Method and device for increasing switching distance
A technology of distance and target base station, which is applied in the field of increasing handover distance and can solve the problems of increasing handover distance, small distance, and inability to meet user needs.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
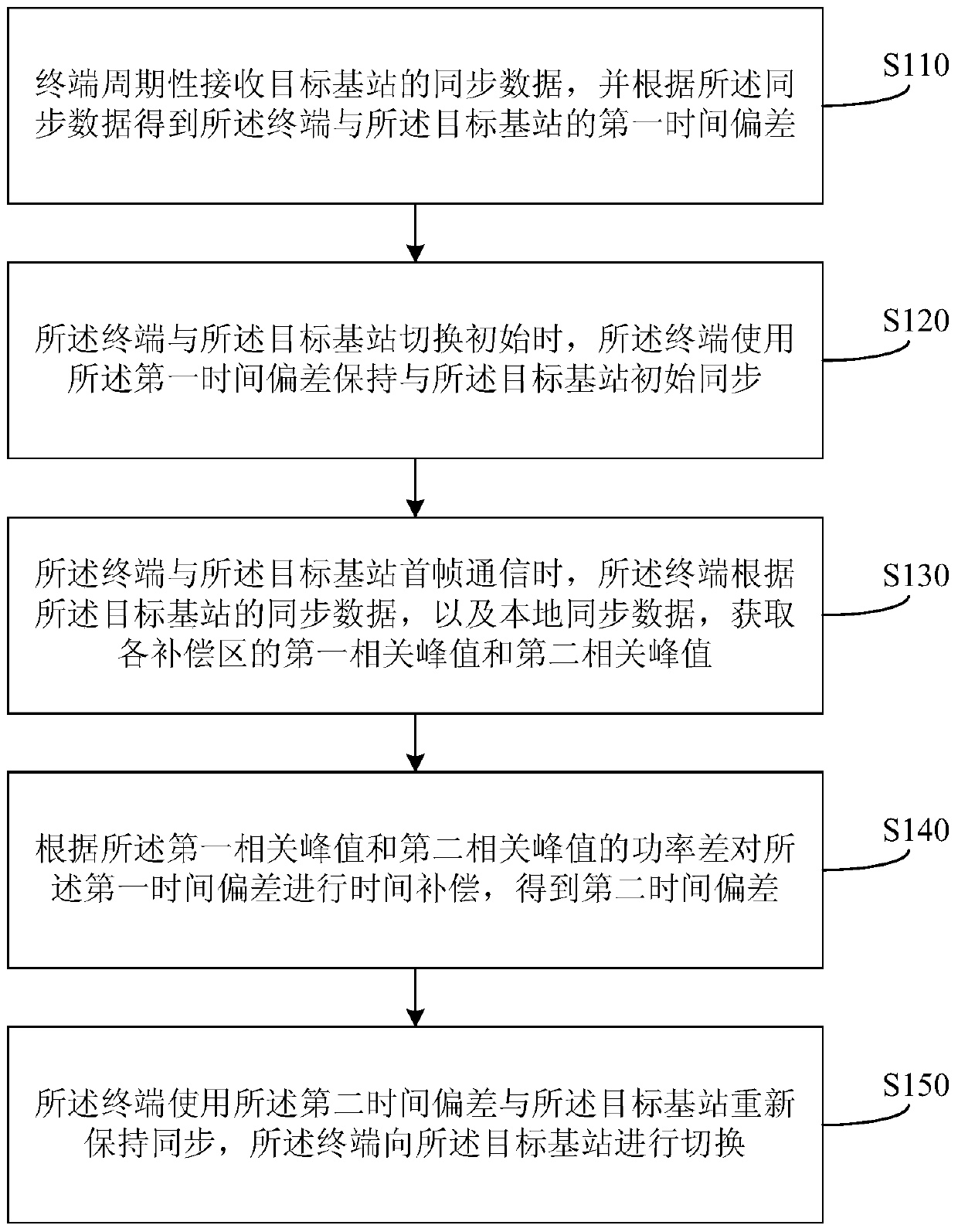
[0053] figure 1 It is a schematic flowchart of a method for increasing the switching distance provided by Embodiment 1 of the present invention. The method can be executed by a device for increasing the switching distance, wherein the device can be implemented by software and / or hardware.
[0054] Such as figure 1 As shown, the method includes:
[0055] S110. The terminal periodically receives synchronization data of the target base station, and obtains a first time offset between the terminal and the target base station according to the synchronization data;
[0056] Exemplarily, the terminal periodically receives the synchronization data sent by the target base station, and the period may be 10 ms or other time periods, which is not limited here. The terminal receives the synchronization data of the target base station according to the preset time period, performs the conversion operation from the time domain to the frequency domain on the received synchronization data, an...
Embodiment 2
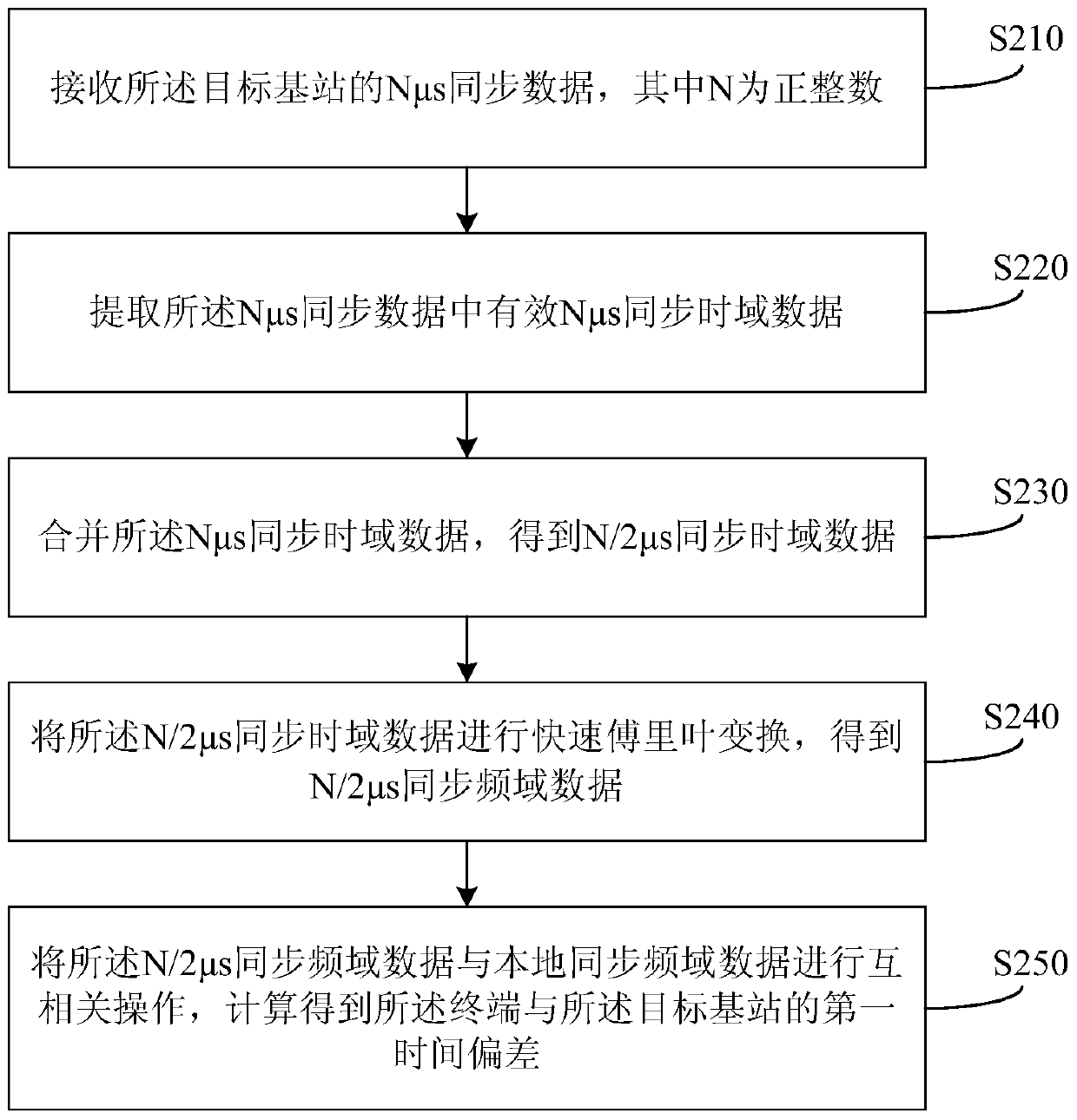
[0067] This embodiment is based on the first embodiment above, and is optimized on the basis of the first embodiment, specifically optimizing the process of obtaining the first time offset. figure 2 is a schematic flowchart of a method for increasing the switching distance provided by Embodiment 2 of the present invention, as shown in figure 2 As shown, the method includes:
[0068] S210. Receive Nμs synchronization data of the target base station, where N is a positive integer;
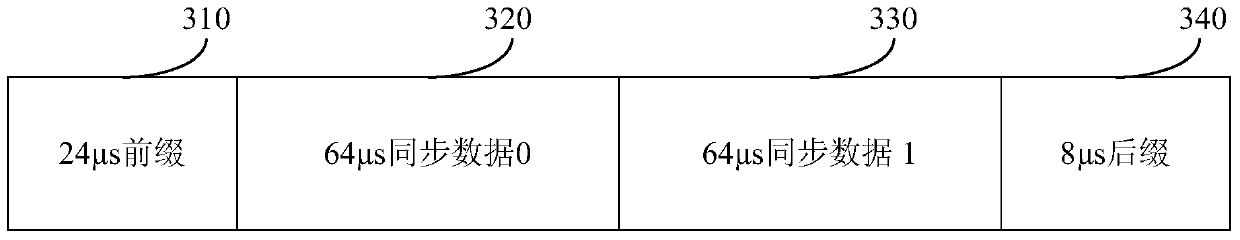
[0069] Exemplarily, the value of N may be 64, or 128, or 256. The synchronous data in this embodiment can be 128 μs synchronous data, namely N is 128, image 3 It is a schematic diagram of the time slot structure of synchronous data in a method for increasing the switching distance provided by Embodiment 2 of the present invention, as shown in image 3 As shown, the synchronous data time slot structure includes four parts: 310-340, wherein, 310 is a 24 μs prefix, 320 is a 64 μs synchronous data ...
Embodiment 3
[0081] This embodiment is based on the foregoing embodiments, and optimization is performed on the basis of the foregoing embodiments, specifically, the process of obtaining the second time offset, that is, the process of time compensation, is optimized. Figure 5 is a schematic flowchart of a method for increasing the switching distance provided by Embodiment 3 of the present invention, as shown in Figure 5 As shown, the method includes:
[0082] S510. Receive Nμs synchronization data of the target base station;
[0083] Exemplarily, the value of N may be 64, or 128, or 256. The synchronous data in this embodiment may be 128 μs synchronous data, that is, N is 128. Receive target base station 128μs synchronization data.
[0084] S520. Extract effective Nμs synchronization time domain data from the Nμs synchronization data;
[0085] Exemplarily, effective 128 μs synchronous time domain data Tsync_128 in the 128 μs synchronous data is extracted.
[0086] S530. Perform fast...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com