Resistive random access memory device
A resistive random access memory technology, applied in electrical components and other directions, can solve problems such as failure of RRAM devices
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
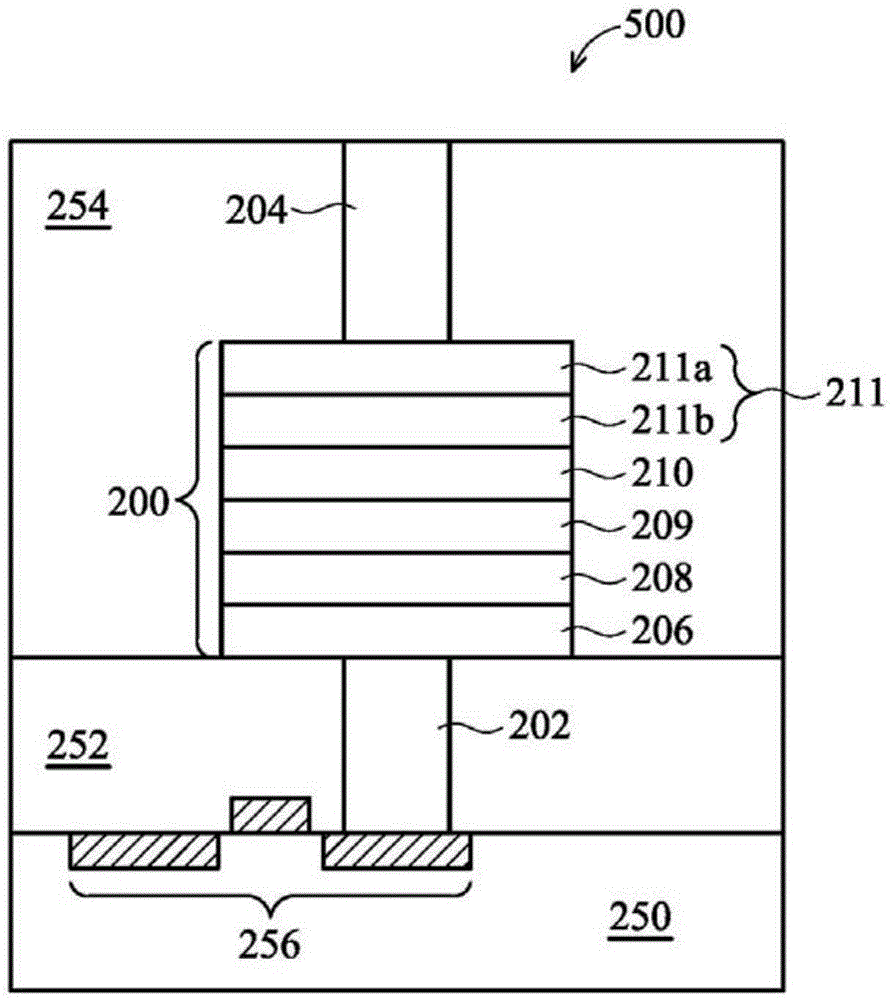
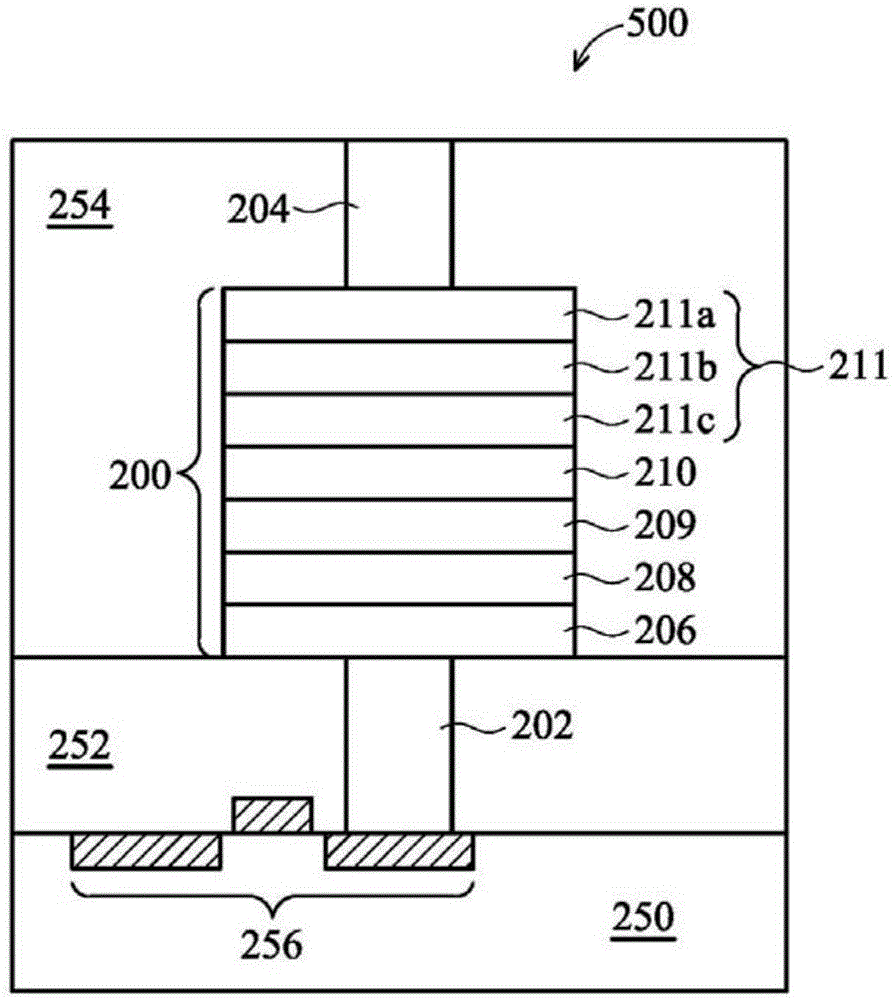
[0023] One embodiment of the present invention provides a non-volatile memory such as a resistive random access memory (RRAM) device. In known RRAM devices, oxygen that migrates from the resistive transition layer into the top electrode due to the applied voltage may diffuse back down to the resistive transition layer, or escape upwards out of the top electrode. The phenomenon of oxygen diffusion / escape in the top electrode described above can render the RRAM device ineffective. To overcome the above oxygen diffusion / escape problem, the present invention provides a novel RRAM stack structure.
[0024] figure 1 It is a cross-sectional view of an RRAM device 500 in an embodiment of the present invention. Such as figure 1 As shown, the RRAM device 500 may be disposed on a semiconductor substrate 250 . In one embodiment, the semiconductor substrate 250 may be a silicon substrate. The main components of the RRAM device 500 include a bottom electrode contact plug 202 disposed o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com