Measurement method and device of power of microwave radiation source signal under interference of non-stable broadband
A technology of microwave radiation and power measurement, which is applied in the field of signal processing, can solve problems such as the inability to effectively measure useful signal power values, and achieve the effects of improving accuracy, robustness, and good adaptability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
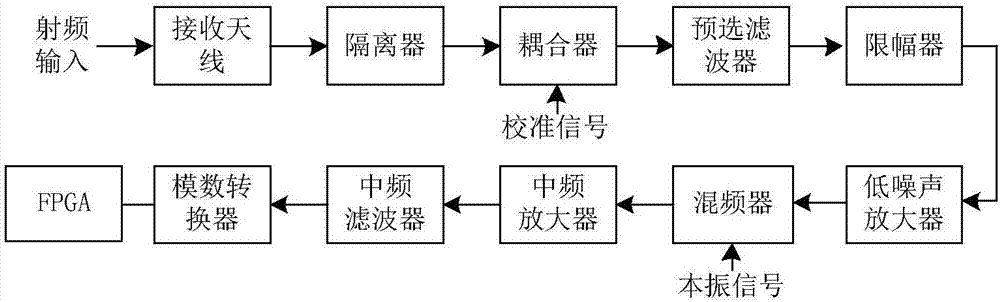
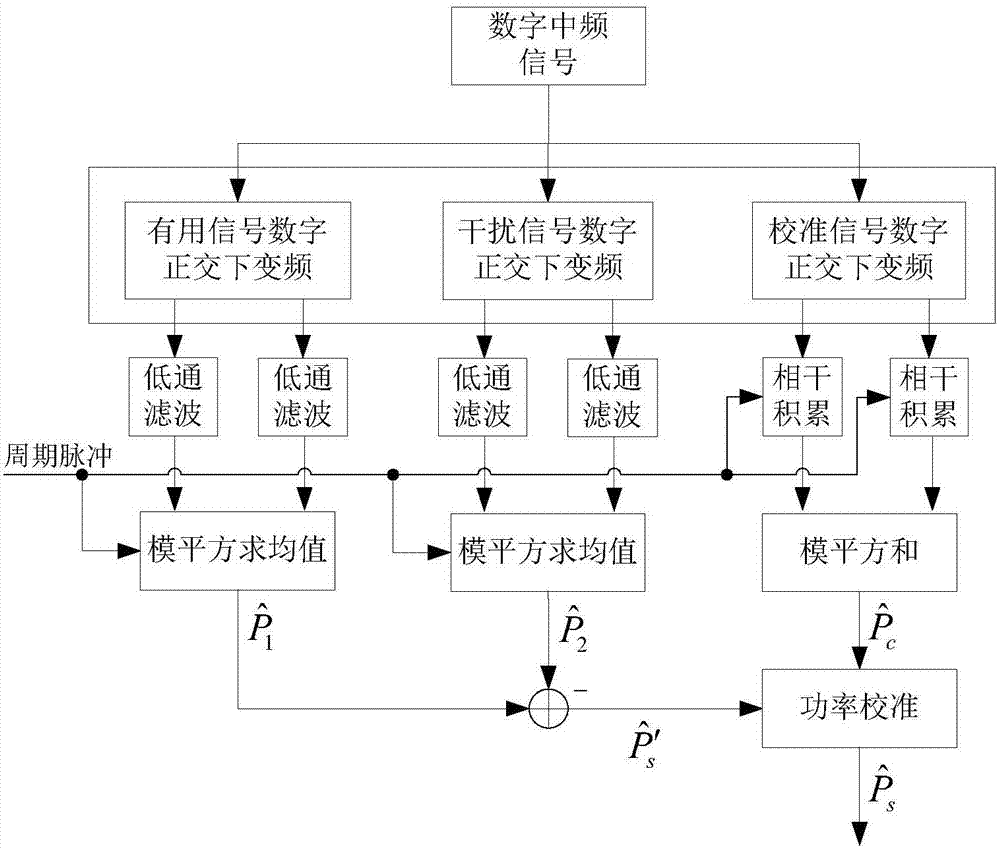
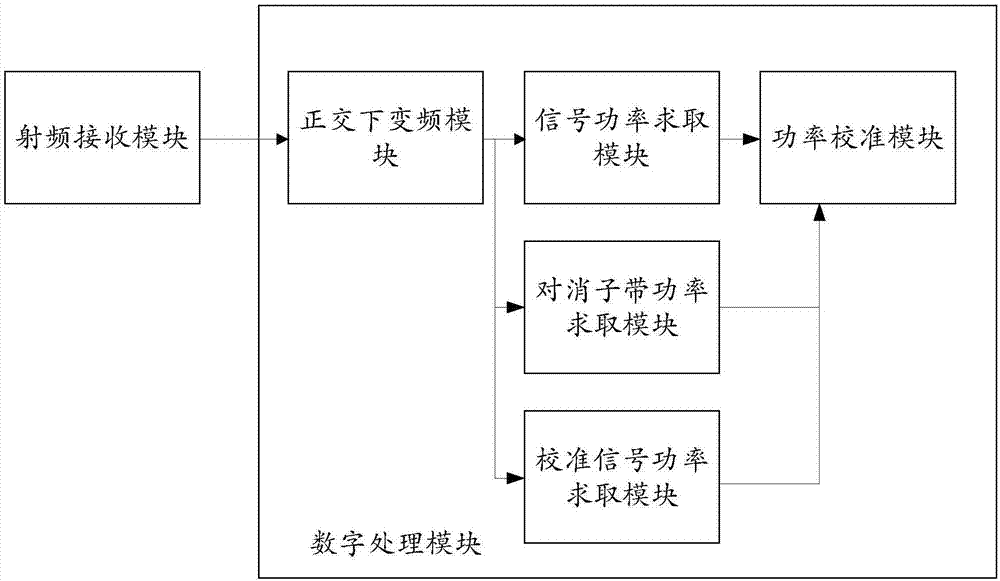
[0049] In order to make the purpose, technical solution and advantages of the present invention clearer, the present invention will be further described in detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings and examples of implementation. attached figure 1 and attached figure 2 The composition block diagram of the microwave radiation source signal power measurement device under the non-stationary broadband interference and the signal processing flow block diagram based on FPGA are described respectively. image 3 From the module point of view, it describes the composition of the device and the division of logic structure inside FPGA.
[0050] In this implementation example, it is assumed that the center frequency of the useful signal to be tested is 10.03GHz, and the bandwidth is 2MHz. The power range of the useful signal entering the receiving port of the power measurement device (receiving output of the receiving antenna) is -110dBm~-80dBm; the calibration signal ha...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com