A low-latency wireless communication method and device
A wireless communication, low-latency technology, applied in the field of low-latency transmission based on long-term evolution, can solve problems such as LTE long air interface delay, and achieve the effect of saving overhead
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
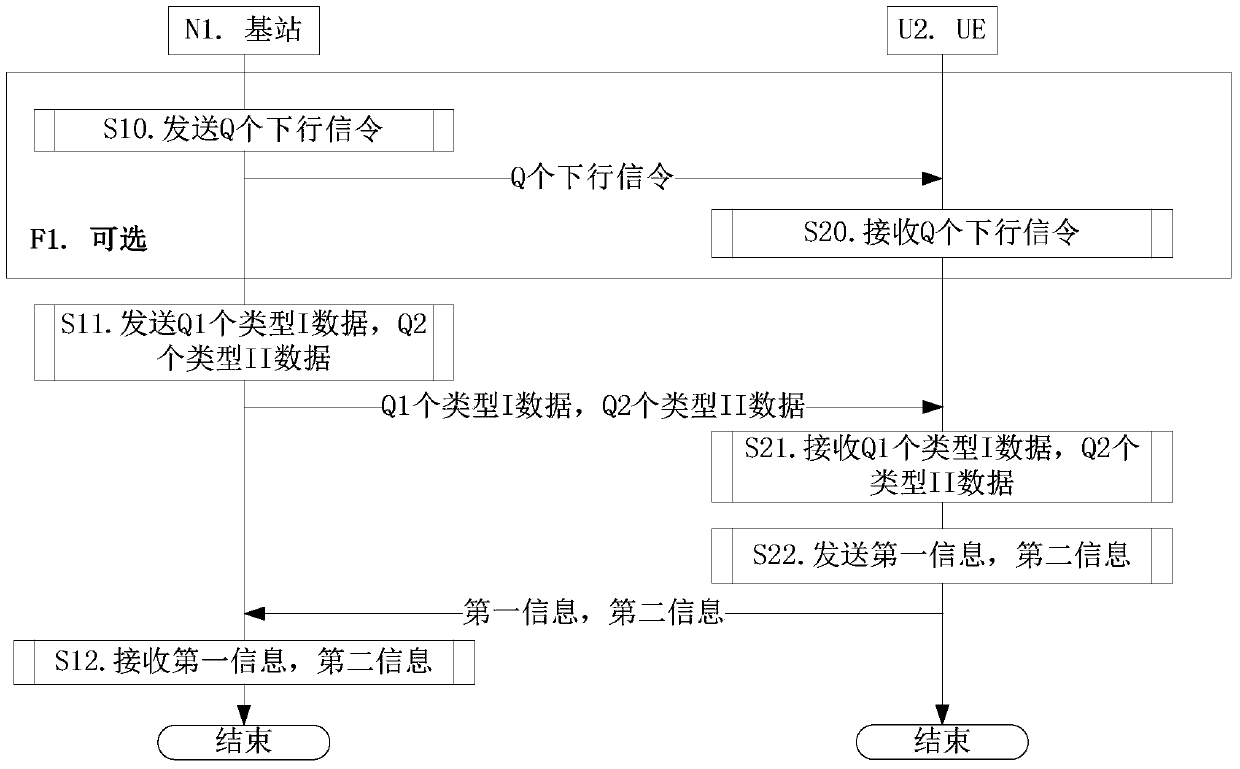
[0103] Embodiment 1 exemplifies uplink HARQ-ACK transmission, as attached figure 1 shown. attached figure 1 In , the base station N1 is the maintenance base station of the serving cell of the UE U2, and the steps identified in the block F1 are optional steps.
[0104] for base station N1 , send Q downlink signaling in step S10, send Q1 type I data and Q2 type II data in step S11, and receive first information and second information in step S12.
[0105] for UE U2 , receiving Q pieces of downlink signaling in step S20, receiving Q1 pieces of type I data and Q2 pieces of type II data in step S21, and sending the first information and the second information in step S22.
[0106] In Embodiment 1, the Q downlink signaling schedules the Q2 Type II data, the Type I data includes one or more Type I transport blocks, and the Type II data includes one or more Type II transport blocks . The first information indicates whether the type I transport block in the Q1 type I data is co...
Embodiment 2
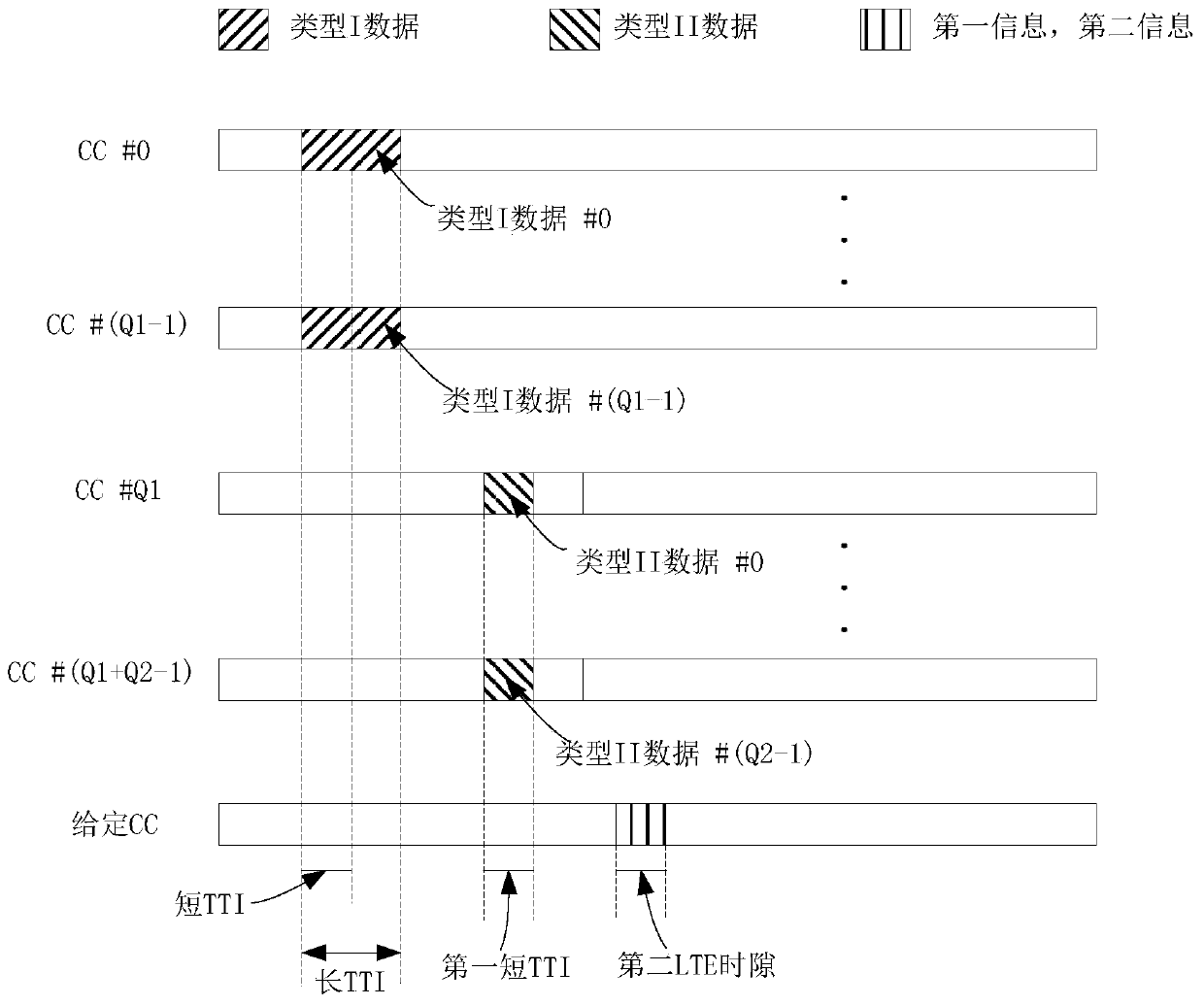
[0112] Embodiment 2 illustrates a schematic diagram of the transmission of the first information and the second information on the same LTE time slot, as shown in the attached figure 2 shown. attached figure 2 Among them, CC identifies the carrier (Component Carrier), the square filled with slash marks the carrier and time interval occupied by Type I data, the square filled with backslash marks the carrier and time interval occupied by Type II data, and the vertical line is filled The squares in identify the carriers and time intervals used to transmit the first information and the second information.
[0113] In Embodiment 2, the base station sends Q1 pieces of type I data and Q2 pieces of type II data to the UE, and the UE sends the first information and the second information to the base station in a second LTE time slot on a given carrier.
[0114]Wherein, the Q1 type I data are respectively transmitted on the Q1 serving cells, that is, the carriers of the serving cell...
Embodiment 3
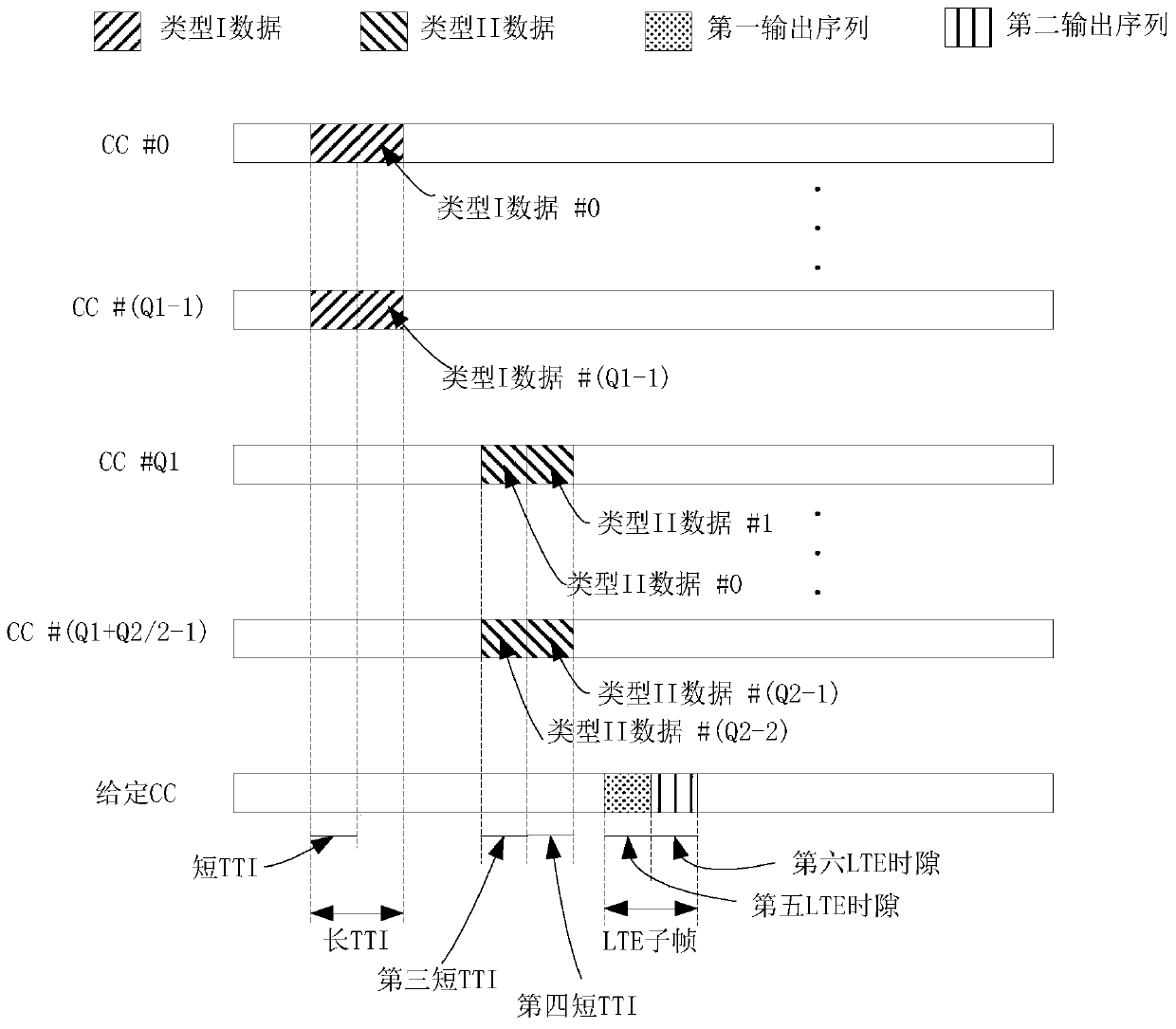
[0121] Embodiment 3 illustrates a schematic diagram of the transmission of the first information on two LTE time slots, as shown in the attached image 3 shown. attached image 3 Among them, CC identifies the carrier, the grid filled with slashes indicates the carrier and time interval occupied by Type I data, the grid filled with backslashes indicates the carrier and time interval occupied by Type II data, and the grid filled with black dots indicates the carrier and time interval occupied by Type II data Carriers and time intervals used to transmit the first output sequence, and squares filled with vertical lines identify carriers and time intervals used to transmit the second output sequence.
[0122] The base station first transmits Q1 type I data and Q2 type II data; then receives modulation symbols modulated by the first output sequence in the fifth LTE time slot on a given carrier, and receives modulation symbols modulated by the first output sequence in the sixth LTE ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com