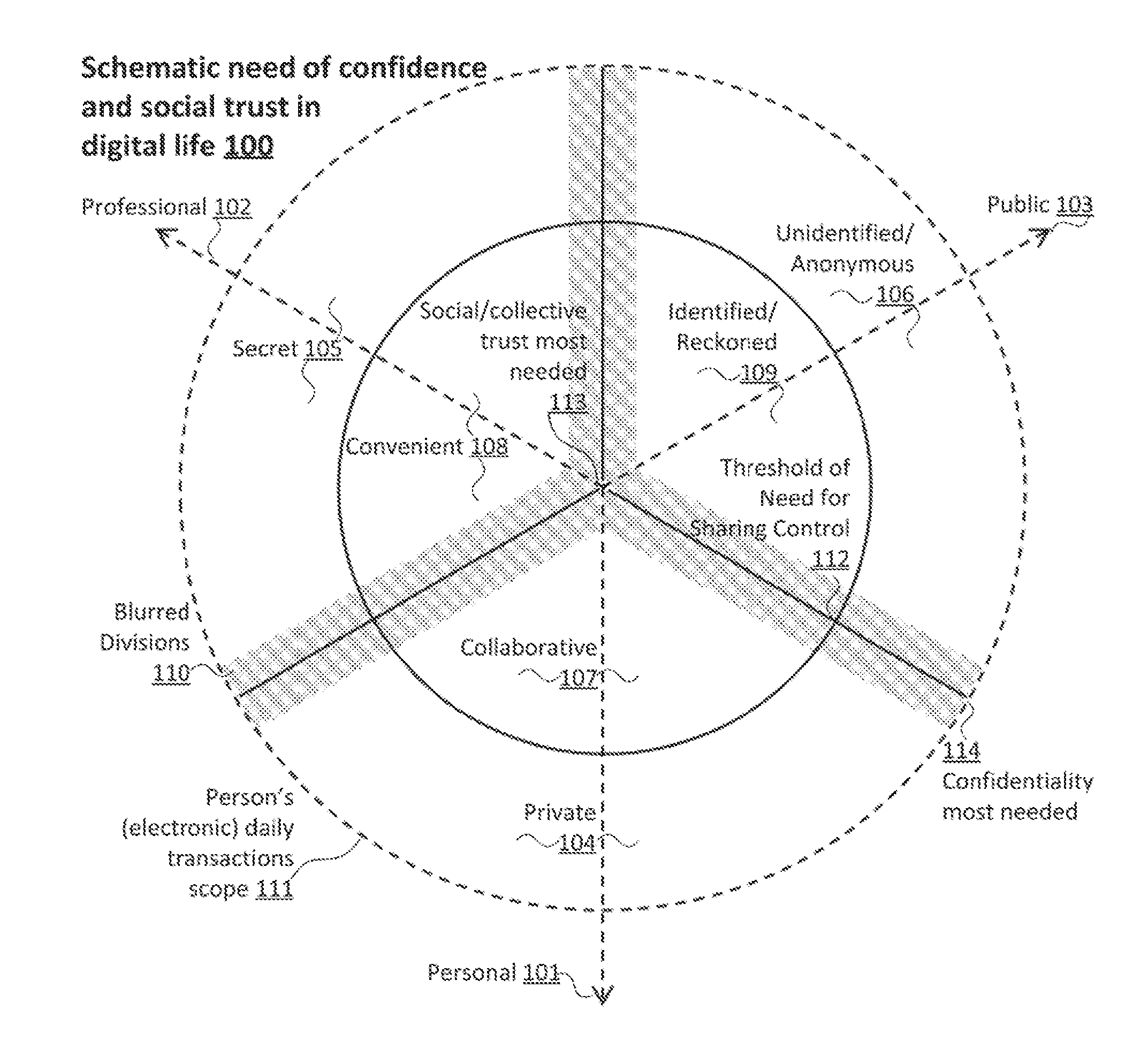
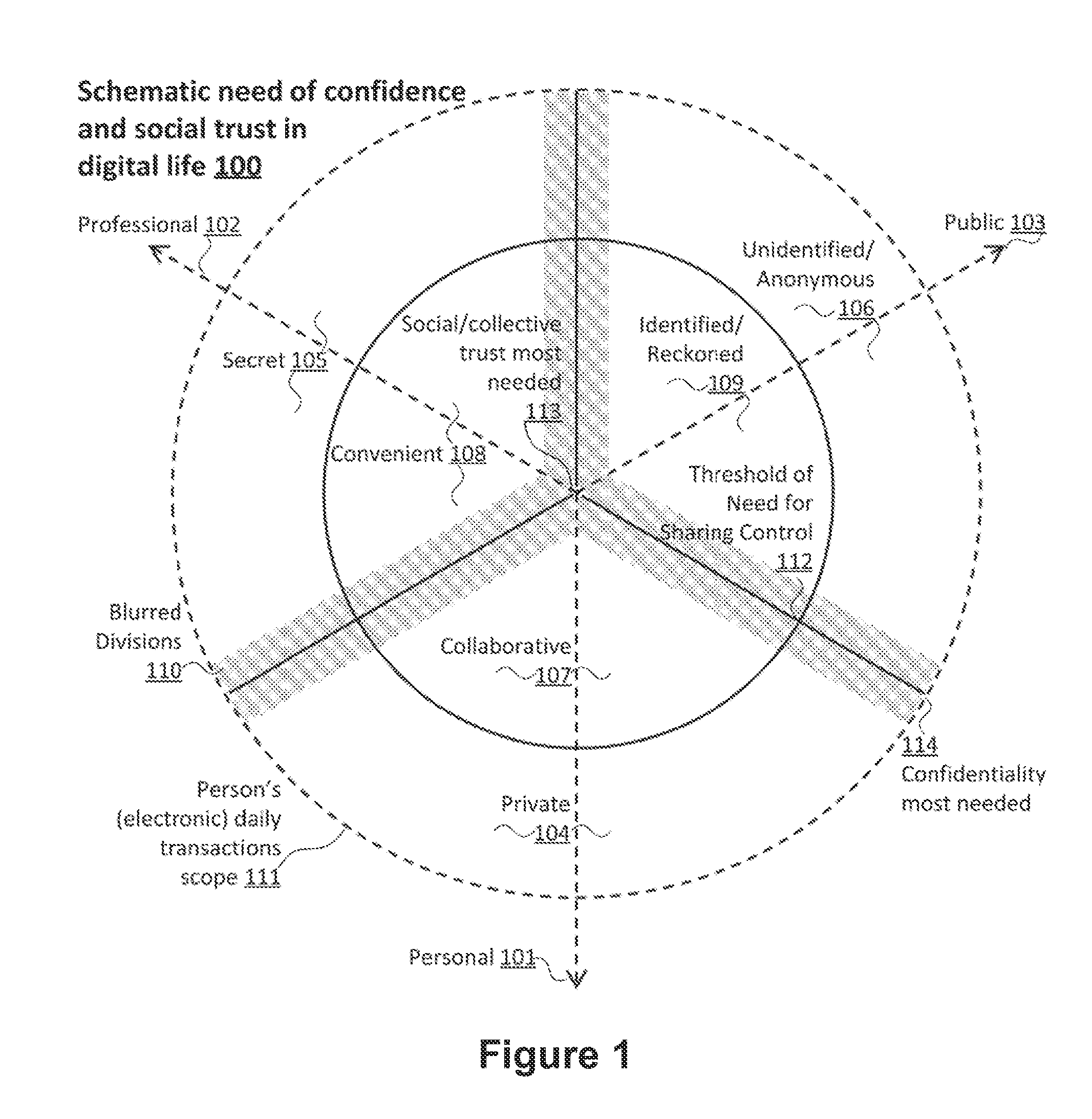
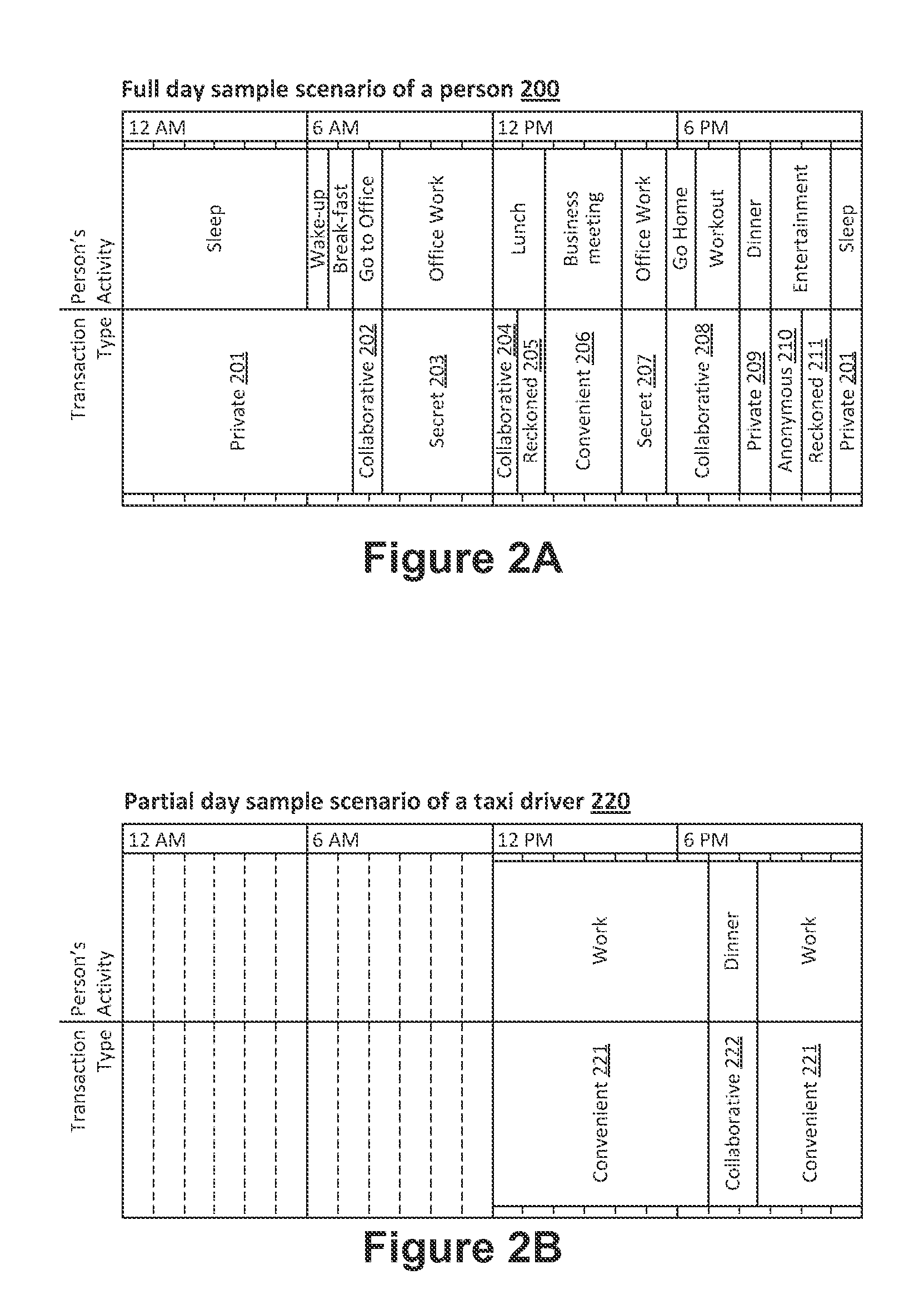
Method for controlling trust and confidentiality in daily transactions of the digital environment
InactiveUS20130061288A1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationConfidentialityEnvironment of Albania
The invention comprises a method for controlling trust and confidentiality during pervasive computing transactions supporting users' daily activities.More specifically, the present invention can be regarded as a new approach for providing users with a digital environment for performing personal, business and public routine tasks in collaboration with others, yet preserving the various levels of control existing in conventional human-to-human transactions.
Owner:INVIT INFORMATION SERVICES
System for pervasive computing
ActiveUS20120124128A1Multiple digital computer combinationsProgram controlApplication softwareUbiquitous computing
A method and system for pervasive computing are disclosed. According to one embodiment, a computer implemented method comprises a server communicating with a first device in a cloud computing environment, wherein the first device can detect surrounding devices, and an application program executable by the server, wherein the application program is controlled by the first device and the output of the application program is directed by the server to one of the devices detected by the first device.
Owner:PENINSULA TECH VENTURES +11
Dynamic access control method of pervasive computing
InactiveCN101039322AImplement authorizationImplement dynamic access controlData switching networksBiological activationMedia access control
The present invention discloses an access control method for common computing environment. The method realizes dynamic access control by combining a hierarchy credit mode with a role-based access control mode. The hierarchy credit mode is a structure with two hierarchies, wherein the bottom credit value determines the role assignment; the upper credit value determines the role activation and the permitted activation. The upper credit value is related to applied context, different upper credit values correspond to different activated roles and permission, thus the obtained service is different. The method is mainly applied in solving the problem of authorization in common computing environment as well as in realizing access control to the applied resources in other dynamic environments.
Owner:HUAZHONG NORMAL UNIV
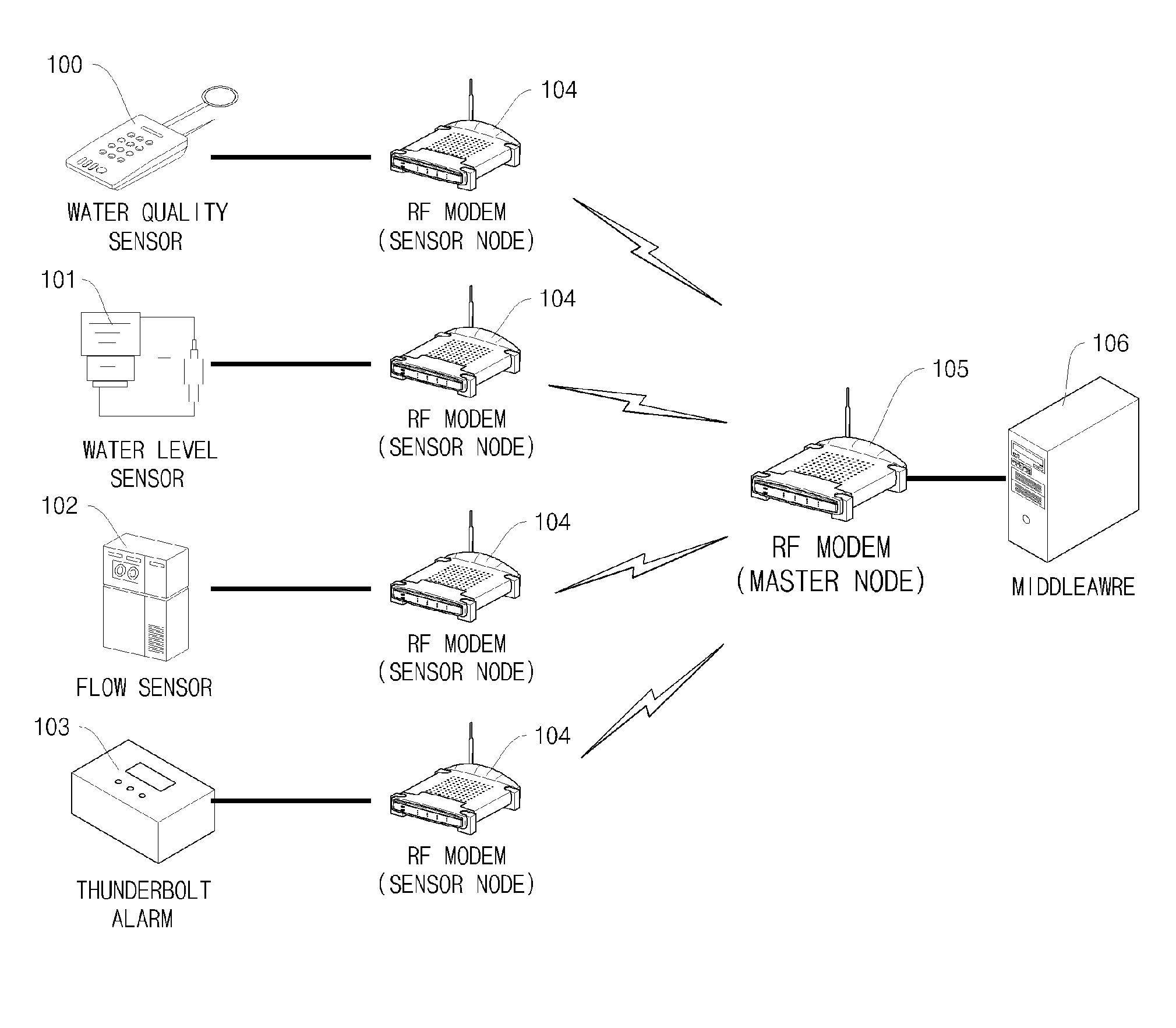
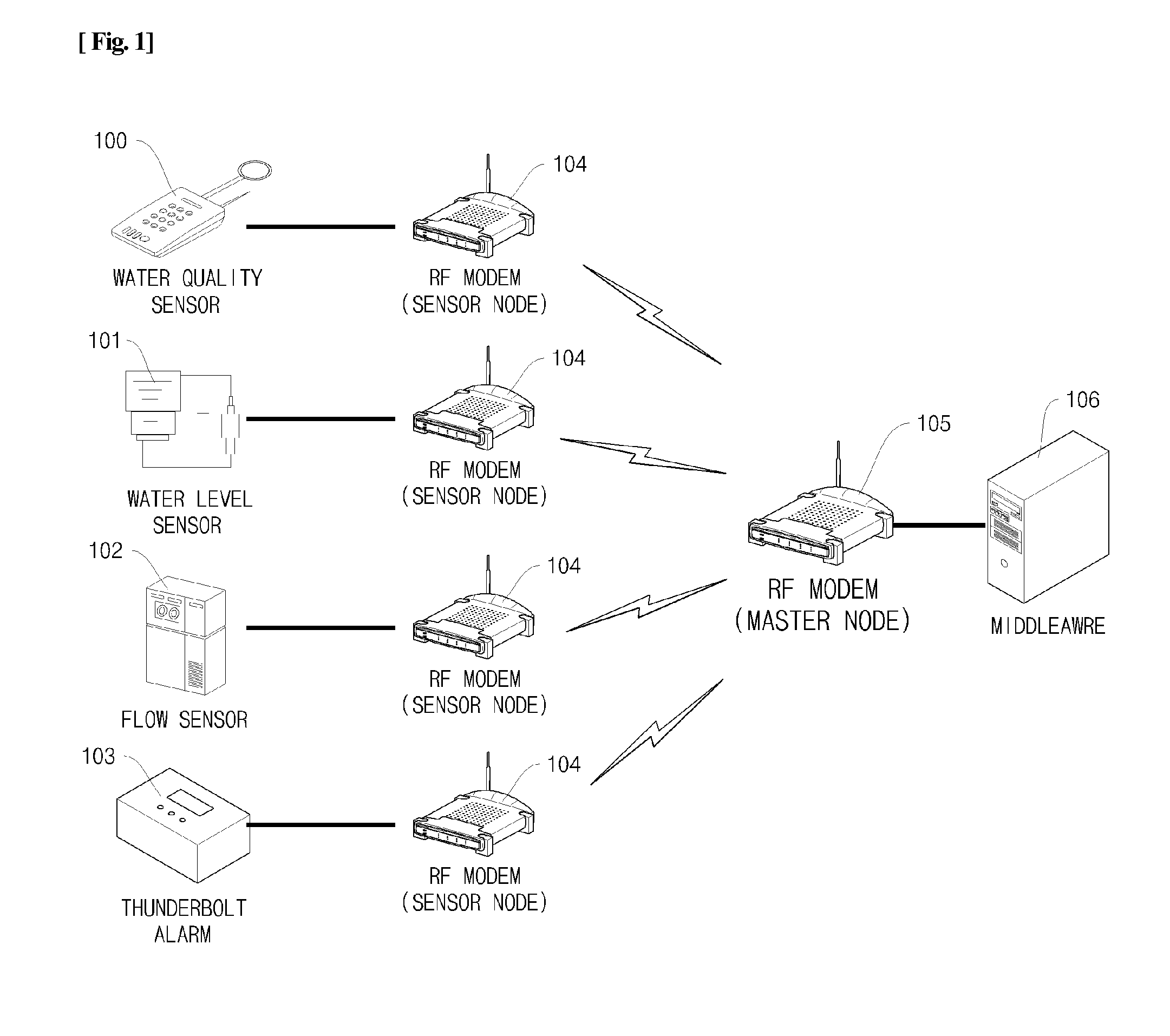
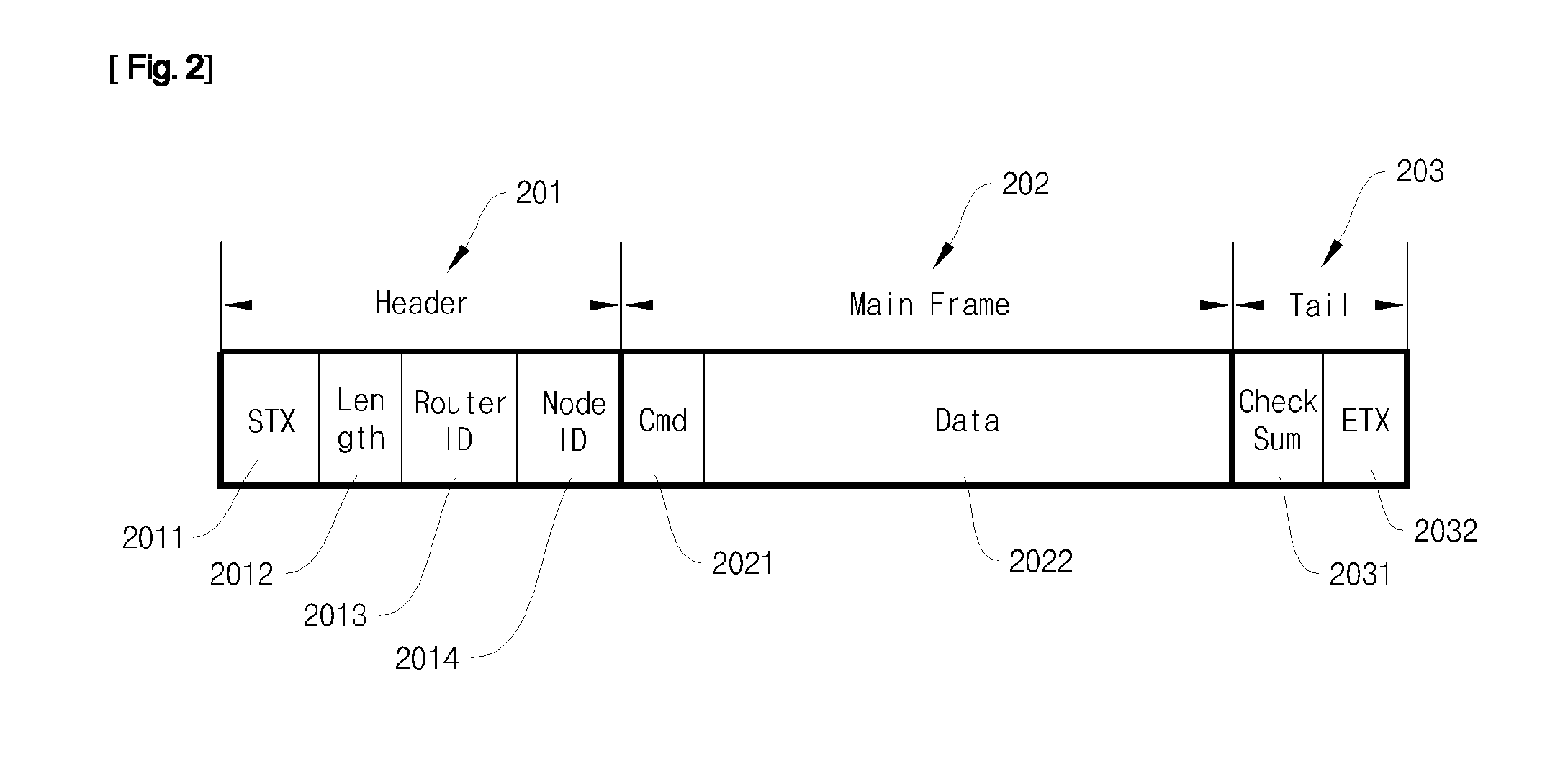
RFID Middleware-Based Sensor Data Stream Processing System and Method
InactiveUS20090284376A1Data switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsData stream processingSensor node
Disclosed herein is a Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) middleware-based sensor data stream processing system and method.The RFID middleware-based sensor data stream processing system of the present invention includes one or more sensors for measuring and collecting surrounding environmental information, sensor nodes for transmitting data collected by the sensors or receiving sensor management commands, a master node for transmitting or receiving data to or from the sensor nodes and for configuring the data received from the one or more sensors into data having a specific protocol structure applied in common to the sensors, and RFID middleware for receiving the sensor data from the master node, converting the sensor data into data of an Electronic Product Code (EPC), and converting the EPC data into data of a Uniform Resource Name (URN) code.Accordingly, the present invention has the advantage of processing various types of sensor data as well as RFID tags through RFID middleware, and thus ubiquitous computing can be efficiently realized.
Owner:JAVA INFORMATION TECH
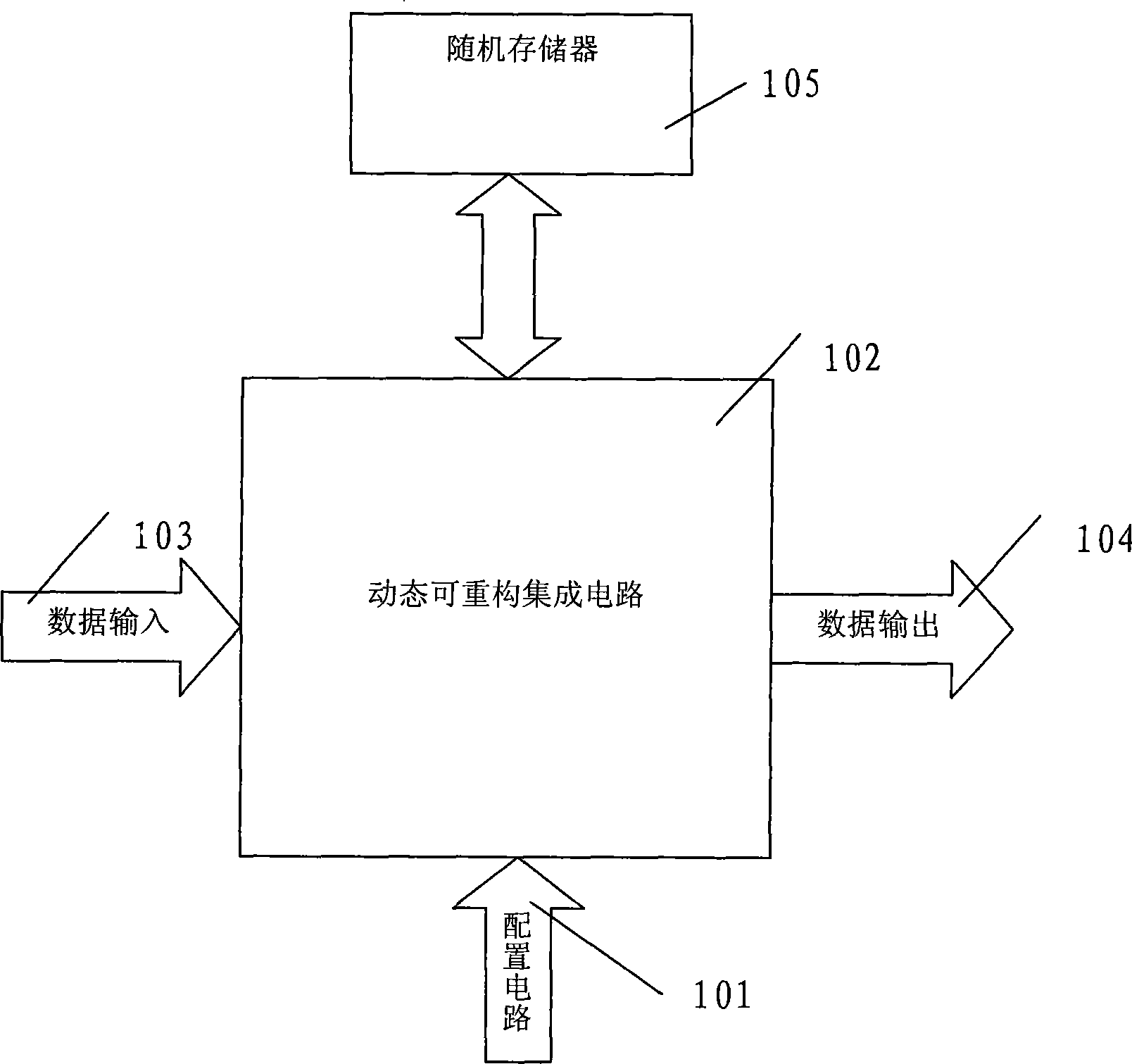
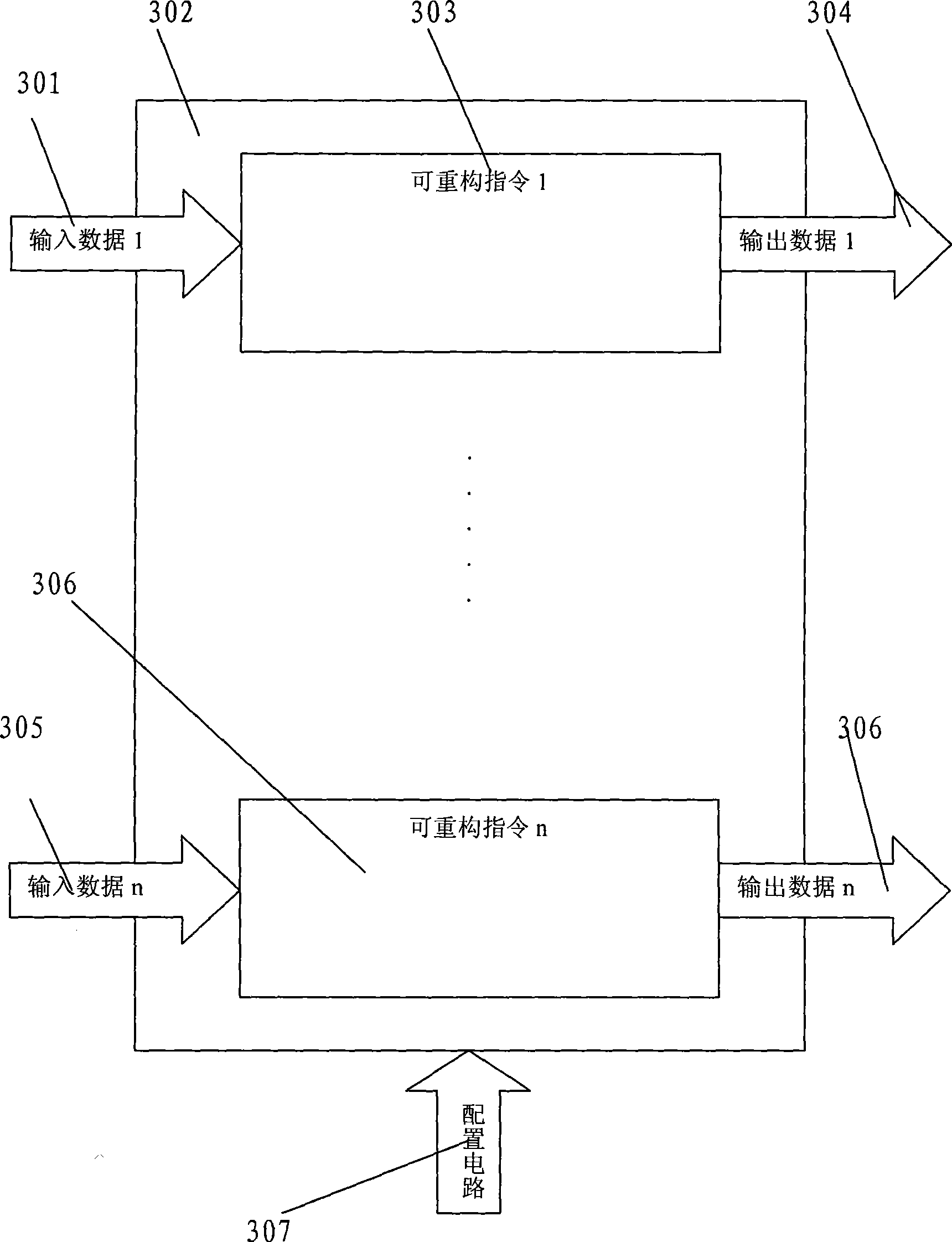
Dynamic reconfigurable instruction computer processor and implementing method
InactiveCN101364214AImprove resource utilizationReduce power consumptionArchitecture with single central processing unitComputer architectureRandom access memory
The invention provides a dynamically reconfigurable instruction computer processor and an implement method, and relates to a dynamically reconfigurable instruction computer processor composed of a dynamically reconfigurable integrated circuit. The dynamically reconfigurable integrated circuit is connected with a configuration circuit, a user data input / output circuit, a random access memory, a keyboard, a mouse and a display of the dynamically reconfigurable integrated circuit, and comprises a plurality of reconfigurable units; each reconfigurable unit is composed of a SRAM reconfigurable circuit with a configuration queue and a configuration clock; when the configuration clock of a corresponding configuration unit is allowed, the configuration unit is configured, namely a configuration instruction is updated; when the configuration clock is prohibited, no configuration data of the configuration unit is updated, so that the prior configuration is reserved, namely the prior reconfigurable instruction is reserved. The project can be widely applied to a PC computer, pervasive computing, an embedded processor, a communication processor and a network processor, particularly a processor of grid computing. The computer processor has broad prospects for application.
Owner:顾士平
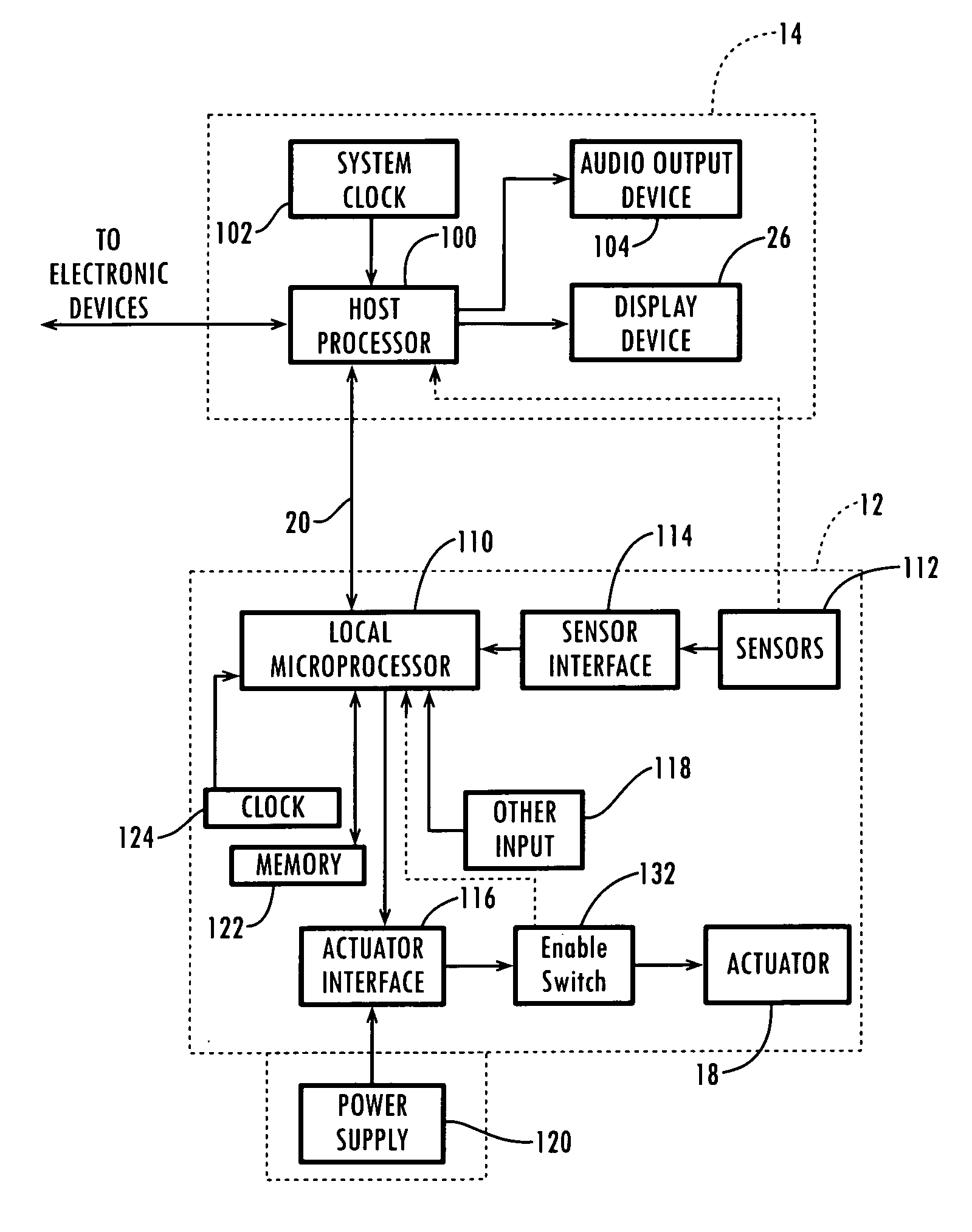
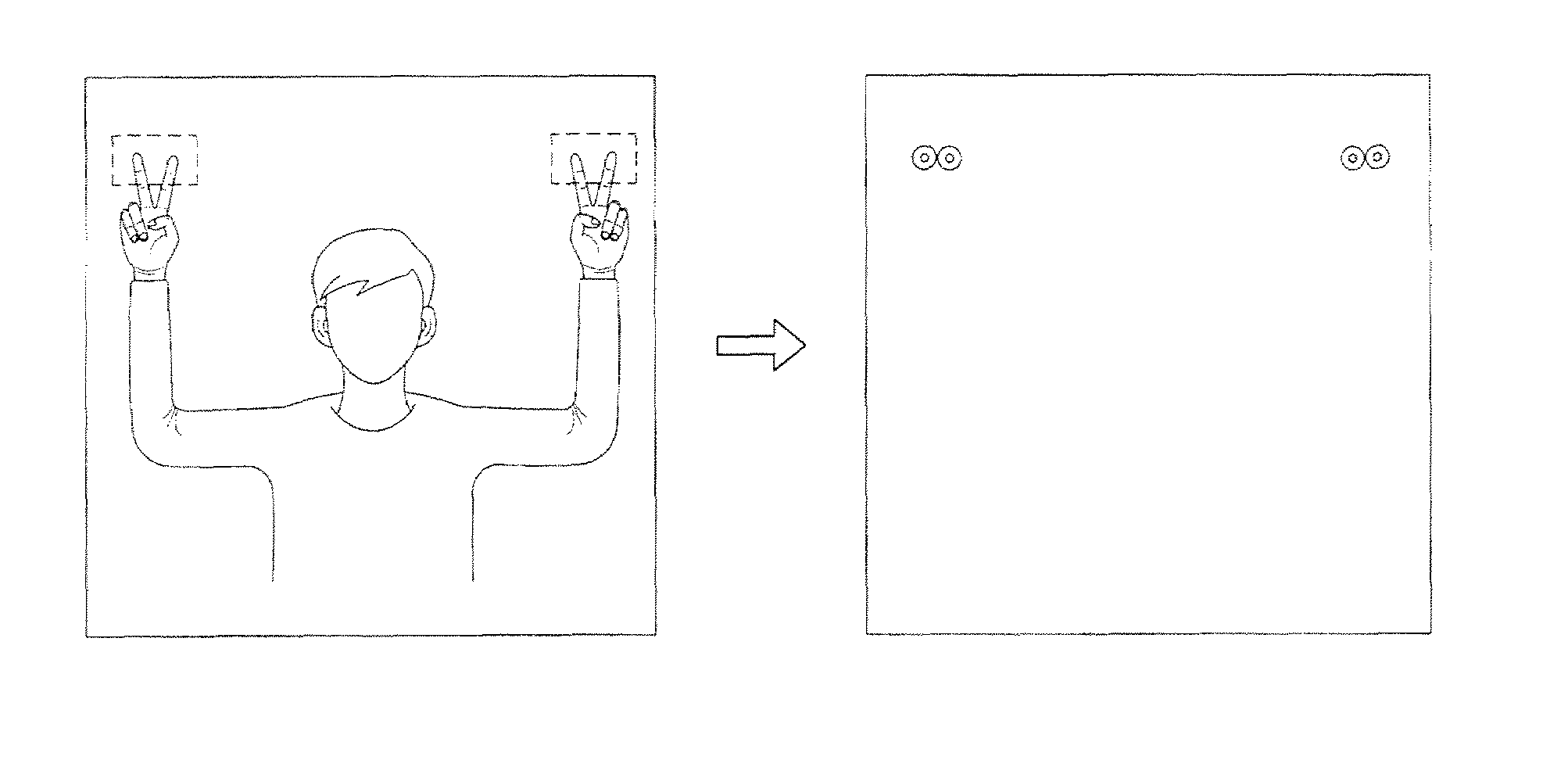
System for controlling devices and information on network by using hand gestures
InactiveUS20100073287A1Enhanced interactionCharacter and pattern recognitionCathode-ray tube indicatorsDisplay deviceUbiquitous computing
The disclosure relates to a system for controlling devices and information on a network by hand gestures, and more particularly, to a system for controlling devices and information on a network by hand gestures in which a device or a file to be controlled is selected by a user and a display device is pointed so that information and data can be shared and that various devices can be coupled to each other easily and can be controlled easily.The system for controlling devices and information on a network by hand gestures can remarkably improve the interaction between various input and display devices and a user under a ubiquitous computing environment.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
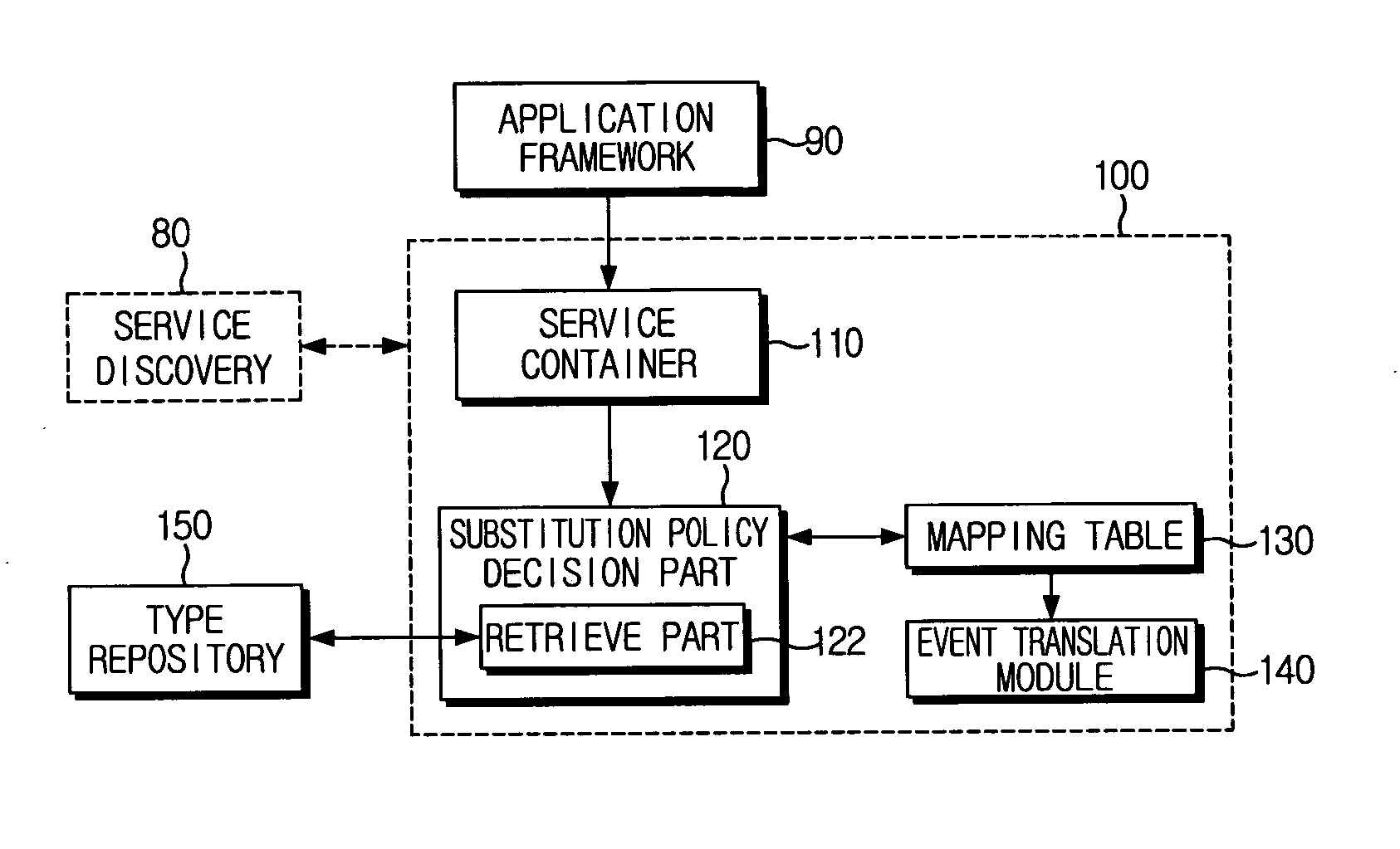
Methods, apparatus, and program products for abstract applications/components in a ubiquitous computing environment
ActiveUS7620737B2Simple configurationDigital data processing detailsInterprogram communicationContext dataApplication software
Methods, apparatus and program products for using historical contextual data in a ubiquitous computing environment. The historical contextual data can be dispersed among components in an environment or logging services as well as stored on a particular component or logging service. The historical contextual data can be used to help create or re-create component configurations within the relevant environment through the use of abstract applications and abstract components. Abstract applications can be specified to create connections with specific components. Abstract applications can also be generalized so that they need not create connections with specific components, but can create component connections that perform a desired function by determining which components to use from the available components, and how to connect the selected components to perform the function.
Owner:XEROX CORP
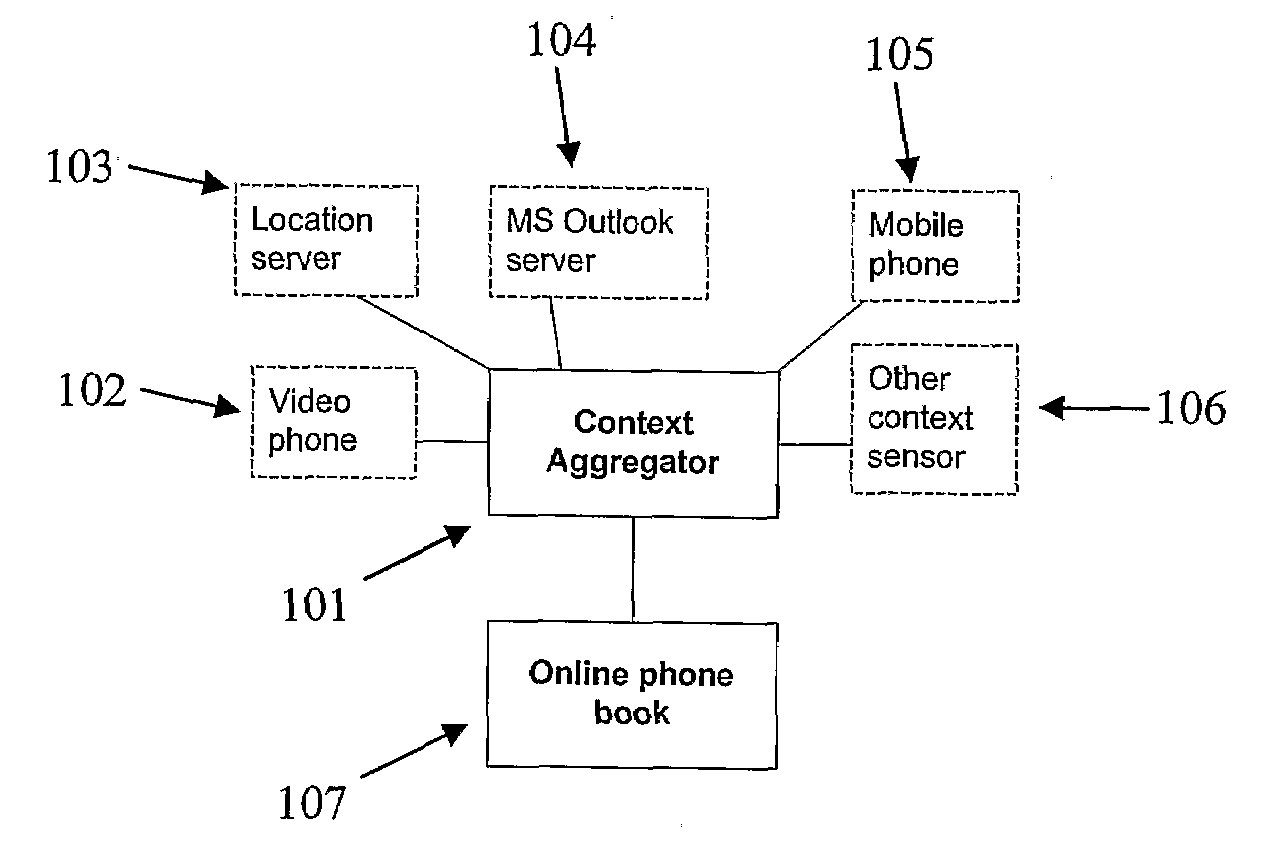
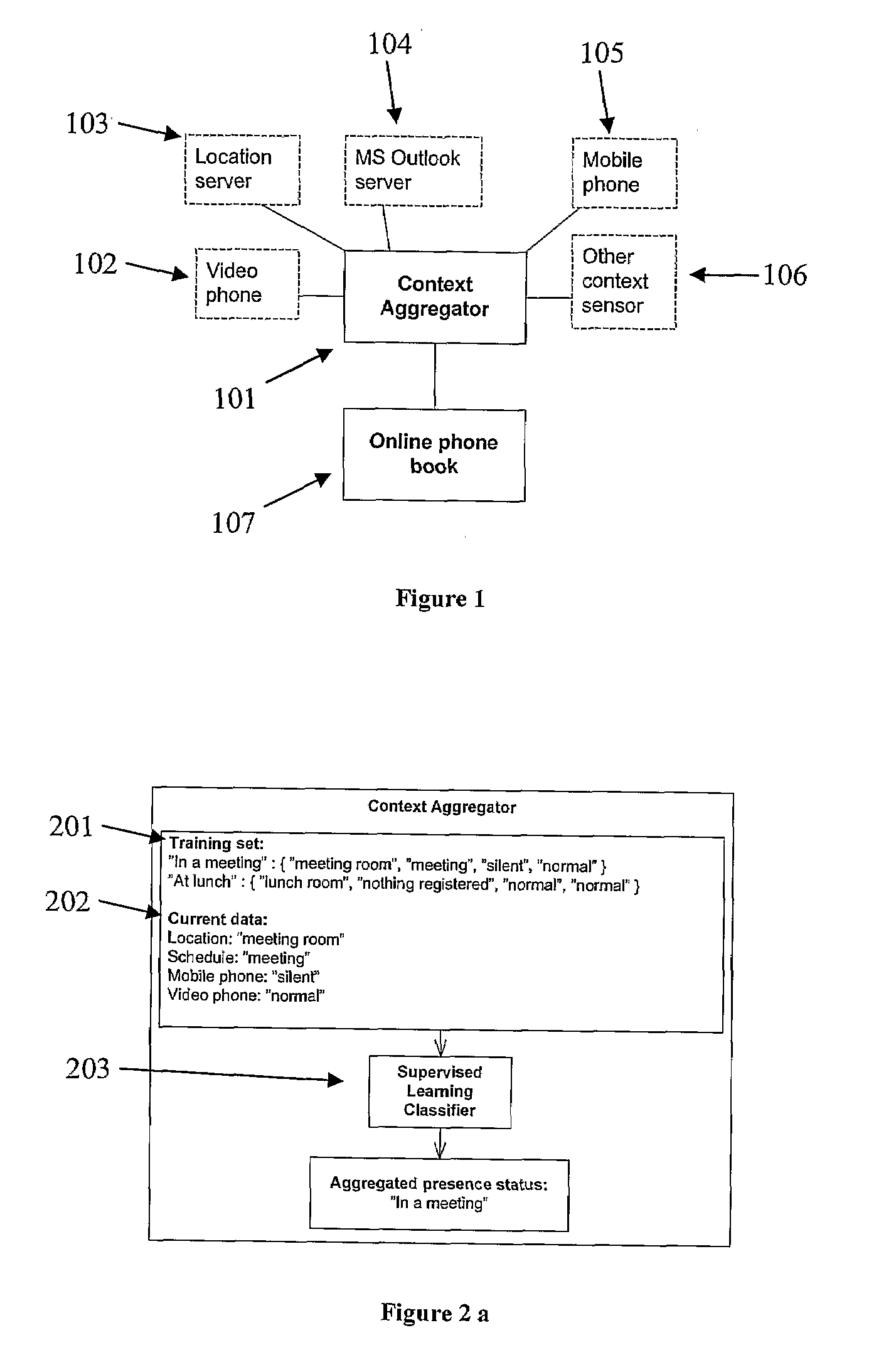
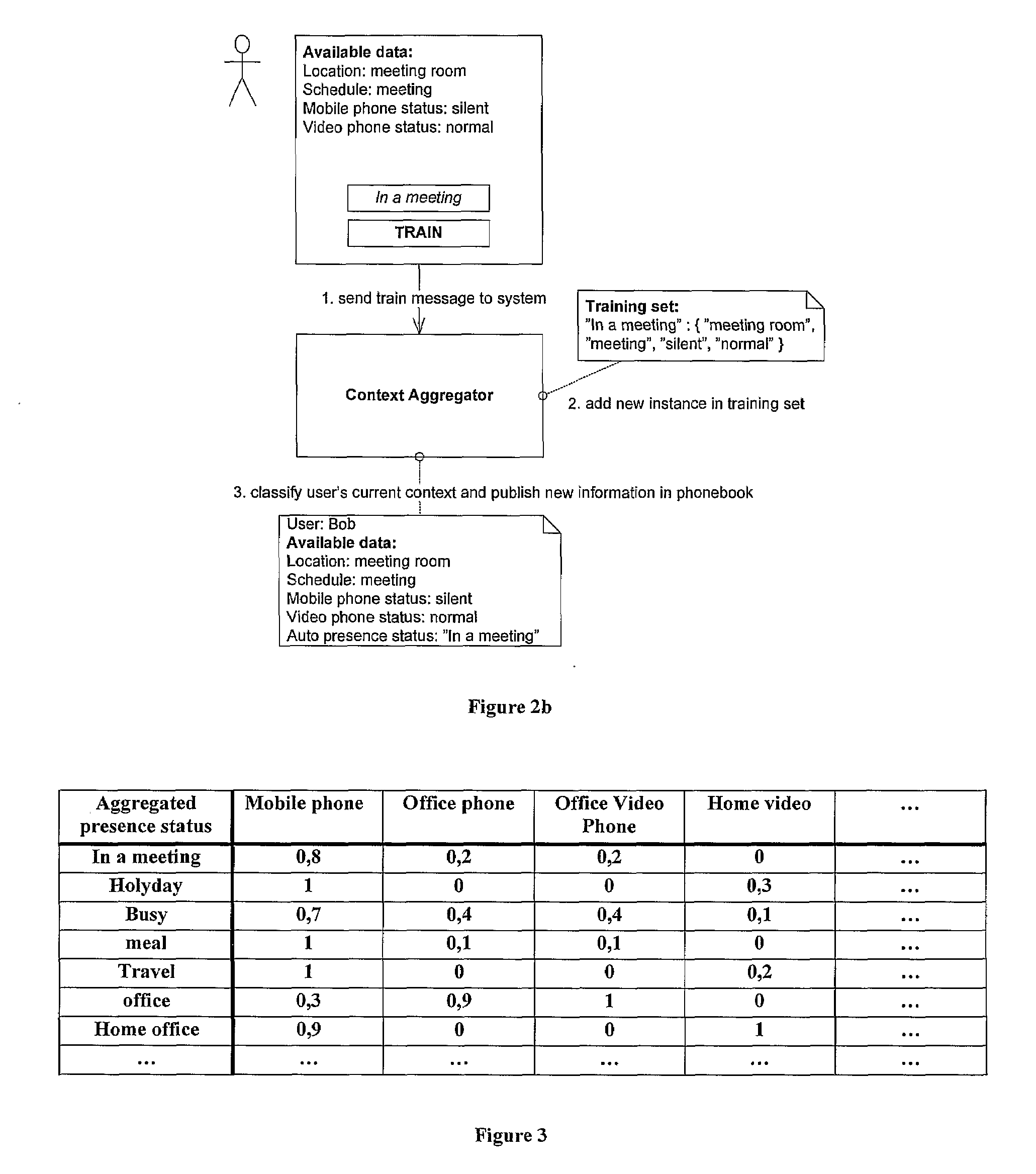
Context aware phonebook
When interacting and talking with each other, humans are quite successful at conveying information and reacting appropriately. That is, they are able to interpret situational information which in most cases is only implicitly given. This ability is in stark contrast to most of the current state-of-the-art computer and telecommunications systems, which in large are unaware of this context information. Consequently, there has recently been great interest in making applications more context-aware so that they can adapt to different situations and be more receptive to user's needs.The purpose of this project was to explore how one through examining different kinds of context information can find ways to automatically set a user's presence status. This presence status is useful as it allows for a person to decide whether it is appropriate to initiate communication or not. Further, it was the mission of this project to review how a policy-based approach could be use together with the mentioned aggregated presence status to increase user personalisation of communication. Finally, the project set out to show how one can model and implement such a context-aware system using Ericsson's service creation framework; ServiceFrame.The project used a model-driven approach (MDA) in which most of the effort went into modelling the functionality of the system using formal UML2.0 models and then transform these into code using code generation tools and MDA viewpoints. During the modelling of the system, it was decided to examine user's context information and from this classify the user's aggregated presence status by utilising a supervised learning classifier. In a proof-of-concept solution, the probabilistic classifier, Naïve Bayes, proved to be an extremely fast and accurate classifier which should be considered as a strong option in any future implementations of the system. Personalisation of communications by design was achieved both through allowing completely personal classification rules, as well as through a policy approach. This policy approach consisted of letting a user construct a personal prioritising of his or hers terminals based on his or her aggregated presence status. It is suggested to expand this approach by also taking the group membership of the entity which requests the user information into account.Using supervised learning makes sure the system is not to be solely dependent on any particular context data sensor but rather having the ability to adapt to an ever-changing environment. With the expected explosion of context sensors in areas such as ubiquitous computing [15], this ability to adapt will become increasingly important in future context-aware systems. In addition to this flexibility, the use of supervised learning also introduces the ability to classify completely unknown scenarios. This means that even if the classifier encounters a new scenario which is has never seen before, it tries to predict a status based on the underlying previous data. It stated that these predictions often have a high degree of accuracy with the right training data.The system used the agent oriented architecture, which it is stated has a good support for personalisation as agents generally are used to represent entities in the real world (e.g. users). Through this approach, the system allows for a completely personal classification of a user's current context. By doing so, it is acknowledged that pre-defined rules does not fit everyone, but should be adapted to give each person a high degree of personalisation.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
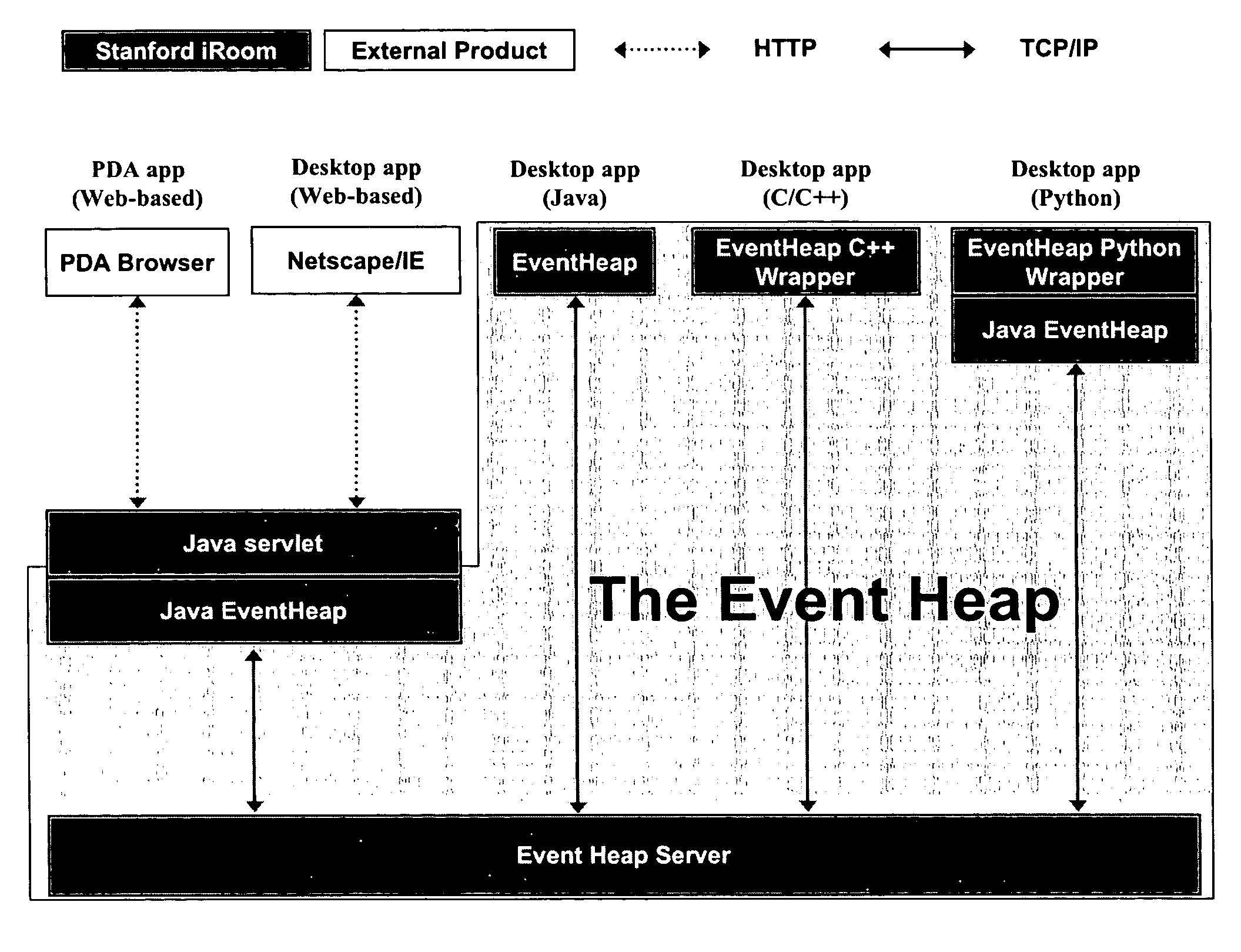
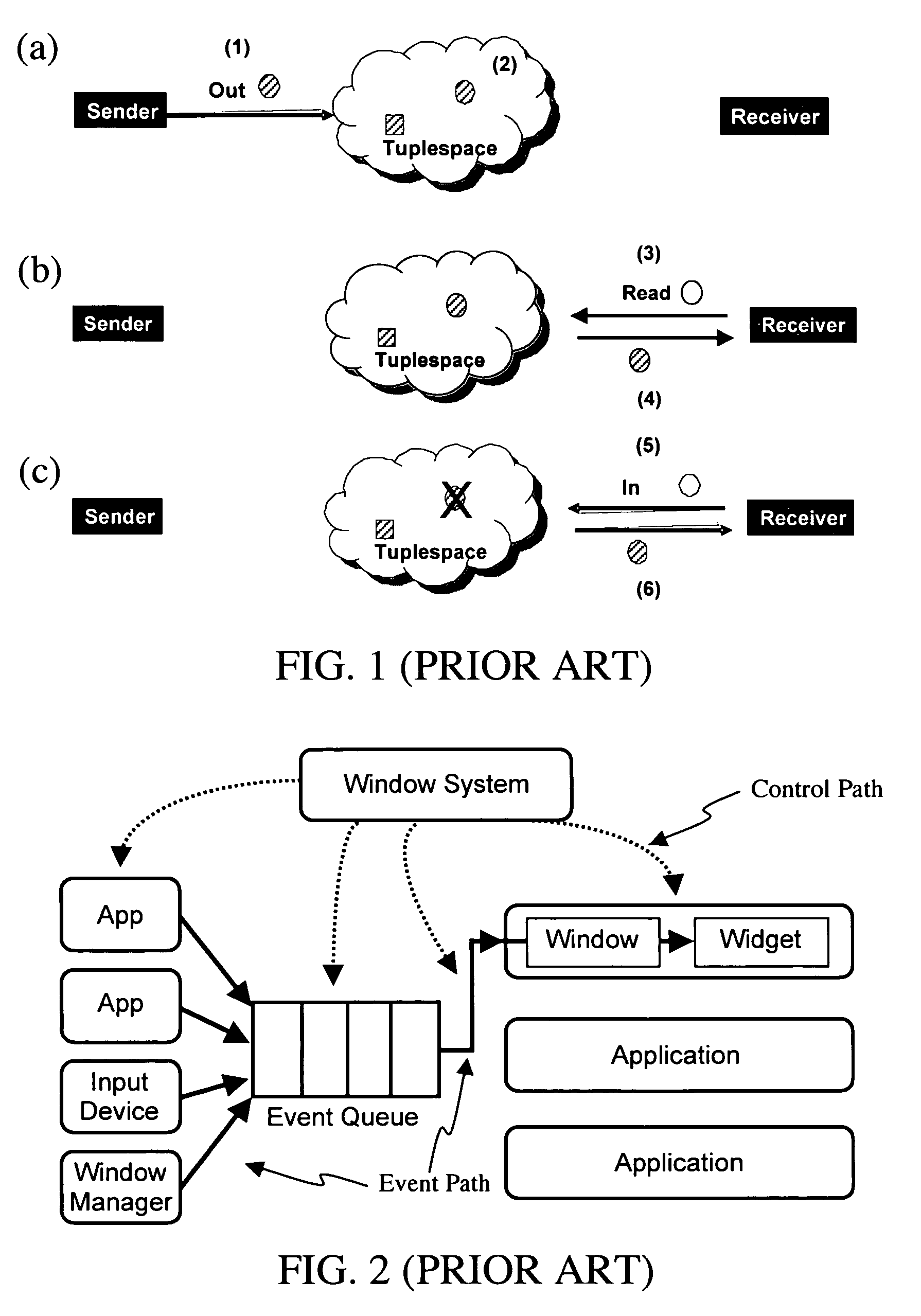
Event heap: a coordination infrastructure for dynamic heterogeneous application interactions in ubiquitous computing environments
ActiveUS7702729B2Effective interactionEasy to parseMultiprogramming arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsTypingWorkspace
An efficient and adaptive middleware infrastructure called the Event Heap system dynamically coordinates application interactions and communications in a ubiquitous computing environment, e.g., an interactive workspace, having heterogeneous software applications running on various machines and devices across different platforms. Applications exchange events via the Event Heap. Each event is characterized by a set of unordered, named fields. Events are routed by matching certain attributes in the fields. The source and target versions of each field are automatically set when an event is posted or used as a template. The Event Heap system implements a unique combination of features, both intrinsic to tuplespaces and specific to the Event Heap, including content based addressing, support for routing patterns, standard routing fields, limited data persistence, query persistence / registration, transparent communication, self-description, flexible typing, logical / physical centralization, portable client API, at most once per source first-in-first-out ordering, and modular restartability.
Owner:TIDEBREAK
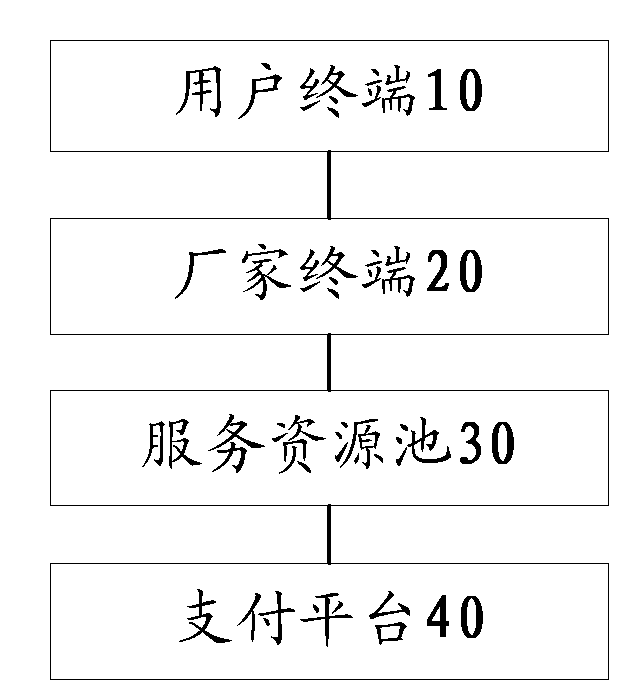
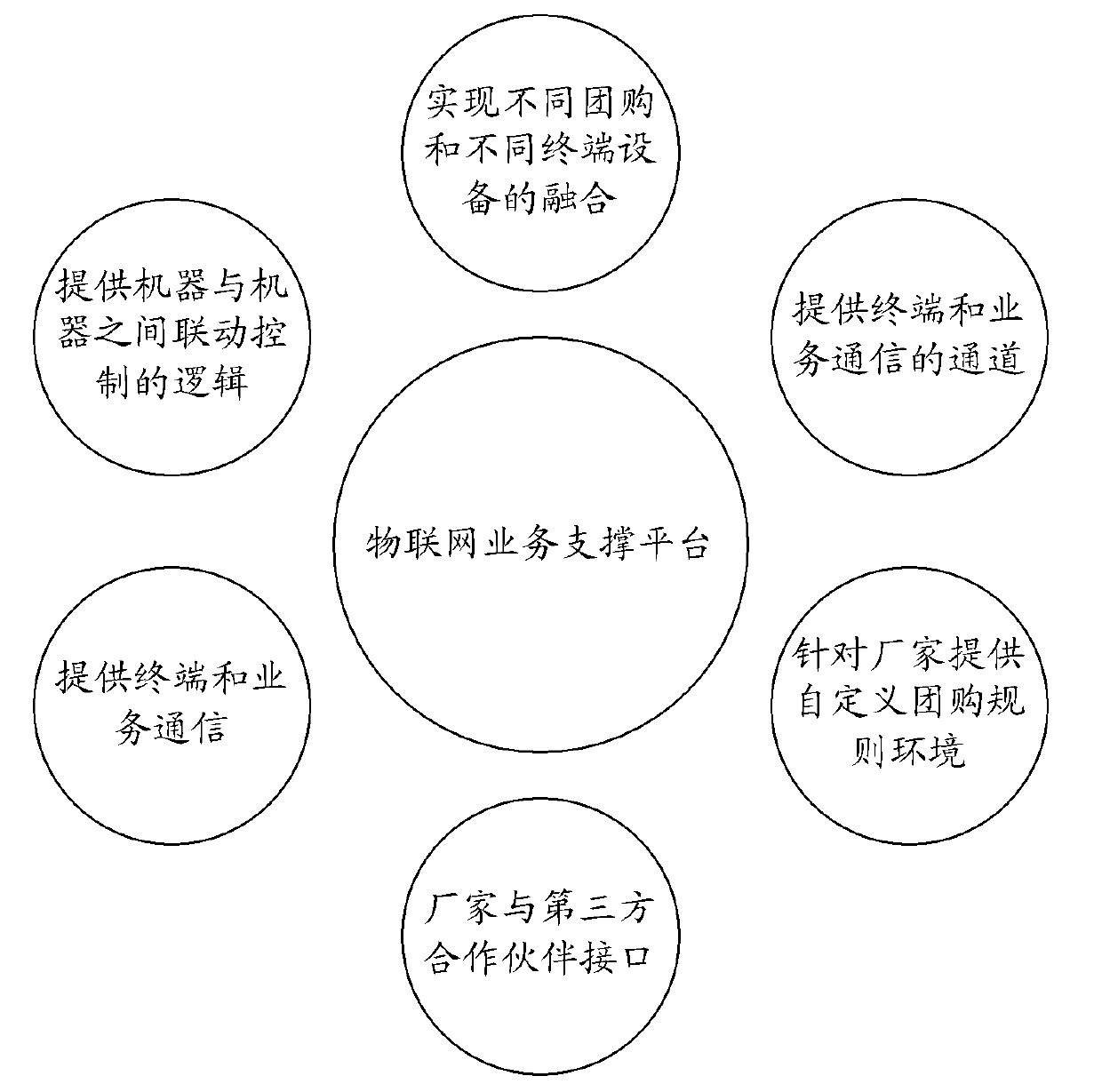
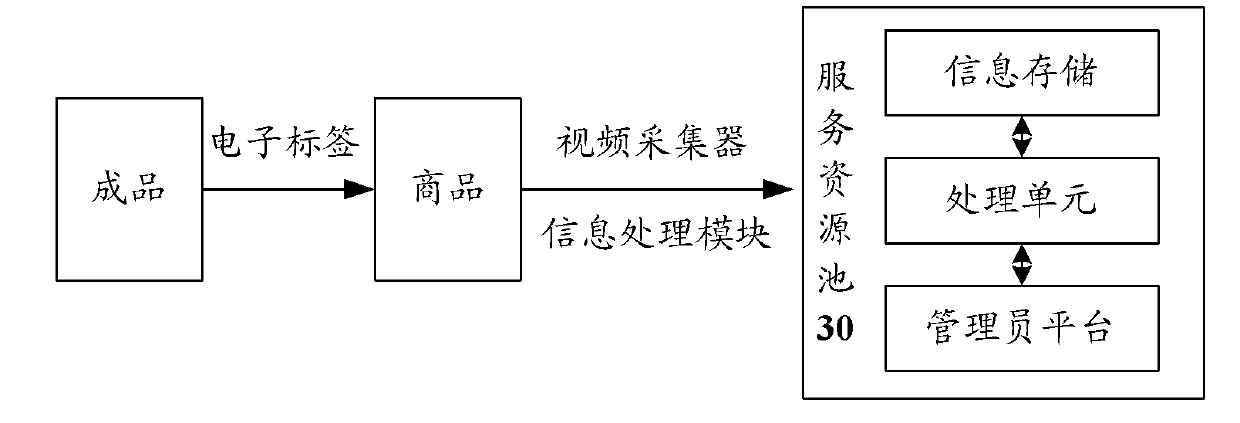
Group purchase processing method and system based on ubiquitous computing environment
InactiveCN102708487AImprove usabilitySolve the experiencePayment architectureCommerceResource poolPayment
The invention discloses a group purchase processing method and a group purchase processing system based on a ubiquitous computing environment. The method comprises the following steps of: constructing a group purchase platform which comprises one or more group purchase data, and sending the group purchase data to a service resource pool; sending a group purchase demand to the service resource pool by a user terminal according to a demand; matching the group purchase demand with the group purchase data by the group purchase platform, and feeding a matched result to the user terminal; and enabling the user terminal to enter a payment flow according to the matched result. By the method and the system, the group purchase platform can be constructed according to demands of users, so that the user experience is enhanced.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com