Dynamic read valley search in non-volatile memory
A non-volatile storage, latch technology, applied in static memory, read-only memory, digital memory information, etc., can solve problems such as change, threshold voltage drift, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
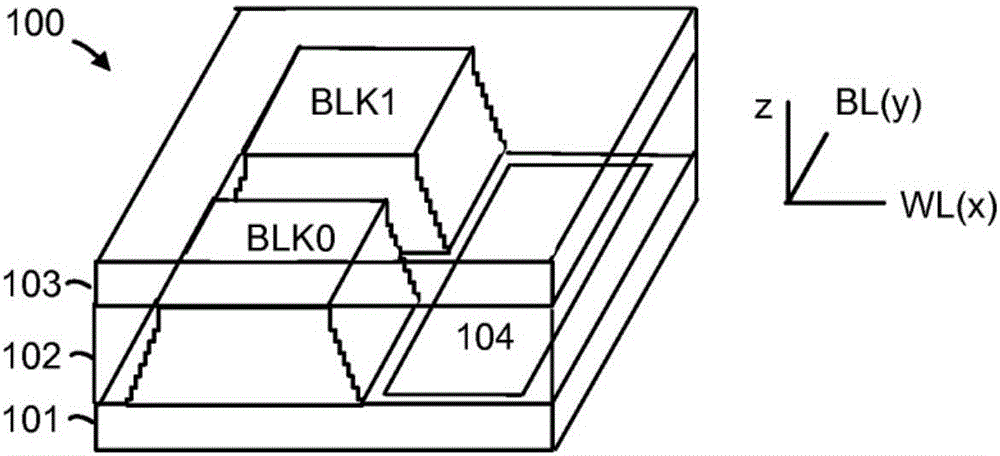
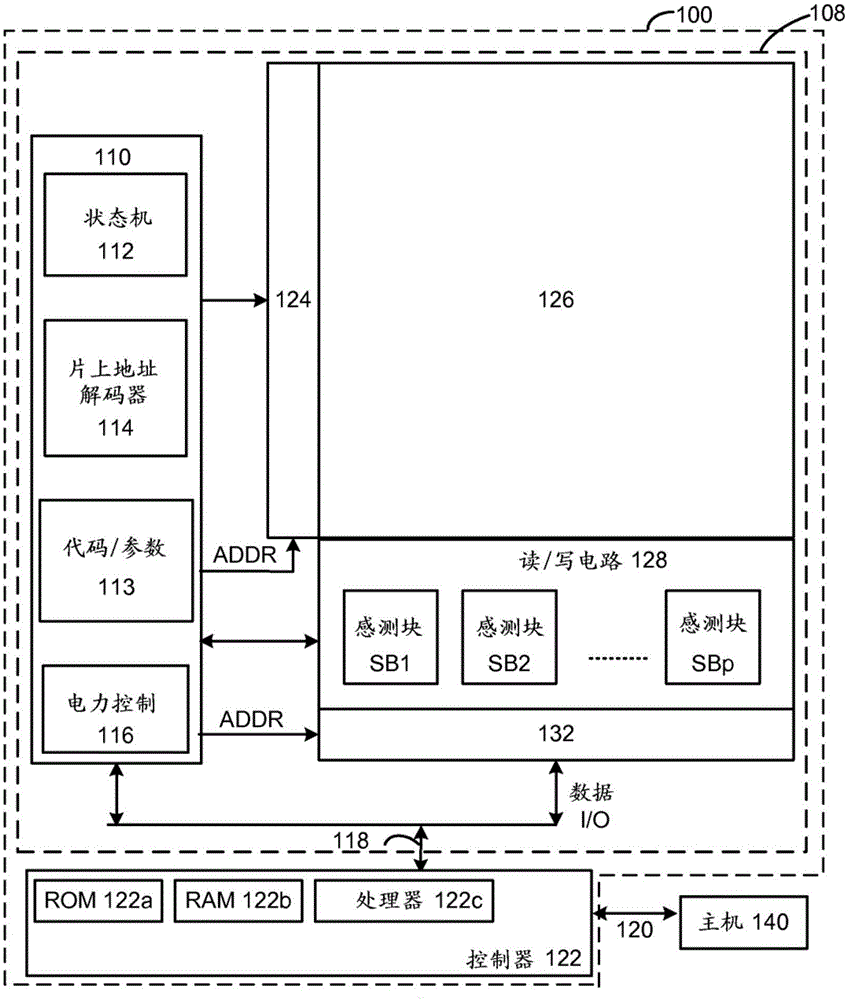
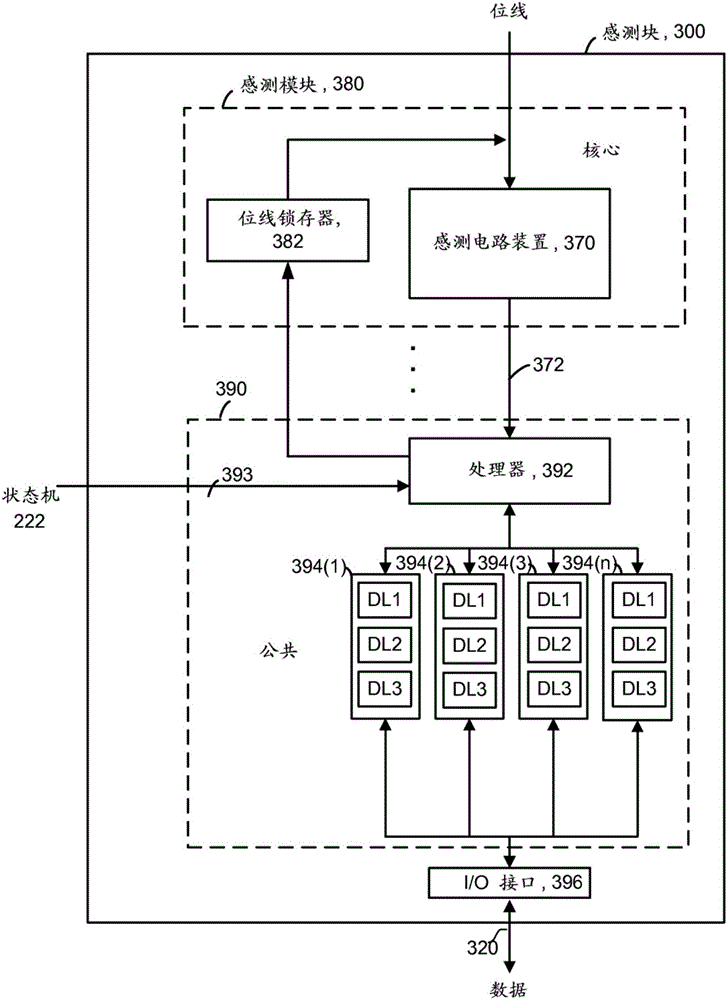
[0031] Techniques for determining dynamic read levels for non-volatile storage elements are disclosed herein. Due to data retention issues, the threshold voltage (V T ) may be offset. Therefore, the read level (CGRV) should be changed / updated to reflect the V T offset. One technique for finding new read levels is to do a valley search. Valley searching refers to a valley between two adjacent threshold voltage distributions. Valley searching may include taking multiple reads to find a valley between two adjacent threshold voltage distributions. The new read level can be based on the location of the trough. In one possible technique, valley searching includes determining a count for non-volatile storage elements having threshold voltages within a threshold voltage window defined by two read levels. This process can be repeated for several threshold voltage windows such that several counts are determined. The process of determining the count may be referred to herein as "s...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap