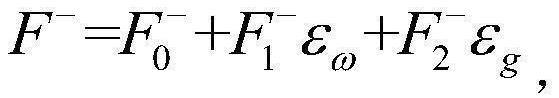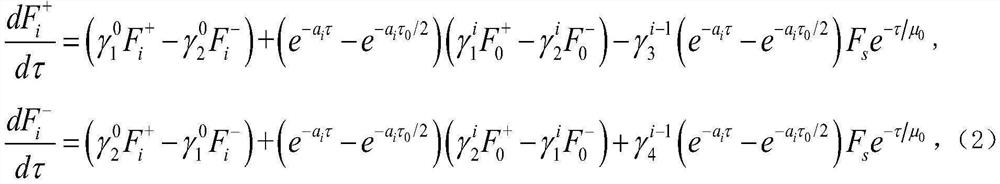A Calculation Method for Radiative Transfer Applicable to Continuous Variation of Cloud Microphysical Properties
A technology of radiative transfer equations and physical properties, which can be used in the measurement of scattering properties, ICT adaptation, climate sustainability, etc., and can solve problems such as time-consuming, inability to directly apply models, and a large number of independent photon experiments
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0078] The technical solution of the present invention is further described below.
[0079] The radiative transfer calculation method applicable to the continuous change of cloud microphysical properties in this embodiment is based on a two-stream approximation scheme, and is characterized in that the method includes the following steps:
[0080] Step 1) Express the radiant flux with continuously changing cloud microphysical properties as the sum of constant term and disturbance term;
[0081] Step 2) The first radiant flux calculated according to the traditional second-flow radiation transfer equation, and setting the first radiant flux as the constant item;
[0082] Step 3) Substituting the parameterized form of the asymmetry factor g and the single scattering albedo ω into the traditional two-stream radiation transfer intensity equation by the perturbation method to form a non-uniformity-caused disturbance term equation group, and through the non-uniformity-caused The dist...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com