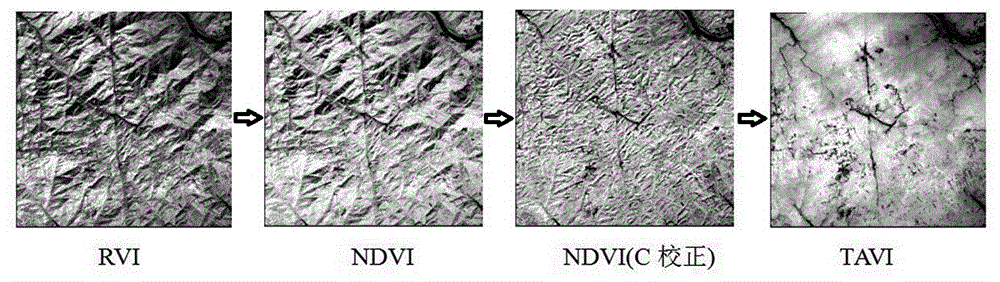
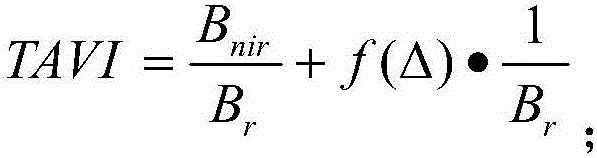TAVI regulatory factor algorithm based on solar altitude
A technology of sun altitude angle and adjustment factor, applied in the directions of calculation, image data processing, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of unfavorable large-scale popularization and application of TAVI, limiting the level of automatic application of TAVI, weak physical meaning, etc., and achieves obvious terrain correction effect. The effect of minimizing data cost and time cost and having strong physical meaning
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0029] The present invention will be further described below with reference to the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
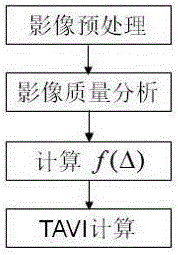
[0030] like figure 2 As shown, the present embodiment provides a TAVI adjustment factor algorithm based on the sun altitude angle, which specifically includes the following steps:
[0031] Step S1: preprocessing the remote sensing image, and generating image apparent reflectance data through the radiometric calibration of the remote sensing image;
[0032] Step S2: analyze the quality of the remote sensing images, and count the apparent reflectance data in the red light band and the near-infrared band of the remote sensing images; analyze whether the reflectivity of the mountain vegetation in these two bands is reasonable, and determine whether the image is normally available; usually the mountain vegetation red light The average reflectance in the band is around 0.05, and the average reflectance in the near-infrared band is greater than 0.2.
[0033] ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com