Joint Depth estimation and semantic segmentation from a single image
A semantic and deep technology, applied in the field of joint depth estimation and semantic annotation, can solve the problems of error propagation and lack of accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
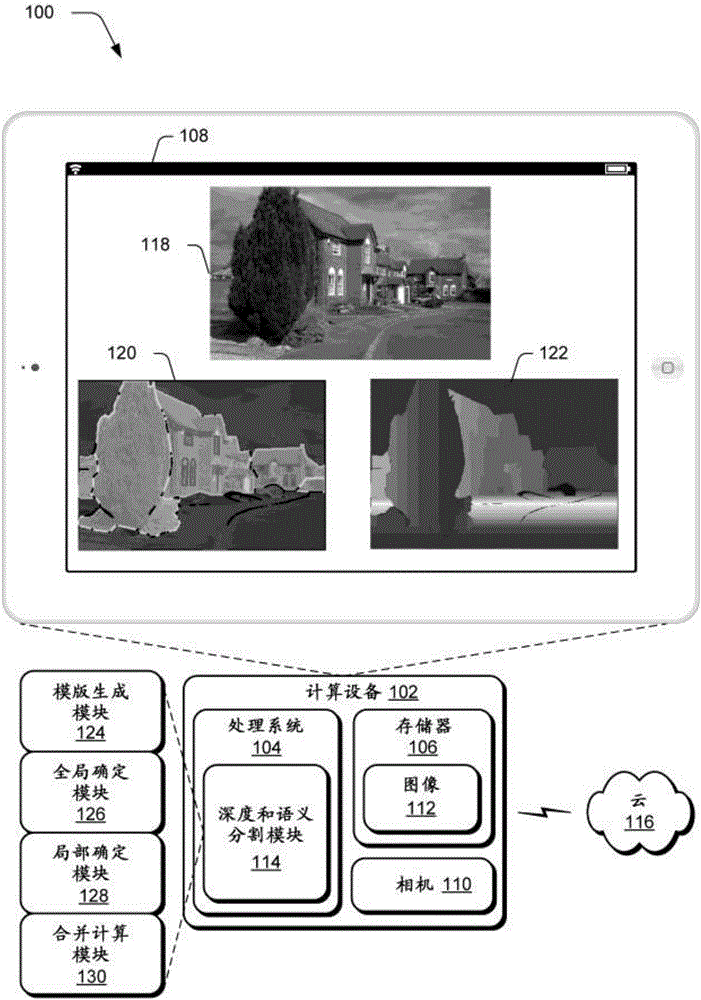
[0025] overview
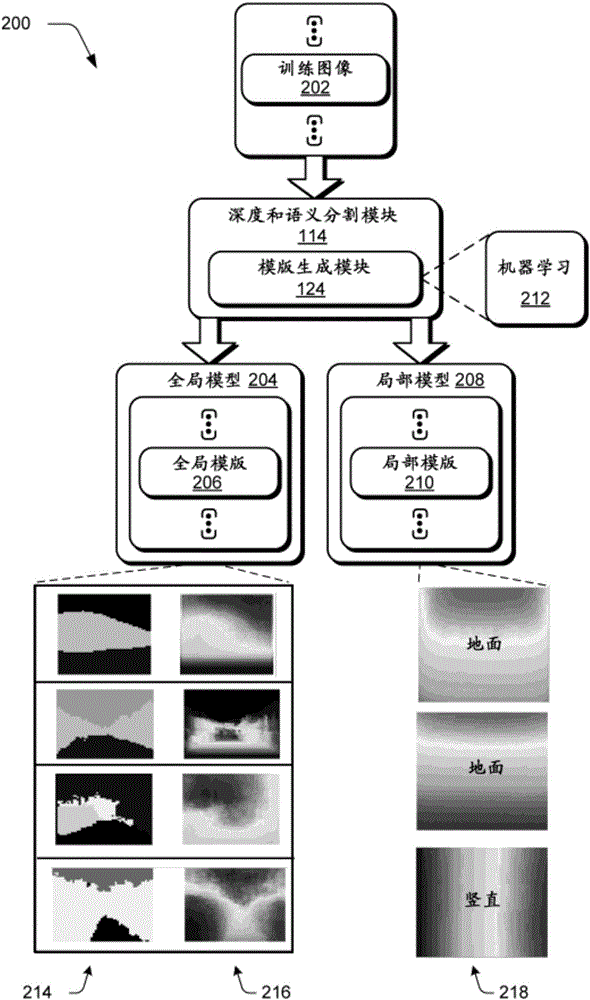
[0026] Semantic segmentation and depth estimation are two fundamental problems in image understanding. Although the two tasks have been found to be strongly related and mutually beneficial, these problems are conventionally addressed separately or sequentially using different techniques, which creates inconsistencies, errors and inaccuracies.
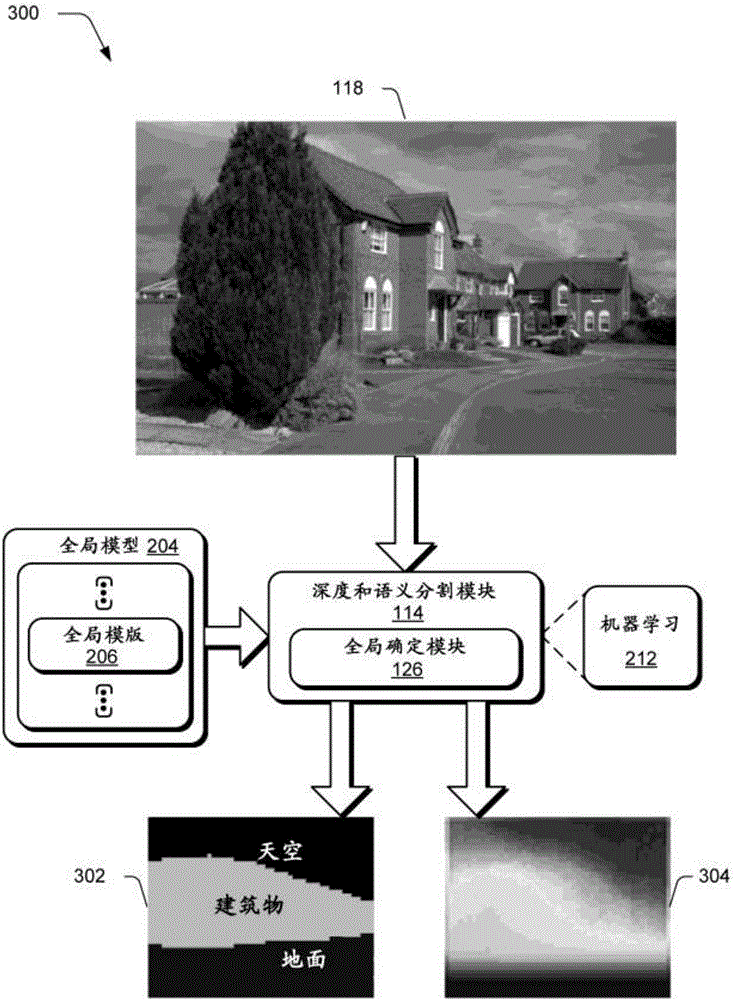
[0027] In the following, we observe the complementary effects from typical failure cases of the two tasks that lead to the description of a unified coarse-to-fine framework for joint semantic segmentation and depth estimation usable on a single image. For example, a framework is proposed that first predicts a coarse global model composed of semantic labels and depth values (e.g., absolute depth values) by machine learning to represent the overall context of an image. Semantic labels describe "what" is represented by corresponding pixels in the image, e.g., sky, plants, ground, walls, buildings, etc. The depth val...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com